python作业堡垒机(第十三周)
作业需求:
1. 所有的用户操作日志要保留在数据库中
2. 每个用户登录堡垒机后,只需要选择具体要访问的设置,就连接上了,不需要再输入目标机器的访问密码
3. 允许用户对不同的目标设备有不同的访问权限,例:
对10.0.2.34 有mysql 用户的权限
对192.168.3.22 有root用户的权限
对172.33.24.55 没任何权限
4. 分组管理,即可以对设置进行分组,允许用户访问某组机器,但对组里的不同机器依然有不同的访问权限
思路解析:
1. 用户操作日志要保留在数据库中,通过课堂学习对paramiko源码进行修改,在demons/interactive.py 63行中获取用户操作,并将操作记录到数据库中。
2. 后面的需求使用数据库,建立多对多关联,反向取主机IP,主机密码,对应的堡垒机用户,并划分组内用户权限 ,具体使用sqlalchemy模块对数据库表进行操作。
3. 针对作业需求,程序添加了查看日志功能,并准许默认用户root查看所有用户操作,其他用户只能查自己下面机器的日志。
4. 添加了缓存redis减少了数据库IO操作。
paramiko 用户操作记录源码:
cmd = []
while True:
r, w, e = select.select([chan, sys.stdin], [], []) # 默认阻塞
if chan in r: # 连接建立好了,channle过来有数据了,
try:
x = u(chan.recv(1024)) # 尝试收数据
if len(x) == 0: # 收数据收不到,
sys.stdout.write('\r\n*** EOF\r\n')
break
sys.stdout.write(x) # 标准输出
sys.stdout.flush() # flush 怕输出不到,远程发来的数据,远程机器返回
except socket.timeout:
pass
if sys.stdin in r: # 标准输入 活动就能返回到r
x = sys.stdin.read(1)
if len(x) == 0:
break
if x == "\r":
cmd_str = "".join(cmd)
print("---->",cmd_str)
cmd = []
else:
cmd.append(x)
chan.send(x)
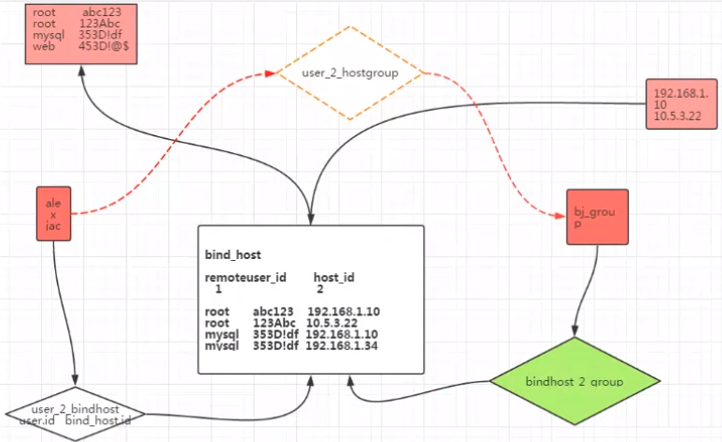
表结构设计图:
README:
作者:yaobin
版本: 堡垒机 示例版本 v0.1
开发环境: python3.6 程序介绍
1. 所有的用户操作日志要保留在数据库中
2. 每个用户登录堡垒机后,只需要选择具体要访问的设置,就连接上了,不需要再输入目标机器的访问密码 3. 允许用户对不同的目标设备有不同的访问权限,例: 对10.0.2.34 有mysql 用户的权限 对192.168.3.22 有root用户的权限 对172.33.24.55 没任何权限 4. 分组管理,即可以对设置进行分组,允许用户访问某组机器,但对组里的不同机器依然有不同的访问权限 文件目录结构
├── bin
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── tiny.py # 主程序
├── conf
│ ├── action_registers.py # 程序命令交互
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── __pycache__
│ │ ├── action_registers.cpython-36.pyc
│ │ ├── __init__.cpython-36.pyc
│ │ └── settings.cpython-36.pyc
│ └── settings.py # 配置文件
├── log
│ └── __init__.py
├── models
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── models_backup.py # 备份测试
│ ├── models.py # 数据库表模块
│ ├── __pycache__
│ │ ├── __init__.cpython-36.pyc
│ │ └── models.cpython-36.pyc
│ └── test.py # redis测试
├── modules
│ ├── actions.py # 欢迎页和程序命令交互
│ ├── common_filters.py # 堡垒机用户主机绑定交互
│ ├── db_conn.py # mysql连接交互
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── interactive.py # ssh传输命令和命令写入交互
│ ├── __pycache__
│ │ ├── actions.cpython-36.pyc
│ │ ├── common_filters.cpython-36.pyc
│ │ ├── db_conn.cpython-36.pyc
│ │ ├── __init__.cpython-36.pyc
│ │ ├── interactive.cpython-36.pyc
│ │ ├── ssh_login.cpython-36.pyc
│ │ ├── utils.cpython-36.pyc
│ │ └── views.cpython-36.pyc
│ ├── ssh_login.py # ssh连接交互
│ ├── utils.py # yaml配置交互
│ └── views.py # 创建表,表数据创建,查看数据库数据交互
├── Server.zip
└── share
└── examples
├── new_bindhosts.yml # 主机绑定关系配置文件
├── new_groups.yml # 组创建,组关系绑定配置文件
├── new_hosts.yml # 主机配置文件
├── new_remoteusers.yml # 主机用户名密码配置文件
└── new_user.yml # 堡垒机用户配置文件
创建表和使用方法:
先要创建数据库:
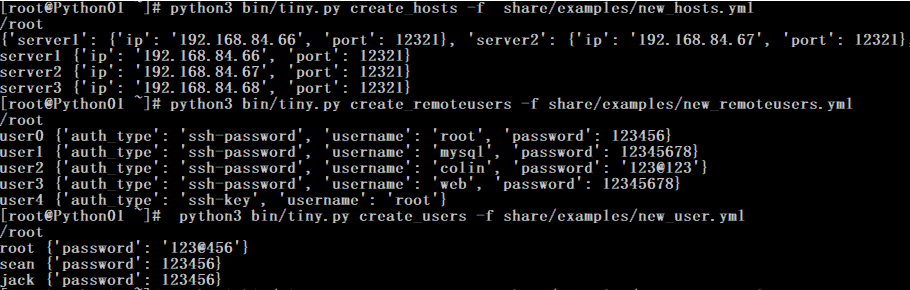
create database tinytest charset utf8; 1. python3 bin/tiny.py syncdb
2. python3 bin/tiny.py create_hosts -f share/examples/new_hosts.yml
3. python3 bin/tiny.py create_remoteusers -f share/examples/new_remoteusers.yml
4. python3 bin/tiny.py create_users -f share/examples/new_user.yml
5. python3 bin/tiny.py create_groups -f share/examples/new_groups.yml
6. python3 bin/tiny.py create_bindhosts -f share/examples/new_bindhosts.yml
7. python3 bin/tiny.py start_session
程序核心代码:
bin
tiny.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Time:2017/12/15 21:22
__Author__ = 'Sean Yao'
import os
import sys
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) print(BASE_DIR)
sys.path.append(BASE_DIR) if __name__ == '__main__':
from modules.actions import excute_from_command_line
excute_from_command_line(sys.argv)
conf
action_registers
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Time:2017/12/14 18:53
__Author__ = 'Sean Yao'
from modules import views actions = {
'start_session': views.start_session, # 连接server
# 'stop': views.stop_server,
'syncdb': views.syncdb, # 同步数据
'create_users': views.create_users, # 创建users
'create_groups': views.create_groups, # 创建组
'create_hosts': views.create_hosts, # 创建主机
'create_bindhosts': views.create_bindhosts, # 创建绑定关系
'create_remoteusers': views.create_remoteusers, # 创建远程用户
'view_user_record': views.user_record_cmd # 查看用户操作命令
}
settings.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Time:2017/12/14 18:53
__Author__ = 'Sean Yao'
# 连接数据库字段
# ConnParams = "mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.84.66/tinydb?charset=utf8"
ConnParams = "mysql+pymysql://root:123456@192.168.84.66/tinytest?charset=utf8"
models
models.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Time:2017/12/14 19:06
__Author__ = 'Sean Yao'
import datetime
from sqlalchemy import Table, Column, Integer, String, DATE, ForeignKey, Enum, UniqueConstraint, DateTime, Text
# uniqueconstraint 联合唯一
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy_utils import ChoiceType, PasswordType # sqlalchemy_utils sqalchemy_utils插件
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker Base = declarative_base() # 基类 # 多对多关联
# 关联表堡垒机用户ID和远程主机ID
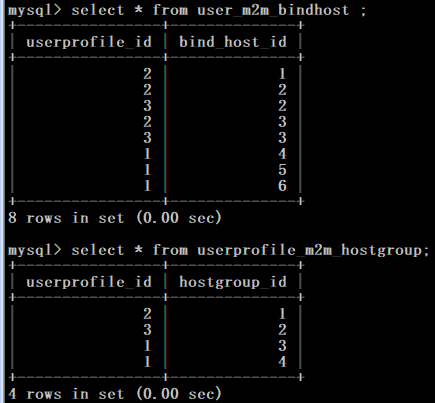
user_m2m_bindhost = Table('user_m2m_bindhost', Base.metadata,
Column('userprofile_id', Integer, ForeignKey('user_profile.id')),
Column('bind_host_id', Integer, ForeignKey('bind_host.id')),)
# 关联表远程主机ID和组
bindhost_m2m_hostgroup = Table('bindhost_m2m_hostgroup', Base.metadata,
Column('bindhost_id', Integer, ForeignKey('bind_host.id')),
Column('hostgroup_id', Integer, ForeignKey('host_group.id')),) # 关联表堡垒机用户和组
user_m2m_hostgroup = Table('userprofile_m2m_hostgroup', Base.metadata,
Column('userprofile_id', Integer, ForeignKey('user_profile.id')),
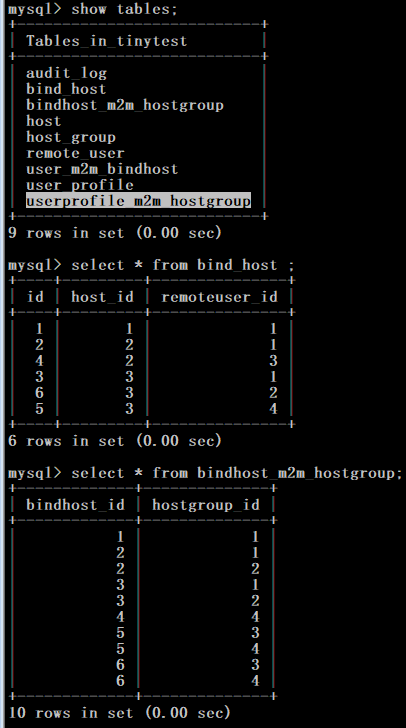
Column('hostgroup_id', Integer, ForeignKey('host_group.id')),) class BindHost(Base):
'''
关联关系
192.168.1.11 web
192.168.1.11 mysql
'''
__tablename__ = "bind_host"
# 联合唯一
__table_args__ = (UniqueConstraint('host_id', 'remoteuser_id', name='_host_remoteuser_uc'),) id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
# 外键
host_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('host.id'))
remoteuser_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('remote_user.id'))
# 外键关联远程主机,反响查绑定的主机
host = relationship('Host', backref='bind_hosts')
# 外键关联堡垒机用户,backref,反向查绑定的堡垒机用户
remote_user = relationship("RemoteUser", backref='bind_hosts') def __repr__(self):
# return "<%s -- %s -- %s>" % (self.host.ip,
# self.remote_user.username,
# self.host_group.name) return "<%s -- %s >" % (self.host.ip, self.remote_user.username) class Host(Base):
'''
远程主机
'''
__tablename__ = 'host'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
hostname = Column(String(64), unique=True)
ip = Column(String(64), unique=True)
port = Column(Integer, default=22)
# 不要让主机关联主机组,这样权限给主机组了,应该是将用户密码和主机组绑定,
# 比如root 123 sh root 123 bj 这样他可以用所有的权限, def __repr__(self):
return self.hostname class HostGroup(Base):
'''
远程主机组
'''
__tablename__ = 'host_group'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
name = Column(String(64), unique=True)
# 通过bindhost_m2m_hostgroup 关联绑定主机和主机组反查到主机组
bind_hosts = relationship("BindHost", secondary="bindhost_m2m_hostgroup", backref="host_groups") def __repr__(self):
return self.name class RemoteUser(Base):
'''
远程主机密码表
'''
__tablename__ = 'remote_user'
# 联合唯一,验证类型,用户名密码
__table_args__ = (UniqueConstraint('auth_type', 'username', 'password', name='_user_passwd_uc'),)
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
AuthTypes = [
('ssh-password', 'SSH/Password'), # 第一个是存在数据库里的,第二个具体的值
('ssh-key', 'SSH/KEY')
]
auth_type = Column(ChoiceType(AuthTypes))
username = Column(String(32))
password = Column(String(128)) def __repr__(self):
return self.username class Userprofile(Base):
'''
堡垒机用户密码表
'''
__tablename__ = 'user_profile'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
username = Column(String(32), unique=True)
password = Column(String(128)) # 多对多关联通过user_m2m_bindhost关联堡垒机表和主机表能反查到堡垒机用户
bind_hosts = relationship("BindHost", secondary='user_m2m_bindhost', backref='user_profiles')
# 多对多关联通过userprofile_m2m_hostgroup关联堡垒机表和组反查到堡垒机用户
host_groups = relationship("HostGroup", secondary='userprofile_m2m_hostgroup', backref='user_profiles') def __repr__(self):
return self.username class AuditLog(Base):
'''
用户操作日志表
'''
__tablename__ = 'audit_log'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
user_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('user_profile.id'))
bind_host_id = Column(Integer, ForeignKey('bind_host.id'))
# # action_choices
# action_choices = [
# (0, 'CMD'),
# (1, 'Login'),
# (2, 'Logout'),
# (3, 'GetFile'),
# (4, 'SendFile'),
# (5, 'Exception'),
# ]
action_choices = [
(u'cmd', u'CMD'),
(u'login', u'Login'),
(u'logout', u'Logout'),
] action_type = Column(ChoiceType(action_choices))
# 命令可能存的数值更大
# cmd = Column(String(255))
cmd = Column(Text(65535))
date = Column(DateTime) user_profile = relationship("Userprofile")
bind_host = relationship("BindHost")
modules
actions.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Time:2017/12/15 21:31
__Author__ = 'Sean Yao' from conf import action_registers
from modules import utils def help_msg():
'''
print help msgs
:return:
'''
print("\033[31;1mAvailable commands:\033[0m")
for key in action_registers.actions:
print("\t", key) def excute_from_command_line(argvs):
'''
:param argvs:
:return:
'''
if len(argvs) < 2:
help_msg()
exit()
if argvs[1] not in action_registers.actions:
utils.print_err("Command [%s] does not exist!" % argvs[1], quit=True)
# utils 工具箱
action_registers.actions[argvs[1]](argvs[1:])
common_filters.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Time:2017/12/18 18:19
__Author__ = 'Sean Yao'
from models import models
from modules.db_conn import engine, session
from modules.utils import print_err def bind_hosts_filter(vals):
''' :param vals:
:return:
'''
print('**>', vals.get('bind_hosts'))
bind_hosts = session.query(models.BindHost).filter(models.Host.hostname.in_(vals.get('bind_hosts'))).all()
if not bind_hosts:
print_err("none of [%s] exist in bind_host table." % vals.get('bind_hosts'), quit=True)
return bind_hosts def user_profiles_filter(vals):
''' :param vals:
:return:
'''
user_profiles = session.query(models.Userprofile).filter(models.Userprofile.username.in_(vals.get('user_profiles'))
).all()
if not user_profiles:
print_err("none of [%s] exist in user_profile table." % vals.get('user_profiles'), quit=True)
return user_profiles
db_conn.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Time:2017/12/15 23:21
__Author__ = 'Sean Yao'
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from conf import settings engine = create_engine(settings.ConnParams)
# 创建与数据库的会话session class ,注意,这里返回给session的是个class,不是实例
SessionCls = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
session = SessionCls()
interactive.py
# Copyright (C) 2003-2007 Robey Pointer <robeypointer@gmail.com>
#
# This file is part of paramiko.
#
# Paramiko is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
# terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
# Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option)
# any later version.
#
# Paramiko is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY
# WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR
# A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License for more
# details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
# along with Paramiko; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
# 59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307 USA. import socket
import sys
from paramiko.py3compat import u
from models import models
# from modules.views import log_recording
import datetime
import redis
import time # windows does not have termios...
try:
import termios
import tty
has_termios = True
except ImportError:
has_termios = False def interactive_shell(chan, user_obj, bind_host_obj, cmd_caches, log_recording):
'''
:param chan:
:param user_obj:
:param bind_host_obj: 主机
:param cmd_caches: 命令列表
:param log_recording: 日志记录
:return:
'''
# 判断是否是windows shell
if has_termios:
posix_shell(chan, user_obj, bind_host_obj, cmd_caches, log_recording)
else:
windows_shell(chan) def posix_shell(chan, user_obj, bind_host_obj, cmd_caches, log_recording):
''' :param chan:
:param user_obj:
:param bind_host_obj:
:param cmd_caches:
:param log_recording:
:return:
'''
import select oldtty = termios.tcgetattr(sys.stdin)
try:
tty.setraw(sys.stdin.fileno())
tty.setcbreak(sys.stdin.fileno())
chan.settimeout(0.0)
cmd = ''
tab_key = False
while True:
r, w, e = select.select([chan, sys.stdin], [], [])
if chan in r:
try:
x = u(chan.recv(1024))
if tab_key:
if x not in ('\x07', '\r\n'):
# print('tab:',x)
cmd += x
tab_key = False
if len(x) == 0:
sys.stdout.write('\r\n*** EOF\r\n')
# test for redis to mysql
break
sys.stdout.write(x)
sys.stdout.flush()
except socket.timeout:
pass
if sys.stdin in r:
x = sys.stdin.read(1)
if '\r' != x:
cmd += x
else:
user_record_cmd = user_obj.username + '_user_record'
pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='192.168.84.66', port=6379)
user_record = [user_obj.id, bind_host_obj.id, 'cmd', cmd,
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())]
r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
r.lpush(user_record_cmd, user_record)
cmd = ''
# 最后用户退出的时候取出来log_item 列表循环写入数据库
if '\t' == x:
tab_key = True
if len(x) == 0:
break
chan.send(x) finally:
termios.tcsetattr(sys.stdin, termios.TCSADRAIN, oldtty) # thanks to Mike Looijmans for this code
def windows_shell(chan):
''' :param chan:
:return:
'''
import threading sys.stdout.write("Line-buffered terminal emulation. Press F6 or ^Z to send EOF.\r\n\r\n") def writeall(sock):
while True:
data = sock.recv(256)
if not data:
sys.stdout.write('\r\n*** EOF ***\r\n\r\n')
sys.stdout.flush()
break
sys.stdout.write(data.decode())
sys.stdout.flush() writer = threading.Thread(target=writeall, args=(chan,))
writer.start() try:
while True:
d = sys.stdin.read(1)
if not d:
break
chan.send(d)
except EOFError:
# user hit ^Z or F6
pass
ssh_login.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Time:2017/12/17 9:54
__Author__ = 'Sean Yao'
import base64
import getpass
import os
import socket
import sys
import traceback
from paramiko.py3compat import input
from models import models
import redis
import datetime
import time import paramiko
try:
import interactive
except ImportError:
from . import interactive def ssh_login(user_obj, bind_host_obj, mysql_engine, log_recording):
'''
ssh登陆
:param user_obj:
:param bind_host_obj:
:param mysql_engine: 连接数据库
:param log_recording: 写日志记录
:return:
'''
# now, connect and use paramiko Client to negotiate SSH2 across the connection
try:
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
client.load_system_host_keys()
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.WarningPolicy())
print('*** Connecting...')
client.connect(bind_host_obj.host.ip,
bind_host_obj.host.port,
bind_host_obj.remote_user.username,
bind_host_obj.remote_user.password,
timeout=30)
cmd_caches = []
chan = client.invoke_shell()
# print(repr(client.get_transport()))
print('*** Here we go!\n')
# 连接redis
pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='192.168.84.66', port=6379)
# 传一个命令列表给redis
user_record = [user_obj.id, bind_host_obj.id, 'login',
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())]
r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
# 用用户名做key前缀,避免冲突
key_name = str(user_obj.username)+'_login'
r.lpush(key_name, user_record)
interactive.interactive_shell(chan, user_obj, bind_host_obj, cmd_caches, log_recording)
chan.close()
client.close()
# 数据库写入操作
login_record = r.lrange(key_name, 0, -1)
login_redis_record = login_record[0].decode().replace('[', '').replace(']', '').split(',')
log_item = models.AuditLog(user_id=login_redis_record[0],
bind_host_id=login_redis_record[1],
action_type='login',
cmd='login',
date=login_redis_record[3].replace("'", ''))
cmd_caches.append(log_item)
log_recording(user_obj, bind_host_obj, cmd_caches)
user_record_cmd = user_obj.username+'_user_record'
cmd_redis_record = r.lrange(user_record_cmd, 0, -1)
for i in cmd_redis_record:
cmd_caches = []
v = i.decode().replace('[', '').replace(']', '').split(',')
v2 = v[3].replace("'", '')
# print(v[0], v[1], v[2], v[3], v[4])
log_item = models.AuditLog(user_id=v[0],
bind_host_id=v[1],
action_type='cmd',
cmd=v2, date=v[4].replace("'", ''))
cmd_caches.append(log_item)
log_recording(user_obj, bind_host_obj, cmd_caches)
# 当退出的时候将redis的值写入到数据库并且清空redis
logout_caches = []
logout_caches.append(models.AuditLog(user_id=user_obj.id,
bind_host_id=bind_host_obj.id,
action_type='logout',
cmd='logout',
date=datetime.datetime.now()))
log_recording(user_obj, bind_host_obj, logout_caches)
# 清空keys
r.delete(key_name)
r.delete(user_record_cmd)
except Exception as e:
print('*** Caught exception: %s: %s' % (e.__class__, e))
traceback.print_exc()
try:
client.close()
except:
pass
sys.exit(1)
utils.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Time:2017/12/15 21:48
__Author__ = 'Sean Yao'
import yaml
try:
from yaml import CLoader as Loader, CDumper as Dumper
except ImportError:
from yaml import Loader, Dumper def print_err(msg, quit=False):
'''
:param msg:
:param quit:
:return:
'''
output = "\033[31;1mError: %s\033[0m" % msg
if quit:
exit(output)
else:
print(output) def yaml_parser(yml_filename):
'''
yaml方法load yaml file and return
:param yml_filename:
:return:
'''
try:
yaml_file = open(yml_filename, 'r')
data = yaml.load(yaml_file)
return data
except Exception as e:
print_err(e)
views.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Time:2017/12/15 21:34
__Author__ = 'Sean Yao'
from models import models
from conf import settings
from modules.utils import print_err, yaml_parser
from modules.db_conn import engine, session
from modules import ssh_login
from modules import common_filters
import codecs def syncdb(argvs):
'''
创建表结构方法
:param argvs:
:return:
'''
print("Syncing DB....")
engine = models.create_engine(settings.ConnParams, echo=True)
models.Base.metadata.create_all(engine) # 创建所有表结构 def create_hosts(argvs):
'''
create 主机
:param argvs:
:return:
'''
if '-f' in argvs:
# 指定一个文件名否则报错
hosts_file = argvs[argvs.index("-f") +1]
else:
print_err("invalid usage, should be:\ncreate_hosts -f <the new hosts file>", quit=True)
source = yaml_parser(hosts_file) # 传文件回来
if source: # 循环字典
print(source)
for key, val in source.items():
print(key, val)
obj = models.Host(hostname=key, ip=val.get('ip'), port=val.get('port') or 22)
# 添加到表
session.add(obj)
session.commit() def create_remoteusers(argvs):
'''
create 堡垒机用户
:param argvs:
:return:
'''
if '-f' in argvs:
remoteusers_file = argvs[argvs.index("-f") +1]
else:
print_err("invalid usage, should be:\ncreate_remoteusers -f <the new remoteusers file>", quit=True)
source = yaml_parser(remoteusers_file)
if source:
for key, val in source.items():
print(key, val)
obj = models.RemoteUser(username=val.get('username'), auth_type=val.get('auth_type'),
password=val.get('password'))
session.add(obj)
session.commit() def create_users(argvs):
'''
create little_finger access user
:param argvs:
:return:
'''
if '-f' in argvs:
user_file = argvs[argvs.index("-f") +1 ]
else:
print_err("invalid usage, should be:\ncreateusers -f <the new users file>",quit=True) source = yaml_parser(user_file)
if source:
for key, val in source.items():
print(key, val)
obj = models.Userprofile(username=key, password=val.get('password'))
if val.get('groups'):
groups = session.query(models.HostGroup).filter(models.HostGroup.name.in_(val.get('groups'))).all()
if not groups:
print_err("none of [%s] exist in group table." % val.get('groups'), quit=True)
obj.groups = groups
if val.get('bind_hosts'):
bind_hosts = common_filters.bind_hosts_filter(val)
obj.bind_hosts = bind_hosts
#print(obj)
session.add(obj)
session.commit() def create_groups(argvs):
'''
create groups
:param argvs:
:return:
'''
if '-f' in argvs:
group_file = argvs[argvs.index("-f") + 1]
else:
print_err("invalid usage, should be:\ncreategroups -f <the new groups file>", quit=True)
source = yaml_parser(group_file)
if source:
for key, val in source.items():
print(key, val)
obj = models.HostGroup(name=key)
if val.get('bind_hosts'):
bind_hosts = common_filters.bind_hosts_filter(val)
obj.bind_hosts = bind_hosts if val.get('user_profiles'):
user_profiles = common_filters.user_profiles_filter(val)
obj.user_profiles = user_profiles
session.add(obj)
session.commit() def create_bindhosts(argvs):
'''
create bind hosts
:param argvs:
:return:
'''
if '-f' in argvs:
bindhosts_file = argvs[argvs.index("-f") + 1]
else:
print_err("invalid usage, should be:\ncreate_hosts -f <the new bindhosts file>",quit=True)
source = yaml_parser(bindhosts_file)
if source:
for key, val in source.items():
print(key, val)
# 获取到了主机
host_obj = session.query(models.Host).filter(models.Host.hostname == val.get('hostname')).first()
# 取hostname
assert host_obj # 断言,必须存在
for item in val['remote_users']: # 判断
print(item)
assert item.get('auth_type')
if item.get('auth_type') == 'ssh-password': # 判断认证password
remoteuser_obj = session.query(models.RemoteUser).filter(
models.RemoteUser.username == item.get('username'),
models.RemoteUser.password == item.get('password')
).first()
else:
# 获取远程用户
remoteuser_obj = session.query(models.RemoteUser).filter(
models.RemoteUser.username == item.get('username'),
models.RemoteUser.auth_type == item.get('auth_type'),
).first()
if not remoteuser_obj: # 没取到,程序退出
print_err("RemoteUser obj %s does not exist." % item, quit=True)
bindhost_obj = models.BindHost(host_id=host_obj.id, remoteuser_id=remoteuser_obj.id)
session.add(bindhost_obj) # 获取到关系后添加session
# for groups this host binds to
if source[key].get('groups'): # 获取组
group_objs = session.query(models.HostGroup).filter(models.HostGroup.name.in_
(source[key].get('groups'))).all()
assert group_objs
print('groups:', group_objs)
bindhost_obj.host_groups = group_objs
# for user_profiles this host binds to
if source[key].get('user_profiles'): # 判断是否直接属于哪一台机器
userprofile_objs = session.query(models.Userprofile).filter(models.Userprofile.username.in_(
source[key].get('user_profiles')
)).all()
assert userprofile_objs
print("userprofiles:", userprofile_objs)
bindhost_obj.user_profiles = userprofile_objs
# print(bindhost_obj)
session.commit() def auth():
'''
用户验证
do the user login authentication
:return:
'''
count = 0
while count < 3:
username = input("\033[32;1mUsername:\033[0m").strip()
if len(username) == 0:
continue
password = input("\033[32;1mPassword:\033[0m").strip()
if len(password) == 0:
continue
user_obj = session.query(models.Userprofile).filter(models.Userprofile.username == username,
models.Userprofile.password == password).first()
if user_obj:
return user_obj
else:
print("wrong username or password, you have %s more chances." % (3-count-1))
count += 1
else:
print_err("too many attempts.") def welcome_msg(user):
WELCOME_MSG = '''\033[32;1m
------------- Welcome [%s] login TinyServer -------------
\033[0m''' % user.username
print(WELCOME_MSG) def start_session(argvs):
print('going to start sesssion ')
user = auth()
if user:
welcome_msg(user)
# print(user.bind_hosts)
# print(user.host_groups)
exit_flag = False
while not exit_flag:
if user.bind_hosts:
# 显示未分组的机器
print('\033[32;1mz.\tungroupped hosts (%s)\033[0m' % len(user.bind_hosts))
for index, group in enumerate(user.host_groups):
print('\033[32;1m%s.\t%s (%s)\033[0m' % (index, group.name, len(group.bind_hosts)))
# 用户输入
choice = input("[%s]:" % user.username).strip()
if len(choice) == 0:
continue
# 如果是z 打印未分组机器
if choice == 'z':
print("------ Group: ungroupped hosts ------")
for index, bind_host in enumerate(user.bind_hosts):
print(" %s.\t%s@%s(%s)" % (index,
bind_host.remote_user.username,
bind_host.host.hostname,
bind_host.host.ip,
))
print("----------- END -----------")
elif choice.isdigit(): # 打印分组的机器
choice = int(choice)
if choice < len(user.host_groups):
print("------ Group: %s ------" % user.host_groups[choice].name)
for index, bind_host in enumerate(user.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts):
print(" %s.\t%s@%s(%s)" % (index,
bind_host.remote_user.username,
bind_host.host.hostname,
bind_host.host.ip,
))
print("----------- END -----------") # host selection 选择机器去登陆
while not exit_flag:
user_option = input("[(b)back, (q)quit, select host to login]:").strip()
if len(user_option) == 0:
continue
if user_option == 'b':
break
if user_option == 'q':
exit_flag = True
if user_option.isdigit():
user_option = int(user_option)
if user_option < len(user.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts):
print('host:', user.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts[user_option])
# print('audit log:', user.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts[user_option].audit_logs)
ssh_login.ssh_login(user, # 传用户,用户组,连上对应的
user.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts[user_option],
session, log_recording)
else:
print("no this option..") def log_recording(user_obj, bind_host_obj, logs):
'''
flush user operations on remote host into DB
:param user_obj:
:param bind_host_obj:
:param logs: list format [logItem1,logItem2,...]
:return:
'''
# print("\033[41;1m--logs:\033[0m", logs)
session.add_all(logs)
session.commit()
def user_record_cmd(argvs):
'''
查看操作记录方法
:param argvs:
:return:
'''
print('going to start view record')
user = auth()
# 默认root可以查所有人的记录
if user.username == 'root':
print('welcome %s ' % user.username)
exit_flag = False
# 用户对象
user_obj = session.query(models.Userprofile).filter().all()
# 循环查看堡垒机用户操作
while not exit_flag:
for user_profile_list in user_obj:
# 打印堡垒机用户,根据堡垒机用户ID选择其管辖的机器并打印日志
print("%s.\t%s" % (user_profile_list.id, user_profile_list.username))
choice = input("[%s]:" % user.username).strip()
for user_profile_list in user_obj:
if str(choice) == str(user_profile_list.id):
if user_profile_list.bind_hosts:
# 显示未分组的机器
print('\033[32;1mz.\tungroupped hosts (%s)\033[0m' % len(user_profile_list.bind_hosts))
else:
print(' no binding groups ')
for index, group in enumerate(user_profile_list.host_groups):
print('\033[32;1m%s.\t%s (%s)\033[0m' % (index, group.name, len(group.bind_hosts)))
choice = input("[%s]:" % user.username).strip()
if choice.isdigit(): # 打印分组的机器
choice = int(choice)
if choice < len(user_profile_list.host_groups):
print("------ Group: %s ------" % user_profile_list.host_groups[choice].name)
for index, bind_host in enumerate(user_profile_list.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts):
print(" %s.\t%s@%s(%s)" % (index,
bind_host.remote_user.username,
bind_host.host.hostname,
bind_host.host.ip,
))
print("----------- END -----------")
# host selection 选择机器去查看操作信息
while not exit_flag:
user_option = input("[(b)back, (q)quit, select host to login]:").strip()
if len(user_option) == 0:
continue
if user_option == 'b':
break
if user_option == 'q':
exit_flag = True
if user_option.isdigit():
user_option = int(user_option)
if user_option < len(user_profile_list.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts):
# print('host:', user_profile_list.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts[user_option])
data = \
session.query(models.AuditLog).filter(
models.AuditLog.user_id == user_profile_list.id,
models.AuditLog.bind_host_id == user_profile_list.host_groups[choice].
bind_hosts[user_option].id).all()
if data:
for index, i in enumerate(data):
# redis 写入value的时候带有了\t \n 等需要转义
# 第一个注释从数据库里读注释的这种不能转移\t,
# 第二个和现行的俩种中文转义有些问题
# print(i.user_id, i.bind_host_id, i.action_type, i.cmd, i.date)
# print(i.user_id, i.bind_host_id, i.action_type,
# codecs.getdecoder("unicode_escape")(i.cmd)[0], i.date)
# print(i.user_id, i.bind_host_id, i.action_type,
# i.cmd.encode().decode('unicode-escape'), i.date)
print(index, i.date, i.cmd.encode().decode('unicode-escape'))
else:
print('no record in host:', user_profile_list.host_groups[choice].
bind_hosts[user_option])
# 其他人只能查自己的操作记录
else:
exit_flag = False
while not exit_flag:
if user.bind_hosts:
# 显示未分组的机器
print('\033[32;1mz.\tungroupped hosts (%s)\033[0m' % len(user.bind_hosts))
for index, group in enumerate(user.host_groups):
print('\033[32;1m%s.\t%s (%s)\033[0m' % (index, group.name, len(group.bind_hosts)))
choice1 = input("[%s]:" % user.username).strip()
# 查询选项
if choice1 == 'z':
print("------ Group: ungroupped hosts ------")
for index, bind_host in enumerate(user.bind_hosts):
print(" %s.\t%s@%s(%s)" % (index,
bind_host.remote_user.username,
bind_host.host.hostname,
bind_host.host.ip,
))
print("----------- END -----------")
elif choice1.isdigit(): # 打印分组的机器
choice = int(choice1)
if choice < len(user.host_groups):
print("------ Group: %s ------" % user.host_groups[choice].name)
for index, bind_host in enumerate(user.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts):
print(" %s.\t%s@%s(%s)" % (index,
bind_host.remote_user.username,
bind_host.host.hostname,
bind_host.host.ip,
))
print("----------- END -----------") # host selection 选择机器去查看操作信息
while not exit_flag:
user_option = input("[(b)back, (q)quit, select host to view record]:").strip()
if len(user_option) == 0:
continue
if user_option == 'b':
break
if user_option == 'q':
exit_flag = True
if user_option.isdigit():
user_option = int(user_option)
if user_option < len(user.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts):
data = session.query(models.AuditLog)\
.filter(models.AuditLog.user_id == user.id,
models.AuditLog.bind_host_id == user.host_groups[choice].
bind_hosts[user_option].id).all()
# print(user.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts[user_option].id)
if data:
for index, i in enumerate(data):
print(index, i.date, i.cmd.encode().decode('unicode-escape'))
else:
print('no record in host:', user.host_groups[choice].bind_hosts[user_option])
else:
print("no this option..")
share
new_bindhosts.yml
bind1:
hostname: server1
remote_users:
- user0:
username: root
auth_type: ssh-password
password: 123456
groups:
- bj_group
user_profiles:
- sean bind2:
hostname: server2
remote_users:
- user0:
username: root
auth_type: ssh-password
password: 123456
groups:
- bj_group
- sh_group
user_profiles:
- sean
- jack bind3:
hostname: server3
remote_users:
- user0:
username: root
auth_type: ssh-password
password: 123456
groups:
- bj_group
- sh_group
user_profiles:
- sean
- jack bind4:
hostname: server2
remote_users:
- user2:
username: colin
auth_type: ssh-password
password: 123@123
groups:
- web_servers
user_profiles:
- root bind5:
hostname: server3
remote_users:
- user3:
username: web
auth_type: ssh-password
password: 12345678
- user1:
username: mysql
auth_type: ssh-password
password: 12345678
groups:
- web_servers
- db_servers
user_profiles:
- root
new_groups.yml
bj_group:
user_profiles:
- sean sh_group:
user_profiles:
- jack db_servers:
user_profiles:
- root web_servers:
user_profiles:
- root
new_hosts.yml
server1:
ip: 192.168.84.66
port: 12321 server2:
ip: 192.168.84.67
port: 12321 server3:
ip: 192.168.84.68
port: 12321
new_remoteusers.yml
user0:
auth_type: ssh-password
username: root
password: 123456 user1:
auth_type: ssh-password
username: mysql
password: 12345678 user2:
auth_type: ssh-password
username: colin
password: 123@123 user3:
auth_type: ssh-password
username: web
password: 12345678 user4:
auth_type: ssh-key
username: root
new_user.yml
root:
password: 123@456 sean:
password: 123456 jack:
password: 123456
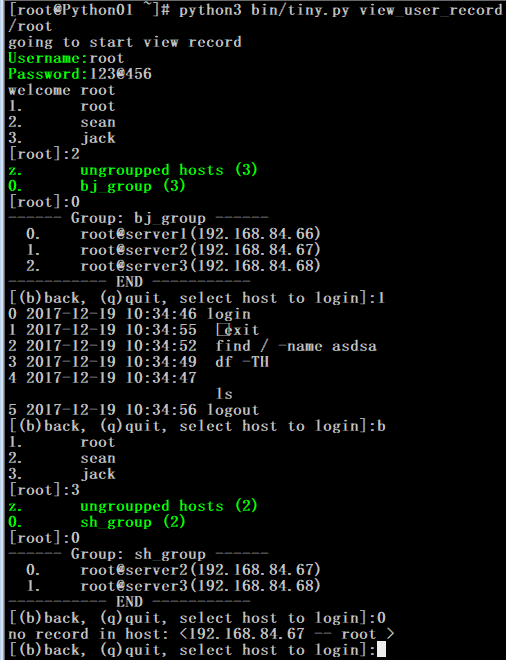
程序测试样图:
1. 创建表和插入表数据
2. 查看绑定关系
3. 登陆和写入命令
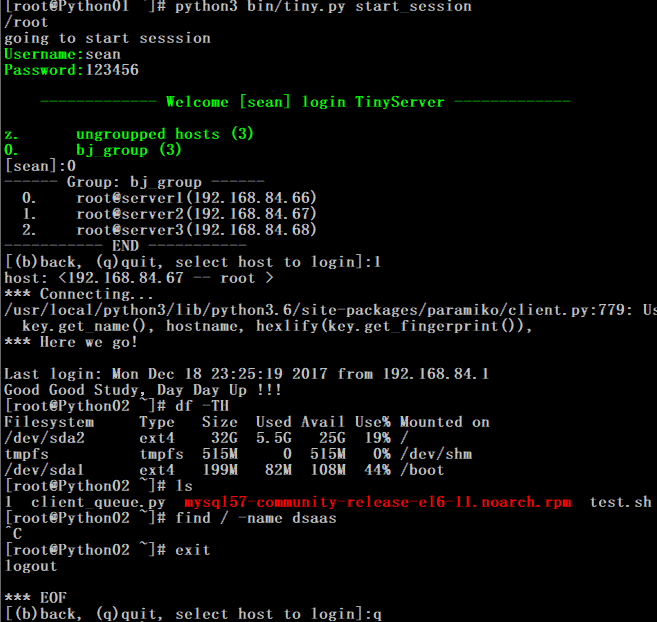
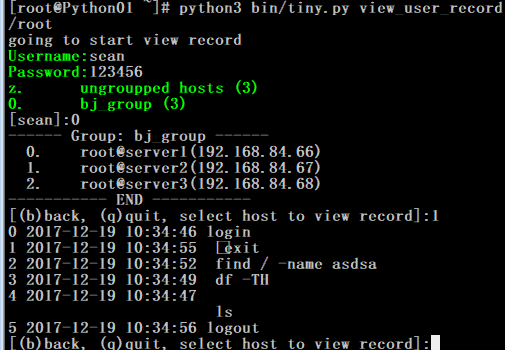
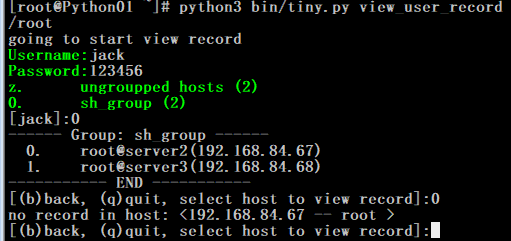
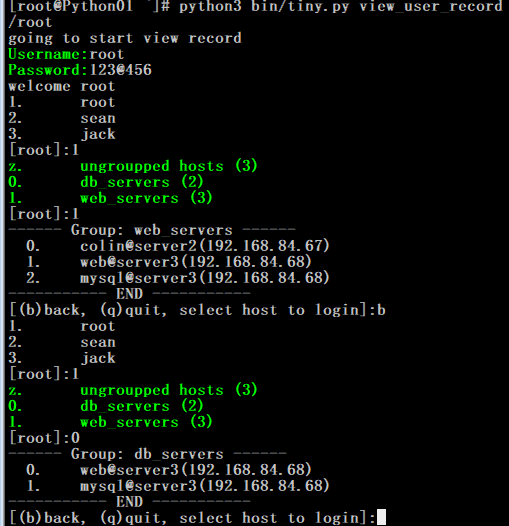
4. 不同用户权限,组权限,登陆权限和查看日志权限
python作业堡垒机(第十三周)的更多相关文章
- 基于python的堡垒机
一 堡垒机的架构 堡垒机的核心架构通常如下图所示: 二.堡垒机的一般执行流程 管理员为用户在服务器上创建账号(将公钥放置服务器,或者使用用户名密码) 用户登陆堡垒机,输入堡垒机用户名密码,显示当前用户 ...
- python之堡垒机(第九天)
本节作业: 通过使用paramiko和sqlalchemy实现堡垒机功能 主要功能实现: 1.用户登录堡垒机后,无需知道密码或密钥可以SSH登录远端服务器: 2.用户对一个组内所有主机批量执行指定命令 ...
- python作业ATM(第五周)
作业需求: 额度 15000或自定义. 实现购物商城,买东西加入 购物车,调用信用卡接口结账. 可以提现,手续费5%. 支持多账户登录. 支持账户间转账. 记录每月日常消费流水. 提供还款接口. AT ...
- Python之堡垒机
本节内容 项目实战:运维堡垒机开发 前景介绍 到目前为止,很多公司对堡垒机依然不太感冒,其实是没有充分认识到堡垒机在IT管理中的重要作用的,很多人觉得,堡垒机就是跳板机,其实这个认识是不全面的,跳板功 ...
- (转)用Python写堡垒机项目
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/ywq935/article/details/78816860 前言 堡垒机是一种运维安全审计系统.主要的功能是对运维人员的运维操作进行审计和权限控制 ...
- python 有关堡垒机的那些事
堡垒机为了保证系统或服务器的安全性,防止运维和开发人员胡乱操作服务器,导致不必要的损失,使用堡垒机来完成对运维和开发人员的授权.用户统一登录堡垒机账号来操作系统或服务器.堡垒机等于成了生产系统的SSO ...
- python作业三级菜单day1(第一周)
一.作业需求: 1. 运行程序输出第一级菜单 2. 选择一级菜单某项,输出二级菜单,同理输出三级菜单 3. 菜单数据保存在文件中 4. 让用户选择是否要退出 5. 有返回上一级菜单的功能 二三级菜单文 ...
- python作业:购物车(第二周)
一.作业需求: 1.启动程序后,输入用户名密码后,如果是第一次登录,让用户输入工资,然后打印商品列表 2.允许用户根据商品编号购买商品 3.用户选择商品后,检测余额是否够,够就直接扣款,不够就提醒 4 ...
- python学习笔记-(十三)堡垒机
1.课前准备: 本次学习堡垒机相关知识:之前,需要安装Python的paramiko模块,该模块基于SSH用于连接远程服务器并执行相关操作. 前提: python3.5程序安装到默认路径下并已添加pa ...
随机推荐
- MySQL复合主键下ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE语句失效问题
问题的起因,假设有一张表,里面保存了交易订单,每张订单有唯一的ID,有最后更新时间,还有数据,详情如下: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 +-------+----------+------+-----+ ...
- 清华集训2015-Day 2
校内测试做到了,于是就把解题报告发出来. 简单回路 一个 \(n\times m\) 的方格纸,有 \(k\) 个障碍点.\(q\) 次询问,每次询问 \((x,y)\) ,问有多少条简单回路经过 \ ...
- nginx通过配置empty_gif解决请求favicon 404的问题
背景介绍 因为一些浏览器在访问网站时会默认去请求网站的favicon,但是我的网站(Tengine)上并没有这些icon图片,因此在访问日志里会出现大量的404错误,会触发一些没必要日志告警.我们可以 ...
- 03.基于IDEA+Spring+Maven搭建测试项目--常用dependency
<!--常用的依赖配置--> <!--未展示完整的pom.xml文件内容--> <properties> <java.version>1.8</j ...
- P1503 鬼子进村
题目背景 小卡正在新家的客厅中看电视.电视里正在播放放了千八百次依旧重播的<亮剑>,剧中李云龙带领的独立团在一个县城遇到了一个鬼子小队,于是独立团与鬼子展开游击战. 题目描述 描述 县城里 ...
- [Codeforces526F]Pudding Monsters 分治
F. Pudding Monsters time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes In this proble ...
- TJOI2013数字根
题面链接 洛谷 sol 我们先不考虑\(0\),发现数字根\(=\)它\(mod 9\). 我们前缀和一波,把区间和变成两数相减. 对于每个\(v\in\{0-8\}\),(这里面的\(mod 9=0 ...
- java多线程 --ConcurrentLinkedQueue 非阻塞 线程安全队列
ConcurrentLinkedQueue是一个基于链接节点的无界线程安全队列,它采用先进先出的规则对节点进行排序,当我们添加一个元素的时候,它会添加到队列的尾部:当我们获取一个元素时,它会返回队列头 ...
- (转)Android数据的四种存储方式SharedPreferences、SQLite、Content Provider和File (三) —— SharePreferences
除了SQLite数据库外,SharedPreferences也是一种轻型的数据存储方式,它的本质是基于XML文件存储key-value键值对数据,通常用来存储一些简单的配置信息.其存储位置在/data ...
- 解题:POI 2013 Triumphal arch
题面 二分答案,问题就转化为了一个可行性问题,因为我们不知道国王会往哪里走,所以我们要在所有他可能走到的点建造,考虑用树形DP解决(这个DP还是比较好写的,你看我这个不会DP的人都能写出来=.=) 定 ...
