ES BM25 TF-IDF相似度算法设置——
Before we move on from relevance and scoring, we will finish this chapter with a more advanced subject: pluggable similarity algorithms. While Elasticsearch uses the Lucene’s Practical Scoring Function as its default similarity algorithm, it supports other algorithms out of the box, which are listed in the Similarity Modules documentation.
Okapi BM25
The most interesting competitor to TF/IDF and the vector space model is called Okapi BM25, which is considered to be a state-of-the-art ranking function. BM25 originates from the probabilistic relevance model, rather than the vector space model, yet the algorithm has a lot in common with Lucene’s practical scoring function.
Both use term frequency, inverse document frequency, and field-length normalization, but the definition of each of these factors is a little different. Rather than explaining the BM25 formula in detail, we will focus on the practical advantages that BM25 offers.
Term-frequency saturation
Both TF/IDF and BM25 use inverse document frequency to distinguish between common (low value) words and uncommon (high value) words. Both also recognize (see Term frequency) that the more often a word appears in a document, the more likely is it that the document is relevant for that word.
However, common words occur commonly. The fact that a common word appears many times in one document is offset by the fact that the word appears many times in all documents.
However, TF/IDF was designed in an era when it was standard practice to remove the most common words (or stopwords, see Stopwords: Performance Versus Precision) from the index altogether. The algorithm didn’t need to worry about an upper limit for term frequency because the most frequent terms had already been removed.
In Elasticsearch, the standard analyzer—the default for string fields—doesn’t remove stopwords because, even though they are words of little value, they do still have some value. The result is that, for very long documents, the sheer number of occurrences of words like the and and can artificially boost their weight.
BM25, on the other hand, does have an upper limit. Terms that appear 5 to 10 times in a document have a significantly larger impact on relevance than terms that appear just once or twice. However, as can be seen in Figure 34, “Term frequency saturation for TF/IDF and BM25”, terms that appear 20 times in a document have almost the same impact as terms that appear a thousand times or more.
This is known as nonlinear term-frequency saturation.
Figure 34. Term frequency saturation for TF/IDF and BM25
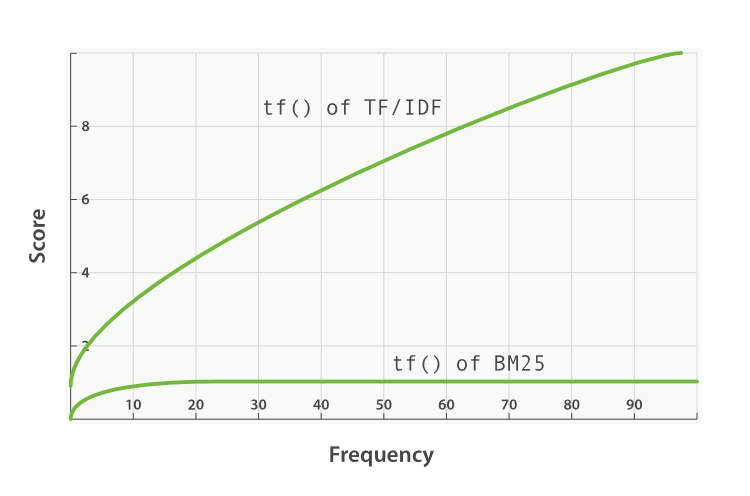
Field-length normalization
In Field-length norm, we said that Lucene considers shorter fields to have more weight than longer fields: the frequency of a term in a field is offset by the length of the field. However, the practical scoring function treats all fields in the same way. It will treat all title fields (because they are short) as more important than all body fields (because they are long).
BM25 also considers shorter fields to have more weight than longer fields, but it considers each field separately by taking the average length of the field into account. It can distinguish between a shorttitle field and a long title field.
In Query-Time Boosting, we said that the title field has a natural boost over the bodyfield because of its length. This natural boost disappears with BM25 as differences in field length apply only within a single field.
ES BM25 TF-IDF相似度算法设置——的更多相关文章
- ES 相似度算法设置(续)
Tuning BM25 One of the nice features of BM25 is that, unlike TF/IDF, it has two parameters that allo ...
- 信息检索中的TF/IDF概念与算法的解释
https://blog.csdn.net/class_brick/article/details/79135909 概念 TF-IDF(term frequency–inverse document ...
- 基于TF/IDF的聚类算法原理
一.TF/IDF描述单个term与特定document的相关性TF(Term Frequency): 表示一个term与某个document的相关性. 公式为这个term在document中出 ...
- ES设置查询的相似度算法
similarity Elasticsearch allows you to configure a scoring algorithm or similarity per field. The si ...
- Elasticsearch由浅入深(十)搜索引擎:相关度评分 TF&IDF算法、doc value正排索引、解密query、fetch phrase原理、Bouncing Results问题、基于scoll技术滚动搜索大量数据
相关度评分 TF&IDF算法 Elasticsearch的相关度评分(relevance score)算法采用的是term frequency/inverse document frequen ...
- 25.TF&IDF算法以及向量空间模型算法
主要知识点: boolean model IF/IDF vector space model 一.boolean model 在es做各种搜索进行打分排序时,会先用boolean mo ...
- 55.TF/IDF算法
主要知识点: TF/IDF算法介绍 查看es计算_source的过程及各词条的分数 查看一个document是如何被匹配到的 一.算法介绍 relevance score算法,简单来说 ...
- tf–idf算法解释及其python代码实现(下)
tf–idf算法python代码实现 这是我写的一个tf-idf的简单实现的代码,我们知道tfidf=tf*idf,所以可以分别计算tf和idf值在相乘,首先我们创建一个简单的语料库,作为例子,只有四 ...
- tf–idf算法解释及其python代码实现(上)
tf–idf算法解释 tf–idf, 是term frequency–inverse document frequency的缩写,它通常用来衡量一个词对在一个语料库中对它所在的文档有多重要,常用在信息 ...
随机推荐
- Xen on Ubuntu
实验环境 ubuntu-14.04.1-desktop-amd64.iso Recommended reference: https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Xen h ...
- Linux相互排斥与同步应用(三):posix线程实现单个生产者和单个消费者模型
[版权声明:尊重原创.转载请保留出处:blog.csdn.net/shallnet 或 .../gentleliu.文章仅供学习交流,请勿用于商业用途] 在第一节说到了 ...
- jsp获取web.xml 里的配置项
ServletContext servletContext = request.getSession().getServletContext(); String titl ...
- SpringMvc自动代理
自动配置的好处是不需要挨个 实现[org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean] ,只需要 advisor 配置和 <bean id=&q ...
- Double类parseDouble()和valueOf()方法的区别
数字类型的String字符串转换为浮点数通常采用parseDouble()和valueOf()方法, 两者主要是存在以下两点区别. 区别一:参数区别Double.parseDouble(java.la ...
- CountDownTimer
package com.daoge.widget; import java.text.DecimalFormat; import android.os.CountDownTimer; import a ...
- MessageDigest和DigestUtils加密算法
总结:使用DigestUtils的方法加密的结果与messageDigest的方法加密结果一致,可使用DigestUtils替换MessageDigest 可省掉部分代码 package com.a ...
- squared-error loss is much more repaidly updated than mean-absolute-deviation when searching for splits
平方差损失能较绝对值差损失更快地更新
- Spanner: Google’s Globally-Distributed Database
https://research.google.com/archive/spanner.html Spanner is Google’s scalable, multi-version, global ...
- CUDA: 原子操作
1.1以上计算功能集支持全局内存上的原子操作, 1.2以上支持共享内存上的原子操作. atomicAdd(add,y)将生成一个原子的操作序列,这个操作序列包括读取地址addr处的值,将y增加到这个值 ...
