代码生成器辅助类Stub、StubQueue与CodeletMark
在解释执行的情况下需要一些类来支持代码生成的过程。
1、InterpreterCodelet与Stub类
Stub类的定义如下:
class Stub VALUE_OBJ_CLASS_SPEC {
public:
// General info/converters
int size() const { ShouldNotCallThis(); return 0; } // must return the size provided by initialize
// Code info
address code_begin() const { ShouldNotCallThis(); return NULL; } // points to the first byte of the code
address code_end() const { ShouldNotCallThis(); return NULL; } // points to the first byte after the code
};
InterpreterCodelet类的定义如下:
class InterpreterCodelet: public Stub {
private:
int _size; // the size in bytes
const char* _description; // a description of the codelet, for debugging & printing
Bytecodes::Code _bytecode; // associated bytecode if any
public:
// Code info
address code_begin() const {
return (address)this + round_to(sizeof(InterpreterCodelet), CodeEntryAlignment);
}
address code_end() const {
return (address)this + size();
}
// ...
int code_size() const {
return code_end() - code_begin();
}
// ...
};
定义了3个属性及一些方法,其内存结构如下:在对齐至CodeEntryAlignment后,紧接着InterpreterCodelet的就是生成的目标代码。如下图所示。
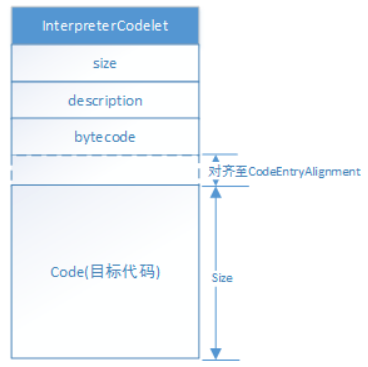
2、StubQueue类
StubQueue是用来保存生成的本地代码的Stub队列,队列每一个元素对应一个InterpreterCodelet对象,InterpreterCodelet对象继承自抽象基类Stub,包含了字节码对应的本地代码以及一些调试和输出信息。
在TemplateInterpreter::initialize()方法中会创建StubQueue对象,如下:
源代码位置:/src/share/vm/interpreter/templateInterpreter.cpp
void TemplateInterpreter::initialize() {
if (_code != NULL)
return;
// 抽象解释器AbstractInterpreter的初始化,AbstractInterpreter是基于汇编模型的解释器的共同基类,
// 定义了解释器和解释器生成器的抽象接口
AbstractInterpreter::initialize();
// 模板表TemplateTable的初始化,模板表TemplateTable保存了各个字节码的模板
TemplateTable::initialize();
// generate interpreter
{
ResourceMark rm;
int code_size = InterpreterCodeSize;
// CodeCache的Stub队列StubQueue的初始化
_code = new StubQueue(new InterpreterCodeletInterface, code_size, NULL,"Interpreter");
// 实例化模板解释器生成器对象TemplateInterpreterGenerator
InterpreterGenerator g(_code);
}
// initialize dispatch table
_active_table = _normal_table;
}
由于TemplateInterpreter继承自AbstractInterpreter,所以在TemplateInterpreter中初始化的_code属性其实就是AbstractInterpreter类中定义的_code属性:
StubQueue* _code
StubQueue类的定义如下:
class StubQueue: public CHeapObj<mtCode> {
private:
StubInterface* _stub_interface; // the interface prototype
address _stub_buffer; // where all stubs are stored
int _buffer_size; // the buffer size in bytes
int _buffer_limit; // the (byte) index of the actual buffer limit (_buffer_limit <= _buffer_size)
int _queue_begin; // the (byte) index of the first queue entry (word-aligned)
int _queue_end; // the (byte) index of the first entry after the queue (word-aligned)
int _number_of_stubs; // the number of buffered stubs
Mutex* const _mutex; // the lock used for a (request, commit) transaction
void check_index(int i) const {
assert(0 <= i && i < _buffer_limit && i % CodeEntryAlignment == 0, "illegal index");
}
bool is_contiguous() const {
return _queue_begin <= _queue_end;
}
int index_of(Stub* s) const {
int i = (address)s - _stub_buffer;
check_index(i);
return i;
}
Stub* stub_at(int i) const {
check_index(i);
return (Stub*)(_stub_buffer + i);
}
Stub* current_stub() const {
return stub_at(_queue_end);
}
// ...
}
这个类的构造函数如下:
StubQueue::StubQueue(
StubInterface* stub_interface,
int buffer_size,
Mutex* lock,
const char* name) : _mutex(lock)
{
intptr_t size = round_to(buffer_size, 2*BytesPerWord);
BufferBlob* blob = BufferBlob::create(name, size); // 在StubQueue中创建BufferBlob _stub_interface = stub_interface; _buffer_size = blob->content_size();
_buffer_limit = blob->content_size();
_stub_buffer = blob->content_begin(); _queue_begin = 0;
_queue_end = 0;
_number_of_stubs = 0;
register_queue(this);
}
首先创建一个BufferBlob对象,然后对StubQueue中的属性进行初始化。调用的register_queue()方法的实现如下:
enum { StubQueueLimit = 10 }; // there are only a few in the world
static StubQueue* registered_stub_queues[StubQueueLimit]; // 长度为10的StubQueue数组
void StubQueue::register_queue(StubQueue* sq) {
for (int i = 0; i < StubQueueLimit; i++) {
if (registered_stub_queues[i] == NULL) {
registered_stub_queues[i] = sq;
return;
}
}
ShouldNotReachHere();
}
StubQueue如下:

队列中的InterpreterCodelet表示一个小例程,比如iconst_1对应的代码,invokedynamic对应的代码,异常处理对应的代码,方法入口点对应的代码,这些代码都是一个个InterpreterCodelet...整个解释器都是由这些小块代码例程组成的,每个小块例程完成解释器的部分功能,以此实现整个解释器。
3、CodeletMark类
InterpreterCodelet依赖CodeletMark完成自动创始和初始化。CodeletMark继承自ResourceMark,允许自动析构,可对临时分配的代码缓存空间或汇编器内存空间自动回收。这个类的定义如下:
// A CodeletMark serves as an automatic creator/initializer for Codelets
// (As a subclass of ResourceMark it automatically GC's the allocated
// code buffer and assemblers). class CodeletMark: ResourceMark {
private:
InterpreterCodelet* _clet; // InterpreterCodelet继承自Stub
InterpreterMacroAssembler** _masm;
CodeBuffer _cb; public:
// 构造函数
CodeletMark(
InterpreterMacroAssembler*& masm,
const char* description,
Bytecodes::Code bytecode = Bytecodes::_illegal):
// AbstractInterpreter::code()获取的是StubQueue*类型的值,调用request()方法获取的
// 是Stub*类型的值,调用的request()方法实现在vm/code/stubs.cpp文件中
_clet( (InterpreterCodelet*)AbstractInterpreter::code()->request(codelet_size()) ),
_cb(_clet->code_begin(), _clet->code_size())
{ // initialize Codelet attributes
_clet->initialize(description, bytecode); // InterpreterMacroAssembler->MacroAssembler->Assembler->AbstractAssembler
// 通过传入的cb.insts属性的值来初始化AbstractAssembler的_code_section与_oop_recorder属性的值
// create assembler for code generation
masm = new InterpreterMacroAssembler(&_cb); // 在构造函数中,初始化r13指向bcp、r14指向本地局部变量表
_masm = &masm;
} // 析构函数
~CodeletMark() {
// align so printing shows nop's instead of random code at the end (Codelets are aligned)
(*_masm)->align(wordSize); // make sure all code is in code buffer
(*_masm)->flush(); // commit Codelet
AbstractInterpreter::code()->commit((*_masm)->code()->pure_insts_size(), (*_masm)->code()->strings()); // make sure nobody can use _masm outside a CodeletMark lifespan
*_masm = NULL;
}
};
在构造函数中主要完成2个任务:
(1)初始化InterpreterCodelet对象_clet。对InterpreterCodelet对象中的3个属性赋值。
(2)创建一个InterpreterMacroAssembler并赋值给masm与_masm,此对象会被用来生成代码。
通常在代码块结束时会自动调用析构函数,在析构函数中完成InterpreterCodelet的提交并清理相关变量的值。
在初始化_clet变量时,调用AbstractInterpreter::code()方法返回AbstractInterpreter类的_code属性的值,这个值在之前TemplateInterpreter::initialize()方法中已经初始化了。继续调用StubQueue类中的request()方法,传递的就是要求分配的用来存储code的大小,通过调用codelet_size()方法来获取,如下:
int codelet_size() {
// Request the whole code buffer (minus a little for alignment).
// The commit call below trims it back for each codelet.
int codelet_size = AbstractInterpreter::code()->available_space() - 2*K;
return codelet_size;
}
request()方法的实现如下:
Stub* StubQueue::request(int requested_code_size) {
assert(requested_code_size > 0, "requested_code_size must be > 0");
if (_mutex != NULL){
_mutex->lock();
}
Stub* s = current_stub();
int requested_size = round_to(stub_code_size_to_size(requested_code_size), CodeEntryAlignment);
if (requested_size <= available_space()) {
if (is_contiguous()) {
// Queue: |...|XXXXXXX|.............|
// ^0 ^begin ^end ^size = limit
assert(_buffer_limit == _buffer_size, "buffer must be fully usable");
if (_queue_end + requested_size <= _buffer_size) {
// code fits in at the end => nothing to do
CodeStrings strings;
stub_initialize(s, requested_size, strings);
return s; // 如果够的话就直接返回
} else {
// stub doesn't fit in at the queue end
// => reduce buffer limit & wrap around
assert(!is_empty(), "just checkin'");
_buffer_limit = _queue_end;
_queue_end = 0;
}
}
}
if (requested_size <= available_space()) {
assert(!is_contiguous(), "just checkin'");
assert(_buffer_limit <= _buffer_size, "queue invariant broken");
// Queue: |XXX|.......|XXXXXXX|.......|
// ^0 ^end ^begin ^limit ^size
s = current_stub();
CodeStrings strings;
stub_initialize(s, requested_size, strings);
return s;
}
// Not enough space left
if (_mutex != NULL){
_mutex->unlock();
}
return NULL;
}
调用的stub_code_size_to_size()方法的实现如下:
// StubQueue类中的方法
int stub_code_size_to_size(int code_size) const {
return _stub_interface->code_size_to_size(code_size);
}
// InterpreterCodeletInterface类中的方法
virtual int code_size_to_size(int code_size) const {
return InterpreterCodelet::code_size_to_size(code_size);
}
// InterpreterCodelet类中的方法
static int code_size_to_size(int code_size) {
// CodeEntryAlignment = 32
// sizeof(InterpreterCodelet) = 32
return round_to(sizeof(InterpreterCodelet), CodeEntryAlignment) + code_size;
}
通过如上的分配内存大小的方式可知内存结构如下:
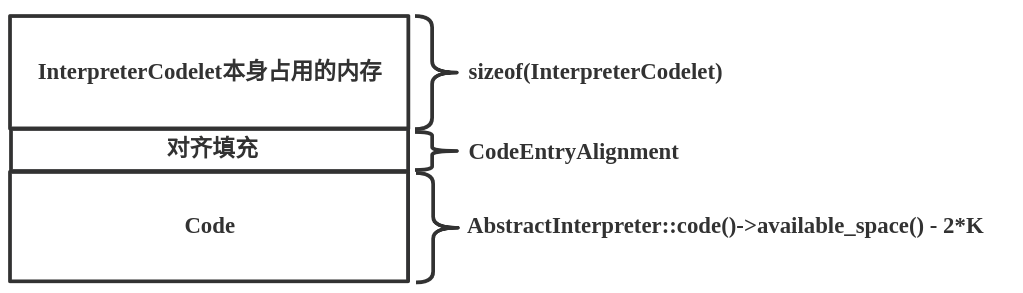
调用的available_space()方法的实现如下:
// StubQueue类中定义的方法
int available_space() const {
int d = _queue_begin - _queue_end - 1;
return d < 0 ? d + _buffer_size : d;
}
is_contiguous()方法的实现如下:
bool is_contiguous() const {
return _queue_begin <= _queue_end;
}
调用的stub_initialize()方法的实现如下:
// 下面都是通过stubInterface来操作Stub的
// Stub functionality accessed via interface
// 在StubQueue类中定义
void stub_initialize(Stub* s, int size,CodeStrings& strings) {
assert(size % CodeEntryAlignment == 0, "size not aligned");
// 通过_stub_interface来操作Stub,会调用s的initialize()方法
_stub_interface->initialize(s, size, strings);
} // 定义在InterpreterCodeletInterface类中
virtual void initialize(Stub* self, int size,CodeStrings& strings){
cast(self)->initialize(size, strings);
} // 定义在InterpreterCodelet类中
void initialize(int size,CodeStrings& strings) {
_size = size;
}
下面来看一下CodeletMark等类的在HotSpot中的具体使用。
在TemplateInterpreter::initialize()方法中初始化InterpreterGenerator对象时,调用的构造函数如下:
InterpreterGenerator::InterpreterGenerator(StubQueue* code)
: TemplateInterpreterGenerator(code) {
generate_all(); // down here so it can be "virtual"
}
在TemplateInterpreterGenerator::generate_all()方法中的实现非常重要,这个方法生成了许多字节码指令以及一些虚拟机辅助执行的代码片段,如下:
{
CodeletMark cm(_masm, "throw exception entrypoints");
// ...
Interpreter::_throw_NullPointerException_entry = generate_exception_handler("java/lang/NullPointerException",NULL);
// ...
}
生成抛出空指针的代码片段。
address generate_exception_handler(const char* name, const char* message) {
return generate_exception_handler_common(name, message, false);
}
调用的generate_exception_handler_common()方法的实现如下:
address TemplateInterpreterGenerator::generate_exception_handler_common(
const char* name, const char* message, bool pass_oop) {
assert(!pass_oop || message == NULL, "either oop or message but not both");
address entry = __ pc();
if (pass_oop) {
// object is at TOS
__ pop(c_rarg2);
}
// expression stack must be empty before entering the VM if an
// exception happened
__ empty_expression_stack();
// setup parameters
__ lea(c_rarg1, ExternalAddress((address)name));
if (pass_oop) {
__ call_VM(rax,
CAST_FROM_FN_PTR(address,InterpreterRuntime::create_klass_exception),
c_rarg1,c_rarg2);
} else {
// kind of lame ExternalAddress can't take NULL because
// external_word_Relocation will assert.
if (message != NULL) {
__ lea(c_rarg2, ExternalAddress((address)message));
} else {
__ movptr(c_rarg2, NULL_WORD);
}
__ call_VM(rax,
CAST_FROM_FN_PTR(address, InterpreterRuntime::create_exception),
c_rarg1, c_rarg2);
}
// throw exception
__ jump(ExternalAddress(Interpreter::throw_exception_entry())); address end = __ pc();
Disassembler::decode(entry, end);
return entry;
}
生成的汇编代码如下:
0x00007fffe10101cb: mov -0x40(%rbp),%rsp
0x00007fffe10101cf: movq $0x0,-0x10(%rbp)
0x00007fffe10101d7: movabs $0x7ffff6e09878,%rsi
0x00007fffe10101e1: movabs $0x0,%rdx
0x00007fffe10101eb: callq 0x00007fffe10101f5
0x00007fffe10101f0: jmpq 0x00007fffe1010288
0x00007fffe10101f5: lea 0x8(%rsp),%rax
0x00007fffe10101fa: mov %r13,-0x38(%rbp)
0x00007fffe10101fe: mov %r15,%rdi
0x00007fffe1010201: mov %rbp,0x200(%r15)
0x00007fffe1010208: mov %rax,0x1f0(%r15)
0x00007fffe101020f: test $0xf,%esp
0x00007fffe1010215: je 0x00007fffe101022d
0x00007fffe101021b: sub $0x8,%rsp
0x00007fffe101021f: callq 0x00007ffff66b3fbc
0x00007fffe1010224: add $0x8,%rsp
0x00007fffe1010228: jmpq 0x00007fffe1010232
0x00007fffe101022d: callq 0x00007ffff66b3fbc
0x00007fffe1010232: movabs $0x0,%r10
0x00007fffe101023c: mov %r10,0x1f0(%r15)
0x00007fffe1010243: movabs $0x0,%r10
0x00007fffe101024d: mov %r10,0x200(%r15)
0x00007fffe1010254: cmpq $0x0,0x8(%r15)
0x00007fffe101025c: je 0x00007fffe1010267
0x00007fffe1010262: jmpq 0x00007fffe1000420
0x00007fffe1010267: mov 0x250(%r15),%rax
0x00007fffe101026e: movabs $0x0,%r10
0x00007fffe1010278: mov %r10,0x250(%r15)
0x00007fffe101027f: mov -0x38(%rbp),%r13
0x00007fffe1010283: mov -0x30(%rbp),%r14
0x00007fffe1010287: retq
0x00007fffe1010288: jmpq 0x00007fffe100f3d3
在这里的重点不是读懂TemplateInterpreterGenerator::generate_exception_handler_common()方法的逻辑及生成的汇编代码,而是要清楚知道CodeletMark的应用,以及generate_exception_handler_common()方法生成的机器码是如何写入InterpreterCodelet中的。之前介绍过InterpreterCodelet与CodeBuffer类,如下: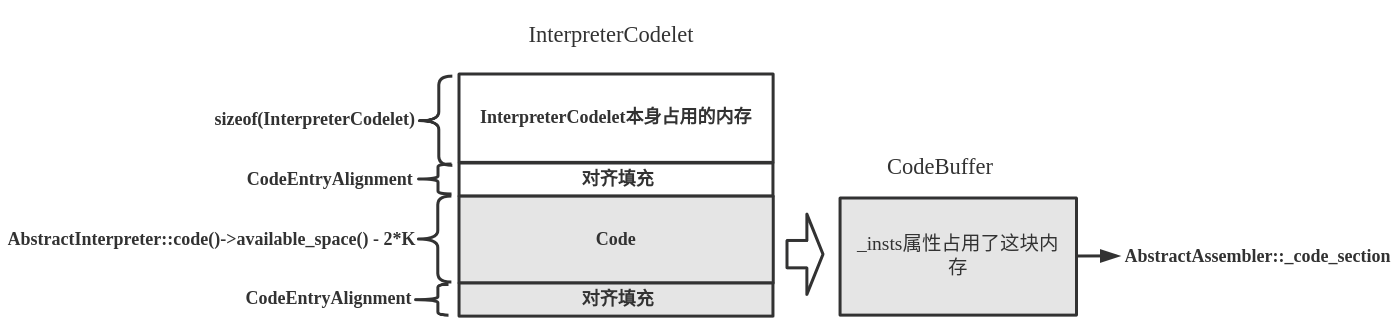
通过CodeBuffer来操作InterpreterCodelet,而CodeBuffer中的代码部分(CodeSection)被赋值给AbstractAssembler::_code_section。
向CodeletMark中传入的_masm参数定义在AbstractInterpreterGenerator类中,如下:
class AbstractInterpreterGenerator: public StackObj {
protected:
InterpreterMacroAssembler* _masm;
// ...
}
generate_exception_handler_common()方法中的__表示一个宏,定义如下:
#define __ _masm->
这样其实就是调用InterpreterMacroAssembler类中的相关方法写机器码,例如
__ pop(c_rarg2);
调用的pop()方法如下:
// 定义在InterpreterMacroAssembler中
void pop(Register r ) {
((MacroAssembler*)this)->pop(r);
} // 定义在Assembler类中
void Assembler::pop(Register dst) {
int encode = prefix_and_encode(dst->encoding());
emit_int8(0x58 | encode);
} // 定义在AbstractAssembler类中
void emit_int8( int8_t x) {
code_section()->emit_int8( x);
}
code_section()方法获取的就是AbstractAssembler的_code_section属性的值。
相关文章的链接如下:
1、在Ubuntu 16.04上编译OpenJDK8的源代码
13、类加载器
14、类的双亲委派机制
15、核心类的预装载
16、Java主类的装载
17、触发类的装载
18、类文件介绍
19、文件流
20、解析Class文件
21、常量池解析(1)
22、常量池解析(2)
23、字段解析(1)
24、字段解析之伪共享(2)
25、字段解析(3)
28、方法解析
29、klassVtable与klassItable类的介绍
30、计算vtable的大小
31、计算itable的大小
32、解析Class文件之创建InstanceKlass对象
33、字段解析之字段注入
34、类的连接
35、类的连接之验证
36、类的连接之重写(1)
37、类的连接之重写(2)
38、方法的连接
39、初始化vtable
40、初始化itable
41、类的初始化
42、对象的创建
43、Java引用类型
50、CallStub栈帧
52、generate_fixed_frame()方法生成Java方法栈帧
54、虚拟机执行模式
作者持续维护的个人博客 classloading.com。
关注公众号,有HotSpot源码剖析系列文章!

代码生成器辅助类Stub、StubQueue与CodeletMark的更多相关文章
- 第12篇-认识CodeletMark
InterpreterCodelet依赖CodeletMark完成自动创建和初始化.CodeletMark继承自ResourceMark,允许自动析构,执行的主要操作就是,会按照Interpreter ...
- HotSpot模板解释器目标代码生成过程源码分析
虽然说解释执行模式是逐字逐句翻译给目标平台运行的,但这样的过程未免太过缓慢,如果能把字节码说的话做成纸条,运行时只要把对应的纸条交给目标平台就可以了,这样,执行速度就会明显提升.JVM的Hotspot ...
- 第11篇-认识Stub与StubQueue
在 第10篇-初始化模板表 我们介绍过TemplateInterpreter::initialize()函数,在这个函数中会调用TemplateTable::initialize()函数初始化模板表, ...
- 如何在Visual Studio中开发自己的代码生成器插件
Visual Studio是美国微软公司开发的一个基本完整的开发工具集,它包括了整个软件生命周期中所需要的大部分工具,如UML工具.代码管控工具.集成开发环境(IDE)等等,且所写的目标代码适用于微 ...
- JavaWeb界面在线配置代码生成器
关于直接main方法运行生成代码可参考我的这篇文章:MP实战系列(六)之代码生成器讲解 在线配置主要参考jeesite和jeecg,gun等开源项目,但是与它们相比又有很多不同? 与jeesite相比 ...
- 从android aidl理解Proxy/stub模式
在小7写的上一篇文章<android IPC通信机制梳理>里,我讲到了如果activity要想和一个跨进程的Service进行通信就需要通过Binder框架,获取到IBinder对象,并调 ...
- iBatis for Net 代码生成器(CodeHelper)附下载地址(已经升级为V 1.1)
CodeHelper是一款可以自己定义模板和生成内容的代码生成器,目前只支持MsSql数据库,这款代码生成器的初衷也只是为了生成MyBatis.net框架的配置文件而写的一个轻量级的代码生成器. Co ...
- java apache-commons-collections中Map辅助类的使用
前言 apache-commons-collections中Map辅助类,很是有用.尽管我们通过原生Map经过业务逻辑处理也能达到相同的作用与效果,但毕竟作为一个开源的工具类辅助类,对它有个了解还是有 ...
- springmvc SSM shiro redis 后台框架 多数据源 代码生成器
A集成代码生成器 [正反双向(单表.主表.明细表.树形表,开发利器)+快速构建表单 下载地址 ; freemaker模版技术 ,0个代码不用写,生成完整的一个模块,带页面.建表sql脚本,处理类 ...
随机推荐
- 关于SignalR 进行双向多步对话
关于ASP.NET SignalR 解释百度百科是这样说的: ASP.NET SignalR 是为 ASP.NET 开发人员提供的一个库,可以简化开发人员将实时 Web 功能添加到应用程序的过程.实时 ...
- rsync 的用法
rsync官方网站: https://www.samba.org/ftp/rsync/rsync.html rsync是可以实现增量备份的工具.配合任务计划,rsync能实现定时或间隔同步,配合ino ...
- 算数组的长度cpp
今天被自己整傻了.... cpp int 型的数组就别想用strlen来求长度了,会报错的. (当然java 里直接用length就可以了...) 所以我建议用vector!!!!!!
- Day08_商品规格管理
学于黑马和传智播客联合做的教学项目 感谢 黑马官网 传智播客官网 微信搜索"艺术行者",关注并回复关键词"乐优商城"获取视频和教程资料! b站在线视频 0.学习 ...
- HTML <body> 标签
HTML <body> 标签 实例 一个简单的 HTML 文档,包含尽可能少的必需的标签: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> ...
- PHP zip_entry_filesize() 函数
定义和用法 The zip_entry_filesize() 函数返回 zip 档案项目的原始文件尺寸(在压缩之前).高佣联盟 www.cgewang.com 语法 zip_entry_filesiz ...
- ABC E - Active Infants 贪心 dp
LINK:Active Infants 一个快省选的人 还在写ABC(莫名觉得丢人 不过也无所谓了. 首先考虑 随便一个排列 我们考虑一下其是不是最优的 容易发现如果最大值没有在边界上的话我们直接把它 ...
- Jenkins总结3-shell脚本
我写shell脚本的功力还很初级,基本都是现学现卖,写得不是很健壮,只能提供个思路,请大家包涵. 我使用的系统只能发函数放到shell最前面.本人还是比较推崇函数式脚本的,方便复用,目前只简单的封装了 ...
- 004_自己尝试go语言中的方法
go语言可以给任意类型定义方法,我在学习过程中,一开始一头雾水,但是随着理解的深入,现在也大概知道了什么叫做方法 之前的一些例子其实讲的并不是特别生动,下面我用一个生动的例子演示一下 首先提出需求.我 ...
- Python基础教程,流程控制语句详解
1.程序结构 计算机在解决问题时,分别是顺序执行所有语句.选择执行部分语句.循环执行部分语句,分别是:顺序结构.选择结构.循环结构.如下图: 很多人学习python,不知道从何学起.很多人学习pyth ...
