【转】static_cast和reinterpret_cast
static_cast和reinterpret_cast揭秘 收藏
本文讨论static_cast<> 和 reinterpret_cast<>。 reinterpret_cast可以转换任意一个32bit整数,包括所有的指针和整数。可以把任何整数转成指针,也可以把任何指针转成整数,以及把指针转化为任意类型的指针,威力最为强大!但不能将非32bit的实例转成指针。总之,只要是32bit的东东,怎么转都行!
static_cast和dynamic_cast可以执行指针到指针的转换,或实例本身到实例本身的转换,但不能在实例和指针之间转换。static_cast只能提供编译时的类型安全,而dynamic_cast可以提供运行时类型安全。举个例子:
class a;class b:a;class c。
上面三个类a是基类,b继承a,c和ab没有关系。
有一个函数void function(a&a);
现在有一个对象是b的实例b,一个c的实例c。
function(static_cast<a&>(b)可以通过而function(static<a&>(c))不能通过编译,因为在编译的时候编译器已经知道c和a的类型不符,因此static_cast可以保证安全。
下面我们骗一下编译器,先把c转成类型a
b& ref_b = reinterpret_cast<b&>c;
然后function(static_cast<a&>(ref_b))就通过了!因为从编译器的角度来看,在编译时并不能知道ref_b实际上是c!
而function(dynamic_cast<a&>(ref_b))编译时也能过,但在运行时就失败了,因为dynamic_cast在运行时检查了ref_b的实际类型,这样怎么也骗不过去了。
在应用多态编程时,当我们无法确定传过来的对象的实际类型时使用dynamic_cast,如果能保证对象的实际类型,用static_cast就可以了。至于reinterpret_cast,我很喜欢,很象c语言那样的暴力转换:) dynamic_cast:动态类型转换
static_cast:静态类型转换
reinterpret_cast:重新解释类型转换
const_cast:常量类型转换
专业的上面很多了,我说说我自己的理解吧:
synamic_cast一般用在父类和子类指针或应用的互相转化;
static_cast一般是普通数据类型(如int m=static_cast<int>(3.14));
reinterpret_cast很像c的一般类型转换操作
const_cast是把cosnt或volatile属性去掉 . 介绍
大多程序员在学C++前都学过C,并且习惯于C风格(类型)转换。当写C++(程序)时,有时候我们在使用static_cast<>和reinterpret_cast<>时可能会有点模糊。在本文中,我将说明static_cast<>实际上做了什么,并且指出一些将会导致错误的情况。 泛型(Generic Types) float f = 12.3;
float* pf = &f;
// static cast<>
// 成功编译, n = 12
int n = static_cast<int>(f);
// 错误,指向的类型是无关的(译注:即指针变量pf是float类型,现在要被转换为int类型) //int* pn = static_cast<int*>(pf);
//成功编译
void* pv = static_cast<void*>(pf);
//成功编译, 但是 *pn2是无意义的内存(rubbish)
int* pn2 = static_cast<int*>(pv);
// reinterpret_cast<>
//错误,编译器知道你应该调用static_cast<>
//int i = reinterpret_cast<int>(f);
//成功编译, 但是 *pn 实际上是无意义的内存,和 *pn2一样
int* pi = reinterpret_cast<int*>(pf);简而言之,static_cast<> 将尝试转换,举例来说,如float-到-integer,而reinterpret_cast<>简单改变编译器的意图重新考虑那个对象作为另一类型。 指针类型(Pointer Types) 指针转换有点复杂,我们将在本文的剩余部分使用下面的类: class CBaseX
{
public:
int x;
CBaseX() { x = ; }
void foo() { printf("CBaseX::foo() x=%d/n", x); }
};
class CBaseY
{
public:
int y;
int* py;
CBaseY() { y = ; py = &y; }
void bar() { printf("CBaseY::bar() y=%d, *py=%d/n", y, *py);
}
};
class CDerived : public CBaseX, public CBaseY
{
public:
int z;
};情况1:两个无关的类之间的转换 // Convert between CBaseX* and CBaseY*
// CBaseX* 和 CBaseY*之间的转换
CBaseX* pX = new CBaseX();
// Error, types pointed to are unrelated
// 错误, 类型指向是无关的
// CBaseY* pY1 = static_cast<CBaseY*>(pX);
// Compile OK, but pY2 is not CBaseX
// 成功编译, 但是 pY2 不是CBaseX
CBaseY* pY2 = reinterpret_cast<CBaseY*>(pX);
// System crash!!
// 系统崩溃!!
// pY2->bar();正如我们在泛型例子中所认识到的,如果你尝试转换一个对象到另一个无关的类static_cast<>将失败,而reinterpret_cast<>就总是成功“欺骗”编译器:那个对象就是那个无关类。 情况2:转换到相关的类 . CDerived* pD = new CDerived();
. printf("CDerived* pD = %x/n", (int)pD);
.
. // static_cast<> CDerived* -> CBaseY* -> CDerived*
//成功编译,隐式static_cast<>转换
. CBaseY* pY1 = pD;
. printf("CBaseY* pY1 = %x/n", (int)pY1);
// 成功编译, 现在 pD1 = pD
. CDerived* pD1 = static_cast<CDerived*>(pY1);
. printf("CDerived* pD1 = %x/n", (int)pD1);
.
. // reinterpret_cast
// 成功编译, 但是 pY2 不是 CBaseY*
. CBaseY* pY2 = reinterpret_cast<CBaseY*>(pD);
. printf("CBaseY* pY2 = %x/n", (int)pY2);
.
. // 无关的 static_cast<>
. CBaseY* pY3 = new CBaseY();
. printf("CBaseY* pY3 = %x/n", (int)pY3);
// 成功编译,尽管 pY3 只是一个 "新 CBaseY()"
. CDerived* pD3 = static_cast<CDerived*>(pY3);
. printf("CDerived* pD3 = %x/n", (int)pD3); ---------------------- 输出 ---------------------------
CDerived* pD = 392fb8
CBaseY* pY1 = 392fbc
CDerived* pD1 = 392fb8
CBaseY* pY2 = 392fb8
CBaseY* pY3 = 390ff0
CDerived* pD3 = 390fec
注意:在将CDerived*用隐式 static_cast<>转换到CBaseY*(第5行)时,结果是(指向)CDerived*(的指针向后) 偏移了4(个字节)(译注:4为int类型在内存中所占字节数)。为了知道static_cast<> 实际如何,我们不得不要来看一下CDerived的内存布局。 CDerived的内存布局(Memory Layout) 本文来自CSDN博客,转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zjl_1026_2001/archive/2008/04/03/2246510.aspx
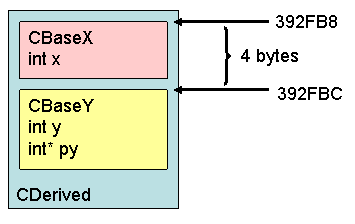
如图所示,CDerived的内存布局包括两个对象,CBaseX 和 CBaseY,编译器也知道这一点。因此,当你将CDerived* 转换到 CBaseY*时,它给指针添加4个字节,同时当你将CBaseY*转换到CDerived*时,它给指针减去4。然而,甚至它即便不是一个CDerived你也可以这样做。
当然,这个问题只在如果你做了多继承时发生。在你将CDerived转换 到 CBaseX时static_cast<> 和 reinterpret_cast<>是没有区别的。 情况3:void*之间的向前和向后转换 因为任何指针可以被转换到void*,而void*可以被向后转换到任何指针(对于static_cast<> 和 reinterpret_cast<>转换都可以这样做),如果没有小心处理的话错误可能发生。 CDerived* pD = new CDerived();
printf("CDerived* pD = %x/n", (int)pD);
CBaseY* pY = pD; // 成功编译, pY = pD + 4
printf("CBaseY* pY = %x/n", (int)pY);
void* pV1 = pY; //成功编译, pV1 = pY
printf("void* pV1 = %x/n", (int)pV1);
// pD2 = pY, 但是我们预期 pD2 = pY - 4
CDerived* pD2 = static_cast<CDerived*>(pV1);
printf("CDerived* pD2 = %x/n", (int)pD2);
// 系统崩溃
// pD2->bar(); ---------------------- 输出 ---------------------------
CDerived* pD = 392fb8
CBaseY* pY = 392fbc
void* pV1 = 392fbc
CDerived* pD2 = 392fbc
一旦我们已经转换指针为void*,我们就不能轻易将其转换回原类。在上面的例子中,从一个void* 返回CDerived*的唯一方法是将其转换为CBaseY*然后再转换为CDerived*。
但是如果我们不能确定它是CBaseY* 还是 CDerived*,这时我们不得不用dynamic_cast<> 或typeid[]。 注释:
. dynamic_cast<>,从另一方面来说,可以防止一个泛型CBaseY* 被转换到CDerived*。
. dynamic_cast<>需要类成为多态,即包括“虚”函数,并因此而不能成为void*。
参考:
. [MSDN] C++ Language Reference -- Casting
. Nishant Sivakumar, Casting Basics - Use C++ casts in your VC++.NET programs
. Juan Soulie, C++ Language Tutorial: Type Casting 本文来自CSDN博客,转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zjl_1026_2001/archive/2008/04/03/2246510.aspx
【转】static_cast和reinterpret_cast的更多相关文章
- c++ 数据类型转换: static_cast dynamic_cast reinterpret_cast const_cast
c++ 数据类型转换: static_cast dynamic_cast reinterpret_cast const_cast [版权声明]转载请注明出处 http://www.cnblogs.c ...
- c++强制类型转换:dynamic_cast、const_cast 、static_cast、reinterpret_cast
c++强制类型转换:dynamic_cast.const_cast .static_cast.reinterpret_cast 博客分类: C/C++ CC++C#编程数据结构 dynamic_ca ...
- static_cast和reinterpret_cast
static_cast和reinterpret_cast 相同点:都是暴力转换,从一个类型转换为另一个类型,对于类指针不会保证安全性 static_cast和reinterpret_cast的区别 ...
- dynamic_cast,const_cast,static_cast,reinterpret_cast 详解
如果直接指针直接强转,将只能访问虚函数的内容,而不能访问特定类中的特定成员或方法!!!! 强制类型转换运算符:C++有四种强制类型转换符,分别是dynamic_cast,const_cast,stat ...
- C++雾中风景11:厘清C++类型转换(static_cast,dynamic_cast,reinterpret_cast,const_cast)
C++是一门弱类型的语言,提供了许多复杂和灵巧类型转换的方式.笔者之前写的Python与Go都是强类型的语言,对这种弱类型的设计实在是接受无力啊~~ ( 生活所迫,工作还得写C++啊~~)C++语言提 ...
- static_cast ,reinterpret_cast
用法:static_cast < type-id > ( expression ) 该运算符把expression转换为type-id类型,但没有运行时类型检查来保证转换的安全性.它主要有 ...
- C++ static_cast dynamic_cast reinterpret_cast const_cast转换
static_cast <type-id> ( expression ) 和C风格的类型转换相似,可以转换一个指针到基类,或者派生类.不做Run-time类型检查,这样转换并不总是安全的. ...
- C++中四种类型转换方式(ynamic_cast,const_cast,static_cast,reinterpret_cast)
Q:什么是C风格转换?什么是static_cast, dynamic_cast 以及 reinterpret_cast?区别是什么?为什么要注意? A:转换的含义是通过改变一个变量的类型为别的类型从而 ...
- 类型转换:static_cast、reinterpret_cast等
一.隐式类型转换 系统自动进行,不需要程序开发人员介入. int m = 3 + 45.6;// 48 把小数部分截掉,也属于隐式类型转换的一部分 double b = 3 + 45.6; // 48 ...
随机推荐
- 全国各大 oj 分类题集...
各种题集从易到难刷到手软 你准备好了吗? 准备剁手吧
- MVC应用程序与单选列表
原文:MVC应用程序与单选列表 前几天,Insus.NET有在MVC应用程序中,练习了<MVC应用程序,动态创建单选列表(RadioButtonList)>http://www.cnblo ...
- poj3207(two-sat)
传送门:Ikki's Story IV - Panda's Trick 题意:给定一个圆,圆上一些点.两点一线.现给出一些线,这些线可以在圆内连起来,也可以在圆外.问有没有可能所有的线画完且不出现相交 ...
- JSP路径出现故障
1.错误叙述性说明 2.错误原因 <%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding=& ...
- hdu1267(递推)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1267 题意:假定一个字符串由m个H和n个D组成,从左到右扫描该串,如果字符H的累计数总是不小于字符D的 ...
- cocos2d-x ndk adt mac 路径配置
export PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/local/mysql/bin export PATH=$PATH:/Applications/MacVim-snapshot-68 expor ...
- linux操作提示:“Can't open file for writing”或“operation not permitted”的解决的方法
在linux上使用vi命令改动一个文件内容的时候,发现无法保存,每次写完使用":q!"命令能够正常退出可是使用":wq!"命令保存文件并退出时出现一下信息提示: ...
- java环境变量设置--编写一年java,竟不会配变量了
java环境变量设置 1.打开我的电脑--属性--高级--环境变量 2.新建系统变量JAVA_HOME 和CLASSPATH 变量名:JAVA_HOME 变量值:C:\Program Files\Ja ...
- 主要的核心思想是取cookie然后发查询请求,不需要浏览器做代理(转)
需求是催生项目和推进项目的不竭动力. 背景: 最近,因为媳妇要做个B超检查,想着去大医院查查应该更放心,所以就把目标瞄准在A医院.早已耳闻A院一号难求万人空巷,所以把所有能接触到的机会都看了一遍,线下 ...
- HUNNU11351:Pythagoras's Revenge
http://acm.hunnu.edu.cn/online/?action=problem&type=show&id=11351&courseid=0 Problem des ...
