producer内存管理分析
1 概述
kafka producer调用RecordAccumulator#append来将消息存到本地内存。消息以TopicPartition为key分组存放,每个TopicPartition对应一个Deque;RcordBatch的消息实际存储在MemoryRecords中;MemoryRecords有Compressor和ByteBuffer两个主要的属性,消息就是存储在ByteBuffer中,Compressor用来将消息写进到ByteBuffer中。消息在生产内存中的模型大致如下:
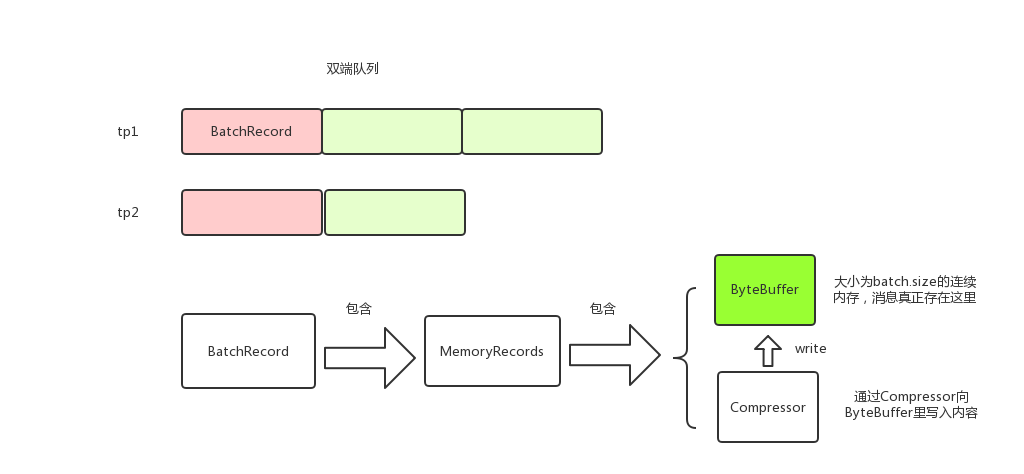
2 RecordAccumulator#append
producer调用send方法的时候,调用RecordAccumulator#append将消息存放到内存中。这里需要注意的是,append获取了两次锁,这样做是为了减少锁的范围。
public RecordAppendResult append(TopicPartition tp,
long timestamp,
byte[] key,
byte[] value,
Callback callback,
long maxTimeToBlock) throws InterruptedException {
appendsInProgress.incrementAndGet();
try {
Deque<RecordBatch> dq = getOrCreateDeque(tp); // 获取tp对应的Deque<RecordBatch>
synchronized (dq) { // 关键, 获取Deque<RecordBatch>的锁才操作
if (closed)
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot send after the producer is closed.");
Deque<RecordBatch> dq = getOrCreateDeque(tp); // 获取tp对应的Deque<RecordBatch>
RecordBatch last = dq.peekLast(); // 往最后一个RecordBatch添加
if (last != null) { // 尝试添加,后面会详细讲
FutureRecordMetadata future = last.tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, callback, time.milliseconds());
if (future != null) //添加成功就返回了
return new RecordAppendResult(future, dq.size() > 1 || last.records.isFull(), false);
}
}
// 没有添加成功,说明最后一个RecordBatch空间不足或者last == null
// 关键, 如果消息体大于batchsize,那么会创建消息体大小的RecordBatch,即RecordBatch不一定和batchsize相等
int size = Math.max(this.batchSize, Records.LOG_OVERHEAD + Record.recordSize(key, value));
// 从BufferPool中分配内存,后面会详细讲
ByteBuffer buffer = free.allocate(size, maxTimeToBlock);
synchronized (dq) { // 重新获取锁,因为allocate的时候不需要锁dq,这里也是尽量减少锁粒度的一种思想
if (closed)
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot send after the producer is closed.");
RecordBatch last = dq.peekLast();
if (last != null) { // 可能在重新获取锁之前其他线程释放了内存,所以这里重新获取下
FutureRecordMetadata future = last.tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, callback, time.milliseconds());
if (future != null) {
free.deallocate(buffer);
return new RecordAppendResult(future, dq.size() > 1 || last.records.isFull(), false);
}
}
// 还没有获取到RecordBatch则申请内存创建新的RecordBatch
MemoryRecords records = MemoryRecords.emptyRecords(buffer, compression, this.batchSize);
RecordBatch batch = new RecordBatch(tp, records, time.milliseconds());
FutureRecordMetadata future = Utils.notNull(batch.tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, callback, time.milliseconds()));
dq.addLast(batch);
incomplete.add(batch);
return new RecordAppendResult(future, dq.size() > 1 || batch.records.isFull(), true);
}
} finally {
appendsInProgress.decrementAndGet();
}
}
3 Compressor
上述代码调用RecordBatch#tryAppend尝试将消息放到RecordBatch,而RecordBatch#tryAppend又调用MemoryRecords#append。
public long append(long offset, long timestamp, byte[] key, byte[] value) {
if (!writable)
throw new IllegalStateException("Memory records is not writable");
int size = Record.recordSize(key, value);
compressor.putLong(offset);
compressor.putInt(size);
long crc = compressor.putRecord(timestamp, key, value);
compressor.recordWritten(size + Records.LOG_OVERHEAD);
return crc;
}
这里的关键是compressor,来分析下Compressor,以putInt为例,实际上是调用了DataOutputStream#writeInt方法
public void putInt(final int value) {
try {
appendStream.writeInt(value); // appendStream是DataOutputStream类型
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new KafkaException("I/O exception when writing to the append stream, closing", e);
}
}
看下Compressor是如何初始化的:
public Compressor(ByteBuffer buffer, CompressionType type) {
// ...
// create the stream
bufferStream = new ByteBufferOutputStream(buffer);
appendStream = wrapForOutput(bufferStream, type, COMPRESSION_DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
}
static public DataOutputStream wrapForOutput(ByteBufferOutputStream buffer, CompressionType type, int bufferSize) {
try {
switch (type) {
case NONE:
return new DataOutputStream(buffer); // 封装了ByteBufferOutputStream
case GZIP:
return new DataOutputStream(new GZIPOutputStream(buffer, bufferSize));
case SNAPPY:
try {
OutputStream stream = (OutputStream) snappyOutputStreamSupplier.get().newInstance(buffer, bufferSize);
return new DataOutputStream(stream);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new KafkaException(e);
}
case LZ4:
try {
OutputStream stream = (OutputStream) lz4OutputStreamSupplier.get().newInstance(buffer);
return new DataOutputStream(stream);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new KafkaException(e);
}
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown compression type: " + type);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new KafkaException(e);
}
}
从上面代码可以看到,和ByteBuffer直接关联的是ByteBufferOutputStream;而DataOutputStream封装了ByteBufferOutputStream,负责处理压缩数据,直观上来看如下图:
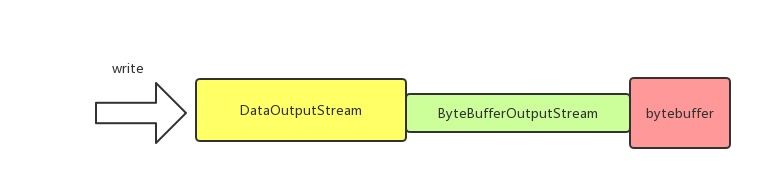
4 BufferPool
BufferPool用于管理producer缓存池,使用配置项buffer.memory来指定缓存池的大小,默认是32M。
4.1 allocate
BufferPool#allocate用于从缓存池中申请内存。BufferPool维护了一个ByteBuffer的双端队列free,表示空闲的ByteBuffer,只有大小为batch.size的内存申请才会从free中去拿去,也就是说free中维护的ByteBuffer都是batch.size大小。
BufferPool几个关键属性
private final long totalMemory;
private final int poolableSize; // 一块连续内存的大小,等于batch.size
private final ReentrantLock lock;
private final Deque<ByteBuffer> free; // 空闲的ByteBuffer列表,每个ByteBuffer都是batch.size大小,只有申请的内存等于batch.size大小才会从free中获取
private final Deque<Condition> waiters;
private long availableMemory; // 还有多少内存可以用,即buffer.memory-已用内存
// ...
}
public ByteBuffer allocate(int size, long maxTimeToBlockMs) throws InterruptedException {
if (size > this.totalMemory)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Attempt to allocate " + size
+ " bytes, but there is a hard limit of "
+ this.totalMemory
+ " on memory allocations.");
this.lock.lock();
try {
if (size == poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty()) // 关键,只有大小等于batch.size的时候才会从free中获取
return this.free.pollFirst();
int freeListSize = this.free.size() * this.poolableSize;
// 剩余总内存够用,但是不能从free中获取,则将free释放一些,然后申请对应大小的内存
if (this.availableMemory + freeListSize >= size) {
freeUp(size); // 释放
this.availableMemory -= size;
lock.unlock();
return ByteBuffer.allocate(size);
} else {
// 关键,剩余总内存不够了,则会阻塞,直到有足够的内存
int accumulated = 0;
ByteBuffer buffer = null;
Condition moreMemory = this.lock.newCondition();
long remainingTimeToBlockNs = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(maxTimeToBlockMs);
this.waiters.addLast(moreMemory); // 添加到等待队列尾
while (accumulated < size) {
long startWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
long timeNs;
boolean waitingTimeElapsed;
try {
waitingTimeElapsed = !moreMemory.await(remainingTimeToBlockNs, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS); // 阻塞
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
throw e;
} finally {
long endWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
timeNs = Math.max(0L, endWaitNs - startWaitNs);
this.waitTime.record(timeNs, time.milliseconds());
}
if (waitingTimeElapsed) {
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
throw new TimeoutException("Failed to allocate memory within the configured max blocking time " + maxTimeToBlockMs + " ms.");
}
remainingTimeToBlockNs -= timeNs;
// check if we can satisfy this request from the free list,
// otherwise allocate memory
if (accumulated == 0 && size == this.poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty()) {
// just grab a buffer from the free list
buffer = this.free.pollFirst();
accumulated = size;
} else {
freeUp(size - accumulated);
int got = (int) Math.min(size - accumulated, this.availableMemory);
this.availableMemory -= got;
accumulated += got;
}
}
Condition removed = this.waiters.removeFirst(); // 从头部获取,后面详细讲
if (removed != moreMemory)
throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong condition: this shouldn't happen.");
// 如果分配后还有剩余空间,即唤醒后续的等待线程
if (this.availableMemory > 0 || !this.free.isEmpty()) {
if (!this.waiters.isEmpty())
this.waiters.peekFirst().signal(); // 唤醒头部
}
// unlock and return the buffer
lock.unlock();
if (buffer == null)
return ByteBuffer.allocate(size);
else
return buffer;
}
} finally {
if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread())
lock.unlock();
}
}
对于allocate有几点需要注意
- 只有大小为batch.size的内存申请才会从free中获取,所以消息大小尽量不要大于batch.size,这样才能充分利用缓存池。为什么申请的内存会不等于batch.size呢,原因是在RecordAccumulator#append中有一句 int size = Math.max(this.batchSize, Records.LOG_OVERHEAD + Record.recordSize(key, value)), 即如果消息大小大于batch.size则会使用消息的大小申请内存。
- 下面代码可能有点疑惑, moreMemory是添加到waiters的尾部的,为什么获取的时候是从头部获取呢?这个原因是,线程唤醒只会唤醒waiters头部的线程,所以当线程被唤醒后,他肯定是已经在waiters头部了,也就是说排在他前面的线程都已经在他之前被唤醒并移除waiters了。
Condition removed = this.waiters.removeFirst(); // 从头部获取,后面详细讲
if (removed != moreMemory)
throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong condition: this shouldn't happen.");
- 申请的总内存查过buffer.memory的时候会阻塞或者抛出异常
4.2 deallocate
BufferPool#deallocate用于将内存释放并放回到缓存池。同allocate一样,只有大小等于batch.size的内存块才会放到free中。
public void deallocate(ByteBuffer buffer) {
deallocate(buffer, buffer.capacity());
}
public void deallocate(ByteBuffer buffer, int size) {
lock.lock();
try {
if (size == this.poolableSize && size == buffer.capacity()) {
buffer.clear();
this.free.add(buffer);// 只有大小等于batch.size的内存块才会放到free中
} else { // 否则的话只是availableMemory改变,无用的ByteBuffer会被GC清理掉
this.availableMemory += size;
}
Condition moreMem = this.waiters.peekFirst(); // 唤醒waiters的头结点
if (moreMem != null)
moreMem.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
producer内存管理分析的更多相关文章
- Android 内存管理分析(四)
尊重原创作者,转载请注明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/gemmem/article/details/8920039 最近在网上看了不少Android内存管理方面的博文,但是文章大多 ...
- memcached 内存管理 分析(转)
Memcached是一个高效的分布式内存cache,了解memcached的内存管理机制,便于我们理解memcached,让我们可以针对我们数据特点进行调优,让其更好的为我所用.这里简单谈一下我对me ...
- Android进程的内存管理分析
尊重原创作者,转载请注明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/gemmem/article/details/8920039 最近在网上看了不少Android内存管理方面的博文,但是文章大多 ...
- iOS 内存管理分析
内存分析 静态分析(Analyze) 不运行程序, 直接检测代码中是否有潜在的内存问题(不一定百分百准确, 仅仅是提供建议) 结合实际情况来分析, 是否真的有内存问题 动态分析(Profile == ...
- cocos 自动内存管理分析
#include "CCAutoreleasePool.h" #include "ccMacros.h" NS_CC_BEGIN static CCPoolMa ...
- spark内存管理分析
前言 下面的分析基于对spark2.1.0版本的分析,对于1.x的版本可以有区别. 内存配置 key 默认 解释 spark.memory.fraction 0.6 spark可以直接使用的内存大小系 ...
- 【转】cocos2d-x与ios内存管理分析(在游戏中减少内存压力)
猴子原创,欢迎转载.转载请注明: 转载自Cocos2D开发网–Cocos2Dev.com,谢谢! 原文地址: http://www.cocos2dev.com/?p=281 注:自己以前也写过coco ...
- cocos2d-x与ios内存管理分析(在游戏中减少内存压力)
转自:http://www.cocos2dev.com/?p=281 注:自己以前也写过cocos2d-x如何优化内存的使用,以及内存不足的情况下怎么处理游戏.今天在微博中看到有朋友介绍了下内存,挺详 ...
- Android内存泄漏分析及调试
尊重原创作者,转载请注明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/gemmem/article/details/13017999 此文承接我的另一篇文章:Android进程的内存管理分析 首先 ...
随机推荐
- 2021 .NET Conf China 主题分享之-轻松玩转.NET大规模版本升级
去年.NET Conf China 技术大会上,我给大家分享了主题<轻松玩转.NET大规模版本升级>,今天把具体分享的内容整理成一篇博客,供大家研究参考学习. 一.先说一下技术挑战和业务背 ...
- Linux安装Python xlrd、xlwt、xlutils模块
一.安装setuptools: 可以先打开setuptools的python官网看看setuptools软件包如何安装: 1 > wget https://bitbucket.org/pypa/ ...
- 跟Excel说拜拜,这款可视化报表制作工具入股不亏!
相信很多人如果看到漂亮的图表都会很感叹,"为什么可以做的这么漂亮,这么好看?","这个应该怎么做呢?用什么工具可以实现呢?".制作漂亮的可视化一般有这样几个方 ...
- JavaSE-万字长文-加载时间长-小白文
Java语法规范 所有的Java语句必须以;结尾! 无论是().[]还是{},所有的括号必须一一匹配! 主方法的代码只能写在{}中! Java基础语法(面向过程) 在学习面向对象之前,我们需要了解面向 ...
- AHUACM寒假集训I(基础数据结构+串串)
H.超级钢琴 luoguP2048 题目大意: 求出一个长N序列中所有长度在L到R的子序列中序列和最大的K个,并求这K个的和 思路: 暴力的话可以求出所有满足要求的子序列然后排序,然后显然会T. 所以 ...
- Android studio常用快捷键导包的设置
下面是一些快捷键的使用还有快速导包的设置 1. Ctrl+G 同时按下Ctrl+G快捷键弹出快速定位框,在框中输入行数点击OK即可快速切换到对应的行数,如图2.17所示. 2. Ctrl+E 同时按下 ...
- kubernetes配置后端存储 rook-ceph
一 Rook概述 1.1 Ceph简介 Ceph是一种高度可扩展的分布式存储解决方案,提供对象.文件和块存储.在每个存储节点上,将找到Ceph存储对象的文件系统和Ceph OSD(对象存储守护程序)进 ...
- GAN实战笔记——第七章半监督生成对抗网络(SGAN)
半监督生成对抗网络 一.SGAN简介 半监督学习(semi-supervised learning)是GAN在实际应用中最有前途的领域之一,与监督学习(数据集中的每个样本有一个标签)和无监督学习(不使 ...
- laravel 和 tp的区别
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoyantongxue/p/15442844.html laravel 数据库储存的时间字段 created_at updated_at ...
- gitee中项目到运行操作,包括:打包、热部署、数据库操作
使用的工具:window10.IDEA 2018.2.3 .navicat110_premium.Git-2.23 1.idea导入gitee代码 复制项目地址 选择git工具 粘贴地址,点击clon ...
