结对作业:四则运算(Java+JavaFX)
一、简介
- 此程序是一个可自动生成,计算小学四则运算题目的项目。
- Github地址:https://github.com/czmDeRepository/SoftwareWork/tree/master/work/Myapp
- 作者:陈忠明,张焜。
二、PSP表
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
180 |
200 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
250 |
300 |
|
Development |
开发 |
400 |
500 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
60 |
50 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
30 |
40 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
10 |
30 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
5 |
10 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
60 |
70 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
200 |
220 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
30 |
50 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
20 |
30 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
50 |
70 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
20 |
20 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
40 |
|
合计 |
1375 |
1660 |
三、效能分析
- 程序理耗时最长的题目生成,判断是否合法和去重以及计算
四、设计实现过程
1,项目说明
自然数:0, 1, 2, …。
- 真分数:1/2, 1/3, 2/3, 1/4, 1’1/2, …。
- 运算符:+, −, ×, ÷。
- 括号:(, )。
- 等号:=。
- 分隔符:空格(用于四则运算符和等号前后)。
- 算术表达式:
e = n | e1 + e2 | e1 − e2 | e1 × e2 | e1 ÷ e2 | (e),
其中e, e1和e2为表达式,n为自然数或真分数。
- 四则运算题目:e = ,其中e为算术表达式。
2,基本需求
- 使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数,例如
Myapp.exe -n 10 将生成10个题目。
- 使用 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围,例如
Myapp.exe -r 10 将生成10以内(不包括10)的四则运算题目。该参数可以设置为1或其他自然数。该参数必须给定,否则程序报错并给出帮助信息。
- 生成的题目中计算过程不能产生负数,也就是说算术表达式中如果存在形如e1− e2的子表达式,那么e1≥ e2。
- 生成的题目中如果存在形如e1÷ e2的子表达式,那么其结果应是真分数。
- 每道题目中出现的运算符个数不超过3个。
- 程序一次运行生成的题目不能重复,即任何两道题目不能通过有限次交换+和×左右的算术表达式变换为同一道题目。例如,23 + 45 = 和45 + 23 = 是重复的题目,6 × 8 = 和8 × 6 = 也是重复的题目。3+(2+1)和1+2+3这两个题目是重复的,由于+是左结合的,1+2+3等价于(1+2)+3,也就是3+(1+2),也就是3+(2+1)。但是1+2+3和3+2+1是不重复的两道题,因为1+2+3等价于(1+2)+3,而3+2+1等价于(3+2)+1,它们之间不能通过有限次交换变成同一个题目。
生成的题目存入执行程序的当前目录下的Exercises.txt文件,格式如下:
- 四则运算题目1
- 四则运算题目2
……
其中真分数在输入输出时采用如下格式,真分数五分之三表示为3/5,真分数二又八分之三表示为2’3/8。
- 在生成题目的同时,计算出所有题目的答案,并存入执行程序的当前目录下的Answers.txt文件,格式如下:
- 答案1
- 答案2
特别的,真分数的运算如下例所示:1/6 + 1/8 = 7/24。
- 程序应能支持一万道题目的生成。
- 程序支持对给定的题目文件和答案文件,判定答案中的对错并进行数量统计,输入参数如下:
Myapp.exe -e <exercisefile>.txt -a <answerfile>.txt
统计结果输出到文件Grade.txt,格式如下:
Correct: 5 (1, 3, 5, 7, 9)
Wrong: 5 (2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
其中“:”后面的数字5表示对/错的题目的数量,括号内的是对/错题目的编号。为简单起见,假设输入的题目都是按照顺序编号的符合规范的题目。
设计思路
- 对于表达式的生成,大致的思路为:
(1) 随机数决定运算符数量n,从而决定操作数的数量(n+1)
(2) 将生成分为2n + 1步
(3) 奇数步骤时:
随机数决定是否生成括号
随机数决定生成的操作数是整数还是分数
(4) 偶数步骤时:
随机数决定生成的运算符是什么符号
其中,每一步生成后,都用append方法进行直接拼接
2.对于解决题目重复的问题:
观察重复题目的一些主要特点:
(1) 所用到的运算符完全相同(不含括号),只是出现的顺序不同
(2) 所用到的操作数完全相同,只是出现的顺序不同
(3) 答案相同
由此得到:当同时满足上述三个条件可视为题目重复。
开始的时候因为也难以解决同时判断三组数据的问题思考了很久,后来突然想到可以把运算符和操作数一起记录后进行排序,然后以其为key与答案一起存入HashMap中,便解决了这个难题。
大致步骤为:
(1) 在生成操作数和运算符的同时,将其加入到一个字符串S中
(2) 表达式完全生成后,对字符串S进行排序
(3) 判断Map中是否存在S的映射
若存在,匹配是否存在相同的答案,若存在相同的答案,则视为重复,否则在值中添加答案A(形式为:“(A)”)
若不存在,添加S 到(A)的映射
3.对于计算过程
(1) 采用前缀表达式,将表达式转为前缀表达式再用栈进行计算。
(2) 将分式封装成Fraction类,并实现其加减乘除方法。
(3) 在计算过程中存在分式则转成Fraction对象进行计算,否在采用简单整数运算
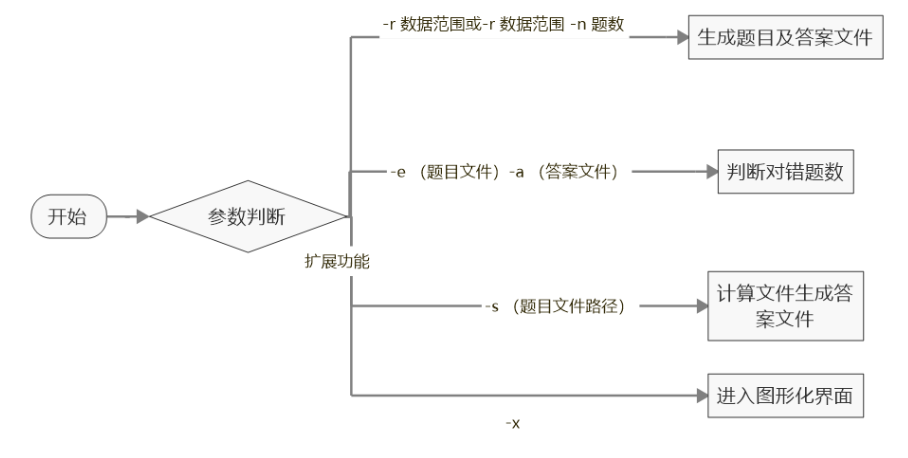
流程图
五、部分源代码
- 分式实例类Fractio类
package com.myapp.entity; /**
* 带分数
*/
public class Fraction {
/**
* 带分数的整数部分
*/
private int integer; /**
* 分子
*/
private int molecule;
/**
* 分母
*/
private int denominator; /**
* @param integer 整数
* @param molecule 分子
* @param denominator 分母
*/
public Fraction(int integer, int molecule, int denominator) {
this.integer = integer;
this.molecule = molecule;
this.denominator = denominator;
} /**
* 加一个整数
*
* @param num
*/
public void add(int num) {
this.integer += num; } /**
* 加一个分式
*
* @return
*/
public void add(Fraction fraction) {
this.integer += fraction.getInteger();
if (this.denominator == fraction.getDenominator()) {
this.molecule += fraction.getMolecule();
} else {
this.molecule = this.molecule * fraction.getDenominator() + fraction.getMolecule() * this.denominator;
this.denominator *= fraction.getDenominator();
}
} /**
* 减法一个整数
* @param num
*/
public boolean reduce(int num) {
this.integer -= num;
if (this.integer < 0) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
} /**
* 减一个分式
*
* @param fraction
*/
public boolean reduce(Fraction fraction) {
this.integer -= fraction.getInteger();
if (this.denominator == fraction.getDenominator()) {
this.molecule -= fraction.getMolecule();
} else {
this.molecule = this.molecule * fraction.getDenominator() - fraction.getMolecule() * this.denominator;
this.denominator *= fraction.getDenominator();
} //分子小于等于0
while (this.molecule < 0) {
this.molecule += this.denominator;
this.integer--;
}
if (this.integer < 0) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
} /**
* 乘一个整数
*
* @param num
*/
public void ride(int num) {
if (this.integer != 0) {
this.molecule += this.integer * this.denominator;
this.integer = 0;
}
this.molecule *= num; } /**
* 乘一个分式
*
* @param fraction
*/
public void ride(Fraction fraction) {
if (this.integer != 0) {
this.molecule += this.integer * this.denominator;
this.integer = 0;
} // if(fraction.getInteger() != 0) {
// fraction.setMolecule(fraction.getInteger() * fraction.getDenominator() +fraction.getMolecule());
// fraction.setInteger(0);
// }
// this.molecule *= fraction.molecule; //不改参数
this.molecule *= fraction.getInteger() * fraction.getDenominator() +fraction.getMolecule(); this.denominator *= fraction.getDenominator(); } /**
* 除以一个整数
* @param num
*/
public boolean divide(int num){
if (num == 0) {
return false;
}
this.molecule += this.integer * this.denominator;
this.integer = 0;
this.denominator *= num;
return true;
} /**
* 除以一个分式
* @param fraction
*/
public boolean divide(Fraction fraction){
if (fraction.getVaule() == 0) {
return false;
}
if (this.integer != 0) {
this.molecule += this.integer * this.denominator;
this.integer = 0;
}
if(fraction.getInteger() != 0) {
this.denominator *= fraction.getInteger() * fraction.getDenominator() +fraction.getMolecule();
}else {
this.denominator *= fraction.getMolecule();
}
this.molecule *= fraction.getDenominator();
return true;
} /**
* 求两数最大公约数
*
* @param a
* @param b
* @return
*/
private static int getCommonDivisor(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) {
return a;
} else {
int remainder = a % b;
a = b;
b = remainder;
return getCommonDivisor(a, b);
}
} /**
* 化简
*/
public void simplification(){
//化简
if (this.molecule > this.denominator) {
this.integer += this.molecule / this.denominator;
this.molecule = this.molecule % this.denominator;
}
//约分
int commonDivisor = getCommonDivisor(this.denominator, this.molecule);
this.denominator /= commonDivisor;
this.molecule /= commonDivisor;
} @Override
public String toString() {
simplification();
if (this.molecule == 0){
//分子为0
return this.integer+"";
} else if (denominator == 1) {
//分母为1
return (this.integer + this.molecule) + "";
} else if (this.integer != 0) {
return this.integer + "'" + this.molecule + "/" + denominator;
} else {
return this.molecule + "/" + denominator;
}
} /**
* 返回小数数值
*
* @return
*/
public double getVaule() {
return this.integer + 1.0 * this.molecule / this.denominator;
} public int getInteger() {
return integer;
} public void setInteger(int integer) {
this.integer = integer;
} public int getMolecule() {
return molecule;
} public void setMolecule(int molecule) {
this.molecule = molecule;
} public int getDenominator() {
return denominator;
} public void setDenominator(int denominator) {
this.denominator = denominator;
} }
- 题目成类
package com.myapp.production; import com.myapp.entity.Fraction;
import com.myapp.util.CalculateUtil;
import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.generic.ALOAD; import java.util.*; public class CreateQuestion { //控制题目个数,默认为10
private int n = 10;
//控制题目中的数值
private int r = -1;
//用于判断重复题目
private Map<ArrayList<String>, String> judge = new IdentityHashMap<>(); public CreateQuestion() { }
public CreateQuestion(int n, int r) {
this.n = n;
this.r = r;
} public void setN(int n) {
this.n = n;
} public void setR(int r) {
this.r = r;
} public Map<String, String> CreateQuestions(){
Map<String, String> questions = new HashMap<>();
int totalNum = n;
while(n > 0) {
String question = this.createArithmeticExpression();
if (question.equals("Error")) continue;
String answer = CalculateUtil.Calculate(question);
// System.out.println(n+"Q:" + question + "\nA:" + answer);
questions.put(question, answer);
n--;
if (n == 0) {
n = totalNum - questions.keySet().size();
}
} return questions;
} public String createArithmeticExpression(){
/**
* @param question 题目
* @param opQuantity 运算符数
* @param step 步骤数
* @param parenthesisPosition 左括号的位置
* @param division 除号的位置
* @param leftParenthesis 左括号数
* @param rightParenthesis 右括号数
* @param adjacent 左括号是否相邻
* @param judge 用于同时储存题目用到的数字和题目用到的运算符(不含括号,下同)
* @param numAL 储存题目用到的数字
* @param opAL 储存题目用到的运算符
* @param re 用于同时储存题目用到的数字和题目用到的运算符以及题目的答案
* @param ans 题目的答案
*/
if (r == -1) {
System.out.println("请先使用\"-r\"设置参数r以控制题目中的数值范围.");
return "Error";
}
if (r <= 1){
System.out.println("参数r不能小于2.");
return "Error";
} StringBuffer question = new StringBuffer();
Random random = new Random(); //随机决定运算符的个数(1-3个)
int opQuantity = random.nextInt(3) + 1;
//根据运算符个数决定操作步数
int step = 2*opQuantity + 1; //决定括号总数
int leftParenthesis = random.nextInt(opQuantity);
int rightParenthesis = 0; int parenthesisPosition = 0;
int division = 0;
boolean adjacent = false; ArrayList<String> numOp = new ArrayList<>(); //当前步数
int i = 1;
while (i <= step){
//单数步骤时生成数字
if (i%2 == 1){
//是否生成括号
switch (leftParenthesis){
case 0: break;
case 1: {
if (i == step - 2) {
question.append("( ");
parenthesisPosition = i;
leftParenthesis--;
rightParenthesis++;
}
else {
switch (random.nextInt(2)){
case 0: break;
case 1: {
question.append("( ");
parenthesisPosition = i;
leftParenthesis--;
rightParenthesis++;
}
}
}
}break;
case 2:{
if (i == 3){
switch (random.nextInt(2)){
case 0: {
question.append("( ");
leftParenthesis--;
rightParenthesis++;
}break;
case 1: {
question.append("( ( ");
leftParenthesis -= 2;
rightParenthesis += 2;
adjacent = true;
}
}
parenthesisPosition = i;
}
if (i == 1){
switch (random.nextInt(3)){
case 0: break;
case 1: {
question.append("( ");
leftParenthesis--;
rightParenthesis++;
parenthesisPosition = i;
}break;
case 2: {
question.append("( ( ");
leftParenthesis -= 2;
rightParenthesis += 2;
adjacent = true;
parenthesisPosition = i;
}
}
}
}
} //生成数字
switch ((random.nextInt(2))){
//生成整数
case 0: {
//除数不能为0
if (i - 1 == division) {
int integer = random.nextInt(r) + 1; Fraction num = new Fraction(0, integer, 1);
numOp.add(num.toString()); question.append(integer);
}
else {
int integer = random.nextInt(r+1); Fraction num = new Fraction(0, integer, 1);
numOp.add(num.toString()); question.append(integer);
}
}break;
//生成分数
case 1: {
/**
* @param integer 整数
* @param molecule 分子
* @param denominator 分母
*
*/
int integer = random.nextInt(r);
int molecule;
int denominator = random.nextInt(r - 1) + 2;
//分子小于分母
molecule = random.nextInt(denominator - 1) + 1; Fraction num = new Fraction(integer, molecule, denominator);
numOp.add(num.toString()); if (integer != 0){
question.append(integer).append("'");
} question.append(molecule).append("/").append(denominator);
}
} //生成右括号
if (rightParenthesis != 0 && parenthesisPosition != i){
if (question.indexOf("(") == 0 && rightParenthesis == 1 && i == step -2){
question.append(" )");
rightParenthesis--;
}
switch (rightParenthesis){
case 1: {
if (i == step) question.append(" )");
else {
switch (random.nextInt(2)){
case 0: break;
case 1: {
question.append(" )");
rightParenthesis--;
}
}
}
}break;
case 2: {
if (adjacent){
question.append(" )");
rightParenthesis--;
}
else {
question.append(" ) )");
rightParenthesis -= 2;
}
}
}
}
}
//偶数步骤时生成运算符
else {
String op = "";
switch (random.nextInt(4)){
case 0: {
op = "+";
question.append(" + ");
}break;
case 1: {
op = "-";
question.append(" - ");
}break;
case 2: {
op = "×";
question.append(" × ");
}break;
case 3: {
op = "÷";
question.append(" ÷ ");
division = i;
}
}
numOp.add(op);
}
i++;
} //若答案计算过程中出现负数或除零错误,则题目生成错误
String ans = CalculateUtil.Calculate(question.toString());
if (ans == null) return "Error"; //将用到的数字和运算符重写排序
sort(numOp); //若用到的数字、运算符相同,题目的答案也相同,则视为重复的题目
if (judge.containsKey(numOp) && judge.get(numOp).equals(ans)) return "Error";
else {
judge.put(numOp, ans);
return question.toString();
}
} //重写方法,使其排序并能保留重复项
public static void sort(List<String> list) {
TreeSet<String> ts = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<String>() { @Override
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
int num = s1.compareTo(s2);
return num==0?1:num;
} }); ts.addAll(list);
list.clear();
list.addAll(ts);
}
}
- 计算工具类
package com.myapp.util; import com.myapp.entity.Fraction; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack; /**
* 计算工具类
*/
public class CalculateUtil { /***
* 获得前缀表达式
* @param exp
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getExpression(String exp) {
// String exp = "1 + ( ( 2 + 3 ) × 4 ) - 5";
Stack<String> charStack = new Stack<>();
Stack<String> expression = new Stack<>();
String[] split = exp.trim().split("\\s+");
int leng = split.length;
for (int i = leng - 1; i >= 0; i--) { // 符号
if (split[i].matches("[+|\\-|×|÷|)]")) {
while (true) {
//如果栈为空或栈顶为")"或者运算符为×÷)
if (charStack.empty() || ")".equals(charStack.peek()) || "×".equals(split[i]) || "÷".equals(split[i]) || ")".equals(split[i])) {
charStack.push(split[i]);
break;
//运算符与栈顶同时为+或-
} else if (split[i].matches("[+|\\-]") && charStack.peek().matches("[+|\\-]")) {
charStack.push(split[i]);
break;
} else {
expression.push(charStack.pop());
}
}
} else if ("(".equals(split[i])) {
while (true) {
if (charStack.peek().equals(")")) {
charStack.pop();
break;
}
expression.push(charStack.pop());
}
} else {
expression.push(split[i]);
} // System.out.println(split[i]); }
while (!charStack.empty()) {
expression.push(charStack.pop());
}
List<String> expList = new ArrayList<>(expression.size());
while (!expression.empty()){
expList.add(expression.pop());
}
return expList;
} /***
* 计算前缀表达式
* @param exp
* @return
*/
public static String Calculate(String exp) {
List<String> expression = getExpression(exp);
String num ;
if (exp.indexOf('÷') > 0 || exp.indexOf('/') > 0) {
Stack<Fraction> numStack = new Stack<>();
Fraction fraction = null;
for (int i = expression.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
num = expression.get(i);
switch (num) {
case "+":
fraction = numStack.pop();
fraction.add(numStack.pop());
numStack.push(fraction);
break;
case "-":
fraction = numStack.pop();
fraction.reduce(numStack.pop());
numStack.push(fraction);
//出现负值直接返回空
if (numStack.peek().getVaule() < 0){
return null;
}
break;
case "×":
fraction = numStack.pop();
fraction.ride(numStack.pop());
numStack.push(fraction);
break;
case "÷":
fraction = numStack.pop();
if (!fraction.divide(numStack.pop())){
//除数为0
return null;
}
numStack.push(fraction);
break;
default:
numStack.push(TransformUtil.expToFraction(num));
} }
return numStack.pop().toString();
} else {
Stack<Integer> numStack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = expression.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
num = expression.get(i);
switch (num) {
case "+":
numStack.push(numStack.pop() + numStack.pop());
break;
case "-":
numStack.push(numStack.pop() - numStack.pop());
//出现负值直接返回空
if (numStack.peek() < 0){
return null;
}
break;
case "×":
numStack.push(numStack.pop() * numStack.pop());
break;
default:
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(num));
} }
return numStack.pop().toString();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) { // String exp = "( 3 + 1'7/8 ) × ( 1/2 )";
// String exp2 = "3 × 1 + ( ( 2 + 3 ) × 4 ) - 5";
String exp = "2 ÷ ( 1/2 - 1/2 )";
System.out.println(Calculate(exp));
// System.out.println(Calculate(exp2));
} }
- Main类
package com.myapp; import com.myapp.production.CreateQuestion;
import com.myapp.util.CalculateUtil;
import com.myapp.util.FileUtil;
import com.myapp.view.Gui;
import javafx.application.Application; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; public class Main {
public static String QUESTION_FILE_NAME = "exercises.txt";
public static String ANSWER_FILE_NAME = "answer.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
switch (args.length) {
case 0:
System.out.println("请输入参数!");
return;
case 1:
if ("-x".equals(args[0])) {
Application.launch(Gui.class);
}
break;
case 2:
switch (args[0]) {
case "-n":
System.out.println("必须使用\"-r\"设置参数r以控制题目中的数值范围.");
break;
case "-r":
//题目中数值(自然数、真分数和真分数分母)的范围
//指定题目数目
CreateQuestion createQuestionR = new CreateQuestion();
createQuestionR.setR(Integer.parseInt(args[1]));
FileUtil.writeQuestion(createQuestionR.CreateQuestions(), QUESTION_FILE_NAME, ANSWER_FILE_NAME);
break;
case "-s":
//指定题目文件计算出答案文件
creatAnswerFile(args[1]);
break;
default:
System.out.println("请输入正确参数");
}
break;
case 4:
if ("-e".equals(args[0]) && "-a".equals(args[2])) {
List[] result = exercisesCheck(args[1], args[3]);
if (result != null) {
System.out.println("Correct: " + result[0].size() + result[0]);
System.out.println("Wrong: " + result[1].size() + result[1]);
}
} else if ("-n".equals(args[0]) && "-r".equals(args[2])) {
FileUtil.writeQuestion(new CreateQuestion(Integer.parseInt(args[1]), Integer.parseInt(args[3])).CreateQuestions(),
QUESTION_FILE_NAME, ANSWER_FILE_NAME);
} else if ("-r".equals(args[0]) && "-n".equals(args[2])) {
FileUtil.writeQuestion(new CreateQuestion(Integer.parseInt(args[3]), Integer.parseInt(args[1])).CreateQuestions(),
QUESTION_FILE_NAME, ANSWER_FILE_NAME);
} else {
System.out.println("请输入正确参数");
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("请输入正确参数");
}
System.out.println("耗时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "毫秒"); } /**
* 检验答案
*
* @param questionFile
* @param answerFile
*/
public static List<Integer>[] exercisesCheck(String questionFile, String answerFile) {
List<Integer> Correct = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> Wrong = new ArrayList<>();
List<String>[] exercises = FileUtil.readQuestion(questionFile, answerFile); if (exercises == null) {
return null;
}
//题目
String answerString;
//答案
String expression;
//题目序号
int i = 1;
//两文件数目不对应时取最短数目文件为标准
int length = exercises[0].size() < exercises[1].size() ? exercises[0].size() : exercises[1].size();
for (int index = 0; index < length; index++) {
//获取对应答案
expression = exercises[0].get(index);
answerString = exercises[1].get(index);
// System.out.println(CalculateUtil.Calculate(expression));
if (answerString.equals(CalculateUtil.Calculate(expression))) {
Correct.add(i++);
} else {
Wrong.add(i++);
}
}
List[] result = new List[2];
result[0] = Correct;
result[1] = Wrong;
return result;
} /**
* 根据题目文件生成答案
*
* @param fileName
*/
public static void creatAnswerFile(String fileName) {
List<String> questions = FileUtil.readFile(fileName);
if (questions == null) {
return;
}
List<String> answers = new ArrayList<>(questions.size());
String answer;
for (String question : questions) {
answer = CalculateUtil.Calculate(question);
if (answer == null) {
answers.add("计算过程出现负数");
} else {
answers.add(answer);
}
}
FileUtil.writeFile(answers, fileName.replaceFirst("\\.txt", "【答案】.txt"));
} }
六、测试图
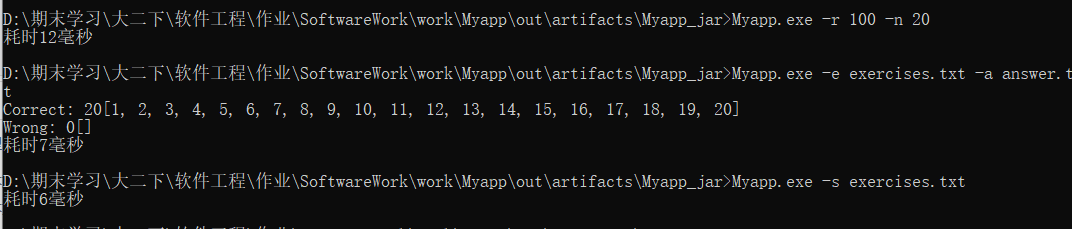
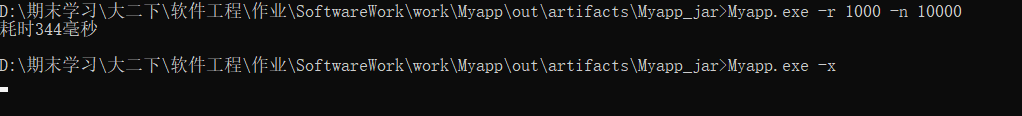
- 命令行测试

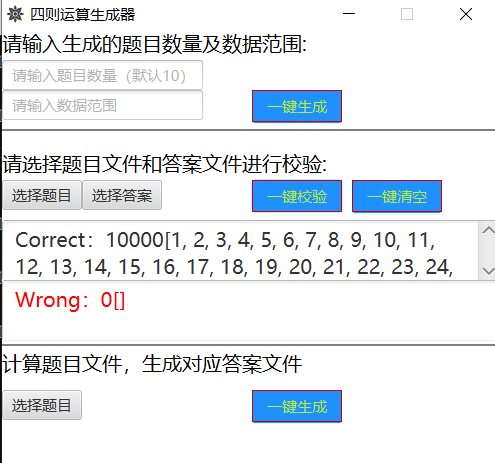
- 可视化图形界面
- 当前目录文件
七、项目小结
- 陈忠明:
知识上学习了前缀表达式的生成及计算,学会用JavaFx实现简单图形界面。
经过本次合作,了解到团队合作讨论交流的重要性,有更多的想法思路碰撞融合产生更好的思路,不同人有不同的编码风格,合作前需先确定编码规范,张焜在项目讨论中有许多独特想法,在一开始讨论就对生成算法有了思路实 在tql,在合作过程中也能及时找出我的bug并提出优化建议。合作使我们的代码质量得到提高。
感谢我的搭档张焜的耐心交流以及其丰富的想法,致想法小天才,找bug小能手坤坤!
- 张焜:
经过本次结对项目,我深刻地体会到了需求分析时,一个人自己想和多个人一起讨论的效率的差距有多大,一个人思考往往会因为疏忽而产生的遗漏,但多个人一起讨论,就容易在别人的想法中找出自己所没有考虑到的东西,也就能更加精确地达成目的。测试的过程中遇到问题,也要及时向对方请教、反馈,否则容易出现更多的问题。
忠明大佬思考比较全面,往往能提出一些我所考虑不到的点,效率之高令也我钦佩不已,也会在我不太明白的时候进行适当地指导,这里非常感谢忠明哥!
结对作业:四则运算(Java+JavaFX)的更多相关文章
- 结对作业——四则运算 Part3. 对于结对编程的总结与思考
结对作业——四则运算 Part3. 对于结对编程的总结与思考 PB15061303 刘梓轩PB16061489 艾寅中 GITHUB 地址 戳这里 目录 Part 1. Core代码编写部分 Part ...
- 结对作业——四则运算 Part2. 封装与对接相关问题
结对作业——四则运算 Part2. 封装与对接相关问题 PB15061303 刘梓轩PB16061489 艾寅中 GITHUB 地址 戳这里 目录 Part 1. Core代码编写部分Part 2. ...
- Core 第三组 结对作业——四则运算 Part1. Core代码编写
结对作业——四则运算 Part1. Core代码编写 PB15061303 刘梓轩PB16061489 艾寅中 GITHUB 地址 戳这里 目录 (因为内容较多,分为了三个部分,但作业系统中只能提交一 ...
- 结对编程四则运算--JAVA实现(徐静、林文敏)
Github项目地址 项目相关要求 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数 (√) Myapp.exe -n 10 // 将生成10个题目 -r 参数控制题目中数值(自然数.真分数和真分数分母)的范围 (√) ...
- 结对作业-四则运算GUI
目录: 一.项目地址二.PSP三.接口设计四.计算模块接口的设计与实现过程五.计算模块接口部分的性能改进六.计算模块部分单元测试展示七.计算模块部分异常处理说明八.界面模块的详细设计过程九.界面模块与 ...
- 20175226 2018-2019-2《java程序设计》结对编程-四则运算(第一周-阶段总结)
结对编程-四则运算(第一周-阶段总结) 需求分析 实现一个四则运算程序,要求: 自动随机生成小学四则运算题目(加,减,乘,除) 支持整数.真分数且支持多项式 能够利用栈的思想,将中缀转换为后缀表达式 ...
- 20175305张天钰Java结对编程四则运算(二)
Java结对编程四则运算(二) 一.题目描述及要求 Git提交粒度不要太粗,建议一个文件/一个类/一个函数/一个功能/一个bug修复都进行提交,不能一天提交一次,更不能一周一次,参考Commit Me ...
- 20175305张天钰Java结对编程四则运算
Java结对编程四则运算 一.题目描述:如何对表达式进行求值运算呢 1.中缀表达式与后缀表达式(娄老师讲解) 中缀表达式就是运算符号在运算数中间的表达式,比如1+2,顾名思义,后缀表达式就是运算符在运 ...
- 结对编程--四则运算(Java)萧英杰 夏浚杰
结对编程--四则运算(Java)萧英杰 夏浚杰 Github项目地址 功能要求 题目:实现一个自动生成小学四则运算题目的命令行程序 使用 -n 参数控制生成题目的个数(实现) 使用 -r 参数控制题目 ...
- 第四,五周——Java编写的电梯模拟系统(结对作业)
作业代码:https://coding.net/u/liyi175/p/Dianti/git 伙伴成员:石开洪 http://www.cnblogs.com/shikaihong/(博客) 这次的作业 ...
随机推荐
- Bug:No mapping for GET /onepill//swagger-ui.html
SpringBoot使用Swagger2本来可以使用的,后来出现的异常No mapping for GET /swagger-ui.html,这个异常其实不用怎么解释,说白了就是找不到了. 遇到这种情 ...
- pandas_使用透视表与交叉表查看业绩汇总数据
# 使用透视表与交叉表查看业绩汇总数据 import pandas as pd import numpy as np import copy # 设置列对齐 pd.set_option("d ...
- PHP gettimeofday() 函数
------------恢复内容开始------------ 实例 返回当前时间: <?php// Print the array from gettimeofday()print_r(gett ...
- PHP utf8_decode() 函数
定义和用法 utf8_decode() 函数把 UTF-8 字符串解码为 ISO-8859-1.高佣联盟 www.cgewang.com 该函数把通过 utf8_encode() 函数编码的 ISO- ...
- PHP str_split() 函数
实例 把字符串 "Hello" 分割到数组中: <?php print_r(str_split("Hello")); ?>高佣联盟 www.cgew ...
- 小甲鱼零基础汇编语言学习笔记第五章之[BX]和loop指令
这一章主要介绍什么是[BX]以及loop(循环)指令怎么使用,loop和[BX]又怎么样相结合,段前缀又是什么鬼,以及如何使用段前缀. 1.[BX]的概念 [BX]和[0]类似 ...
- CF802C Heidi and Library hard 费用流 区间k覆盖问题
LINK:Heidi and Library 先说一下简单版本的 就是权值都为1. 一直无脑加书 然后发现会引起冲突,可以发现此时需要扔掉一本书. 扔掉的话 可以考虑扔掉哪一本是最优的 可以发现扔掉n ...
- 【新生学习】第二周:卷积神经网络_part_1
DEADLINE: 2020-08-01 22:00 写在最前面: 本周学习的是卷积神经网络,是本课程重点中的重点,大家务必要熟练掌握. 本周的学习任务包括 视频学习 . 代码练习 .论文讲解 三部分 ...
- 文档写作利器:Markdown
大佬的文章,写的很好,里面推荐的Markdown编辑工具很不错,值的推荐. 文档写作利器:Markdown_网络_xcbeyond|疯狂源自梦想,技术成就辉煌-CSDN博客https://blog.c ...
- Java 二维数组及方法概况
数组 数组是指一组数据的集合,数组中的每个数据被称作元素.在数组中可以存放任意类型的元素,但同一个数组里存放的元素类型必须一致. 数组的定义 在Java中,可以使用以下格式来定义一个数组. 数据类型[ ...
