HDU 5489 Difference of Clustering 图论
Difference of Clustering
A clustering algorithm takes many member entities as input and partition them into clusters. In this problem, a member entity must be clustered into exactly one cluster. However, we don’t have any pre-knowledge of the clusters, so different algorithms may produce different number of clusters as well as different cluster IDs. One thing we are sure about is that the memberIDs are stable, which means that the same member ID across different algorithms indicates the same member entity.
To compare two clustering algorithms, we care about three kinds of relationship between the old clusters and the new clusters: split, merge and 1:1. Please refer to the figure below.
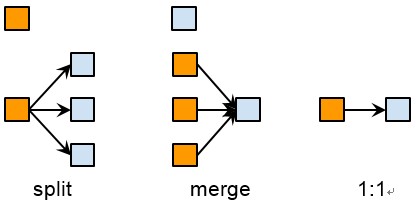
Let’s explain them with examples. Say in the old result, m0, m1, m2 are clustered into one cluster c0, but in the new result, m0 and m1 are clustered into c0, but m2 alone is clustered into c1. We denote the relationship like the following:
● In the old, c0 = [m0, m1, m2]
● In the new, c0 = [m0, m1], c1 = [m2]
There is no other members in the new c0 and c1. Then we say the old c0 is split into new c0 and new c1. A few more examples:
● In the old, c0 = [m0, m1, m2]
● In the new, c0 = [m0, m1, m2].
This is 1:1.
● In the old, c0 = [m0, m1], c1 = [m2]
● In the new, c0 = [m0, m1, m2]
This is merge. Please note, besides these relationship, there is another kind called “n:n”:
● In the old, c0 = [m0, m1], c1 = [m2, m3]
● In the new, c0 = [m0, m1, m2], c1 = [m3]
We don’t care about n:n.
In this problem, we will give you two sets of clustering results, each describing the old and the new. We want to know the total number of splits, merges, and 1:1 respectively.
Each test case starts with a line containing an integer N indicating the number of member entities (0≤N≤106 ). In the following N lines, the i-th line contains two integers c1 and c2, which means that the member entity with ID i is partitioned into cluster c1 and cluster c2 by the old algorithm and the new algorithm respectively. The cluster IDs c1 and c2 can always fit into a 32-bit signed integer.
3
0 0
0 0
0 1
4
0 0
0 0
1 1
1 1
Case #2: 0 0 2
///
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<bitset>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
using namespace std ;
typedef __int64 ll;
#define mem(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define meminf(a) memset(a,127,sizeof(a));
#define memfy(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof(a));
#define TS printf("111111\n");
#define FOR(i,a,b) for( int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define FORJ(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define READ(a,b,c) scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)
#define mod 1000000007
#define inf 100000000
inline ll read()
{
ll x=,f=;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<''||ch>'')
{
if(ch=='-')f=-;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>=''&&ch<='')
{
x=x*+ch-'';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
//**************************************** #define maxn 1000000+6
struct ss
{
int to,next;
} e[maxn];
struct node
{
int x,index;//0,1;
};
int head[maxn],n,a,b,t,in[maxn][],A,B,C;
map<pair<int ,int >,int >mp;
map<int ,int >vis,vis2;
map<int ,vector<int > >mpp,mpp2;
vector<int >V1,V2;
vector<int >::iterator it;;
int main()
{ int T=read();
int oo=;
while(T--)
{
// init();
scanf("%d",&n);
mp.clear();
V1.clear();
V2.clear();
mpp2.clear();
mpp.clear();
vis.clear();
vis2.clear();
int k=;
FOR(i,,n)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(mp[make_pair(a,b)])continue;
mpp[a].push_back(b);
mpp2[b].push_back(a);
if(!vis[a])
V1.push_back(a);
if(!vis2[b])
V2.push_back(b);
vis[a]=;
vis2[b]=;
mp[make_pair(a,b)]=;
}
A=;
B=;
C=;
int sum;
for(int i=; i<V1.size(); i++)
{
sum=;
for(it=mpp[V1[i]].begin(); it!=mpp[V1[i]].end(); it++)
{
sum+=mpp2[*it].size();
}
if(sum==mpp[V1[i]].size())
{
if(sum==)
C++;
else
{
A++;
}
}
}
for(int i=; i<V2.size(); i++)
{
sum=;
for(it=mpp2[V2[i]].begin(); it!=mpp2[V2[i]].end(); it++)
{
sum+=mpp[*it].size();
}
if(sum==mpp2[V2[i]].size())
{ //cout<<mpp[V2[i]].size()<<endl;
if(sum==)
C++;
else
{
B++;
}
}
}
printf("Case #%d: ",oo++);
cout<<A<<" "<<B<<" "<<C/<<endl; }
return ;
}
代码
HDU 5489 Difference of Clustering 图论的更多相关文章
- HDU 5486 Difference of Clustering 图论
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5486 题意: 给你每个元素一开始所属的集合和最后所属的集合,问有多少次集合的分离操作,并操作和不变操 ...
- HDU 5486 Difference of Clustering 暴力模拟
Difference of Clustering HDU - 5486 题意:有n个实体,新旧两种聚类算法,每种算法有很多聚类,在同一算法里,一个实体只属于一个聚类,然后有以下三种模式. 第一种分散, ...
- HDU 5487 Difference of Languages(BFS)
HDU 5487 Difference of Languages 这题从昨天下午2点开始做,到现在才AC了.感觉就是好多题都能想出来,就是写完后debug很长时间,才能AC,是不熟练的原因吗?但愿孰能 ...
- 2015合肥网络赛 HDU 5489 Removed Interval LIS+线段树(树状数组)
HDU 5489 Removed Interval 题意: 求序列中切掉连续的L长度后的最长上升序列 思路: 从前到后求一遍LIS,从后往前求一遍LDS,然后枚举切开的位置i,用线段树维护区间最大值, ...
- hdu 4715 Difference Between Primes
题目连接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4715 Difference Between Primes Description All you kn ...
- HDU 5489 Removed Interval (LIS变形)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5489 给你n个数,要删去其中连续的L个,问你删去之后的LIS最大是多少? 我们先预处理出以i下标为开头 ...
- HDU 5936 Difference 【中途相遇法】(2016年中国大学生程序设计竞赛(杭州))
Difference Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- 【二分】【最长上升子序列】HDU 5489 Removed Interval (2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Hefei Online)
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5489 题目大意: 一个N(N<=100000)个数的序列,要从中去掉相邻的L个数(去掉整个区间 ...
- HDU 5487 Difference of Languages
Difference of Languages Time Limit: 1000ms Memory Limit: 32768KB This problem will be judged on HDU. ...
随机推荐
- (转)Hibernate框架基础——映射普通属性
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/52739871 持久化对象与OID 对持久化对象的要求 提供一个无参的构造器.使Hibernat ...
- CAD从二制流数据中加载图形(com接口Delphi语言)
主要用到函数说明: _DMxDrawX::ReadBinStream 从二制流数据中加载图形,详细说明如下: 参数 说明 VARIANT varBinArray 二制流数据,是个byte数组 BSTR ...
- API Studio 5.1.2 版本更新:加入全局搜索、支持批量测试API测试用例、读取代码注解生成文档支持Github与码云等
最近在EOLINKER的开发任务繁重,许久在博客园没有更新产品动态了,经过这些日子,EOLINKER又有了长足的进步,增加了更多易用的功能,比如加入全局搜索.支持批量测试API测试用例.读取代码注解生 ...
- 带返回值的线程Callable
- 17Aspectij
17Aspectij-2018/07/31 1.Aspectj基于xml 前置通知 method : 通知,及方法名 pointcut :切入点表达式,此表达式只能当前通知使用. pointcut-r ...
- Codeforces 280C - Game on Tree
传送门:280C - Game on Tree 不知道期望是啥的请自行Baidu或Google,(溜了 题目大意,有一棵有根树,每次随机选择一个节点,将这个节点和它的子树删除,问将整棵树删除的期望次数 ...
- Linux---文件目录管理
1. Linux文件目录架构 Linux的目录结构与win的目录有很大不同,首先,没有盘符的概念:然后Linux使用斜杠/标识目录,Linux首先建立一个根目录,然后将其他文件系统挂载到这个目录下. ...
- Linux学习笔记记录(六)
- fillder抓取APP数据之小程序
1.下载fillder ,fillder官网:https://www.telerik.com/fiddler 2.安装好后设置fillder: 工具—>选项,打开设置面板.选择HTTPS选项卡. ...
- 腾讯云,搭建Http静态服务器环境
任务时间:15min ~ 30min 搭建静态网站,首先需要部署环境.下面的步骤,将告诉大家如何在服务器上通过 Nginx 部署 HTTP 静态服务. 安装 Nginx 在 CentOS 上,可直接使 ...
