Java 树结构的基础部分(一)
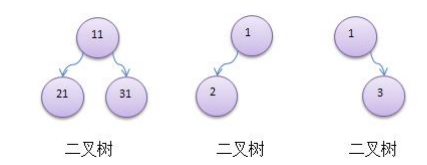
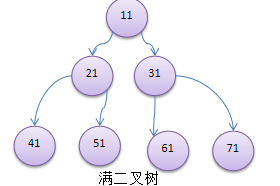
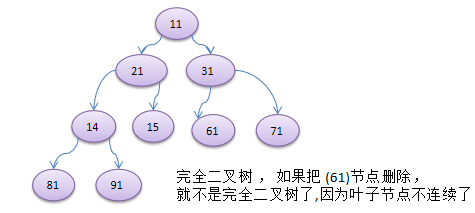

代码实现
在最后面

package com.lin.tree_0308;
public class BinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
HeroNode heroNode1 = new HeroNode(1, "伍六七");
HeroNode heroNode2 = new HeroNode(2, "梅花十一");
HeroNode heroNode3 = new HeroNode(3, "梅花十三");
HeroNode heroNode4 = new HeroNode(4, "江主任");
HeroNode heroNode5 = new HeroNode(5, "希义");
heroNode1.setLeft(heroNode2);
heroNode1.setRight(heroNode3);
heroNode3.setRight(heroNode4);
heroNode3.setLeft(heroNode5);
binaryTree.setRoot(heroNode1);
// System.out.println("前序遍历:");
// binaryTree.preOrder();
// System.out.println("中序遍历:");
// binaryTree.infixOrder();
//
// System.out.println("后序遍历");
// binaryTree.postOrder();
// System.out.println("前序查找:");
// HeroNode preOrderSearch = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(5);
// if(preOrderSearch != null) {
// System.out.println(preOrderSearch);
// } else {
// System.out.println("没有找到");
// }
// System.out.println("中序查找:");
// HeroNode infixOrderSearch = binaryTree.infixOrderSearch(5);
// if(infixOrderSearch != null) {
// System.out.println(infixOrderSearch);
// } else {
// System.out.println("没有找到");
// }
//
// System.out.println("后序查找:");
// HeroNode postOrderSearch = binaryTree.postOrderSearch(5);
// if(postOrderSearch != null) {
// System.out.println(postOrderSearch);
// } else {
// System.out.println("没有找到");
// }
System.out.println("删除前");
binaryTree.preOrder();
binaryTree.delNode(2);
System.out.println("删除后");
binaryTree.preOrder();
}
}
class BinaryTree{
private HeroNode root;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
// 删除节点
public void delNode(int no) {
if (root != null) {
// 如果只有一个root
if (root.getNo() == no) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delNode(no);
}
} else {
System.out.println("空树!");
}
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if(this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空!");
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if(this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空!");
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if(this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空!");
}
}
// 前序查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if(root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 中序查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 后序查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
class HeroNode{
private String name;
private int no;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode [name=" + name + ", no=" + no + "]";
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); // 输出父节点
if(this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this); // 输出父节点
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
// 前序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
System.out.println(this); // 输出父节点
}
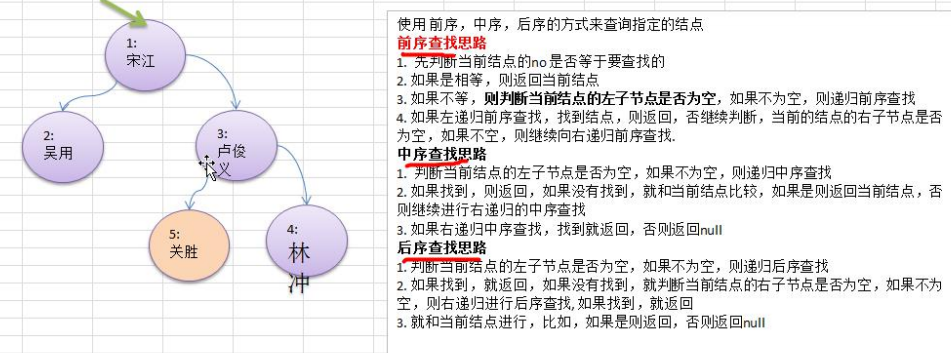
// 前序查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
System.out.println("1");
// 比较当前节点是不是
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 1 判断当前节点的左节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归前序查找
// 2 如果左递归前序查找,找到节点,则返回
HeroNode resNode = null;
if(this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {// 说明左子树找到了
return resNode;
}
// 1 左递归如果没有找到,则继续判断
// 2 当前节点的右节点是否为空,如果不为空,则继续向右递归前序查找
if(this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
// 这时候不管有没有找到都要返回resNode
return resNode;
}
// 中序查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
HeroNode resNode = null;
if(this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("1");
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
if(this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 后序查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
HeroNode resNode = null;
if(this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
if(this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("1");
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 如果都没有找到
return resNode;
}
/**
*
* @Description:1 因为我们的二叉树是单向,所以我们是判断当前节点的子节点是否需要删除节点,而不是直接去判断当前节点是否需要删除节点。<br>
* 2 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,并且左子节点就是要删除节点,就将this.left = null;并且就返回(结束递归删除) <br>
* 3 如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,并且右子节点就是要删除节点,就将this.right = null;并且就返回(结束递归删除) <br>
* 4 如果第2和第3都没有删除节点,那么我们就需要向左子树进行递归删除<br>
* 5 如果第4补也没有删除节点,则向右子树进行递归删除<br>
* @author LinZM
* @date 2021-3-8 15:17:32
* @version V1.8
*/
public void delNode(int no) {
if(this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
if(this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
if(this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no);
}
if(this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}
}
仅供参考,有错误还请指出!
有什么想法,评论区留言,互相指教指教。
觉得不错的可以点一下右边的推荐哟
Java 树结构的基础部分(一)的更多相关文章
- Java 树结构的基础部分(二)
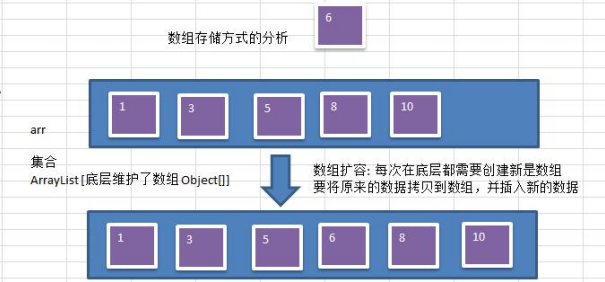
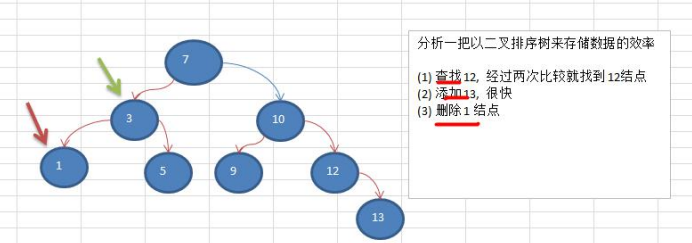
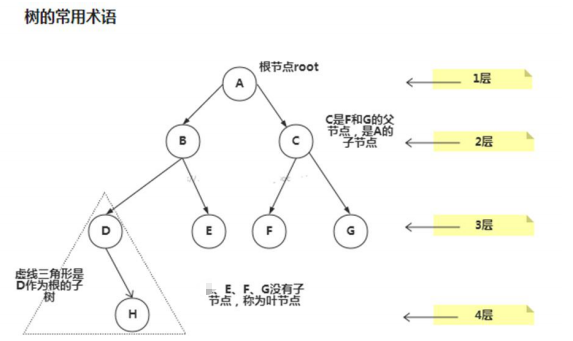
1 顺序存储二叉树 1.1 顺序存储二叉树的概念 基本说明 从数据存储来看,数组存储方式和树的存储方式可以相互转换,即数组可以转换成树,树也可以转换成数组, 看下面的示意图. 要求: 1) 右 ...
- 如何夯实(Java)编程基础,并深入学习和提高
如何夯实(Java)编程基础,并深入学习和提高? 240赞同反对,不会显示你的姓名 匿名用户 240 人赞同 多学习...网上自学的学习网站很多,见以下榜单~一.汇总榜单: 公开课_学习网站导航 收录 ...
- Java开发的基础条件:
------------Java开发的基础条件:Java相关的基础+对编程的自己的理解+调试代码+自己的坚持 一定要谦逊,不人云亦云,不去妄言某一门语言或技术好或坏!不是哪门技术有问题,而是(不会用才 ...
- Java多线程系列--“基础篇”11之 生产消费者问题
概要 本章,会对“生产/消费者问题”进行讨论.涉及到的内容包括:1. 生产/消费者模型2. 生产/消费者实现 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p ...
- Java多线程系列--“基础篇”04之 synchronized关键字
概要 本章,会对synchronized关键字进行介绍.涉及到的内容包括:1. synchronized原理2. synchronized基本规则3. synchronized方法 和 synchro ...
- Java多线程系列--“基础篇”02之 常用的实现多线程的两种方式
概要 本章,我们学习“常用的实现多线程的2种方式”:Thread 和 Runnable.之所以说是常用的,是因为通过还可以通过java.util.concurrent包中的线程池来实现多线程.关于线程 ...
- Java多线程系列--“基础篇”03之 Thread中start()和run()的区别
概要 Thread类包含start()和run()方法,它们的区别是什么?本章将对此作出解答.本章内容包括:start() 和 run()的区别说明start() 和 run()的区别示例start( ...
- Java多线程系列--“基础篇”05之 线程等待与唤醒
概要 本章,会对线程等待/唤醒方法进行介绍.涉及到的内容包括:1. wait(), notify(), notifyAll()等方法介绍2. wait()和notify()3. wait(long t ...
- Java多线程系列--“基础篇”06之 线程让步
概要 本章,会对Thread中的线程让步方法yield()进行介绍.涉及到的内容包括:1. yield()介绍2. yield()示例3. yield() 与 wait()的比较 转载请注明出处:ht ...
随机推荐
- centos 7下设置.net core项目开机自启动
1.在etc/systemd/system下创建xxx.service文件 例如:vi /etc/systemd/system/ubif.service2.编辑 ubif.service内容如下: [ ...
- 获取csc.exe路径
using System.Runtime.InteropServices; var frameworkPath = RuntimeEnvironment.GetRuntimeDirectory(); ...
- DSSM在召回和粗排的应用举例
0.写在前面的话 DSSM(Deep Structured Semantic Models)又称双塔模型,因其结构简单,在推荐系统中应用广泛:下面仅以召回.粗排两个阶段的应用举例,具体描述下DSSM在 ...
- vuepress config favicon
vuepress config favicon .vuepress/public favicons https://vuepress.vuejs.org/guide/assets.html#publi ...
- Sentry 中文版
Sentry 中文版 汉化 https://sentry.io/settings/account/details/ 打开用户设置 User settings 语言选择中文 Simplified Chi ...
- 钓鱼教程 All In One
钓鱼教程 All In One youtube https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=钓鱼教程&sp=CAM%3D 钓鱼证 https:// ...
- js uppercase the first letter of string
js uppercase the first letter of string js String.toUpperCase `-webkit-border-image`.split(`-`).filt ...
- Serverless & FaaS
Serverless & FaaS Function as a Service 通过 Functions(一个事件驱动型无服务器计算平台,还可以解决复杂的业务流程问题)更加高效地进行开发; 在 ...
- vue学习遇到的问题
1.vue脚手架的安装,解决链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/qcq0703/p/14439467.html2.2.2.0+ 的版本里,当在组件上使用 v-for 时,key 现在 ...
- Filter理解
web中Filter通过<init-param>添加参数.web.xml中的配置: <filter> <filter-name>AuthFilter</fil ...
