142. Linked List Cycle II【easy】
142. Linked List Cycle II【easy】
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
解法一:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
} ListNode * slow = head;
ListNode * fast = head; while (fast->next != NULL && fast->next->next != NULL) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next; if (fast == slow) {
return findNode(fast, head);
}
} return NULL;
} ListNode * findNode(ListNode * fast, ListNode * head)
{
while (fast != head) {
fast = fast->next;
head = head->next;
} return head;
} };
首先先看是否有环,有环的话我们要把其中一个指针移动到链表head节点,另外一个指针不变,然后这两个指针同时往前分别走一步,直到相等为止就是环的入口点;这个问题的算法证明如下:
问题1:如何判断单链表中是否存在环(即下图中从结点E到结点R组成的环)?

设一快一慢两个指针(Node *fast, *low)同时从链表起点开始遍历,其中快指针每次移动长度为2,慢指针则为1。则若无环,开始遍历之后fast不可能与low重合,且fast或fast->next最终必然到达NULL;若有环,则fast必然不迟于low先进入环,且由于fast移动步长为2,low移动步长为1,则在low进入环后继续绕环遍历一周之前fast必然能与low重合(且必然是第一次重合)。于是函数可写如下:
bool hasCircle(Node* head, Node* &encounter)
{
Node *fast = head, *slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow)
{
encounter = fast;
return true;
}
}
encounter = NULL;
return false;
}
问题2:若存在环,如何找到环的入口点(即上图中的结点E)?
解答:如图中所示,设链起点到环入口点间的距离为x,环入口点到问题1中fast与low重合点的距离为y,又设在fast与low重合时fast已绕环n周(n>0),且此时low移动总长度为s,则fast移动总长度为2s,环的长度为r。则
s + nr = 2s,n>0 ①
s = x + y ②
由①式得 s = nr
代入②式得
nr = x + y
x = nr - y ③
现让一指针p1从链表起点处开始遍历,指针p2从encounter处开始遍历,且p1和p2移动步长均为1。则当p1移动x步即到达环的入口点,由③式可知,此时p2也已移动x步即nr - y步。由于p2是从encounter处开始移动,故p2移动nr步是移回到了encounter处,再退y步则是到了环的入口点。也即,当p1移动x步第一次到达环的入口点时,p2也恰好到达了该入口点。于是函数可写如下:
Node* findEntry(Node* head, Node* encounter)
{
Node *p1 = head, *p2 = encounter;
while(p1 != p2)
{
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
return p1;
}
另外一个解释也比较好:
求解单链表环入口点的步骤:
1:使用“指针追赶”方法找到相遇点(网上资料很多,此处略)。
2:指针p1从链表头、p2从相遇点,同时出发,一次移动一个节点,再次的相遇点便是环的入口点。
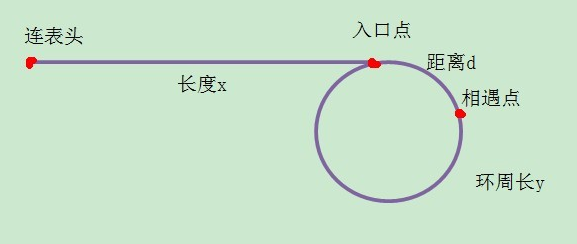
证明导向:p1从表头走,能与p2从相遇点走再次相遇,那么说明p1走到入口点时,p2可能刚好走了y-d(其中d是入口点与第一次相遇点的距离)个节点,或者走了几圈再加上y-d个节点。故就要找到y-d与x的关系。
第一次相遇:S慢:表示一次移动一个节点的指针所走的路程(即节点个数)
S快:表示一次移动两个节点的指针所走的路程(节点个数)
S慢 = x + d
S快 = 2(x + d)
S快 - S慢 = n倍y
则有:x + d = ny
x = ny - d = (n - 1)y + (y - d)
由此便说明了:x 个节点就相当于(n - 1)倍环周长加上y - d,正好是第一次相遇点到入口点的距离。
证明参考自:
http://blog.csdn.net/wuzhekai1985/article/details/6725263
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6a0e04380101a9o2.html
142. Linked List Cycle II【easy】的更多相关文章
- 【算法分析】如何理解快慢指针?判断linked list中是否有环、找到环的起始节点位置。以Leetcode 141. Linked List Cycle, 142. Linked List Cycle II 为例Python实现
引入 快慢指针经常用于链表(linked list)中环(Cycle)相关的问题.LeetCode中对应题目分别是: 141. Linked List Cycle 判断linked list中是否有环 ...
- 141. Linked List Cycle&142. Linked List Cycle II(剑指Offer-链表中环的入口节点)
题目: 141.Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it. 142.Given a linked list, return the ...
- leetcode 141. Linked List Cycle 、 142. Linked List Cycle II
判断链表有环,环的入口结点,环的长度 1.判断有环: 快慢指针,一个移动一次,一个移动两次 2.环的入口结点: 相遇的结点不一定是入口节点,所以y表示入口节点到相遇节点的距离 n是环的个数 w + n ...
- 219. Contains Duplicate II【easy】
219. Contains Duplicate II[easy] Given an array of integers and an integer k, find out whether there ...
- 680. Valid Palindrome II【easy】
680. Valid Palindrome II[easy] Given a non-empty string s, you may delete at most one character. Jud ...
- 【LeetCode】142. Linked List Cycle II (2 solutions)
Linked List Cycle II Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cyc ...
- Java for LeetCode 142 Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. Foll ...
- 【LeetCode】142. Linked List Cycle II
Difficulty:medium More:[目录]LeetCode Java实现 Description Given a linked list, return the node where t ...
- [LeetCode] 142. Linked List Cycle II 单链表中的环之二
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. To r ...
随机推荐
- 【找规律】Codeforces Round #392 (Div. 2) C. Unfair Poll
C. Unfair Poll time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- 【函数式权值分块】【块状链表】bzoj3065 带插入区间K小值
显然是块状链表的经典题.但是经典做法的复杂度是O(n*sqrt(n)*log^2(n))的,出题人明确说了会卡掉. 于是我们考虑每个块内记录前n个块的权值分块. 查询的时候差分什么的,复杂度就是O(n ...
- 显示字符 Exercise06_12
/** * @author 冰樱梦 * 时间:2018年下半年 * 题目:显示字符 *1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 : ; < = > ? @ A B C D E F G H I J ...
- NSOperation的并发与非并发
NSoperation也是多线程的一种,NSopertaion有2种形式 (1) 并发执行 并发执行你需要重载如下4个方法 //执行任务主函数,线程运行的入口函数 - (v ...
- JavaScript对JSON数据进行排序
var ajson= { "result":[ { "cid":1, "name":"aaa", "price ...
- gitk图形界面中文乱码情况
当打开gitk图形界面时,文件中的中文部分乱码了,这大部分是因为编码格式的问题,为了跟上时代的脚步,本人建议都是用utf-8编码. 为了方便,我将全局配置为utf-8编码: git config -- ...
- Shader and Program编程基本概念 - 转
原地址:http://blog.csdn.net/myarrow/article/details/7737313 一.本文关注的问题: • Shader and program 对象介绍• 创建并编译 ...
- RabbitMQ,Apache的ActiveMQ,阿里RocketMQ,Kafka,ZeroMQ,MetaMQ,Redis也可实现消息队列,RabbitMQ的应用场景以及基本原理介绍,RabbitMQ基础知识详解,RabbitMQ布曙
消息队列及常见消息队列介绍 2017-10-10 09:35操作系统/客户端/人脸识别 一.消息队列(MQ)概述 消息队列(Message Queue),是分布式系统中重要的组件,其通用的使用场景可以 ...
- 利用CMD查看系统硬件信息
利用CMD查看系统硬件信息对于在windows下查看系统信息大家一定不陌生了,我现在说几个最常用的方法,对命令感兴趣的朋友看看,(给菜鸟看的,老手就不要笑话我了,大家都是从那个时候过来的,^_^).一 ...
- .Net使用程序发送邮件时的问题
在做项目的时候,不可避免的会用到给用户发送邮件的问题,一开始我用的是qq的smtp服务器,但是会出错,不管账号密码,服务器地址端口等怎么配置都是出错.后百度之,发现可能是qq服务器本身就是禁止这个功能 ...
