Spring 核心组件总结
spring核心组件总结
spring介绍
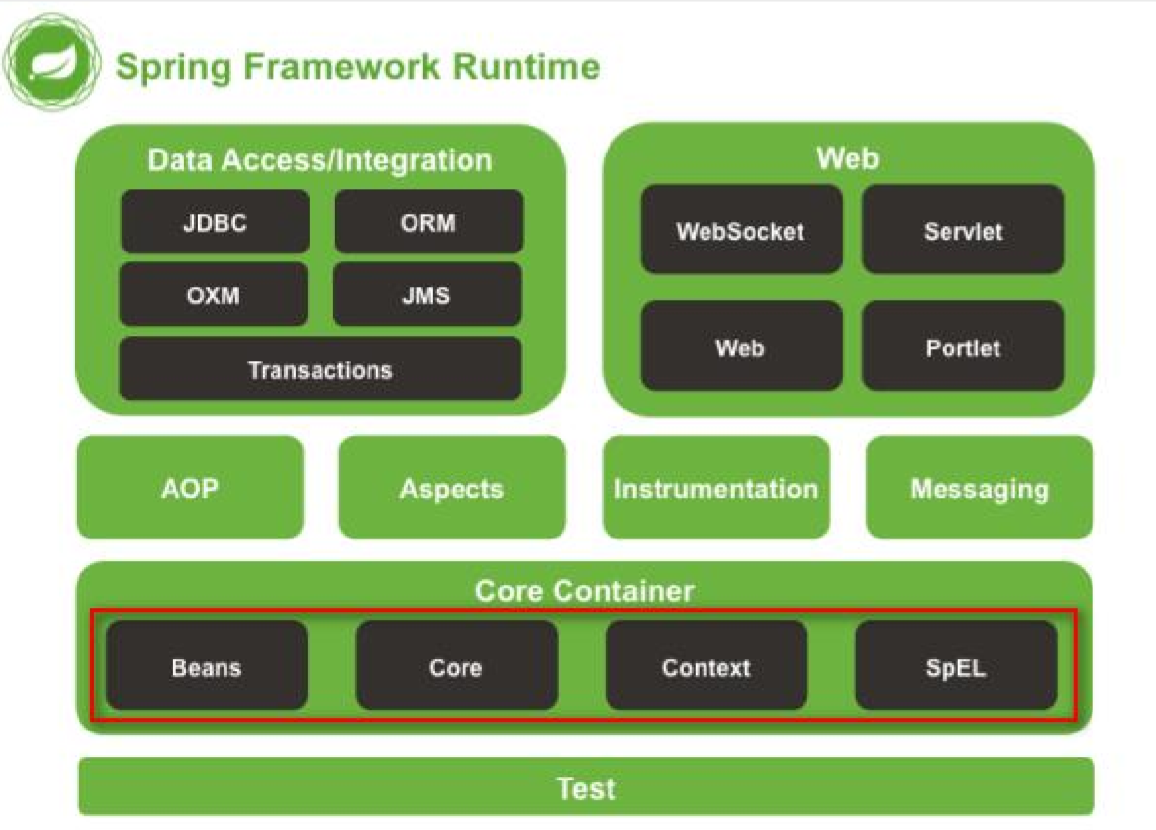
spring概念
IOC: Inverse Of Control 控制反转
将我们创建对象的方式反转了,以前创建对象是由我们开发人员自己维护,包括依赖注入关系也是自己注入。
使用了spring之后,对象的创建以及依赖关系,由spring完成创建以及注入。
控制反转就是反转了对象的创建方式。从我们自己创建反转给了spring
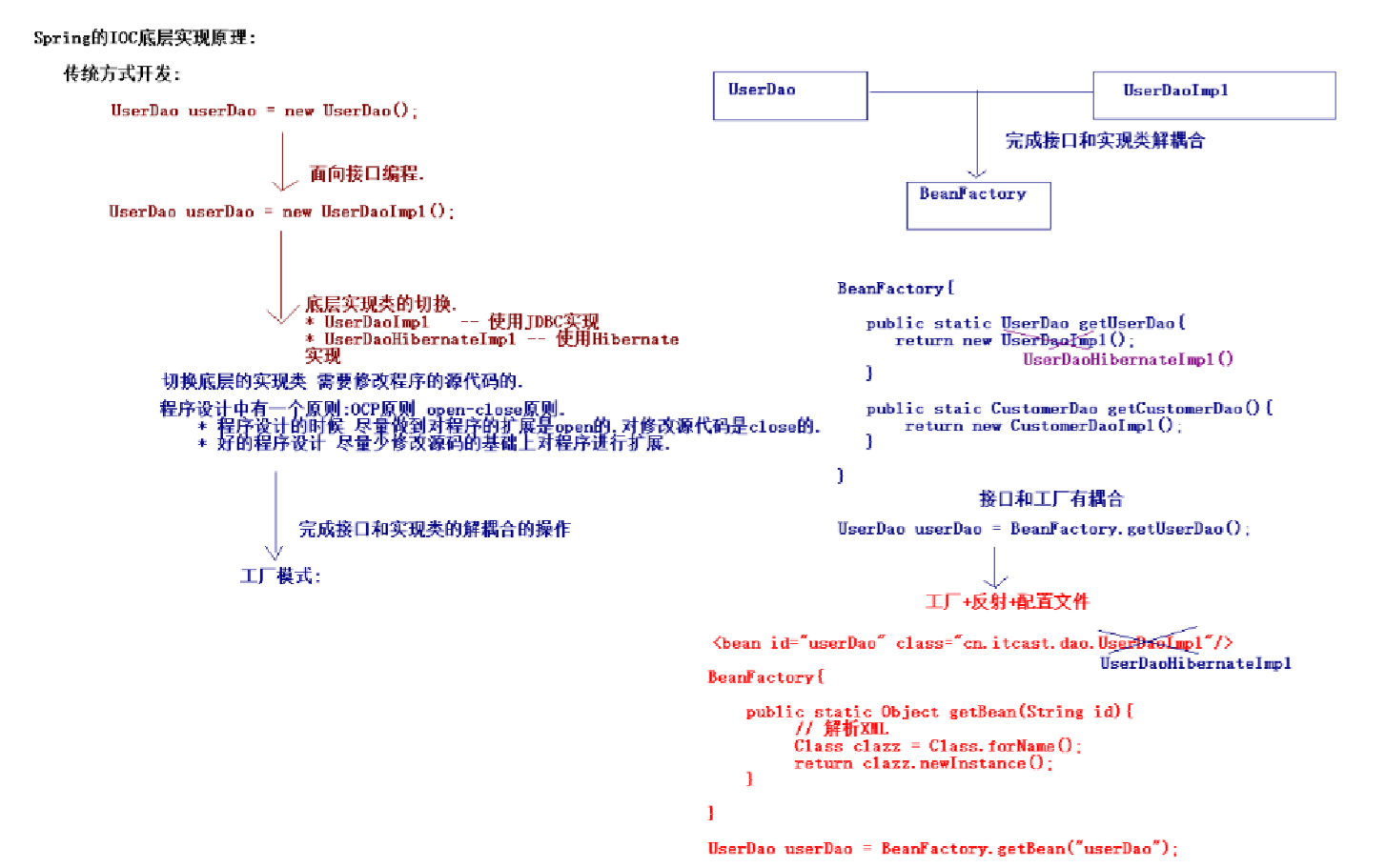
DI: Dependency Injection 依赖注入
实现ioc思想需要 DI提供支持
注入方式:1)set方式注入 2) 构造方法注入 3) 字段注入(不推荐)
注入类型:1) 值类型注入 2)引用类型注入
AOP 面向切面的编程 (横向重复,纵向抽取)
举例:拦截器(身份校验)、过滤器(编码处理)、动态代理(事务)
spring aop实现原理
动态代理(优先):被代理对象必须要实现接口,才能产生代理对象.如果没有接口将不能使用动态代理技术
cglib代理(没有接口):第三方代理技术,cglib代理.可以对任何类生成代理.代理的原理是对目标对象进行继承代理. 如果目标对象被final修饰.那么该类无法被cglib代理.
spring名词解释

aop依赖所需包
aop代码演示(xml配置)
//通知类
public class MyAdvice {
//前置通知
// |-目标方法运行之前调用
//后置通知(如果出现异常不会调用)
// |-在目标方法运行之后调用
//环绕通知
// |-在目标方法之前和之后都调用
//异常拦截通知
// |-如果出现异常,就会调用
//后置通知(无论是否出现 异常都会调用)
// |-在目标方法运行之后调用
//----------------------------------------------------------------
//前置通知
public void before(){
System.out.println("这是前置通知");
}
//后置通知
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("这是后置通知(出现异常不执行)!!");
}
//环绕通知
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("这是环绕通知之前的部分!");
Object proceed = pjp.proceed();//璋冪敤鐩爣鏂规硶
System.out.println("这是环绕通知之后的部分");
return proceed;
}
//异常通知
public void afterException(){
System.out.println("这是异常通知,出现异常执行!");
}
//后置通知
public void after(){
System.out.println("这是后置通知(出现异常也会调用)!!");
}
}
<!-- 1.配置目标对象 -->
<bean name="userService" class="com.yoci.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 2.配置通知对象 -->
<bean name="myAdvice" class="com.yoci.springaop.MyAdvice"></bean>
<!-- 3.配置将通知织入目标对象 -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点
public void cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl.save()
void cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl.save()
* cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl.save()
* cn.itcast.service.UserServiceImpl.*()
* cn.itcast.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..)
* cn.itcast.service..*ServiceImpl.*(..)
-->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.yoci.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="pc"/>
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
<!-- 指定名为before方法作为前置通知 -->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pc"/>
<!-- 后置 -->
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="pc" />
<!-- 环绕通知 -->
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc"/>
<!-- 异常拦截通知 -->
<aop:after-throwing method="afterException" pointcut-ref="pc"/>
<!-- 后置 -->
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pc"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
aop代码演示(注解配置)
//通知类
@Aspect
public class MyAdvice {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.yoci.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void pointcut(){}
@Before("MyAdvice.pointcut()")
public void before(){
System.out.println("这是前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.yoci.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("这是后置通知(出现异常不执行)!!");
}
@Around("execution(* com.yoci.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("这是环绕通知之前的部分!");
Object proceed = pjp.proceed();//调用目标方法
System.out.println("这是环绕通知之后的部分");
return proceed;
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.yoci.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void afterException(){
System.out.println("这是异常通知,出现异常执行!");
}
@After("execution(* com.yoci.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("这是后置通知(出现异常也会调用)!!");
}
}
<!-- 1.配置目标对象 -->
<bean name="userService" class="com.yoci.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!-- 2.配置通知对象 -->
<bean name="myAdvice" class="com.yoci.annotationaop.MyAdvice"></bean>
<!-- 3.开启使用注解完成织入 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
spring 中的工厂(容器)
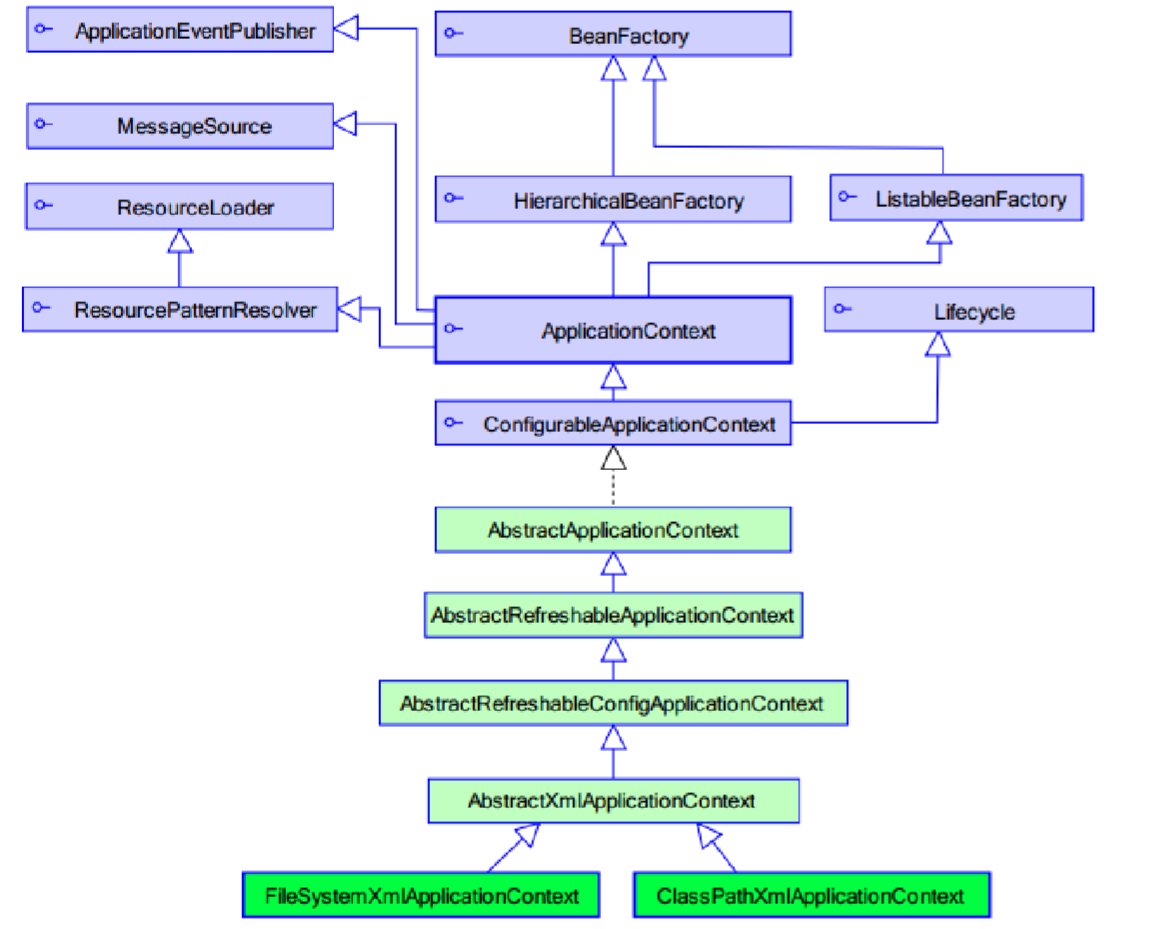
ApplicationContext接口由两个实现类:
1) ClassPathXmlApplicationContext: 加载类路径下的spring的配置
2)FilesSystemXmlApplicationContext:加载本地磁盘下的spring的配置
BeanFactrory(过时)
BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的区别:
1)BeanFactory:是在getBean的时候才会生成类的实例
2)ApplicationContext:是在加载applicationContext.xml(容器启动)时就会创建
spring配置详解
Bean元素
<!-- 将User对象交给spring容器管理 -->
<!-- Bean元素:使用该元素描述需要spring容器管理的对象
class属性:被管理对象的完整类名.
name属性:给被管理的对象起个名字.获得对象时根据该名称获得对象.
可以重复.可以使用特殊字符.
id属性: 与name属性一模一样.
名称不可重复.不能使用特殊字符.
结论: 尽量使用name属性.
-->
<bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" ></bean>
<!-- 导入其他spring配置文件 -->
<!-- 分模块配置 -->
<import resource="cn/itcast/b_create/applicationContext.xml"/>
Bean元素进阶
scope属性(作用域)
1)singleton(默认值):单例对象.被标识为单例的对象在spring容器中只会存在一个实例
2)prototype:多例原型.被标识为多例的对象,每次再获得才会创建.每次创建都是新的对象.整合struts2时,ActionBean必须配置为多例的.
3)request:web环境下.对象与request生命周期一致.
4)session:web环境下,对象与session生命周期一致.
5)global-session:global-session和Portlet应用相关。当你的应用部署在Portlet容器中工作时,它包含很多portlet。如果你想要声明让所有的portlet共用全局的存储变量的话,那么这全局变量需要存储在global-session中。
生命周期属性
1)init-method:配置一个方法作为生命周期初始化方法.spring会在对象创建之后立即调用.
2)destory-method:配置一个方法作为生命周期的销毁方法.spring容器在关闭并销毁所有容器中的对象之前调用.
<bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User"
init-method="init" destroy-method="destory" ></bean>
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Car car;
public Car getCar() {return car;}
public void setCar(Car car) {this.car = car;}
public String getName() {return name;}
public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}
public Integer getAge() {return age;}
public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}
public void init(){
System.out.println("我是初始化方法!");
}
public void destory(){
System.out.println("我是销毁方法!");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", car=" + car + "]";
}
}
spring创建对象的方式
1)空参构造方式
2)静态工厂(了解)
3)实例工厂(了解)
<!-- 创建方式1:空参构造创建 -->
<bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User"
init-method="init" destroy-method="destory" ></bean>
<!-- 创建方式2:静态工厂创建
调用UserFactory的createUser方法创建名为user2的对象.放入容器
-->
<bean name="user2"
class="cn.itcast.b_create.UserFactory"
factory-method="createUser" ></bean>
<!-- 创建方式3:实例工厂创建
调用UserFactory对象的createUser2方法创建名为user3的对象.放入容器
-->
<bean name="user3"
factory-bean="userFactory"
factory-method="createUser2" ></bean>
<bean name="userFactory"
class="cn.itcast.b_create.UserFactory" ></bean>
public class UserFactory {
public static User createUser(){
System.out.println("静态工厂创建User");
return new User();
}
public User createUser2(){
System.out.println("实例工厂创建User");
return new User();
}
}
spring属性注入
<!-- set方式注入: -->
<bean name="user" class="com.yoci.entity.User" >
<!-- 值类型注入 -->
<property name="name" value="zhangsan"></property>
<property name="age" value="22"></property>
<!-- 引用类型注入 -->
<property name="car" ref="car"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 将car对象配置到容器当中 -->
<bean name="car" class="com.yoci.entity.Car">
<property name="name" value="兰博基尼"></property>
<property name="color" value="黄色"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 构造函数注入 -->
<bean name="user1" class="com.yoci.entity.User">
<!-- name属性: 构造函数的参数名 -->
<!-- index属性: 构造函数的参数索引 -->
<!-- type属性: 构造函数的参数类型-->
<constructor-arg name="name" index="0" value="李四" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="car" index="1" ref="car" ></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- p名称空间注入 -->
<!--
1.导入P名称空间 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
2.使用p:属性完成注入
-值类型: p:属性名="值"
-对象类型: p:属性名-ref="bean名称" -->
<bean name="user2" class="com.yoci.entity.User" p:name="wangwu" p:age="26" p:car-ref="car"></bean>
<!-- spEL注入 -->
<bean name="user3" class="com.yoci.entity.User">
<property name="name" value="#{user1.name}"></property>
<property name="age" value="#{user2.age}"></property>
<property name="car" ref="car"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 复杂类型注入 -->
<bean name="collection" class="com.yoci.entity.Collection">
<!-- 如果数组中只准备注入一个值(对象),直接使用value|ref即可
<property name="arr" value="tom" ></property>
-->
<!-- array注入,多个元素注入 -->
<property name="arr">
<array>
<value>tom</value>
<value>jack</value>
<ref bean="user2"></ref>
</array>
</property>
<!--
如果List中只准备注入一个值(对象),直接使用value|ref即可
<property name="list" value="jack" ></property>
-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>zhangsan</value>
<value>李四</value>
<ref bean="user"/>
</list>
</property>
<!-- map类型注入 -->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="url" value="www.yoci.com"></entry>
<entry key="user3" value-ref="user"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!-- prperties 类型注入 -->
<property name="prop">
<props>
<prop key="driverClass">com.jdbc.mysql.Driver</prop>
<prop key="userName">root</prop>
<prop key="password">1234</prop>
</props>
</property>
spring事务
什么是事务:
事务逻辑上的一组操作,组成这组操作的各个逻辑单元,要么一起成功,要么一起失败。
事务特性
原子性 :强调事务的不可分割.
一致性 :事务的执行的前后数据的完整性保持一致.
隔离性 :一个事务执行的过程中,不应该受到其他事务的干扰
持久性 :事务一旦结束,数据就持久到数据库
如果不考虑隔离性引发安全性问题:
脏读 :一个事务读到了另一个事务的未提交的数据
不可重复读 :一个事务读到了另一个事务已经提交的 update 的数据导致多次查询结果不一致.
虚幻读 :一个事务读到了另一个事务已经提交的 insert 的数据导致多次查询结果不一致.
解决读问题:设置事务隔离级别
未提交读 :脏读,不可重复读,虚读都有可能发生
已提交读 :避免脏读。但是不可重复读和虚读有可能发生
可重复读 :避免脏读和不可重复读.但是虚幻读有可能发生.
串行化的 :避免以上所有读问题.
Mysql 默认:可重复读 Oracle 默认:读已提交
事务的操作对象
在spring中玩事务管理.最为核心的对象就TransactionManager对象
事务的属性介绍
事务隔离级别:
1 读未提交 2 读已提交 4 可重复读 8 串行化
是否只读:
true/false
事务的传播行为:
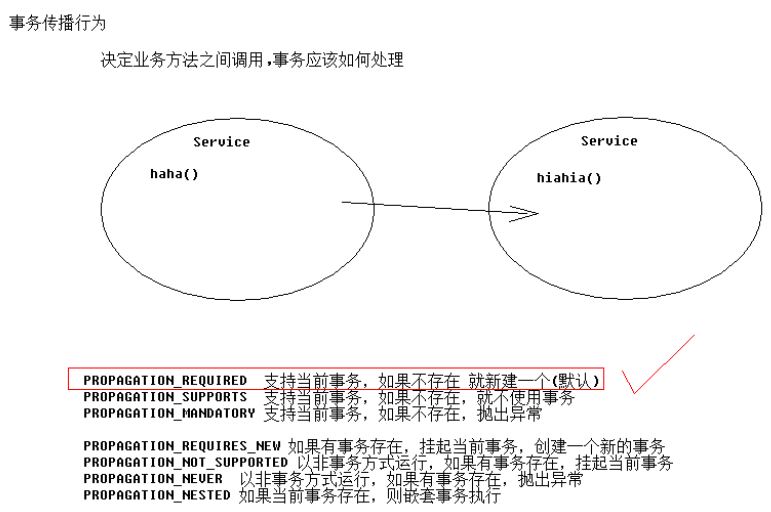
spring代码(xml配置)
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<!-- 通知 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 以方法为单位,指定方法应用什么事务属性
isolation:隔离级别
propagation:传播行为
read-only:是否只读
-->
<!-- 传播行为 -->
<tx:method name="save*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="persist*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="update*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="modify*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="delete*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="remove*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
<tx:method name="get*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="find*" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="true" />
<tx:method name="transfer" isolation="REPEATABLE_READ" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 切面 -->
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice"
pointcut="execution(* cn.itcast.crm.service.*.*(..))" />
</aop:config>
spring代码(注解配置)
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<!-- 开启使用注解管理aop事务 -->
<tx:annotation-driven/>
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=true)
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao ad ;
private TransactionTemplate tt;
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,readOnly=false)
public void transfer(final Integer from,final Integer to,final Double money) {
//减钱
ad.decreaseMoney(from, money);
int i = 1/0;
//加钱
ad.increaseMoney(to, money);
}
}
spring注解
开启spring注解
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd ">
<!--
引入:
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd
-->
<!-- 指定扫描cn.itcast.bean报下的所有类中的注解.
注意:扫描包时.会扫描指定报下的所有子孙包
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.itcast.bean"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
注解使用介绍
@Component("user") = <bean name="user" class="cn.itcast.bean.User" />
// service层
@Service("user")
// web层
@Controller("user")
// dao层
@Repository("user")
//指定对象的作用范围
@Scope(scopeName="singleton/prototype")
//属性注入,推荐使用set方法注入方式, 第一种破坏封装性
@Value("18")
private Integer age;
@Value("tom")
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//自动装配
@Autowired //问题:如果匹配多个类型一致的对象.将无法选择具体注入哪一个对象.
@Qualifier("car2")//使用@Qualifier 配合 @Autowired注解告诉spring容器自动装配哪个名称的对象
//手动装配,指定注入哪个名称的对象
@Resource(name="car")
private Car car;
//在对象被创建后调用.init-method
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("我是初始化方法!");
}
//在销毁之前调用.destory-method
@PreDestroy
public void destory(){
System.out.println("我是销毁方法!");
}
spring整合junit测试
导入aop+test包
//帮我们创建容器
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//指定创建容器时使用哪个配置文件
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
//指定多个配置文件时
@ContextConfiguration(locations = { "classpath*:/spring1.xml", "classpath*:/spring2.xml" })
public class Demo {
//将名为user的对象注入到u变量中
@Resource(name="user")
private User u;
@Test
public void fun1(){
System.out.println(u);
}
}
Spring 核心组件总结的更多相关文章
- Spring核心组件剖析
简介 Spring框架如今已成为服务端开发框架中的主流框架之一,是web开发者的利器.然而,真正让人着迷的,还是与其实现相关的 原理,设计模式以及许多工程化的思想.本文主要探讨Spring的三大核心组 ...
- Spring 核心组件工作原理简析
Spring Framework 的核心组件有三个: Spring Core,Spring Context 和 Spring Beans,它们奠定了 Spring 的基础并撑起了 Spring 的框架 ...
- spring核心组件
spring的对象是bean组件,就像面向对象的object,bean包装的是object.context的作用,发现每个bean之间的关系,为他们之间建立好这种关系并进行维护.所以,可以把conte ...
- Spring核心组件知识梳理
Spring的一些概念和思想 Spring的核心:AOP.IOC. 简单点说,就是把对象交给Spring进行管理,通过面向切面编程来实现一些"模板式"的操作,使得程序员解放出来,可 ...
- spring的核心组件及作用(一)
Spring的核心组件有: Context Core Bean. 如果要在这三个核心组件上挑出一个最核心的组件,那就是Bean组件了. Spring的特性功能有:WEB ORM AOP ...
- Spring初学
一.spring体系结构spring核心组件 1.Beans(包装应用程序自定义对象Object,Object中存有数据) 2.Core (资源加载,资源抽象,建立维护与bean之间的一些关系所需的一 ...
- Spring(一)Spring的第一滴血
前言 开始工作了,但是一进来公司本来是做爬虫和数据分析的,但是走了一个后端的,导致我必须要去顶替他的工作.因为这个项目使用的是Spring. SpringMVC.Hibernate所以我又要去回忆一下 ...
- Spring第一天——入门与IOC
大致内容 spring基本概念 IOC入门 [17.6.9更新],如何学习spring? 掌握用法 深入理解 不断实践 反复总结 再次深入理解与实践 一.Spring相关概念 1.概述: Sprin ...
- Spring在项目中需要的配置
要想了解Spring,首先要了解三层架构.....自行百度. 1.Spring相关概念: 少数jar+某一个功能的配置文件 Spring容器(轻量级):帮我们管理业务逻辑层,有很多业务逻辑对象,需要对 ...
随机推荐
- 统计进程打开了多少文件,定位too many open files
[root@ostack1 ~]# lsof -p 18628 | wc -l 114
- JQuery - 动态添加Html后,如何使CSS生效,JS代码可用?
今天在开发JQuery Mobile程序时候,需要从服务器取得数据,随后显示在页面上的Listview控件中,数据完整获取到了,也动态添加到Listview控件中,但是数据对应的CSS没有任何效果了, ...
- POJ 1577Falling Leaves(二叉树的建立)
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1577 解题思路:题目是中文就不翻译了,网上都说这题很水,但本蒟蒻虽然知道是倒过来建立二叉搜索树,可是实现不了,得到小伙伴的关键递归思想 ...
- MVC的默认约定
MVC项目中有很多默认约定,一种是对项目目录分配的约定,比如默认情况下需要将Javascript文件放置在Script文件夹中,但这并不妨碍你将这个文件夹重新命名,也可以将整个文件夹放置到任何想要放置 ...
- (转)LINUX CENTOS7下安装PYTHON
LINUX CENTOS7下安装PYTHON 原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/lclq/p/5620196.html Posted on 2016-06-27 14:58 南宫羽香 ...
- css设置:图片文字等不能被选择
-webkit-user-select: none; -moz-user-select: none; -ms-user-select: none; user-select: none;
- 模板模式(TemplateMethod)
什么是Template Method模式 在父类中定义处理流程的框架,在子类中实现具体处理的模式就称为Template Mehtod模式.模板模式的关键是:子类可以置换掉父类的可变部分,但是子类却不可 ...
- Android中的各种访问权限Permission含义
android.permission.EXPAND_STATUS_BAR 允许一个程序扩展收缩在状态栏,android开发网提示应该是一个类似Windows Mobile中的托盘程序 android. ...
- Linux运维中遇到的常见问题
1.CentOS启动tomcat出现乱码的解决方案1.打开tomcat下的server.xml配置文件,在connect标签中添加编码属性:URIEncoding="UTF-8"2 ...
- Go语言学习笔记十一: 切片(slice)
Go语言学习笔记十一: 切片(slice) 切片这个概念我是从python语言中学到的,当时感觉这个东西真的比较好用.不像java语言写起来就比较繁琐.不过我觉得未来java语法也会支持的. 定义切片 ...
