Codeforces Good Bye 2018
咕bye 2018,因为我这场又咕咕咕了
无谓地感慨一句:时间过得真快啊(有毒
A.New Year and the Christmas Ornament
分类讨论后等差数列求和
又在凑字数了
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int a,b,c;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
printf("%d",min(min((a+)*,b*),(c-)*));
return ;
}
B.New Year and the Treasure Geolocation
坐标分别加起来除个$n$,没了
凑字数++
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
long long n,a,b,t1,t2;
int main()
{
scanf("%lld",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) scanf("%lld%lld",&t1,&t2),a+=t1,b+=t2;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) scanf("%lld%lld",&t1,&t2),a+=t1,b+=t2;
printf("%lld %lld",a/n,b/n);
return ;
}
C.New Year and the Sphere Transmission
分解因数后变成了等差数列求和
凑字数停不下来了?
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=;
int n,cnt,facs[N];
long long ans[N];
int gcd(int a,int b)
{
return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i*i<=n;i++)
if(n%i==)
{
facs[++cnt]=i;
if(i*i!=n)
facs[++cnt]=n/i;
}
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++)
{
int g=gcd(facs[i],n),tot=n/g;
ans[i]=1ll*(n-g+)*tot/;
}
sort(ans+,ans++cnt);
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++)
printf("%lld ",ans[i]);
return ;
}
D.New Year and the Permutation Concatenation
不错的题 终于不在凑字数了
考虑容斥,计算不合法的方案数,这里我们要讲一讲如何实现next_permutation,是这样的:
以 1 3 5 4 2 为例
1.从序列末尾向前扫,直到一个位置pos序列开始下降 1 3 5 4 2
2.从后面这段递减的序列里找到第一个大于*pos的数,将pos位置的数与它交换 1 4 5 3 2
3.排序— —即翻转后面这段原来递减的序列 1 4 2 3 5
这样我们发现后面原来长度为n-pos的这段递减的序列被破坏了,而它原来是可以跟后面的一个排列配对的
那么显然对每个长度$len$统计有长度为$len$的递减序列的排列去掉即可(除了一种情况— —len==n,这时候没有排列能和它配对)
这样一来对每个$len$前$n-len$个可以随便排,后面$len$个又有$C_n^{len}$种选法,所以总方案数就是$\sum\limits_{len=1}^{n-1}\frac{n!}{len!}$,然后从总数里把这个容斥掉即可
#include<cstdio>
const int N=,mod=;
int n,x,y,ans,fac[N],inv[N];
void exGCD(int &x,int &y,int a,int b)
{
if(!b) x=,y=;
else exGCD(y,x,b,a%b),y-=a/b*x;
}
int Inv(int nm,int md)
{
exGCD(x,y,nm,md);
return (x%md+md)%md;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n),fac[]=inv[]=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) fac[i]=1ll*fac[i-]*i%mod;
inv[n]=Inv(fac[n],mod),ans=1ll*n*fac[n]%mod;
for(int i=n-;i;i--) inv[i]=1ll*inv[i+]*(i+)%mod;
for(int i=;i<=n-;i++) ans-=1ll*fac[n]*inv[i]%mod,ans=(ans+mod)%mod;
printf("%d",ans);
return ;
}
E.New Year and the Acquaintance Estimation
观察样例/仔细分析/动手推理可以发现答案是一段隔2连续的区间!(我是第一种
所以只要求上下界就好了,怎么求呢?二分
怎么想到二分的呢?没想到,但是题目贴心地给了一个wiki的链接,里面有这样一个东西

这个定理可以在图的度数降序排好序的情况下检查图是否可行,这明摆着是告诉我们二分啊=。=
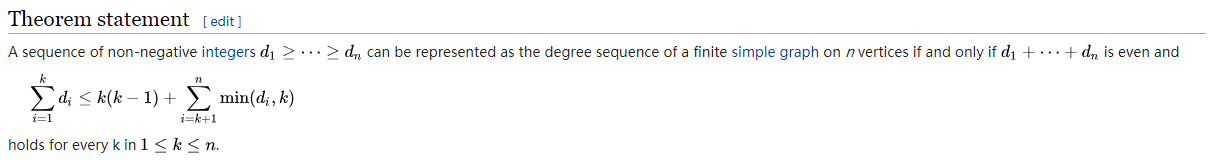
我们发现这个式子别的都好说,就是这个
$\sum\limits_{i=k+1}^{n}min(d_i,k)$
很麻烦啊,好像需要什么主席树/multiset?
并不需要,边扫边维护还未出现过的度数小于当前的$k$的点数的和sum即可,说白了就是前缀和,然后每次用$n-i-sum$更新。为什么?因为这就是后面那个式子里$k$的的贡献的增加量(未出现过的大于等于$k$的数)
注意二分+检查之后偏移的方向
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=;
int mem[N],tmp[N],bkt[N];
int n,l,r,rd,ld,hd,sum,odd;
bool cmp(int a,int b)
{
return a>b;
}
int check(int x)
{
int p=,pos=;
memset(bkt,,sizeof bkt);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(mem[i]<x&&p<i)
pos=++p,tmp[pos]=x;
tmp[++p]=mem[i];
}
if(!pos) pos=++p,tmp[pos]=x;
for(int i=;i<=p;i++) bkt[tmp[i]]++;
long long lsum=,rsum=,fsum=;
for(int i=;i<=p;i++)
{
lsum+=tmp[i],bkt[tmp[i]]--;
rsum+=*(i-),rsum-=min(tmp[i],i-);
fsum+=bkt[i-],rsum+=n-i+-fsum;
if(lsum>rsum) return i>=pos?:-;
}
return ;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&mem[i]),sum+=mem[i];
odd=sum%,sort(mem+,mem++n,cmp);
l=,r=(n-odd)/,ld=rd=-;
while(l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)/;
if(check(*mid+odd)<) l=mid+;
else ld=mid,r=mid-;
}
l=ld,r=(n-odd)/;
while(l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)/;
if(check(*mid+odd)>) r=mid-;
else rd=mid,l=mid+;
}
if(ld==-||rd==-) printf("-1");
else for(int i=ld;i<=rd;i++) printf("%d ",*i+odd);
return ;
}
F.New Year and the Mallard Expedition
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=;
char mapp[N]; long long len[N];
long long n,wat,spa,ans,sta;
int main()
{
scanf("%lld",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%lld",&len[i]);
scanf("%s",mapp+);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(mapp[i]=='G')
{
ans+=len[i]*;
spa+=len[i]*;
sta+=len[i];
}
else if(mapp[i]=='W')
{
wat=true;
ans+=len[i]*;
sta+=len[i];
}
else if(mapp[i]=='L')
{
if(sta<len[i])
{
ans+=(wat?:)*(len[i]-sta);
sta=len[i];
}
ans+=len[i];
sta-=len[i];
}
spa=min(spa,sta);
}
if(sta) ans-=sta+spa;//ans-=(5-1)*spa/2,ans-=(3-1)*(sta-spa)/2;
printf("%lld",ans);
return ;
}
首先模拟,草地先走路,水里游泳,岩浆飞过去。在这个过程中我们记录一下是否遇到了水,因为如果遇到岩浆飞不过去的情况,需要在之间走来走去/游来游去积攒体力。模拟的同时记录一个“可以用飞行代替行走”的路程的消耗,这个东西步步和你的耐力取min,最后如果它小于耐力就把它代表的行走换成飞行,如果还剩下一些就把一些游泳也换成飞行
Codeforces Good Bye 2018的更多相关文章
- Codeforces:Good Bye 2018(题解)
Good Bye 2018! 题目链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1091 A. New Year and the Christmas Ornament 题意: 给 ...
- Codeforces Good Bye 2018 D (1091D) New Year and the Permutation Concatenation
题意:给n!个n的排列,按字典序从小到大连成一条序列,例如3的情况为:[1,2,3, 1,3,2, 2,1,3 ,2,3,1 ,3,1,2 ,3,2,1],问其中长度为n,且和为sum=n*(n+1) ...
- Good Bye 2018 (A~F, H)
目录 Codeforces 1091 A.New Year and the Christmas Ornament B.New Year and the Treasure Geolocation C.N ...
- Good Bye 2018
Good Bye 2018 2018年最后一场CF,OVER! 弱弱的我只能做出3道A,B,D~~~~ 最后几分钟,感觉找到了C题的规律,结束的那一刻,提交了一发 "Wrong answer ...
- codeforces Good bye 2016 E 线段树维护dp区间合并
codeforces Good bye 2016 E 线段树维护dp区间合并 题目大意:给你一个字符串,范围为‘0’~'9',定义一个ugly的串,即串中的子串不能有2016,但是一定要有2017,问 ...
- Good Bye 2018题解
Good Bye 2018题解 题解 CF1091A [New Year and the Christmas Ornament] 打完cf都忘记写题解了qwq 题意就是:给你一些黄,蓝,红的球,满足蓝 ...
- Codeforces 1091 Good Bye 2018
占个坑先,希望不要掉的太惨了吧,不要掉到上一次之前的rating upt:flag竟然没到,开心. A - New Year and the Christmas Ornament 好像没什么可说的. ...
- codeforces Good Bye 2015 B. New Year and Old Property
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/611/B 题目意思:就是在 [a, b] 这个范围内(1 ≤ a ≤ b ≤ 10^18)统计出符合二进制 ...
- Codeforces Good Bye 2015 D. New Year and Ancient Prophecy 后缀数组 树状数组 dp
D. New Year and Ancient Prophecy 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/611/problem/C Description L ...
随机推荐
- ubuntu安装中文输入法必看
ubuntu安装中文输入法必看以下两篇文章,按照顺序来做: http://www.2cto.com/os/201207/144189.html http://www.cnblogs.com/slide ...
- jenkins配置01--用户添加及权限配置
原文出自:https://www.cnblogs.com/kevingrace/p/6019707.html 下面重点记录下jenkins安装后的一些配置: (1)添加用户权限 jenkins初次登陆 ...
- kerkee demo编译连接过程中遇到的问题及解决方法(iOS)
https://github.com/kercer/kerkee_ios 1.刚打开这个demo的时候是下图这个样子的,我们很自然的可以想到将kerkee.xcoderproj添加到项目里面 2.将k ...
- js 基础拓展
1.关于 try catch 的用法 <body> <div>请输出一个 5 到 10 之间的数字:</div> <input id="demo&q ...
- 使用Fabric自动化你的任务
Fabric是一个Python库,可以通过SSH在多个host上批量执行任务.你可以编写任务脚本,然后通过Fabric在本地就可以使用SSH在大量远程服务器上自动运行.这些功能非常适合应用的自动化部署 ...
- profibus总线和profibus dp的区别
profibus总线和profibus dp的区别:PROFBUS是一种国际性的开放式的现场总线标准,它既可以用于高速并且对于时间苛求的数据传输,也可以用于大范围的复杂通讯场合.PROFBUS-DP是 ...
- 累计进度条 PSP 饼图
累计进度条 PSP 饼图 每周例行报告 本周PSP 类别 任务 开始时间 结束时间 被打断时间 总计工作时间 2016年9月24日 读书 构建之法-6.7章 19:00 20:00 2 58m ...
- 通过分析java heap dump解决生产问题
最近在生产环境遇到一个问题,正常情况下,ECS CPU始终保持在10%以下,内存也只占用40%左右,但是连续2天出现了CPU占用100%的情况,然后系统卡住.看阿里云的ECS监控,能看到CPU飙到了1 ...
- express和数据库(MySQL)的交互(二)
一.安装express前面都讲了 1.express. cnpm || npm install express --save 2.中间件 a.cnpm || npm install body-pars ...
- Windows 常见错误总结
本篇主要记录Windows 系统使用中存在的问题和解决方案,会保持持续更新...(若你们遇到的问题或有更好的解决方法,还望在评论区留言,谢谢) 1.win10 unable to save C:\wi ...
