STM32F4 External event -- WFE 待机模式
The STM32F4xx are able to handle external or internal events in order to wake up the core (WFE).
The wakeup event can be generated either by:
(I've removed normal external interrupt mode details)
or configuring an external or internal EXTI line in event mode.
When the CPU resumes from WFE,
it is not necessary to clear the peripheral interrupt pending bit
or the NVIC IRQ channel pending bit as the pending bit corresponding to the event line is not set.
唤醒事件管理
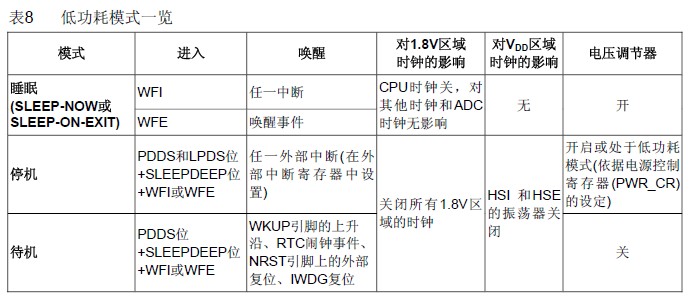
STM32 可以处理外部或内部事件来唤醒内核(WFE)。唤醒事件可以通过下述配置产生:
在外设的控制寄存器使能一个中断,但不在NVIC中使能,同时在Cortex-M3的系统控制寄存器中使能SEVONPEND位。
当CPU从WFE恢复后,需要清除相应外设的中断挂起位和外设NVIC中断通道挂起位(在NVIC中断清除挂起寄存器中)。
配置一个外部或内部EXTI线为事件模式,当CPU从WFE恢复后,因为对应事件线的挂起位没有被置位,
不必清除相应外设的中断挂起位或NVIC中断通道挂起位。
SEVONPEND位,这个位是什么作用呢?权威指南这么说:
发生异常悬起时请发送事件,用于在一个新的中断悬起时从 WFE 指令处唤醒。
不管这个中断的优先级是否比当前的高,都唤醒。
如果没有 WFE导致睡眠,则下次使用 WFE 时将立即唤醒
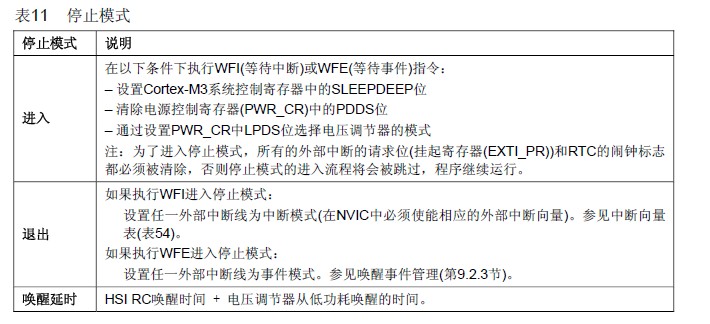
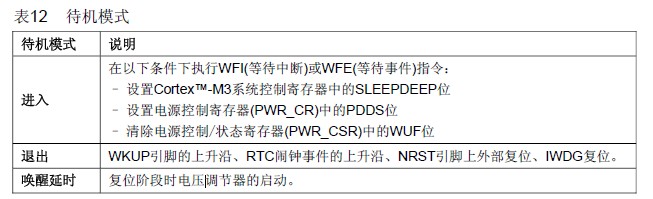
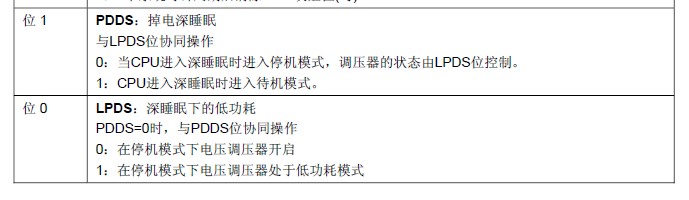
在以下条件下执行WFI(等待中断)或WFE(等待事件)指令:
– 设置Cortex-M3系统控制寄存器中的SLEEPDEEP位
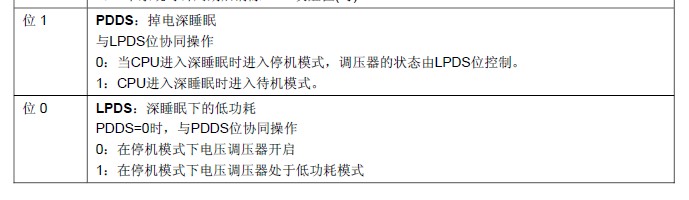
– 清除电源控制寄存器(PWR_CR)中的PDDS位 进入
– 通过设置PWR_CR中LPDS位选择电压调节器的模式
注:为了进入停止模式,所有的外部中断的请求位(挂起寄存器(EXTI_PR))
和RTC的闹钟标志都必须被清除,否则停止模式的进入流程将会被跳过,程序继续运行
如果执行WFI进入停止模式: 设置任一外部中断线为中断模式(在NVIC中必须使能相应的外部中断向量)。
如果执行WFE进入停止模式: 设置任一外部中断线为事件模式。
//进入停止模式
{
u32 tmpreg tmpreg = PWR->CR;
tmpreg &= ~(<<); //清除PWR_CR的PDDS
tmpreg |=(<<); //设置PWR_CR的 LPDS
PWR->CR = tmpreg;
SCB->SCR|=<<; //使能SLEEPDEEP位 (SYS->CTRL)
__WFI(); //执行WFI指令
}

//进入待机模式
void Sys_Standby(void)
{
SCB->SCR|=<<; // 使能SLEEPDEEP位 (SYS->CTRL)
RCC->APB1ENR|=<<; // 使能电源时钟
PWR->CSR|=<<; // 设置WKUP用于唤醒
PWR->CR|=<<; // 清除Wake-up 标志(WUF位)
PWR->CR|=<<; // PDDS置位
__WFI(); // 执行WFI指令
}
So it appears the main purpose is to enable wakeups without generating an interrupt
or having to respond to interrupts during normal operation.
It's not mentioned in that guide and I'm not sure how applicable is to the STM32 architecture
but on some other devices similar schemes can be useful to catch fast events without generating an interrupt.
For example you may have an application where it's important to capture that a sub-microsecond event has occurred,
but there's no need to respond to it quickly so you can just check a flag to see if it's occurred.
4.3.3 of the reference manual says:
If the WFE instruction is used to enter Sleep mode, the MCU exits Sleep mode as soon as an event occurs.
This event can be either an interrupt enabled in the peripheral control register but not in the NVIC,
or an EXTI line configured in event mode.
Has anybody managed to set WFE and exit it using "an interrupt enabled in the peripheral control register but not in the NVIC" ?
This implies any interrupt flag will do it, but it only wakes up for me if the interrupt is set in the nvic (and executes).
I haven't tried it myself, but it looks like there are two way to do it.
The ST reference manual seems to be referring the method 1 below:
1) Using the Event mask register.
Beside from enabling the interrupt in the peripheral control, you also need to set the Event Mask Register (EXTI_EMR)
(section 8.3.2) to enable the peripheral to trigger the event signal.
And base on the circuit diagram in figure 16 (section 8.2.2) you also need to make sure
you set the interrupt source as rising edge trigger or falling edge trigger.
(so in total you must set up as least two registers on top of the peripheral's interrupt enable).
2) Use SEVONPEND feature on NVIC
This control bit is in bit[4] of NVIC System Control Register (0xE000ED10) is SEVONPEND control for NVIC.
When a new interrupt pending occurred, this should be able to
generate a internal event in the NVIC to wake up the core
To use the event mask resister, I think the event needs to be one of those linked to an exti line.
However, setting the SEVONPEND bit works perfectly :)
If anyone's looking, theres a firmware library function to do it:
NVIC_SystemLPConfig(NVIC_LP_SEVONPEND, ENABLE);
I have noticed that my __WFE(); sometimes returns immdiately.
This is described in D.7.68 of the ARMv7M Architecture Application Level Reference Manual:
If the Event Register is set, Wait For Event clears it and returns immediately.
By calling WFE twice in succession:
If the Event Register is Set, the first WFE will clear it, and the second will sleep.
If the Event Register is not set, the first will sleep until it is set, and then the second will clear it.
However, this is clearly unsafe, since if the actual event occurs before the first WFE
(e.g. delayed by an interrupt) then it will sleep until a further event occurs (if one ever does).
Does anybody know the address of the Event Register to clear it properly?
The arm "Application Level" manual suggests calling ClearEventRegister(),
and the proper manual is not available for download.
Use the following assembly sequence:
SEV ; Send Event , this set the event register to 1
WFE ; 1st WFE will not cause sleep, but will cause event reg to clear
WFE ; 2nd WFE will cause sleep
Excellent, thanks again Joseph!
Just another note to anyone else trying this;
before calling WFE make sure that you clear the pending bit in the nvic
that you are waiting to see change (e.g. call NVIC_ClearIRQChannelPendingBit).
I forgot to mention a corner case:
If you use SEV - WFE - WFE sequence, and if there is a interrupt take place
between the two WFE, the event register will get set again
and the second WFE will not enter sleep.
Alternatively, you could use a loop to handle this
int loopexit = ;
while ( loopexit == )
{
__WFE( ); // Try to sleep
if ( Check_If_Work_Need_To_Be_Done( ) )
{
Do_Some_Work( );
}
loopexit = Check_If_Want_To_Exit_Sleep( );
}
In this way it doesn't matter what is the current value of the event register,
as it will repeat the __WFE until it entered sleep or if you want it to exit from sleep.
Here is an example of using WFE with EXTI. Hope that helps you.
int main( void )
{ /*!< At this stage the microcontroller clock setting is already configured,
this is done through SystemInit() function which is called from startup
file (startup_stm32f37x.s) before to branch to application main.
To reconfigure the default setting of SystemInit() function, refer to
system_stm32f37x.c file
*/ /* Configure PA0 in interrupt mode */
EXTI0_Config( ); /* Configure LEDs */
STM_EVAL_LEDInit( LED1 );
STM_EVAL_LEDInit( LED2 );
STM_EVAL_LEDInit( LED4 ); /* SysTick interrupt each 10 ms */
if ( SysTick_Config( SystemCoreClock / ) )
{
/* Capture error */
while ( );
} /* LED1 On */
STM_EVAL_LEDOn( LED1 ); /* Request to enter STOP mode with regulator in low power mode */
PWR_EnterSTOPMode( PWR_Regulator_LowPower, PWR_STOPEntry_WFE ); /* LED1 On */
STM_EVAL_LEDOn( LED2 ); while ( )
{
}
} /**
* @brief Configure PA0 in interrupt mode
* @param None
* @retval None
*/ static void EXTI0_Config( void )
{
EXTI_InitTypeDef EXTI_InitStructure;
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure; /* Enable GPIOA clock */
RCC_AHBPeriphClockCmd( RCC_AHBPeriph_GPIOA, ENABLE ); /* Configure PA0 pin as input floating */
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_PuPd = GPIO_PuPd_NOPULL;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_0;
GPIO_Init( GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure );
/* Enable SYSCFG clock */
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd( RCC_APB2Periph_SYSCFG, ENABLE ); /* Connect EXTI0 Line to PA0 pin */
SYSCFG_EXTILineConfig( EXTI_PortSourceGPIOA, EXTI_PinSource0 ); /* Configure EXTI0 line */
EXTI_InitStructure.EXTI_Line = EXTI_Line0;
EXTI_InitStructure.EXTI_Mode = EXTI_Mode_Event;
EXTI_InitStructure.EXTI_Trigger = EXTI_Trigger_Rising;
EXTI_InitStructure.EXTI_LineCmd = ENABLE;
EXTI_Init( &EXTI_InitStructure );
}
/* init the TIM7 */
RCC->APB1ENR |= RCC_APB1ENR_TIM7EN;
TIM7->PSC = ; // => 1 MHz timer clock frequency (at PCLK=8 MHz)
TIM7->ARR = - ; // => 1 kHz interrupt rate
TIM7->DIER = TIM_DIER_UIE; // enable the update interrupt
NVIC_EnableIRQ( TIM7_IRQn );
TIM7->CR1 |= TIM_CR1_CEN; // start the timer RCC->APB1ENR |= RCC_APB1Periph_PWR; /* Configure PA0 pin as input floating */
RCC->AHBENR |= RCC_AHBPeriph_GPIOA;
RCC->APB2ENR |= RCC_APB2Periph_SYSCFG;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_0;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IN;
GPIO_Init( GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure ); EXTI_InitStructure.EXTI_Line = EXTI_Line0;
EXTI_InitStructure.EXTI_Mode = EXTI_Mode_Event;
EXTI_InitStructure.EXTI_Trigger = EXTI_Trigger_Rising;
EXTI_InitStructure.EXTI_LineCmd = ENABLE;
EXTI_Init( &EXTI_InitStructure );
SYSCFG_EXTILineConfig( EXTI_PortSourceGPIOA, EXTI_PinSource0 );
PWR_WakeUpPinCmd( PWR_WakeUpPin_1, ENABLE ); /* Configure the pin to be toggled: PB2 */
RCC->AHBENR |= RCC_AHBPeriph_GPIOB;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_1;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_OUT;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_OType = GPIO_OType_PP;
GPIO_Init( GPIOB, &GPIO_InitStructure ); /* Configure PWR registers to enter STOP mode */
PWR->CR &= 0xFFFFFFFC; // clear the PDDS and LPDS bits
PWR->CR |= 0x00000000; // STOP Mode: Regulator on
//PWR->CR |= 0x00000001; // STOP Mode: Regulator off /* Set SLEEPDEEP bit of Cortex System Control Register */
SCB->SCR |= SCB_SCR_SLEEPDEEP_Msk;
__WFE( );
/* after waking-up from STOP mode this is the first instruction to be executed */
SCB->SCR &= (uint32_t) ~( (uint32_t) SCB_SCR_SLEEPDEEP_Msk ); /* Configure PB1 as Output */
GPIOB->ODR = 0x00000002;
Seeing the following explanation for WFE command from ARM,
I suspect that the event register is 1. But I don't have an explanation why.
This is the ARM explanation:
WFE is a hint instruction.
If the event register is 0, WFE suspends execution until one of the following events occurs:
- an exception, unless masked by the exception mask registers or the current priority level
- an exception enters the Pending state, if SEVONPEND in the System Control Register is set
- a Debug Entry request, if Debug is enabled
- an event signaled by a peripheral or another processor in a multiprocessor system using the SEV instruction.
If the event register is 1, WFE clears it to 0 and returns immediately.
That is why the second WFE works fine.
We have 2 instructions for entering low-power standby state
where most clocks are gated: WFI and WFE.
WFE: Wait For Event
WFI: Wait For Interrupt
They differ slightly in their entry and wake-up conditions,
with the main difference being that WFE makes use of the event register,
the SEV instruction and EVENTI, EVENTO signals. WFI is targeted at entering either standby, dormant or shutdown mode,
where an interrupt is required to wake-up the processor. A usage for WFE is to put it into a spinlock loop.
Where a CPU wants to access a shared resource such as shared memory,
we can use a semaphore flag location managed by exclusive load and store access.
If multiple CPUs are trying to access the resource,
one will get access and will start to use the resource
while the other CPUs will be stuck in the spinlock loop. To save power, you can insert the WFE instruction into the loop
so the CPUs instead of looping continuously will enter STANDBTWFE.
Then the CPU who has been using the resource should execute SEV instruction
after it has finished using the resource.
This will wake up all other CPUs from STANDBYWFE
and another CPU can then access the shared resource. The reason for having EVENTI and EVENTO is to export a pulse on EVENTO
when an SEV instruction is executed by any of the CPUs.
This signal would connect to EVENTI of a second Cortex-A5 MPCore cluster
and would cause any CPUs in STANDBYWFE state to leave standby. So these signals just expand the usage of WFE mode across multiple clusters.
If you have a single cluster, then you do not need to use them.
STM32F4 External event -- WFE 待机模式的更多相关文章
- STM32F4 External interrupts
STM32F4 External interrupts Each STM32F4 device has 23 external interrupt or event sources. They are ...
- STM32学习笔记(九) 外部中断,待机模式和事件唤醒
学会知识只需要不段的积累和提高,但是如何将知识系统的讲解出来就需要深入的认知和系统的了解.外部中断和事件学习难度并不高,不过涉及到STM32的电源控制部分,还是值得认真了解的,在本文中我将以实际代码为 ...
- 亲测实验,stm32待机模式和停机模式唤醒程序的区别,以及唤醒后程序入口
这两天研究了STM32的低功耗知识,低功耗里主要研究的是STM32的待机模式和停机模式.让单片机进入的待机模式和停机模式比较容易,实验中通过设置中断口PA1来响应待机和停机模式. void EXTI1 ...
- 第23章 RTX 低功耗之待机模式
以下内容转载自安富莱电子: http://forum.armfly.com/forum.php STM32F103 待机模式介绍 本章节我们主要讲解待机模式,待机模式可实现系统的最低功耗.该模式是在 ...
- FreeRTOS 低功耗之待机模式
STM32F103 如何进入待机模式在 FreeRTOS 系统中,让 STM32 进入待机模式比较容易,调用固件库函数PWR_EnterSTANDBYMode 即可. STM32F103 如何退出待机 ...
- (STM32F4) External Interrupt
外部中斷(External Interupt) 在MCU中是很常見而且很常用到的基本function,所以就不多做解釋.不過因為每顆MCU的配置都不太一樣所以在此記錄下來. External Inte ...
- stm32 待机模式
低功耗模式 降低系统时钟速度 不使用APBx和AHB外设时,将对应的外设时钟关闭 睡眠模式(Cortex™-M3内核停止,所有外设包括Cortex-M3核心的外设,如NVIC.系统时钟(SysTick ...
- windows mobile 开发:让GPS一直在待机模式下也能运行
最近,遇到一个需求,就是每 30 秒更新一次 GPS 位置,在测试过程中,发现在系统待机后,更新 GPS 位置就不能正常运行了,搜索后,发现如下的解决方案,实际应用了之后,有效,赞!!! http:/ ...
- 【原创】STM32低功耗模式及中断唤醒(基于BMI160及RTC)的研究
预研目标 六轴静止时,终端进入低功耗模式:六轴震动时,终端正常工作模式,从而极大减少非工作时的电流消耗. 解决方案 机器静止时,依据六轴算法,CPU进入休眠(停止)模式:机器工作时,触发六轴中断唤醒C ...
随机推荐
- __class__属性与元类
class M(type): def __str__(self): return "gege" aa = "ccf" cc = "ccc" ...
- Mybatis逆向工程——(十四)
逆向工程可以快速将数据库的表生成JavaBean,同时生成对单标操作的Mapper.java与Mapper.xml,极大地提高了开发速度. 1.jar包
- Linux内核源码分析--内核启动之(2)Image内核启动(汇编部分)(Linux-3.0 ARMv7) 【转】
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-25909619-id-4938389.html 在完成了zImage自解压之后,就跳转到了解压后的内核(也就是vmlinux的bin ...
- 006_mac osx 应用跨屏幕
一般情况下 mac osx 中一个应用程序只能在一个屏幕上显示,作为从 windows 转过来的用户有点不太习惯,Goolge 后发现还是有解决方案的(虽然不是很好用). 打开 Mac 的系统偏好设置 ...
- Dede更新提示DedeTag Engine Create File False的解决办法
第一种情况:列表.频道.文章等命名规则未填写或填写错误 此种情况较为少见,因为初级用户一般不会去修改这些东西,情况可以大致分为: 命名规则未填写(即为空)解决方法:只需填好相应的规则即可,重新选择栏目 ...
- Intellij Idea启用Git可视化界面
第一步. 第二步. 然后点击OK 验证
- Docker 图形化页面管理工具使用
一.Docker图形化工具 docker 图形页面管理工具常用的有三种,DockerUI ,Portainer ,Shipyard .DockerUI 是 Portainer 的前身,这三个工具通过d ...
- forEach的坑
使用js里的forEach来遍历数组的时候需要注意的是:break,return语句不能使其中断,它还是会继续遍历完数组的每一个元素 错误代码: function nameExit(name){ da ...
- spring过滤器
什么是过滤器 Spring 中不能处理用户请求,但可以用来提供过滤作用的一种Servlet规范.在请求进入容器之后,还未进入Servlet之前进行预处理,并且在请求结束返回给前端这之间进行后期处理.具 ...
- 011.KVM-V2V迁移
一 虚拟化存储池 1.1 创建虚拟化存储池 [root@kvm-host ~]# mkdir -p /data/vmfs 1.2 定义存储池与目录 [root@kvm-host ~]# virsh p ...
