Visualize real-time data streams with Gnuplot
(September 2008)
For the last couple of years, I've been working on European Space Agency (ESA) projects - writing rather complex code generators. In the ESA project I am currently working on, I am also the technical lead; and I recently faced the need to (quickly) provide real-time plotting of streaming data. Being a firm believer in open-source, after a little Googling I found Gnuplot. From my (somewhat limited) viewpoint, Gnuplot appears to be the LaTEX equivalent in the world of graphs: amazing functionality that is also easily accessible. Equally important, Gnuplot follows the powerful paradigm that UNIX established: it comes with an easy to use scripting language, thus allowing its users to prescribe actions and "glue" Gnuplot together with other applications - and form powerful combinations.
To that end, I humbly submit a little creation of mine: a Perl script that spawns instances of Gnuplot and plots streaming data in real-time.
Plotting data in real-time
Interfacing over standard input
My coding experience has taught me to strive for minimal and complete interfaces: to that end, the script plots data that will arrive over the standard input, one sample per line. The samples are just numbers (integers / floating point numbers), and must be prefixed with the stream number ("0:", "1:", etc). Each plot window will also be configured to display a specific number of samples.
The resulting script is relatively simple - and easy to use:
bash ./driveGnuPlots.pl Usage: ./driveGnuPlots.pl <options>
where options are (in order): NumberOfStreams How many streams to plot (windows)
Stream1_WindowSampleSize <Stream2...> This many window samples for each stream
Stream1_Title <Stream2_Title> ... Title used for each stream
(Optional) Stream1_geometry <...>. Sizes and positions in pixels The last parameters (the optionally provided geometries of the gnuplot windows)
are of the form:
WIDTHxHEIGHT+XOFF+YOFF
Note that the script uses the "autoscale" feature of GnuPlot, to automatically adapt to the incoming value ranges.
An example usage scenario: plotting sine and cosine
Let's say we want to see a sine and a cosine run side-by-side, in real-time. We also want to watch the cosine "zooming-in" by 10x (time-scale wise). The following code will print our test samples:
#!/usr/bin/perl -w
use strict; use Time::HiRes qw/sleep/; # First, set the standard output to auto-flush
select((select(STDOUT), $| = 1)[0]); # And loop 5000 times, printing values...
my $offset = 0.0;
while(1) {
print "0:".sin($offset)."\n";
print "1:".cos($offset)."\n";
$offset += 0.1;
if ($offset > 500) {
last;
}
sleep(0.02);
}
We'll use this code to test our plotting script: the data for two streams (sine and cosine) are printed in the expected format: one sample (one number) printed per line. To distinguish between the two streams, the sample is prefixed with "0:", "1:", etc. Notice that we explicitly set the autoflush flag for our standard output: we need the data output to be unbuffered, otherwise our plotting script will receive data in bursts (when the data are flushed from the producer), and the plots will "jerk" forward.
This is how we test the plotting script (assuming we saved the sample code above in sinuses.pl): <
bash$ ./sinuses.pl | ./driveGnuPlots.pl 2 50 500 "Sine" "Cosine"
To stop the plotting, use Ctrl-C on the terminal you spawned from.
The parameters we passed to driveGnuPlots.pl are:
- 2 is the number of streams
- The window for the first stream (sine) will be 50 samples wide
- The window for the second stream (cosine) will be 500 samples wide (hence the different "zoom" factor)
- The titles of the two streams follow
When executed, the script spawns one gnuplot per each stream, and displays the graphs in a clear, flicker-free manner. If you don't like the Gnuplot settings I used (e.g. the grid, or the colors, or...) feel free to change them: the setup code that defines the plotting parameters starts at line 82 of the script.
Executive summary: plotting streaming data is now as simple as selecting them out from your "producer" program (filtering its standard output through any means you wish: grep, sed, awk, etc), and outputing them, one number per line. Just remember to prefix with the stream number ("0:", "1:", etc, to allow for multiple streams), and make sure you flush your standard output, e.g.
For this kind of output:
bash$ /path/to/programName
...(other stuff)
Measure: 7987.3
...(other stuff)
Measure: 8364.4
Measure: 8128.1
...
You would do this:
bash$ /path/to/programName | \
grep --line-buffered '^Measure:' | \
awk -F: '{printf("0:%f\n", $2); fflush();}' | \
driveGnuPlots.pl 1 50 "My data"
In the code above, grep filters out the lines that start with "Measure:", and awk selects the 2nd column ($2) and prefixes it with "0:" (since this is the 1st - and only, in this example - stream we will display). Notice that we used the proper options to force the standard output's flushing for both grep (--line-buffered) and awk (fflush() called).
Preparing for a demo
You don't want to move the GnuPlot windows after they are shown, do you? So you can just specify their placement, in "WIDTHxHEIGHT+XOFF+YOFF" format (in pixels):
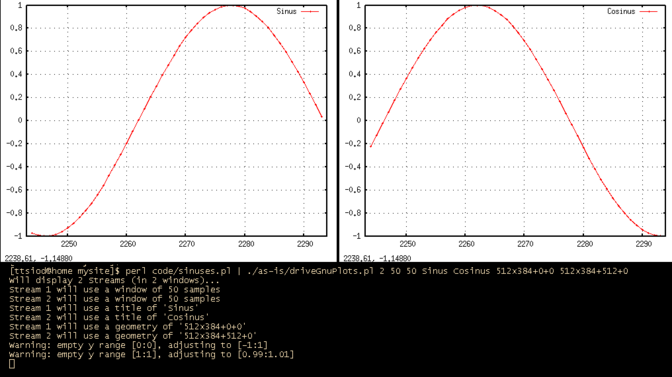
bash$ ./sinus.pl | ./driveGnuPlots.pl 2 50 50 Sinus Cosinus 512x384+0+0 512x384+512+0
The provisioning of titles and GnuPlot window placement information, makes the script very well-suited for live demonstrations.
P.S. UNIX power in all its glory: it took me 30min to code this, and another 30 to debug it. Using pipes to spawned copies of gnuplots, we are able to do something that would require one or maybe two orders of magnitude more effort in any conventional programming language (yes, even accounting for custom graph libraries - you do have to learn their API and do your windows/interface handling...)
Visualize real-time data streams with Gnuplot的更多相关文章
- FunDA(9)- Stream Source:reactive data streams
上篇我们讨论了静态数据源(Static Source, snapshot).这种方式只能在预知数据规模有限的情况下使用,对于超大型的数据库表也可以说是不安全的资源使用方式.Slick3.x已经增加了支 ...
- NTFS格式下的Alternate Data Streams
今天我写点NTFS的交换数据流以及其带来的安全问题(Alternate Data Stream/ADS) =============================================== ...
- Awesome Big Data List
https://github.com/onurakpolat/awesome-bigdata A curated list of awesome big data frameworks, resour ...
- 翻译-In-Stream Big Data Processing 流式大数据处理
相当长一段时间以来,大数据社区已经普遍认识到了批量数据处理的不足.很多应用都对实时查询和流式处理产生了迫切需求.最近几年,在这个理念的推动下,催生出了一系列解决方案,Twitter Storm,Yah ...
- Exploring the 7 Different Types of Data Stories
Exploring the 7 Different Types of Data Stories What makes a story truly data-driven? For one, the n ...
- The difference between text mode and binary mode with file streams
FIO14-C. Understand the difference between text mode and binary mode with file streams Skip to e ...
- THE R QGRAPH PACKAGE: USING R TO VISUALIZE COMPLEX RELATIONSHIPS AMONG VARIABLES IN A LARGE DATASET, PART ONE
The R qgraph Package: Using R to Visualize Complex Relationships Among Variables in a Large Dataset, ...
- Flink应用案例:How Trackunit leverages Flink to process real-time data from industrial IoT devices
January 22, 2019Use Cases, Apache Flink Lasse Nedergaard Recently there has been significant dis ...
- explore your hadoop data and get real-time results
deep api integration makes getting value from your big data easy 深度api集成使你大数据訪问更加easy Elasticsearch ...
随机推荐
- Winform窗体实现简单的二维码生成和保存
二维码的生成需要用到二维码生成的类库,ThoughtWorks.QRCode.dll 步骤: 第一步:下载二维码生成类库,ThoughtWorks.QRCode.dll 第二步:新建winform项目 ...
- WCF使用泛型方法的问题
public IList getModelList(string type, string SQL, List<string> list){ try { IList Mlist = new ...
- 浏览器-Tomcat服务器-请求与响应
浏览器访问服务器,本质就是请求资源. 比如请求静态资源:index.html,我们在浏览器地址栏输入:www.a.com/index.html,浏览器为了支持HTTP协议,发送的数据必须符合HTTP协 ...
- linux下导入、导出mysql数据库命令 下载文件到本地
一.下载到本地 yum install lrzsz sz filename 下载 rz filename 上传 linux下导入.导出mysql数据库命令 一.导出数据库用mysqldump命 ...
- Python 学习之进制与编码
进制 日常生活中,我们最熟悉的数据就是十进制计数.它的数值部分由十个不同的数字符号0.1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9来表示,我们把这些数字符号叫做数码,表示十种不同的状态.数码处于不同的位置(或数 ...
- MessageFormat格式化的一些问题
如果格式化字符串中包含单引号,处理方法是用2个单引号进行转义,如果是数字,则需要加上格式: MessageFormat.format("(''{0}'',''{1}'',{2,number, ...
- 高效构建Web应用 教你玩转Play框架 http://www.anool.net/?p=577
Play 框架是一个完整的Web应用开发框架,覆盖了Web应用开发的各个方面.Play 框架在设计的时候借鉴了流行的 Ruby on Rails 和 Grails 等框架,又有自己独有的优势.使用 P ...
- artTemplate 介绍
artTemplate 是新一代 javascript 模板引擎,它采用预编译方式让性能有了质的飞跃,并且充分利用 javascript 引擎特性,使得其性能无论在前端还是后端都有极其出色的表现. 编 ...
- 2015年第12本(英文第8本):the Old Man and the Sea 老人与海
书名:The Old Man and The Sea(老人与海) 作者:Ernest Hemingway 单词数:2.7万 不重复单词数:2600 首万词不重复单词数:1500 蓝思值:940 阅读时 ...
- ubuntu下nagios配置
参考文献: http://www.cnblogs.com/mchina/archive/2013/02/20/2883404.html http://my.oschina.net/duangr/blo ...
