Why String is Immutable or Final in Java
The string is Immutable in Java because String objects are cached in String pool. Since cached String literals are shared between multiple clients there is always a risk, where one client's action would affect all another client. For example, if one client changes the value of String "Test" to "TEST", all other clients will also see that value as explained in the first example. Since caching of String objects was important from performance reason this risk was avoided by making String class Immutable. At the same time, String was made final so that no one can compromise invariant of String class e.g. Immutability, Caching, hashcode calculation etc by extending and overriding behaviors. Another reason of why String class is immutable could die due to HashMap.
Important and popularity of String as data type, transfer object and mediator has also made it popular in Java interviews. Why String is immutable in Java is one of the most frequently asked String Interview questions in Java, which starts with discussion of, what is String, how String in Java is different than String in C and C++, and then shifted towards what is immutable object in Java , what are the benefits of immutable object, why do you use them and which scenarios should you use them. This question sometimes also asked, "Why String is final in Java".
On a similar note, if you are preparing for Java interviews, I would suggest you take a loot at the Java Programming interview exposed book, an excellent resource for senior and mid-level Java programmer. It contains questions from all important Java topic including multi-threading, collection, GC, JVM internals and framework like Spring and Hibernate, as shown below:
Why String is Final in Java
As I said, there could be many possible answers to this question, and the only designer of String class can answer it with confidence. I was expecting some clue in Joshua Bloch's Effective Java book, but he also didn't mention it. I think following two reasons make a lot of sense on why String class is made Immutable or final in Java:
String A = "Test"
String B = "Test"
Now String B called, "Test".toUpperCase() which change the same object into "TEST", so A will also be "TEST" which is not desirable. Here is a nice diagram which shows how String literals are created in heap memory and String literal pool.
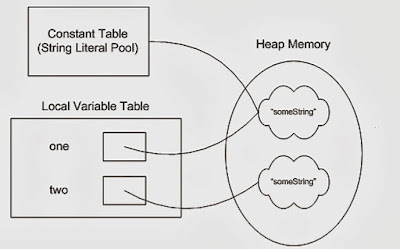
2) String has been widely used as parameter for many Java classes e.g. for opening network connection, you can pass hostname and port number as string, you can pass database URL as a string for opening database connection, you can open any file in Java by passing the name of the file as argument to File I/O classes.
In case, if String is not immutable, this would lead serious security threat, I mean someone can access to any file for which he has authorization, and then can change the file name either deliberately or accidentally and gain access to that file. Because of immutability, you don't need to worry about that kind of threats. This reason also gels with, Why String is final in Java, by making java.lang.String final, Java designer ensured that no one overrides any behavior of String class.
不可变对象是线程安全的
3)Since String is immutable it can safely share between many threads which is very important for multithreaded programming and to avoid any synchronization issues in Java, Immutability also makes String instance thread-safe in Java, means you don't need to synchronize String operation externally. Another important point to note about String is the memory leak caused by SubString, which is not a thread related issues but something to be aware of.
String对象的不可变性使得可以缓存这个实例的哈希码
4) Another reason of Why String is immutable in Java is to allow String to cache its hashcode, being immutable String in Java caches its hashcode, and do not calculate every time we call hashcode method of String, which makes it very fast as hashmap key to be used in hashmap in Java. This one is also suggested by Jaroslav Sedlacek in comments below. In short because String is immutable, no one can change its contents once created which guarantees hashCode of String to be same on multiple invocations.
字节码加载的安全性
5) Another good reason of Why String is immutable in Java suggested by Dan Bergh Johnsson on comments is: The absolutely most important reason that String is immutable is that it is used by the class loading mechanism, and thus have profound and fundamental security aspects. Had String been mutable, a request to load "java.io.Writer" could have been changed to load "mil.vogoon.DiskErasingWriter"
Security and String pool being primary reason of making String immutable, I believe there could be some more very convincing reasons as well, Please post those reasons as comments and I will include those on this post. By the way, above reason holds good to answer, another Java interview questions "Why String is final in Java". Also to be immutable you have to be final so that your subclass doesn't break immutability. what do you guys think?
Why String is Immutable or Final in Java的更多相关文章
- String的不变性到final在java中用法
final在Java语言里面啥意思 final修饰一个类,那么这个类就是不可继承.string就是一个非常有名的被final修饰的类,不过他的更加有名的是“不可被修改”. 究竟什么是不可改变?stri ...
- JAVA —— String is immutable. What exactly is the meaning? [duplicate]
question: I wrote the following code on immutable Strings. public class ImmutableStrings { public st ...
- java问题解读,String类为什么是final的
一.理解final 望文生义,final意为“最终的,最后的”,我理解为“不能被改变的”,它可以修饰类.变量和方法. 所以我是否可以理解为被它所修饰的类.变量和方法都不能被改变呢?答案是”是“,因为有 ...
- 为什么Java中的String是设计成不可变的?(Why String is immutable in java)
There are many reasons due to the string class has been made immutable in Java. These reasons in vie ...
- Why string is immutable in Java ?
This is an old yet still popular question. There are multiple reasons that String is designed to be ...
- Why String is immutable in Java ?--reference
String is an immutable class in Java. An immutable class is simply a class whose instances cannot be ...
- java的String类型为什么是final
(转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/ikuman/archive/2013/08/27/3284410.html) 最佳答案: 主要是为了“效率” 和 “安全性” 的缘故.若 Str ...
- JAVA 中为什么String 是immutable的
本文翻译自:http://www.programcreek.com/2013/04/why-string-is-immutable-in-java/ 这是一个很老但很流行的问题,这里有几个原因Stri ...
- Java问题解读系列之String相关---String类为什么是final的?
今天看到一篇名为<Java开发岗位面试题归类汇总>的博客,戳进去看了一下题目,觉得有必要夯实一下基本功了,所以打算边学边以博客的形式归纳总结,每天一道题, 并将该计划称为java问题解读系 ...
随机推荐
- 使用 urllib 发送请求
urllib.request.urlopen(url, data=None, timeout=n) 用于发送HTTP请求并得到响应内容 In []: import urllib.request In ...
- Ubuntu12.04编译Android2.3.4
Ubuntu12.04编译Android2.3.4 1.下载Ubuntuubuntu-12.04-dvd-i386.iso2.使用U盘安装,启动盘制作用unetbootin-windows-568工具 ...
- c语言学习笔记---预编译
专题三: 1) 预编译 处理所有的注释,以空格代替, 将所有的#define删除,并且展开所有的宏定义, 处理条件编译指令#if,#ifdef,#elif,#else,#endif 处理# ...
- Struts在Web.xml中的配置及Struts1和Struts2的区别
(1)配置Struts的ActionServlet <servlet>元素来声明ActionServlet <servlet-name>元素:用来定义Servle ...
- PHP关于按位取反结果的推导过程
哎呀几年过去,都快把大学学的计算机导论的知识给忘完了,现在来回顾一下按位去反的流程: <?php /** 首先来补充一下基础知识: php中有4个位运算,分别是&与 |或 ^异或 ~取反 ...
- 安卓下junit测试
安卓下junit测试 第一种方法: 1,在AndroidManifest.xml下,加入如下红色代码 <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.a ...
- 剑指offer——35复杂链表的复制
这题很是巧妙. 突破了常规思维. 竟然可以把传入进来的链表和复制的链表链在一起.然后再算出slibling指针.最后在分离. 直接把空间复杂度变为O(1)了. 很巧妙,很实用. 题目: 请实现函数Co ...
- c++ 友元类 与 友元类派生类
定义: 当一个类B成为了另外一个类A的“朋友”时,那么类A的私有和保护的数据成员就可以被类B访问.我们就把类B叫做类A的友元. 用法: 在A类中加入: friend class B; 下面这个程序说明 ...
- Json.NET Deserialize时如何忽略$id等特殊属性
由于$id.$ref等是默认Json.NET的特殊属性,在反序列化时不会将其对应的值填充,例如: [DataContract] public class MyObject { [DataMember( ...
- slf4j + log4j 是如何初始化的
SLF4J的全称是 Simple Logging Facade for Java(简单java日志门面) SLF4J自己不提供具体的日志功能实现,只是提供了一个统一的日志门面,在这个统一的门面之下,用 ...
