【Python爬虫】BeautifulSoup网页解析库
BeautifulSoup解析 HTML或XML
阅读目录
- 初识Beautiful Soup
- Beautiful Soup库的4种解析器
- Beautiful Soup类的基本元素
- 基本使用
- 标签选择器
- 节点操作
- 标准选择器
- find_all( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
- find( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
- CSS选择器
- 实例:中国大学排名爬虫
初识Beautiful Soup
官方文档:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/#
中文文档:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/index.zh.html
Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文本中提取数据的Python库,它能对HTML、XML格式进行解析成树形结构并提取相关信息。
Beautiful Soup库是一个灵活又方便的网页解析库,处理高效,支持多种解析库(后面会介绍),利用它不用编写正则表达式即可方便地实现网页信息的提取。
安装
Beautiful Soup 3 目前已经停止开发,推荐在现在的项目中使用Beautiful Soup 4,安装方法:
pip install beautifulsoup4
Beautiful Soup库的4种解析器
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python标准库 | BeautifulSoup(markup, "html.parser") | Python的内置标准库、执行速度适中 、文档容错能力强 | Python 2.7.3 or 3.2.2)前的版本中文容错能力差 |
| lxml HTML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, "lxml") | 速度快、文档容错能力强 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| lxml XML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, "xml") | 速度快、唯一支持XML的解析器 | 需要安装C语言库 |
| html5lib | BeautifulSoup(markup, "html5lib") | 最好的容错性、以浏览器的方式解析文档、生成HTML5格式的文档 | 速度慢、不依赖外部扩展 |
如果仅是想要解析HTML文档,只要用文档创建 BeautifulSoup 对象就可以了。Beautiful Soup会自动选择一个解析器来解析文档.但是还可以通过参数指定使用那种解析器来解析当前文档。BeautifulSoup 第一个参数应该是要被解析的文档字符串或是文件句柄,第二个参数用来标识怎样解析文档.如果第二个参数为空,那么Beautiful Soup根据当前系统安装的库自动选择解析器,解析器的优先数序: lxml, html5lib, Python标准库(python自带的解析库).
安装解析器库:
pip install html5lib
pip install lxml
Beautiful Soup类的基本元素
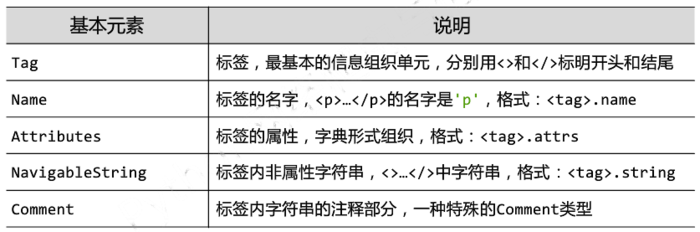
基本使用
容错处理,文档的容错能力指的是在html代码不完整的情况下,使用该模块可以识别该错误。
使用BeautifulSoup解析上述代码,能够得到一个 BeautifulSoup 的对象,并能按照 标准的缩进格式结构输出
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.prettify()) #处理好缩进,结构化显示
print(soup.title.string)
<html>
<head>
<title>
The Dormouse's story
</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse">
<b>
The Dormouse's story
</b>
</p>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<!-- Elsie -->
</a>
,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">
Lacie
</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">
Tillie
</a>
;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">
...
</p>
</body>
</html>
The Dormouse's story
输出结果
标签选择器
选择标签元素(存在多个时取第一个)
获取标签名称 + 获取标签 + 获取标签内容 + 获取标签属性
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title" name="dromouse"><b>The is pppp</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
""" soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.title) #获取改标签 <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
print(soup.title.name) #获取标签名 print(soup.title.text) #获取标签内容
print(soup.p.text)
print(soup.p.string) dic = soup.p.attrs #获取 p标签所有属性返回一个字典结构
print(dic) #获取 p标签所有属性返回一个字典结构
print(dic["name"])
print(soup.p.attrs["class"]) #获取指定属性值,返回列表
print(soup.p["class"])
打印输出:
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
title
The Dormouse's story
The is pppp
The is pppp
{'class': ['title'], 'name': 'dromouse'}
dromouse
['title']
['title']
标签嵌套选择
html = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<div class="title" name="dromouse"><b class='bb bcls xiong'>The Dormouse's story</b></div>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1"><!-- Elsie --></a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.div.b['class']) #标签嵌套选择 print(soup.p.stripped_strings) #<generator object stripped_strings at 0x000002C7CC772830>
print(list(soup.p.stripped_strings))
print(soup.p.text)
打印输出:
['bb', 'bcls', 'xiong']
<generator object stripped_strings at 0x000002471D323830>
['Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were', ',', 'Lacie', 'and', 'Tillie', ';\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.']
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
,
Lacie and
Tillie;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
节点操作



子节点和子孙节点
对于一个标签的儿子节点不仅包括标签节点,也包括字符串节点,空格表示为'\n'
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.p.contents) #子节点列表,将<p>所有子节点存在列表中 print("======================================================================>")
print(soup.p.children) #子节点的可迭代类型,<list_iterator object at 0x0000029154DF7FD0>
for i, child in enumerate(soup.p.children):
print(i, str(child).strip()) #child 是bs4.element 对象 print("======================================================================>")
print(soup.p.descendants) #子孙节点的迭代类型,<generator object descendants at 0x000001C7583D2888>
for i, child in enumerate(soup.p.descendants):
print(i, child)
打印输出:
['\n Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n ', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>, '\n', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>, '\n and\n ', <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>, '\n and they lived at the bottom of a well.\n ']
======================================================================>
<list_iterator object at 0x000001C2E2AB6EF0>
0 Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
1 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
2
3 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
4 and
5 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
6 and they lived at the bottom of a well.
======================================================================>
<generator object descendants at 0x000001C2E2AA3830>
0
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were 1 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
2 3 <span>Elsie</span>
4 Elsie
5 6 7 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
8 Lacie
9
and 10 <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
11 Tillie
12
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
父节点和祖先节点
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.a.parent) print("========================================================================>")
print(soup.a.parents) #祖先节点,返回可迭代类型
for item in soup.a.parents:
print(item)
打印输出:
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
========================================================================>
<generator object parents at 0x000001A078752830>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body></html>
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body></html>
兄弟节点
html = """
<html>
<head>
<title>The Dormouse's story</title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="story">
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a>
and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(list(enumerate(soup.a.next_sibling))) #下一个兄弟节点
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.next_siblings))) #下面所有的兄弟节点
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.previous_sibling))) #上一个兄弟节点
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.previous_siblings))) #上面所有的兄弟节点
打印输出:
[(0, '\n')]
[(0, '\n'), (1, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>), (2, '\n and\n '), (3, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>), (4, '\n and they lived at the bottom of a well.\n ')]
[(0, '\n'), (1, ' '), (2, ' '), (3, ' '), (4, ' '), (5, ' '), (6, ' '), (7, ' '), (8, ' '), (9, ' '), (10, ' '), (11, ' '), (12, ' '), (13, 'O'), (14, 'n'), (15, 'c'), (16, 'e'), (17, ' '), (18, 'u'), (19, 'p'), (20, 'o'), (21, 'n'), (22, ' '), (23, 'a'), (24, ' '), (25, 't'), (26, 'i'), (27, 'm'), (28, 'e'), (29, ' '), (30, 't'), (31, 'h'), (32, 'e'), (33, 'r'), (34, 'e'), (35, ' '), (36, 'w'), (37, 'e'), (38, 'r'), (39, 'e'), (40, ' '), (41, 't'), (42, 'h'), (43, 'r'), (44, 'e'), (45, 'e'), (46, ' '), (47, 'l'), (48, 'i'), (49, 't'), (50, 't'), (51, 'l'), (52, 'e'), (53, ' '), (54, 's'), (55, 'i'), (56, 's'), (57, 't'), (58, 'e'), (59, 'r'), (60, 's'), (61, ';'), (62, ' '), (63, 'a'), (64, 'n'), (65, 'd'), (66, ' '), (67, 't'), (68, 'h'), (69, 'e'), (70, 'i'), (71, 'r'), (72, ' '), (73, 'n'), (74, 'a'), (75, 'm'), (76, 'e'), (77, 's'), (78, ' '), (79, 'w'), (80, 'e'), (81, 'r'), (82, 'e'), (83, '\n'), (84, ' '), (85, ' '), (86, ' '), (87, ' '), (88, ' '), (89, ' '), (90, ' '), (91, ' '), (92, ' '), (93, ' '), (94, ' '), (95, ' ')]
[(0, '\n Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n ')]
标准选择器 find/find_all(* * * * *)
基于bs4库的HTML内容查找方法
<>.find_all(name,attrs,recursive,text,**kwargs) # 返回一个列表类型,存储查找的结果
name 对标签名称的检索字符串
attrs 对标签属性值的检索字符串,可标注属性检索
recursive 是否对子孙全部搜索,默认True
text 对文本内容进行检索
其他的 find 方法:

find_all( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
可根据标签名、属性、内容查找文档
name
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all('ul'))
print(type(soup.find_all('ul')[0]))
[<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>, <ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>]
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for ul in soup.find_all('ul'):
print(ul.find_all('li'))
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>]
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
属性attrs
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list2 list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.find_all(attrs={'id': 'list-1'})) #推荐这种写法
print(soup.find_all(id="list-1")) #类似于**kwargs传值,与上一种写法效果相同 print(soup.find_all(attrs={'class': 'list-small'}))
print(soup.find_all(class_="list2"))
打印输出:
[<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>]
[<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>]
[<ul class="list2 list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>]
[<ul class="list2 list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>]
text
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all(text='Foo'))
['Foo', 'Foo']
find( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
find返回单个元素,find_all返回所有元素
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find('ul'))
print(type(soup.find('ul')))
print(soup.find('page'))
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
None
find_parents() find_parent()
find_parents()返回所有祖先节点,find_parent()返回直接父节点。
find_next_siblings() find_next_sibling()
find_next_siblings()返回后面所有兄弟节点,find_next_sibling()返回后面第一个兄弟节点。
find_previous_siblings() find_previous_sibling()
find_previous_siblings()返回前面所有兄弟节点,find_previous_sibling()返回前面第一个兄弟节点。
find_all_next() find_next()
find_all_next()返回节点后所有符合条件的节点, find_next()返回第一个符合条件的节点
find_all_previous() 和 find_previous()
find_all_previous()返回节点后所有符合条件的节点, find_previous()返回第一个符合条件的节点
CSS选择器(* * * * * )
通过select()直接传入CSS选择器即可完成选择
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>World</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') print(soup.select('.panel .panel-heading'))
print(soup.select('ul li'))
print(soup.select('#list-2 .element'))
print(type(soup.select('ul')[0]))
输出结果:
[<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>, <div class="panel-heading">
<h4>World</h4>
</div>]
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>, <li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
<class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for ul in soup.select('ul'):
print(ul.select('li'))
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>, <li class="element">Jay</li>]
[<li class="element">Foo</li>, <li class="element">Bar</li>]
获取属性
ul.attrs['id']
ul['id']
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for ul in soup.select('ul'):
print(ul['id'])
print(ul.attrs['id'])
list-1
list-1
list-2
list-2
获取内容
li.get_text()
html='''
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h4>Hello</h4>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
'''
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for li in soup.select('li'):
print(li.get_text())
Foo
Bar
Jay
Foo
Bar
总结:
- 推荐使用lxml解析库,必要时使用html.parser
- 标签选择筛选功能弱但是速度快
- 建议使用find()、find_all() 查询匹配单个结果或者多个结果
- 如果对CSS选择器熟悉建议使用select()
实例:中国大学排名爬虫
步骤1:从网络上获取大学排名网页内容getHTMLText()
步骤2:提取网页内容中信息到合适的数据结构fillUnivList()
步骤3:利用数据结构展示并输出结果printUnivLise()
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import bs4 def getHTMLText(url):
try:
r = requests.get(url, timeout=30)
r.raise_for_status()
r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding
return r.text
except:
return "error" def fillUnivList(ulist, html):
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
for tr in soup.find('tbody').children:
if isinstance(tr, bs4.element.Tag): # 过滤掉非标签类型
tds = tr('td')
ulist.append([tds[0].string, tds[1].string, tds[3].string]) # 中文对齐问题的解决:
# 采用中文字符的空格填充 chr(12288)
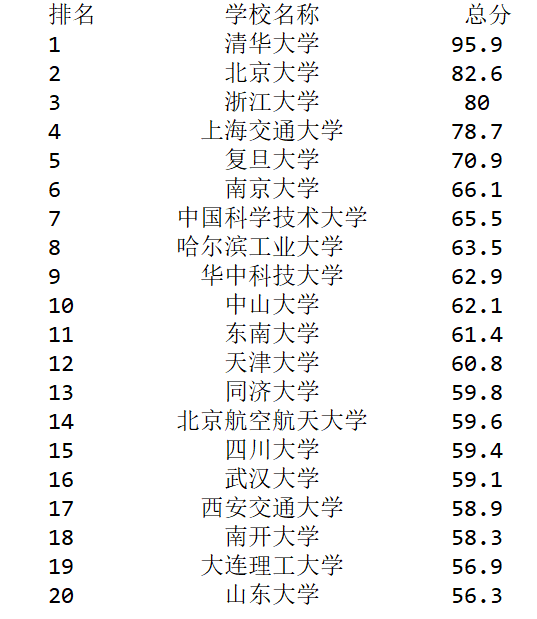
def printUnivList(ulist, num):
tplt = "{0:^10}\t{1:{3}^10}\t{2:^10}"
print(tplt.format("排名", "学校名称", "总分", chr(12288)))
for i in range(num):
u = ulist[i]
print(tplt.format(u[0], u[1], u[2], chr(12288))) def main():
uinfo = []
url = 'http://www.zuihaodaxue.cn/zuihaodaxuepaiming2019.html'
html = getHTMLText(url)
fillUnivList(uinfo, html)
printUnivList(uinfo, 20) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
代码
采集到的数据使用pyecharts进行数据可视化展示
import requests,json,re,bs4
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup header = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/69.0.3472.3 Safari/537.36'} def getHtmlText(url):
try:
ret = requests.get(url , headers=header , timeout=30)
ret.encoding = "utf8"
ret.raise_for_status()
return ret.text
except:
return None def fillUnivList(ulist,html):
soup = BeautifulSoup(html,"lxml")
for tr in soup.tbody.children:
if isinstance(tr, bs4.element.Tag): #判断tr是否是bs4.element.Tag类型
tds = tr("td")
# print(tds)
ulist.append([tds[0].string,tds[1].string,tds[2].string,tds[3].string]) # 中文对齐问题的解决:
# 采用中文字符的空格填充 chr(12288)
def printUnivList(ulist, num):
tplt = "{0:^10}\t{1:{3}^10}\t{2:^10}"
print(tplt.format("排名", "学校名称", "总分", chr(12288)))
for i in range(num):
u = ulist[i]
print(tplt.format(u[0], u[1], u[3], chr(12288))) #pyecharts数据可视化展示
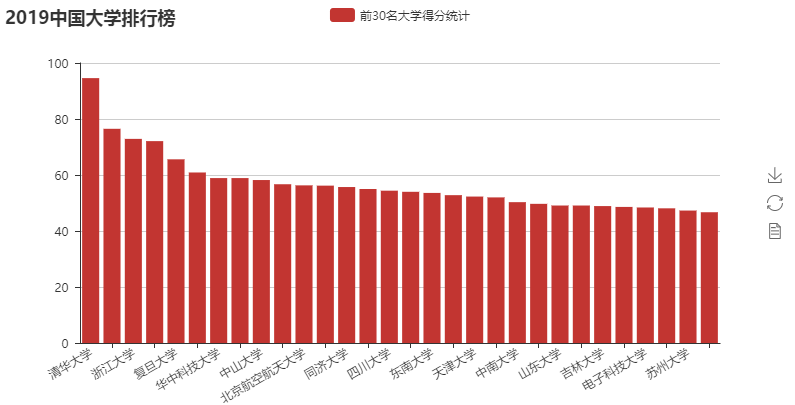
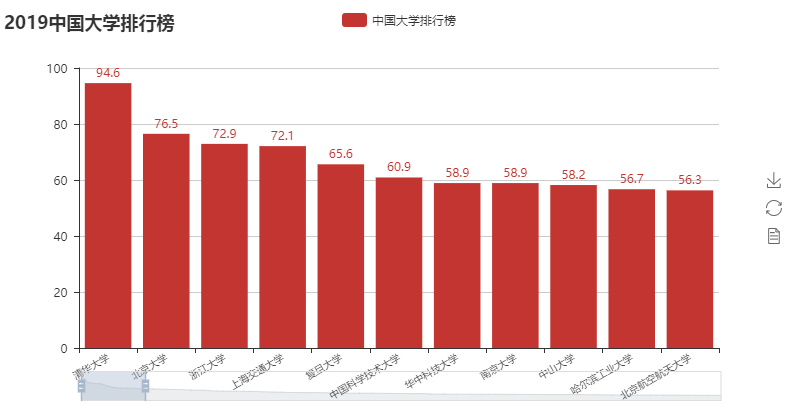
def showData(ulist,num):
from pyecharts import Bar
attrs = []
vals = []
for i in range(num):
attrs.append(ulist[i][1])
vals.append(ulist[i][3])
bar = Bar("2019中国大学排行榜")
bar.add(
"中国大学排行榜",
attrs,
vals,
is_datazoom_show=True,
datazoom_type="both",
datazoom_range=[0, 10],
xaxis_rotate=30,
xaxis_label_textsize=8,
is_label_show=True,
)
bar.render("2019中国大学排行榜4.html") def showData_funnel(ulist,num):
from pyecharts import Funnel
attrs = []
vals = []
for i in range(num):
attrs.append(ulist[i][1])
vals.append(ulist[i][3])
funnel = Funnel(width=1000,height=800)
funnel.add(
"大学排行榜",
attrs,
vals,
is_label_show=True,
label_pos="inside",
label_text_color="#fff",
)
funnel.render("2019中国大学排行榜4.html") def main():
uinfo = []
url = 'http://www.zuihaodaxue.cn/zuihaodaxuepaiming2019.html'
html = getHtmlText(url)
fillUnivList(uinfo, html)
print(uinfo)
# showData(uinfo,100)
showData_funnel(uinfo,20)
# printUnivList(uinfo, 30) if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
代码

补充1:
语法:isinstance(object,type)
作用:来判断一个对象是否是一个已知的类型。
其第一个参数(object)为对象,第二个参数(type)为类型名(int...)或类型名的一个列表((int,list,float)是一个列表)。其返回值为布尔型(True or flase)。
若对象的类型与参数二的类型相同则返回True。若参数二为一个元组,则若对象类型与元组中类型名之一相同即返回True。
下面是两个例子:
例一
>>> a = 4
>>> isinstance (a,int)
True
>>> isinstance (a,str)
False
>>> isinstance (a,(str,int,list))
True
例二
>>> a = "b"
>>> isinstance(a,str)
True
>>> isinstance(a,int)
False
>>> isinstance(a,(int,list,float))
False
>>> isinstance(a,(int,list,float,str))
True
补充2:
Response.raise_for_status()
如果发送了一个错误请求(一个 4XX 客户端错误,或者 5XX 服务器错误响应),我们可以通过 Response.raise_for_status() 来抛出异常:
>>> bad_r = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/status/404')
>>> bad_r.status_code
404
>>> bad_r.raise_for_status()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "requests/models.py", line 832, in raise_for_status
raise http_error
requests.exceptions.HTTPError: 404 Client Error
但是,由于我们的例子中 r 的 status_code 是 200 ,当我们调用 raise_for_status()时,得到的是:
>>> r.raise_for_status()
None
参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/0bug/p/8260834.html
http://pyecharts.org/#/
https://www.cnblogs.com/kongzhagen/p/6472746.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/haiyan123/p/8289560.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/haiyan123/p/8317398.html
【Python爬虫】BeautifulSoup网页解析库的更多相关文章
- Python_爬虫_BeautifulSoup网页解析库
BeautifulSoup网页解析库 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup 0.BeautifulSoup网页解析库包含 的 几个解析器 Python标准库[主要,系统自带;] ...
- 【Python爬虫】PyQuery解析库
PyQuery解析库 阅读目录 初始化 基本CSS选择器 查找元素 遍历 获取信息 DOM操作 伪类选择器 PyQuery 是 Python 仿照 jQuery 的严格实现.语法与 jQuery 几乎 ...
- Python爬虫3大解析库使用导航
1. Xpath解析库 2. BeautifulSoup解析库 3. PyQuery解析库
- python爬虫之网页解析
CSS Selector 与Xpath path = ‘D:\\Postgraduate\\Python\\python_projects\\Python视频 分布式 爬虫Scrapy入门到精通\\第 ...
- Python爬虫-- BeautifulSoup库
BeautifulSoup库 beautifulsoup就是一个非常强大的工具,爬虫利器.一个灵活又方便的网页解析库,处理高效,支持多种解析器.利用它就不用编写正则表达式也能方便的实现网页信息的抓取 ...
- Python网页解析库:用requests-html爬取网页
Python网页解析库:用requests-html爬取网页 1. 开始 Python 中可以进行网页解析的库有很多,常见的有 BeautifulSoup 和 lxml 等.在网上玩爬虫的文章通常都是 ...
- Python的网页解析库-PyQuery
PyQuery库也是一个非常强大又灵活的网页解析库,如果你有前端开发经验的,都应该接触过jQuery,那么PyQuery就是你非常绝佳的选择,PyQuery 是 Python 仿照 jQuery 的严 ...
- python爬虫知识点总结(一)库的安装
环境要求: 1.编程语言版本python3: 2.系统:win10; 3.浏览器:Chrome68.0.3440.75:(如果不是最新版有可能影响到程序执行) 4.chromedriver2.41 注 ...
- python爬虫---BeautifulSoup的用法
BeautifulSoup是一个灵活的网页解析库,不需要编写正则表达式即可提取有效信息. 推荐使用lxml作为解析器,因为效率更高. 在Python2.7.3之前的版本和Python3中3.2.2之前 ...
随机推荐
- 教你一招:解决Win 10安装软件时提示:文件系统错误 (-1073740940)
1.win+R输入 gpedit.msc 2.左边计算机配置 windows设置——安全设置——本地策略——安全选项 3.在安全选项右边选择 用户账户控制:管理员批准模式中管理员的提升权限提示的行为, ...
- 为app录制展示gif
已同步更新至个人blog:http://dxjia.cn/2015/07/make-gif-for-app/ 在github上好多不错的开源项目展示demo的时候,都是采用了一个gif图片,很生动具体 ...
- RMAN正确地删除Archivelog以及设置有备库的归档删除策略
原文链接:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_64e166580100xks5.html 如何正确地删除Archivelog: Archivelog并不能直接得从OS层直接物 ...
- laravel5.4中验证与错误提示设置
1.对于交互提交数据,验证如: #验证 $this->validate(\request(),[ 'title' => 'required|string|min:3|max:20', 'c ...
- [React] 05 - Route: connect with ExpressJS
基础: 初步理解:Node.js Express 框架 参见:[Node.js] 08 - Web Server and REST API 进阶: Ref: 如何系统地学习 Express?[该网页有 ...
- Hadoop -- HDFS 读写数据
一.HDFS读写文件过程 1.读取文件过程 1) 初始化FileSystem,然后客户端(client)用FileSystem的open()函数打开文件 2) FileSyst ...
- ios开发之--给WebView加载进度条
不是新东西,就是在项目里面用到H5页面的时候,中间加载延迟的时候,在最上面加载一个进度条,代码如下: // 获取屏幕 宽度.高度 bounds就是屏幕的全部区域 #define KDeviceWidt ...
- 8. Oracle通过rman进行克隆
一. 安装规划 IP ROLE 192.168.1.235 克隆对象 192.168.1.221 克隆库 二. 备库创建相应的dump文件夹 # 在主库查询对应的dump目录 select name, ...
- perl 遍历指定目录下的所有文件,替换指定文本内容,返回受影响的文件路径
不会读取 影藏文件 main #!/usr/bin/perl use autodie; use utf8; use Encode qw(decode encode); if(@ARGV ne 3){ ...
- http方式访问svn
接下来做一下svn的http访问 首先,说一下,svn的http访问时依赖apache的dav_svn模块,然后赋予www-data访问权限,进行版本控制 我的服务器环境Ubuntu16.04 准备工 ...
