A/B Testing with Practice in Python (Part One)
I learned A/B testing from a Youtube vedio. The link is https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bu7OqjYk0jM.
I will divide the note into two parts. The first part is generally an overview of hypothesis testing. Most concepts can be found in the article "Statistics Basics: Main Concepts in Hypothesis Testing" and I will focus on pratical applications here.







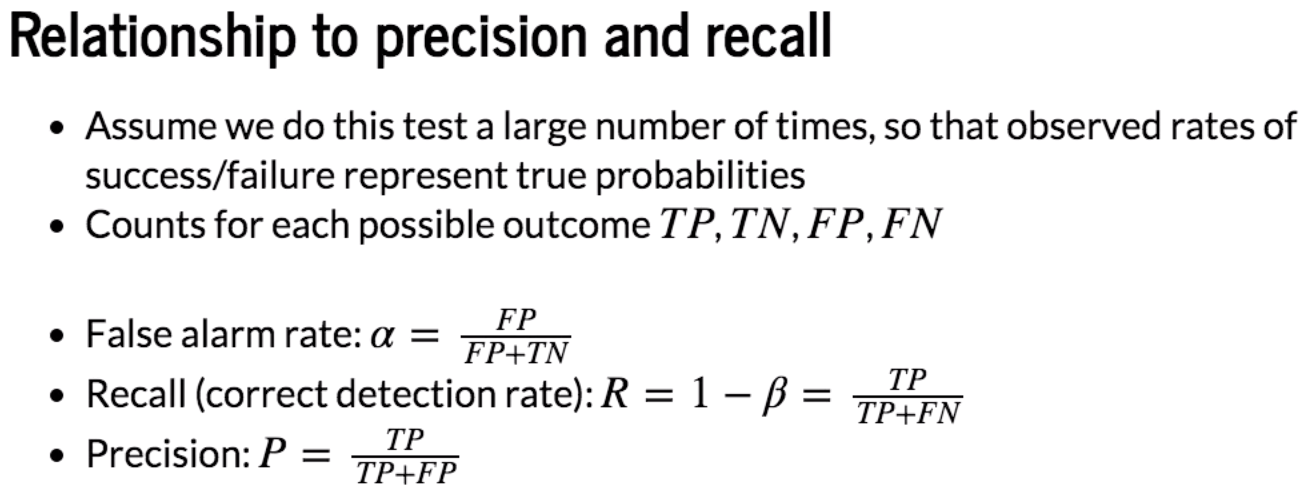
|
Actual Predicted |
T (H1) | F (H0) |
| T (H1) | TP | FP (α) |
| F (H0) | FN (β) | TN |
P = TP/(TP+FN)
R = 1-β =TP/(TP+FN)
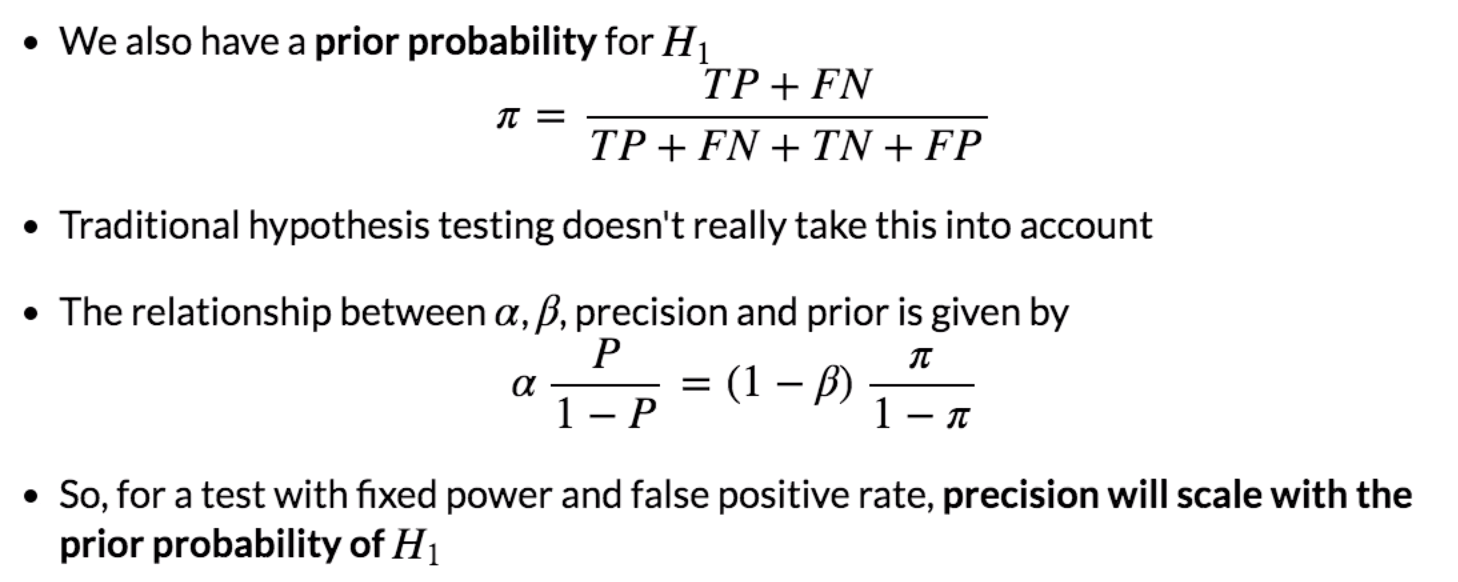

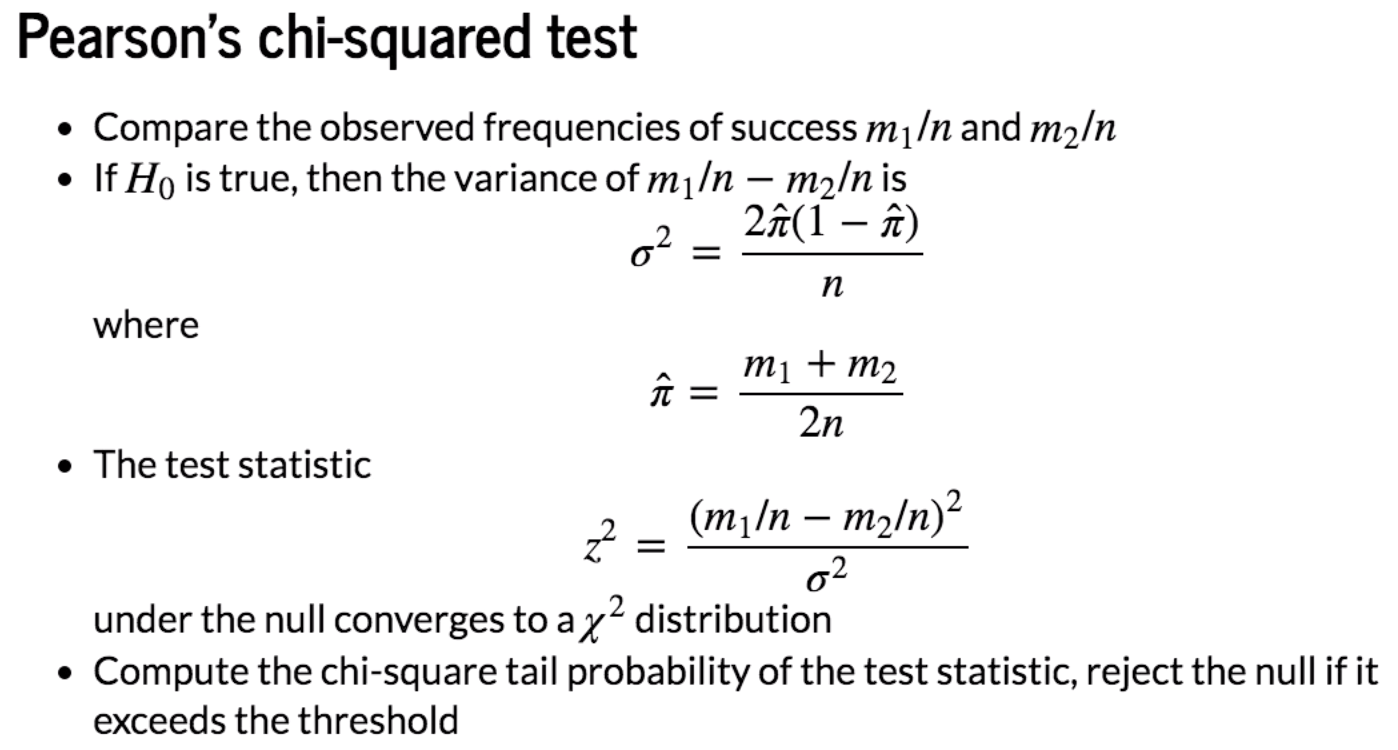
Python Example
Case #1: Alternate hypothesis is true
n = 100
p1 = 0.4
p2 = 0.6 # Compute distributions
x = np.arange(0,n+1)
pmf1 = stats.binom.pmf(x,n,p1)
pmf2 = stats.binom.pmf(x,n,p2)
plot(x,pmf1,pmf2)
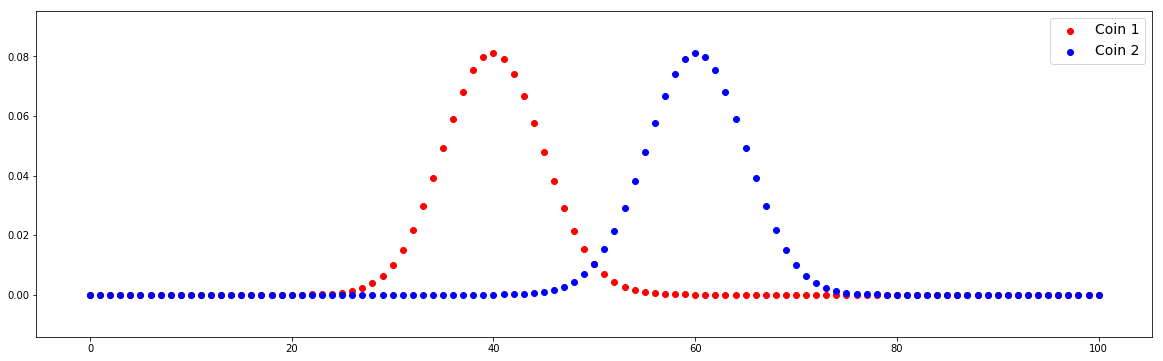
We can find that the distributions between Coin 1 and Coin 2 are different. We check different values of m1 and m2.
# Example outcomes
m1, m2 = 40, 60
table = [[m1, n-m1], [m2, n-m2]]
chi2, pval, dof, expected = stats.chi2_contingency(table)
decision = 'reject H0' if pval<0.05 else 'accept H0'
print('{} ({})'.format(pval,decision))
0.007209570764742524 (reject H0)
# Example outcomes
m1, m2 = 43, 57
table = [[m1, n-m1], [m2, n-m2]]
chi2, pval, dof, expected = stats.chi2_contingency(table)
decision = 'reject H0' if pval<0.05 else 'accept H0'
print('{} ({})'.format(pval,decision))
0.06599205505934735 (accept H0)
In the secod example, m1 and m2 are not different significantly to reject H0.
Case #2: Null hypothesis is true
n = 100
p1 = 0.5
p2 = 0.5 # Compute distributions
x = np.arange(0,n+1)
pmf1 = stats.binom.pmf(x,n,p1)
pmf2 = stats.binom.pmf(x,n,p2)
plot(x,pmf1,pmf2)
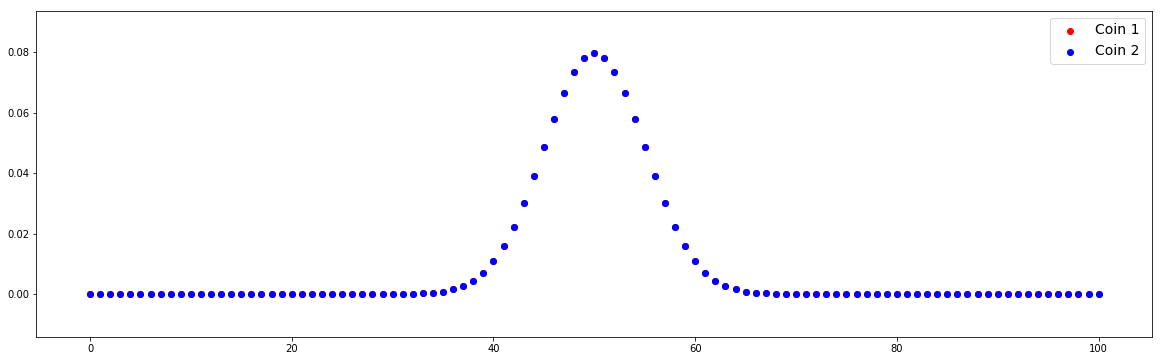
In this case, two distributions overlap because we define the same value of p1 and p2.
# Example outcomes
m1, m2 = 49, 51
table = [[m1, n-m1], [m2, n-m2]]
chi2, pval, dof, expected = stats.chi2_contingency(table)
decision = 'reject H0' if pval<0.05 else 'accept H0'
print('{} ({})'.format(pval,decision))
0.887537083981715 (accept H0)
Actuall, we can only say that m1 and m2 are not different significantly to reject H0. It doesn't mean we should accept H0. The explanation is given in the previous article.
# Example outcomes
m1, m2 = 42, 58
table = [[m1, n-m1], [m2, n-m2]]
chi2, pval, dof, expected = stats.chi2_contingency(table)
decision = 'reject H0' if pval<0.05 else 'accept H0'
print('{} ({})'.format(pval,decision))
0.033894853524689295 (reject H0)


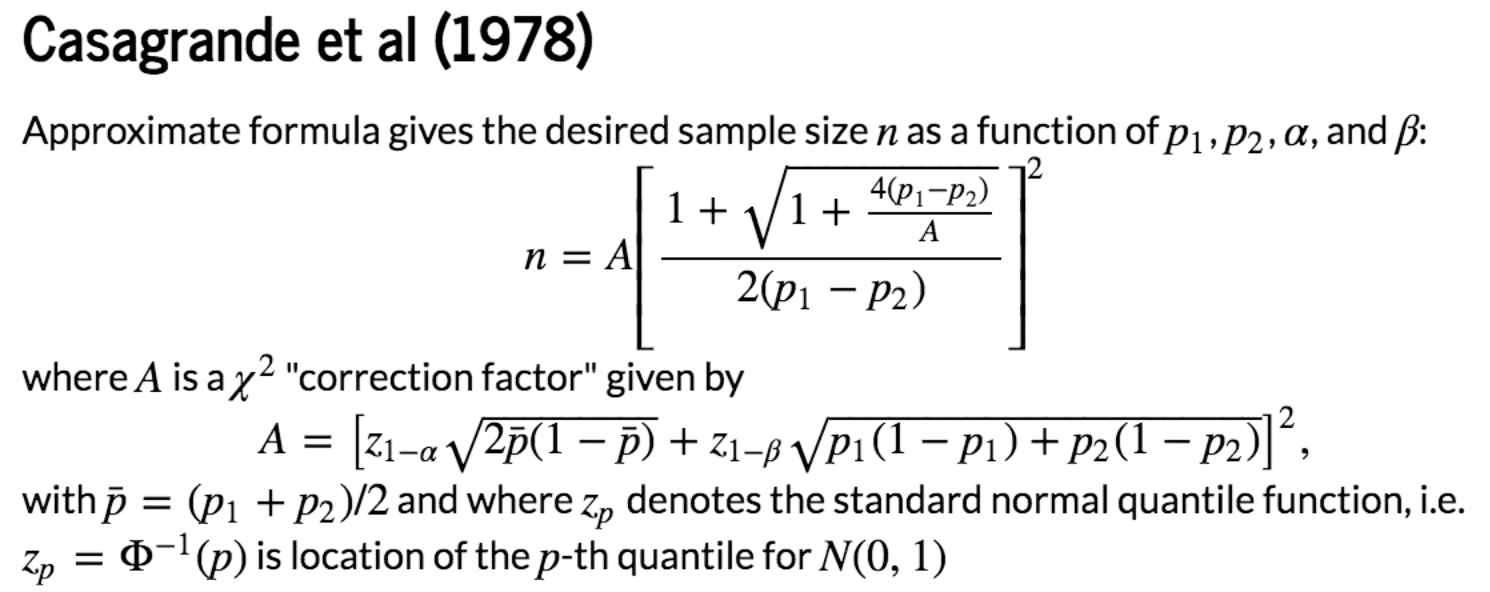

Firstly, calculate the sample size:
p1, p2 = 0.0500, 0.0515
alpha = 0.05
beta = 0.05 # Evaluate quantile function
p_bar = (p1+p2)/2.0
za = stats.norm.ppf(1-alpha/2) # Two-sided test
zb = stats.norm.ppf(1-beta) # Compute correction factor
A = (za*np.sqrt(2*p_bar*(1-p_bar))+ zb*np.sqrt(p1*(1-p1)+p2*(1-p2)))**2 #Estimate samples required
n = A*(((1+np.sqrt(1+4*(p1-p2)/A)))/(2*(p1-p2)))**2 print (n) # we need 2n users
555118.7638311392
So for test and control combined we'll need at least 2n = 1.1 million users. This is where this stuff gets hard and you're trying to measure something that doesn't happen often which is usally the thing to care because if it's rare, it's usually valuable. When you're trying to change it, you usually can't change it much because if you can change it a lot then your business would be easier usually it's harder to change the thing you care the most about. So in that case, it's like the hardest case where a/b testing the most values are unchange.
Next we can perform a/b testing:
n = 555119
n_trials = 10000 # Simulate experimental results when null is true
control0 = stats.binom.rvs (n,p1,size = n_trials)
test0 = stats.binom.rvs(n, p1, size = n_trials) # Test and control are the same
tables0 = [[[a, n-a], [b, n-b]] for a, b in zip(control0, test0)]
results0 = [stats.chi2_contingency(T) for T in tables0]
decisions0 = [x[1] <= alpha for x in results0] # Simulate experimental results when alternate is true
control1 = stats.binom.rvs (n,p1,size = n_trials)
test1 = stats.binom.rvs(n, p2, size = n_trials) # Test and control are the same
tables1 = [[[a, n-a], [b, n-b]] for a, b in zip(control1, test1)]
results1 = [stats.chi2_contingency(T) for T in tables1]
decisions1 = [x[1] <= alpha for x in results1] # Compute false alarm and correct detection rates
alpha_est = sum(decisions0)/float(n_trials)
power_est = sum(decisions1)/float(n_trials) print('Theoretical false alarm rate = {:0.4f}, '.format(alpha)+
'empirical false alarm rate = {:0.4f}'.format(alpha_est))
print('Theoretical power = {:0.4f}, '.format(1-beta)+
'empirical power = {:0.4f}'.format(power_est))
Theoretical false alarm rate = 0.0500, empirical false alarm rate = 0.0509
Theoretical power = 0.9500, empirical power = 0.9536

A/B Testing with Practice in Python (Part One)的更多相关文章
- A/B Testing with Practice in Python (Part Two)
This is the second part of A/B testing notes, which contains the practical issues and alternatives o ...
- [Python + Unit Testing] Write Your First Python Unit Test with pytest
In this lesson you will create a new project with a virtual environment and write your first unit te ...
- Testing shell commands from Python
如何测试shell命令?最近,我遇到了一些情况,我想运行shell命令进行测试,Python称为万能胶水语言,一些自动化测试都可以完成,目前手头的工作都是用python完成的.但是无法从Python中 ...
- [The Basics of Hacking and Penetration Testing] Learn & Practice
Remember to consturct your test environment. Kali Linux & Metasploitable2 & Windows XP
- Automation Testing - Best Practice(书写规范)
Coding Standards Coding Standards are suggestions that will help us to write automation Scripts code ...
- Machine and Deep Learning with Python
Machine and Deep Learning with Python Education Tutorials and courses Supervised learning superstiti ...
- python安装locustio报错error: invalid command 'bdist_wheel'的解决方法
locust--scalable user load testing tool writen in Python(是用python写的.规模化.可扩展的测试性能的工具) 安装locustio需要的环境 ...
- Python框架、库以及软件资源汇总
转自:http://developer.51cto.com/art/201507/483510.htm 很多来自世界各地的程序员不求回报的写代码为别人造轮子.贡献代码.开发框架.开放源代码使得分散在世 ...
- Awesome Python
Awesome Python A curated list of awesome Python frameworks, libraries, software and resources. Insp ...
随机推荐
- python学习笔记十二:类的定义
demo #!/usr/bin/python class Person: name = 'jim' age = 25 def say(self): print 'My name is ' + self ...
- lnmp一键安装环境中nginx开启pathinfo
问题及原理可参考:http://www.laruence.com/2009/11/13/1138.html 如果是用lnmp脚本一键安装的开发环境,可以通过如下方式开户pathinfo: 1.注释ng ...
- 【Regularization】林轩田机器学习基石
正则化的提出,是因为要解决overfitting的问题. 以Linear Regression为例:低次多项式拟合的效果可能会好于高次多项式拟合的效果. 这里回顾上上节nonlinear transf ...
- ES6常用片段
promise: --在return里面: methods:{ getSellData(){ return axios.get('/api/seller').then((res=>{ retur ...
- codeblocks17.12 debug 报错:ERROR: You need to specify a debugger program in the debuggers's settings.
DebugERROR: You need to specify a debugger program in the debuggers's settings.(For MinGW compilers, ...
- 安卓自动化robotium工具简单使用(二)
在学习安卓的这段时间里,刚好有个朋友有一个APP的应用需要开发. 我马上就动手开始做着试试,在完成开发的同时写了相应的自动化测试代码,使用的是robotium. 才接触安卓没几天,写的不太好,如果有好 ...
- hadoop-hdfs(三)
HDFS概念 1 数据块* HDFS的一个数据块默认是64M,与元数据分开管理. 优点: 数据块的大小设计的较大,所以寻址占传输的时间比例较小,只需要计算传输速度即可. 便于简化管理,利于计算剩余空间 ...
- ALPHA(10)
目录 组员情况 组员1(组长):胡绪佩 组员2:胡青元 组员3:庄卉 组员4:家灿 组员5:凯琳 组员6:翟丹丹 组员7:何家伟 组员8:政演 组员9:黄鸿杰 组员10:刘一好 组员11:何宇恒 展示 ...
- 想了一天的题目QAQ 毛线数列的最值
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <iostream> #i ...
- Android初学者必知会的编程规范
在安卓学习中,我们首先需要掌握的就是Android编程的一些规范,只有掌握了这些规范,后面的深入学习才能开展.今天小编在一个Android培训网站上搜罗了一些,Android初学者不得不知的开发规范, ...
