Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2)——B. Mike and Shortcuts(BFS+小坑)
3 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Recently, Mike was very busy with studying for exams and contests. Now he is going to chill a bit by doing some sight seeing in the city.
City consists of n intersections numbered from 1 to n. Mike starts walking from his house located at the intersection number 1 and goes along some sequence of intersections. Walking from intersection number i to intersection j requires |i - j| units of energy. The total energyspent by Mike to visit a sequence of intersections p1 = 1, p2, ..., pk is equal to  units of energy.
units of energy.
Of course, walking would be boring if there were no shortcuts. A shortcut is a special path that allows Mike walking from one intersection to another requiring only 1 unit of energy. There are exactly n shortcuts in Mike's city, the ith of them allows walking from intersection i to intersection ai (i ≤ ai ≤ ai + 1) (but not in the opposite direction), thus there is exactly one shortcut starting at each intersection. Formally, if Mike chooses a sequence p1 = 1, p2, ..., pk then for each 1 ≤ i < k satisfying pi + 1 = api and api ≠ pi Mike will spend only 1 unit of energy instead of |pi - pi + 1| walking from the intersection pi to intersection pi + 1. For example, if Mike chooses a sequencep1 = 1, p2 = ap1, p3 = ap2, ..., pk = apk - 1, he spends exactly k - 1 units of total energy walking around them.
Before going on his adventure, Mike asks you to find the minimum amount of energy required to reach each of the intersections from his home. Formally, for each 1 ≤ i ≤ n Mike is interested in finding minimum possible total energy of some sequence p1 = 1, p2, ..., pk = i.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200 000) — the number of Mike's city intersection.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (i ≤ ai ≤ n , 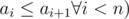 , describing shortcuts of Mike's city, allowing to walk from intersection i to intersection ai using only 1 unit of energy. Please note that the shortcuts don't allow walking in opposite directions (from ai to i).
, describing shortcuts of Mike's city, allowing to walk from intersection i to intersection ai using only 1 unit of energy. Please note that the shortcuts don't allow walking in opposite directions (from ai to i).
In the only line print n integers m1, m2, ..., mn, where mi denotes the least amount of total energy required to walk from intersection 1 to intersection i.
3
2 2 3
0 1 2
5
1 2 3 4 5
0 1 2 3 4
7
4 4 4 4 7 7 7
0 1 2 1 2 3 3
In the first sample case desired sequences are:
1: 1; m1 = 0;
2: 1, 2; m2 = 1;
3: 1, 3; m3 = |3 - 1| = 2.
In the second sample case the sequence for any intersection 1 < i is always 1, i and mi = |1 - i|.
In the third sample case — consider the following intersection sequences:
1: 1; m1 = 0;
2: 1, 2; m2 = |2 - 1| = 1;
3: 1, 4, 3; m3 = 1 + |4 - 3| = 2;
4: 1, 4; m4 = 1;
5: 1, 4, 5; m5 = 1 + |4 - 5| = 2;
6: 1, 4, 6; m6 = 1 + |4 - 6| = 3;
7: 1, 4, 5, 7; m7 = 1 + |4 - 5| + 1 = 3.
这题基本不能用SPFA,20W个点,边多到存不下,SPFA会WA4,然后试了下BFS,也WA4,发现有个坑,第四组中到第10个点的最短距离是8,是1走捷径到17,再一步一步往回走到10即1+7=8而不是直接从1走到10的直接距离9,显然这里需要往回走。BFS里面多写一个往回走的方向搜索就好了
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<sstream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MM(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
typedef long long LL;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const int N=200010; int vis[N];
int cut[N];
int d[N];
queue<pii>Q; void init()
{
MM(vis,0);
MM(cut,-1);
MM(d,0);
while (!Q.empty())
Q.pop();
}
void bfs(const int &s)
{
Q.push(pii(s,0));
while (!Q.empty())
{
pii now=Q.front();
Q.pop();
vis[now.first]=1;
d[now.first]=now.second;
int v;
v=cut[now.first];
if(!vis[v]&&v!=-1)
{
Q.push(pii(v,now.second+1));
vis[v]=1;
}
v=now.first+1;
if(!vis[v])
{
Q.push(pii(v,now.second+1));
vis[v]=1;
}
v=now.first-1;
if(!vis[v])
{
Q.push(pii(v,now.second+1));
vis[now.first-1]=1;
}
}
return ;
}
int main(void)
{
int n,i,j,a,b;
while (~scanf("%d",&n))
{
init();
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a);
cut[i]=a;
}
bfs(1);
for (i=1; i<=n; i++)
printf("%d%s",d[i],i==n?"\n":" ");
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2)——B. Mike and Shortcuts(BFS+小坑)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) B. Mike and Shortcuts bfs
B. Mike and Shortcuts 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/689/problem/B Description Recently, Mi ...
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) E. Mike and Geometry Problem 离散化 排列组合
E. Mike and Geometry Problem 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/689/problem/E Description Mike ...
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) C. Mike and Chocolate Thieves 二分
C. Mike and Chocolate Thieves 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/689/problem/C Description Bad ...
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) A. Mike and Cellphone 水题
A. Mike and Cellphone 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/689/problem/A Description While swimmi ...
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) E. Mike and Geometry Problem 【逆元求组合数 && 离散化】
任意门:http://codeforces.com/contest/689/problem/E E. Mike and Geometry Problem time limit per test 3 s ...
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) E. Mike and Geometry Problem 离散化+逆元
E. Mike and Geometry Problem time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input ...
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2)A. Mike and Cellphone
A. Mike and Cellphone time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces Round #361 (Div. 2) E. Mike and Geometry Problem
题目链接:传送门 题目大意:给你n个区间,求任意k个区间交所包含点的数目之和. 题目思路:将n个区间都离散化掉,然后对于一个覆盖的区间,如果覆盖数cnt>=k,则数目应该加上 区间长度*(cnt ...
- set+线段树 Codeforces Round #305 (Div. 2) D. Mike and Feet
题目传送门 /* 题意:对于长度为x的子序列,每个序列存放为最小值,输出长度为x的子序列的最大值 set+线段树:线段树每个结点存放长度为rt的最大值,更新:先升序排序,逐个添加到set中 查找左右相 ...
随机推荐
- DVWA之命令注入(command injection)
Command injection就是指通过提交恶意构造的参数破坏命令语句结构,从而达到执行恶意命令的目的 LOW 无论是Windows还是Linux,都可以使用&&连接多个命令 执行 ...
- Python3实现自动备份
需求 将重要文件备份到指定目录,存档文件名称为“当前日期.zip”. 前提 1) Windows系统 2) Python 3以上版本 旗舰版 #!usr/bin/python # -*- coding ...
- Windows定时任务管理以及服务管理
1.NSSM.exe https://nssm.cc/ 2.Topshelf 引用地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/guogangj/p/10093102.html#4136330
- NBUT 1117 Kotiya's Incantation(字符输入处理)
题意: 比较两个串,有三种情况:完全相同,可见字符相同,不同.每个字符串以'-'结尾.难点在输入. 思路: 字符逐个读入,直到'-'为止,读出两串就可以直接进行判断.如果不足两串则结束.输入时需要注意 ...
- Servlet和JSP之JSTL学习
JSTL JSTL就是JSP标准标签库(JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library, JSTL)是一个定制标签库的集合,用来解决像遍历Map或集合.条件测试.XML处理 ...
- (转)SpringMVC学习(一)——SpringMVC介绍与入门
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/72231272 SpringMVC介绍 SpringMVC是什么? SpringMVC和Stru ...
- 51nod 算法马拉松17 解题报告 以后不能赛中写题解(查逐梦者抄袭本人代码...
B题(数学题: 问(1+sqrt(2)) ^n 能否分解成 sqrt(m) +sqrt(m-1)的形式 如果可以 输出 m%1e9+7 否则 输出no n<=1e18 刚看题没思路 暴力一下 ...
- 动态规划初步-单向STP
一.题目 给一个m行n列(m <= 10,n <= 100)的整数矩阵,从第一列任何位置出发每次往右.右下.右上走一格,最终达到最后一列.要求经过的整数之和最小.整个矩阵是环形的,即第一行 ...
- python基础一 day14 生成器函数进阶
def generator(): print(123) content = yield 1 print('=======',content) print(456) arg = yield 2 '''' ...
- 爬虫4_python2
import urllib2 response = urllib2.urlopen("https://www.baidu.com") print response.read() 构 ...
