Android开发初体验
本文通过开发一个应用来学习Android基本概念及构成应用的UI组件。
开发的应用名叫GeoQuiz,它能给出一道道地理知识问题。用户点击true或false按钮回答问题,应用即时做出反馈
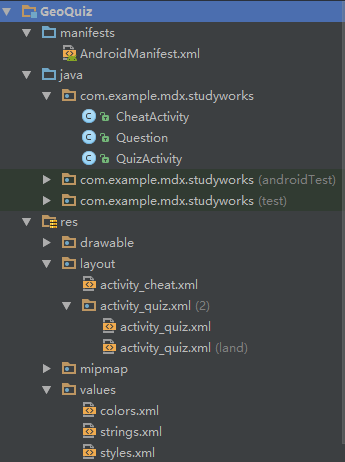
第一步请先自行创建一个新项目,目录如下
1. 用户界面设计
- 在XML文件(activity_quiz.xml)中定义组件
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/question_text_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="24dp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/true_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/true_button"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/false_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/false_button"/>
</LinearLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/cheat_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/cheat_button"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/pre_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/pre_button"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/arrow_left"/>
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/next_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/arrow_right"
android:contentDescription="@string/next_button"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
activity_quiz.xml 效果图

- 创建字符串资源
最好不要硬编码设置组件的文本信息,如:android:text="True"。较好的做法是将文字内容放置在独立的字符串资源XML文件中,然后引用它们,如:android:text="@string/true_button"。
找到app/res/values目录,打开string.xml文件
添加字符串资源
<resources>
<string name="app_name">GeoQuiz</string>
<string name="true_button">True</string>
<string name="false_button">False</string>
<string name="pre_button">Pre</string>
<string name="next_button">Next</string>
<string name="correct_toast">Correct!</string>
<string name="incorrect_toast">Incorrect!</string>
<string name="question_oceans">The Pacific Ocean is larger than
the Atlantic Ocean.</string>
<string name="question_mideast">The Suez Canal connects the Red Sea
and the Indian Ocean.</string>
<string name="question_africa">The source of the Nile River is in Egypt.</string>
<string name="question_americas">The Amazon River is the longest river in the Americas.</string>
<string name="question_asia">Lake Baikal is the world\'s oldest and deepest
freshwater lake.</string>
<string name="warning_text">Are you sure you want to do this?</string>
<string name="show_answer_button">SHOW ANSWER</string>
<string name="cheat_button">CHEAT!</string>
<string name="judgment_toast">Cheating is wrong.</string>
<string name="fist_page">This is the first page!</string>
</resources>
2. 从布局XML到视图对象
- activity子类的实例创建后,onCreate(Bundle)方法会被调用,同时需要获取并管理用户界面,可再调用setContentView(int layoutResID),根据传入的布局资源ID参数,生成指定布局视图并将其放在屏幕上,布局文件包含的组件也随之以各自的属性定义完成实例化。
public class QuizActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_quiz);
}
}
- 资源和资源ID
- 使用资源ID在代码中获取相应的资源。activity_quiz.xml布局的资源ID为R.layout.activity_quiz。
- 应用当前所有的资源放置在R.java文件中。切换至Project视图,展开目录app/build/generated/source/r.debug即可看到。R.java文件在Android项目编译过程中自动生成,修改布局或字符串等资源后,需再次运行应用,才会得到更新。
- 为需要的组件添加资源ID。如:android:id="@+id/idName"。
- 组件的应用
private Button mTrueButton;//在activity_quiz.java添加成员变量
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
......
mTrueButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.true_button);//引用组件
mTrueButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//设置监听事件
}
});
}
3. 创建提示消息
Android的toast是用来通知用户的简短弹出消息。调用Toast类的以下方法可创建toast:
public static Toast makeText(Context context,int resId,int durattion)
- Context参数通常是Activity的一个实例(Activity本身就是Context的子类)。
- 第二个参数是toast要显示字符串消息的资源ID。
- 第三个参数用来指定toast消息的停留时间。通常是Toast常量中的一个。
//举个例子来说
Toast.makeText(QuizActivity.this,R.string.incorrect_toast,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
4. Android与MVC设计模式
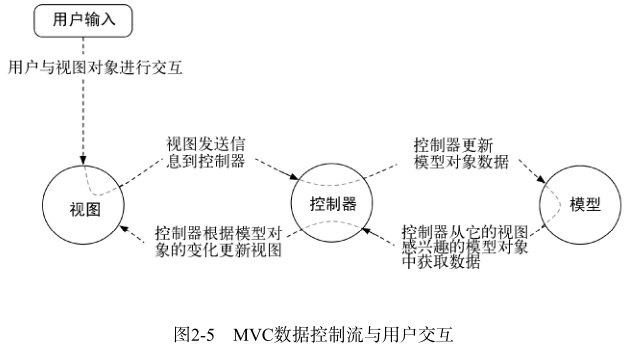
- 应用对象按模型、控制器和视图的类别分为三部分。Android应用基于模型-
控制器-视图(Model-View-Controller,MVC)的架构模式进行设计。MVC设计模式表明,应用的任何对象,归根结底都属于模型对象、视图对象以及控制对象中的一种。
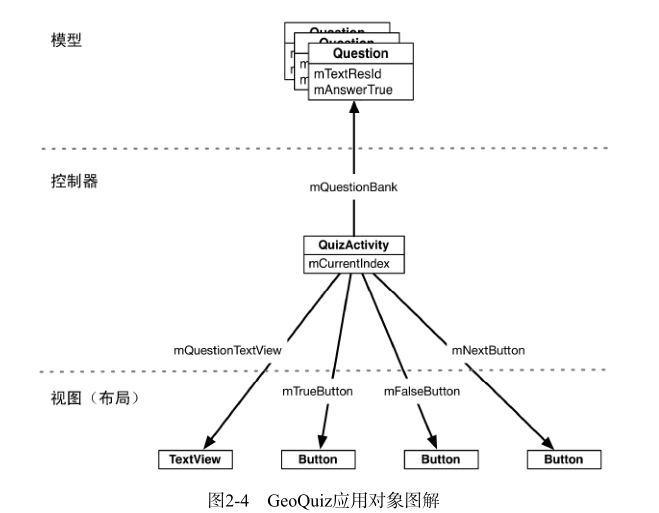
- 我们使用 QuizActivity 创建 Question 数组对象。继而通过与 TextView 以及三个 Button 的交互,在屏幕上显示地理知识问题,并根据用户的回答作出反馈,如图2-4所示。
- 模型层 Question类代码
public class Question {
private int mTextResId;//保存地理知识问题字符串的资源ID。资源ID总是int类型
private boolean mAnswerTrue;//问题答案
public Question(int textResId,boolean answerTrue){
mTextResId=textResId;
mAnswerTrue=answerTrue;
}
public int getTextResId() {
return mTextResId;
}
public void setTextResId(int textResId) {
mTextResId = textResId;
}
public boolean isAnswerTrue() {
return mAnswerTrue;
}
public void setAnswerTrue(boolean answerTrue) {
mAnswerTrue = answerTrue;
}
}
对于有前缀m的成员变量生成getter与setter方法
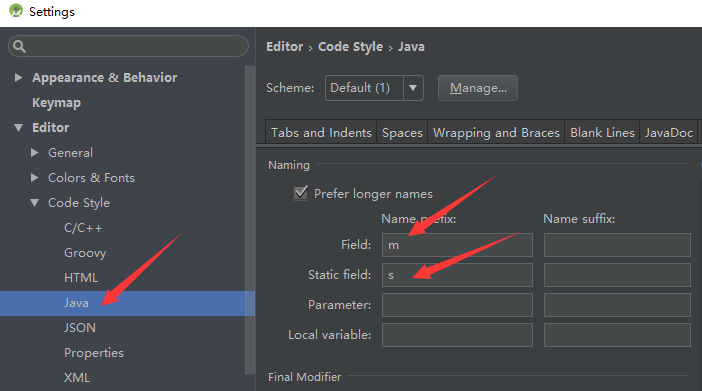
首先,配置Android Studio识别成员变量的 m 前缀。
打开Android Studio首选项对话框(Mac用户选择Android Studio菜单,Windows用户选择File →
Settings菜单)。分别展开Editor和Code Style选项,在Java选项下选择CodeGeneration选项页。在Naming表单中,选择Fields行,添加m作为fields的前缀。若要添加静态变量前缀s,则添加 s 作为Static Fields的前缀。如下图。
- 控制器层QuizActivity.java
public class QuizActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ImageButton mNextButton;
private TextView mQuestionTextView;
private Question[] mQuestionBank=new Question[]{
new Question(R.string.question_oceans,true),
new Question(R.string.question_mideast,false),
new Question(R.string.question_africa,false),
new Question(R.string.question_americas,true),
new Question(R.string.question_asia,true)
};
private int mCurrentIndex=0;
}
5. 添加图片资源
1.将图片添加到drawable对应目录中,后缀名为.png、.jpg、.gif的文件都会自动获得资源ID
- mdpi:中等像素密度屏幕(约160dpi)
- hdpi:高等像素密度屏幕(约240dpi)
- xhdpi:超高像素密度屏幕(约320dpi)
- xxdpi:超超高像素密度屏幕(约480dpi)
2. 在XML文件中引用资源
- 为next按钮增加图片(activity_quiz.xml)
<Button
android:id="@+id/next_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/next_button"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/arrow_righ
android:drawablePadding="4dp"/>
以@string/开头的定义是引用字符串资源
以@drawable/开头的定义是引用drawable资源
ImageButton组件继承自ImageView。Button组件则继承自TextView。ImageView和TextView继承自View
也可以ImageButton组件替换Button组件。删除next按钮的text以及drawable属性定义,并添加ImageView属性。
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/next_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@drawable/arrow_right"
android:contentDescription="@string/next_button"/>
6. activity的生命周期

设备旋转时,系统会销毁当前QuizActivity实例,然后创建一个新的QuizActivity实例。所以每次旋转设备用户每次都会从第一题开始,现在来修正这个缺陷。
- 创建水平模式布局
右键单击res目录选择New->Android resource directory。资源类型选择layout,保持Source set的main选项不变,选择待选资源列表中的Orientation,然后单击>>按钮将其移动到已选资源特征区域。
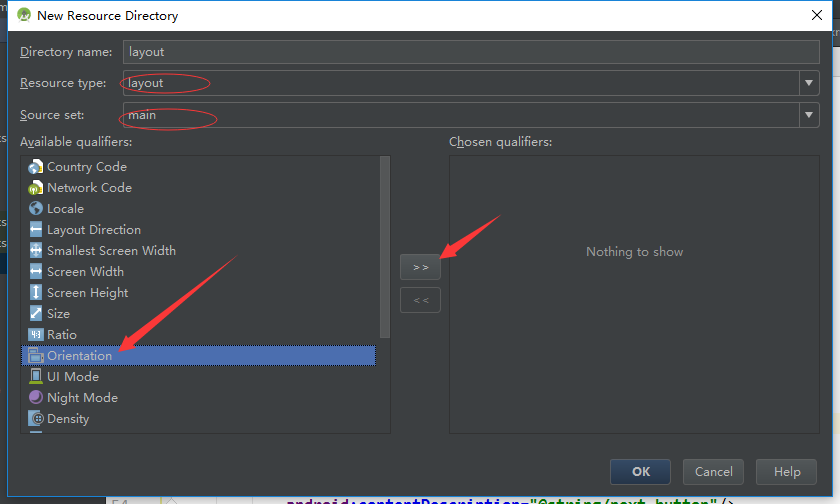
最后,确认选中Screen orientation下拉列表中的Landscape选项,并确保目录名显示为layout-land
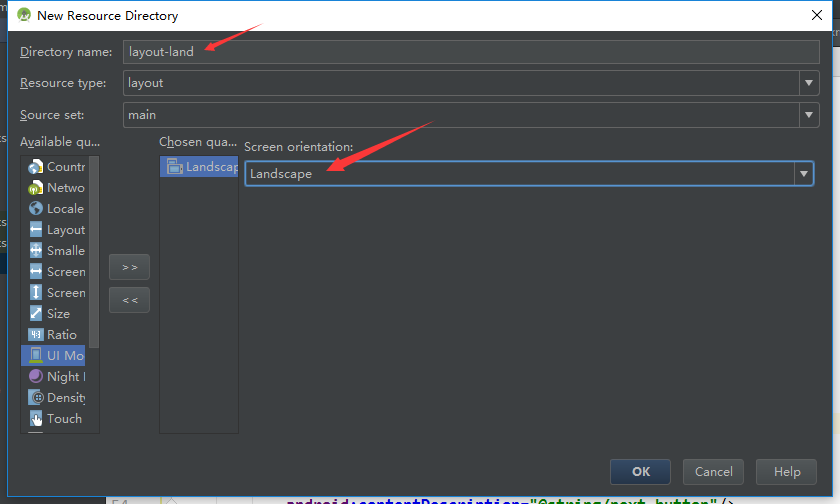
这里的-land后缀名是配置修饰符的另一个使用例子。Android依靠res子目录的配置修饰符定位最佳资源以匹配当前设备配置。设备处于水平方向时,Android会找到并使用res/layout-land目录下的布局资源。其它情况下,它会默认使用res/layout目录下的布局资源。
- 将res/layout目录下的activity_quiz.xml文件复制到res/layout-land目录。
注意:两个布局文件的文件名必须相同,这样它们才能以同一个资源ID被引用
- 水平模式布局修改(layout-land/activity_quiz.xml)
FrameLayout替换了最上层的LinearLayout。FrameLayout是最简单的ViewGroup组件,它一概不管如何安排其子视图的位置。FrameLayout子视图的位置排列取决于它们各自的android:layout_gravity属性。
<FrameLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/question_text_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:padding="24dp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/true_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/true_button"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/false_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/false_button"/>
</LinearLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/cheat_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|center"
android:text="@string/cheat_button"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/pre_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|left"
android:text="@string/pre_button"
android:drawableLeft="@drawable/arrow_left"
android:drawablePadding="4dp"/>
<ImageButton
android:id="@+id/next_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|right"
android:src="@drawable/arrow_right"
android:contentDescription="@string/next_button"/>
</FrameLayout>
- 保存数据以应对设备旋转
覆盖以下Activity方法
protected void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState)
- 该方法通常在onStop()方法之前由系统调用,除非用户按后退键。
- 该方法的默认实现要求所有activity视图将自身数据状态保存在Bundle对象中。Bundle是存储字符串键与限定类型值之间映射关系(键值对)的一种结构。
public class QuizActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
......
private int mCurrentIndex=0;
private static final String KEY_INDEX="index";
@Override
protected void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(savedInstanceState);
savedInstanceState.putInt(KEY_INDEX,mCurrentIndex);
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_quiz);
if(savedInstanceState!=null){
mCurrentIndex=savedInstanceState.getInt(KEY_INDEX,0);
}
......
}
......
}
7. 日志
public static int d(String tag,String msg)//输出日志信息d:debug
方法的第一个参数通常是以类名为值的TAG常量传入
public class QuizActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG="QuizActivity";
......
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.d(TAG,"onCreate(Bundle) called");
setContentView(R.layout.activity_quiz);
......
}
}
| 日志级别 | 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| ERROR | Log.e(...) | 错误 |
| WARNING | Log.w(...) | 警告 |
| INFO | Log.i(...) | 信息型消息 |
| DEBUG | Log.w(...) | 调试输出 |
| VERBOSE | Log.v(...) | 仅用于开发 |
所有的日志记录方法都有两种参数签名:string类型的tag参数和msg参数;除tag和msg参数外再加上Throwable实例参数
9. 第二个activity
新activity将带来第二个用户界面,方便用户偷看问题的答案
第二个activity的布局组件的定义(activity_cheat.xml)
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.mdx.studyworks.CheatActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="24dp"
android:text="@string/warning_text"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/answer_text_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="24dp"
tools:text="Answer"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/show_answer_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/show_answer_button"/>
</LinearLayout>
activity_cheat.xml 效果图
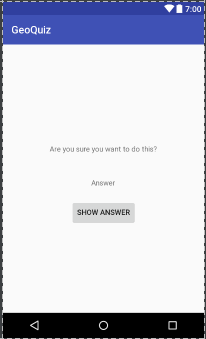
- 注意用于显示答案的TextView组件,它的tools和tools:text属性的命名空间比较特别。该命名空间可以覆盖某个组件的任何属性。这样,可在预览中看到效果,而在运行时Answer文字不会显现出来。
- 应用的所有activity都必须在manifest配置文件中声明,这样操作系统才能找到它们。
//在manifest配置文件中声明CheatActivity
<activity android:name=".CheatActivity">
</activity>
启动activity
public void startActivity(Intent intent)
activity调用startActivity(Intent)方法时,调用请求实际发给了操作系统的ActivityManager。ActivityManager负责创建Activity实例并调用其onCreate(Bundle)方法
public Intent(Context pageContext,Class<?> cls)
传入该方法的Class类型参数告诉ActivityManager应该启动哪个activity
Context参数告诉ActivityManager在哪里可以找到它
mCheatButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.cheat_button);
mCheatButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//从QuizActivity启动CheatActivity
Intent i=new Intent(QuizActivity.this,CheatActivity.class);
startActivity(i);
}
});
activity间数据传递
- 使用 intent extra
将extra数据信息添加给intent,调用Intent.putExtra(...)方法
public Intent putExtra(String name,boolean value)
Intent i=new Intent(QuizActivity.this,CheatActivity.class);
i.putExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_IS_TRUE,answerIsTrue);
startActivity(i)
从extra获取数据
public boolean getBooleanExtra(String name,boolean defaultValue)
mAnswerIsTrue=getIntent().getBooleanExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_IS_TRUE,false);
Activity.getIntent()方法返回了由startActivity(Intent)方法转发的Intent对象
- 从子activity获取返回结果
//父activity
/*第二个参数是请求码,*/
public void startActivityForResult(Intent intent,int requestCode)
//子activity发送返回信息给父activity,有2种方法
public final void setResult(int resultCode)
public final void setResult(int resultCode,Intent data)
resultCode可以是以下任意一个预定义常量
- Activity.RESULT_OK ,即1
- Activity.RESULT_CANCELED ,即0
如需自定义结果代码,还可使用另一个常量:RESULT_FIRST_USER
//父,QuizActivity
private static final int REQUEST_CODE_CHEAT=0;
mCheatButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
boolean answerIsTrue=mQuestionBank[mCurrentIndex].isAnswerTrue();
Intent i=new Intent(QuizActivity.this,CheatActivity.class);
i.putExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_IS_TRUE,answerIsTrue);
startActivityForResult(i,REQUEST_CODE_CHEAT);
}
});
//处理返回结果
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
//super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
//结果码不一致
if (resultCode!= Activity.RESULT_OK){
return;
}
//结果码一致
if (requestCode==REQUEST_CODE_CHEAT){
if (data==null){
return;
}
//解析结果intent
mIsCheater=data.getBooleanExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_SHOW,false);
}
}
//子,CheatActivity
Intent data=new Intent();
data.putExtra(EXTRA_ANSWER_SHOW,isAnswerShown);
setResult(RESULT_OK,data);//设置返回结果
10. activity的使用与管理
被指定为应用的第一个activity
<!--指定第一个activity是QuizActivity-->
<activity android:name=".QuizActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
Android开发初体验的更多相关文章
- Xamarin.iOS开发初体验
aaarticlea/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAKwAAAA+CAIAAAA5/WfHAAAJrklEQVR4nO2c/VdTRxrH+wfdU84pW0
- Microsoft IoT Starter Kit 开发初体验-反馈控制与数据存储
在上一篇文章<Microsoft IoT Starter Kit 开发初体验>中,讲述了微软中国发布的Microsoft IoT Starter Kit所包含的硬件介绍.开发环境搭建.硬件 ...
- IOS开发初体验
IOS开发初体验 搭建开发环境 不多说什么了,开发环境的搭建太简单了,上App Store搜索XCode下载就行了,说多了都是眼泪 创建第一个IOS项目--HolleIOS 创建工程 选择工程创建位置 ...
- 中文代码示例之NW.js桌面应用开发初体验
先看到了NW.js(应该是前身node-webkit的缩写? 觉得该起个更讲究的名字, 如果是NorthWest之意的话, logo(见下)里的指南针好像也没指着西北啊)和Electron的比较文章: ...
- Online开发初体验——Jeecg-Boot 在线配置图表
Online开发——初体验(在线配置图表) 01 通过JSON数据,快速配置图形报表 02 通过SQL数据,快速配置图形报表 03 图表模板配置,实现不同数据源图表合并展示 04 图表布局,支持单排. ...
- Apache Beam入门及Java SDK开发初体验
1 什么是Apache Beam Apache Beam是一个开源的统一的大数据编程模型,它本身并不提供执行引擎,而是支持各种平台如GCP Dataflow.Spark.Flink等.通过Apache ...
- Visual Studio 2015 移动跨平台开发初体验
微软换了新 CEO 后变化很大,对我们团队最有利的消息就是 Visual Studio 2015 支持移动应用跨平台开发. 还记不记得很早之前,Xamarin 宣布与微软成为合作伙伴的消息.显然,Xa ...
- Microsoft IoT Starter Kit 开发初体验
1. 引子 今年6月底,在上海举办的中国国际物联网大会上,微软中国面向中国物联网社区推出了Microsoft IoT Starter Kit ,并且免费开放1000套的申请.申请地址为:http:// ...
- ThinkPHP -- 开发初体验及其几个配置文件的介绍
ThinkPHP是一款不错的轻量级的PHP+MVC框架,它吸取了Ruby On Rails的特性,不仅将Model.View.Controller分开,而且实现了ORM.模板标签等高级特性. 开 ...
随机推荐
- 【CV论文阅读】Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks
由RCNN到FAST RCNN一个很重要的进步是实现了多任务的训练,但是仍然使用Selective Search算法来获得ROI,而FASTER RCNN就是把获得ROI的步骤使用一个深度网络RPN来 ...
- Java线程池几个參数的理解
线程池几个參数的理解: 比方去火车站买票, 有10个售票窗体, 但仅仅有5个窗体对外开放. 那么对外开放的5个窗体称为核心线程数, 而最大线程数是10个窗体.假设5个窗体都被占用, 那么后来的人就必 ...
- Codeforces Round #245 (Div. 1)——Guess the Tree
题目链接 题意: n个节点,给定每一个节点的子树(包含自己)的节点个数.每一个节点假设有子节点必定大于等于2.求这种数是否存在 n (1 ≤ n ≤ 24). 分析: 用类似DP的思路,从已知開始.这 ...
- linux程序设计——运行SQL语句(第八章)
8.3 使用C语言訪问MySQL数据 8.3.3 运行SQL语句 运行SQL语句的主要API函数被恰当的命名为: int mysql_query(MYSQL *connection, const ...
- ubuntu拨号上网以及路由设置
1.宽带拨号 配置宽带连接信息:pppoeconf 拨号:pon dsl-provider 断开连接:poff dsl-provider 查看拨号日志:plog 2.路由设置 以下为rc.local文 ...
- Linux下CMake使用介绍
CMake是一个跨平台的编译自己主动配置工具,它使用一个名为CMakeLists.txt的文件来描写叙述构建过程,能够产生标准的构建文件.它能够用简单的语句来描写叙述全部平台的安装(编译过程).它能够 ...
- ROS人脸检测 使用webcam实现
github地址https://github.com/ngunauj/facedetection 熟悉ros环境.ubuntu16.04 + ros kinetic版本.使用笔记本自带摄像头,完成人脸 ...
- innerxml and outerxml
xml文件如下 <root> <a></a> <b></b> <c></c> <a></a> ...
- C# 获得资源文件下图片的路径
最终实现正确的代码是: button8.Image = System.Drawing.Image.FromFile(@"..\\..\\Resources\\GAOJIBAN.png&quo ...
- 洛谷 P1312 [ NOIP 2011 ] Mayan游戏 —— 搜索+模拟
题目:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1312 还是不擅长这种题,所以参考了一下TJ: 其实也很好搜,按字典序,先搜右移,再搜左移: 不交换相同颜色的两个 ...