python 五子棋
Python菜鸟快乐游戏编程_pygame(博主录制,2K分辨率,超高清)
https://study.163.com/course/courseMain.htm?courseId=1006188025&share=2&shareId=400000000398149
参考http://www.skywind.me/blog/archives/1029
http://blog.csdn.net/skywind/article/details/8164713
https://github.com/skywind3000/gobang
gobang
Gobang game with artificial intelligence in 900 Lines !!
How to play
Download:
git clone https://github.com/skywind3000/gobang.git gobang
play in normal mode:
python gobang/gobang.py
play in hard mode:
python gobang/gobang.py hard
Game Rule
Make five or more stones in a in to win. You will make your move by enter the coordinate value (row + column) of the chess-board to defeat the AI competitor.
Play it in the console:
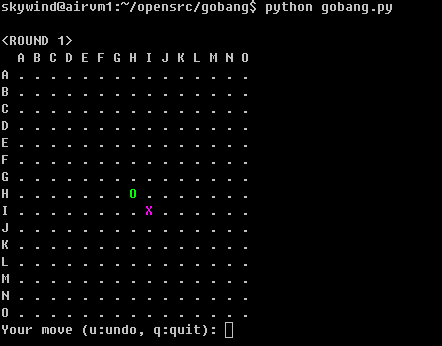
Character 'O' - black stone (you) Character 'X' - white stone (computer)
if you want to make a new move below the white stone 'X', just enter 'JI' (row is 'J', and column is 'I'):
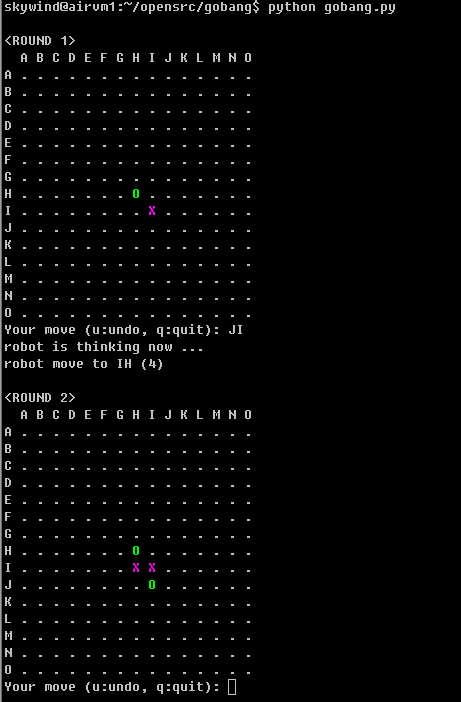
After entering 'JI' the computer will think for a few seconds and makes its move too. Then another turn begins, you can input new row-col values to continue playing until someone wins.
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys, time #----------------------------------------------------------------------
# chessboard: 棋盘类,简单从字符串加载棋局或者导出字符串,判断输赢等
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
class chessboard (object): def __init__ (self, forbidden = 0):
self.__board = [ [ 0 for n in xrange(15) ] for m in xrange(15) ]
self.__forbidden = forbidden
self.__dirs = ( (-1, 0), (-1, 1), (0, 1), (1, 1), (1, 0), \
(1, -1), (0, -1), (-1, -1) )
self.DIRS = self.__dirs
self.won = {} # 清空棋盘
def reset (self):
for j in xrange(15):
for i in xrange(15):
self.__board[i][j] = 0
return 0 # 索引器
def __getitem__ (self, row):
return self.__board[row] # 将棋盘转换成字符串
def __str__ (self):
text = ' A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O\n'
mark = ('. ', 'O ', 'X ')
nrow = 0
for row in self.__board:
line = ''.join([ mark[n] for n in row ])
text += chr(ord('A') + nrow) + ' ' + line
nrow += 1
if nrow < 15: text += '\n'
return text # 转成字符串
def __repr__ (self):
return self.__str__() def get (self, row, col):
if row < 0 or row >= 15 or col < 0 or col >= 15:
return 0
return self.__board[row][col] def put (self, row, col, x):
if row >= 0 and row < 15 and col >= 0 and col < 15:
self.__board[row][col] = x
return 0 # 判断输赢,返回0(无输赢),1(白棋赢),2(黑棋赢)
def check (self):
board = self.__board
dirs = ((1, -1), (1, 0), (1, 1), (0, 1))
for i in xrange(15):
for j in xrange(15):
if board[i][j] == 0: continue
id = board[i][j]
for d in dirs:
x, y = j, i
count = 0
for k in xrange(5):
if self.get(y, x) != id: break
y += d[0]
x += d[1]
count += 1
if count == 5:
self.won = {}
r, c = i, j
for z in xrange(5):
self.won[(r, c)] = 1
r += d[0]
c += d[1]
return id
return 0 # 返回数组对象
def board (self):
return self.__board # 导出棋局到字符串
def dumps (self):
import StringIO
sio = StringIO.StringIO()
board = self.__board
for i in xrange(15):
for j in xrange(15):
stone = board[i][j]
if stone != 0:
ti = chr(ord('A') + i)
tj = chr(ord('A') + j)
sio.write('%d:%s%s '%(stone, ti, tj))
return sio.getvalue() # 从字符串加载棋局
def loads (self, text):
self.reset()
board = self.__board
for item in text.strip('\r\n\t ').replace(',', ' ').split(' '):
n = item.strip('\r\n\t ')
if not n: continue
n = n.split(':')
stone = int(n[0])
i = ord(n[1][0].upper()) - ord('A')
j = ord(n[1][1].upper()) - ord('A')
board[i][j] = stone
return 0 # 设置终端颜色
def console (self, color):
if sys.platform[:3] == 'win':
try: import ctypes
except: return 0
kernel32 = ctypes.windll.LoadLibrary('kernel32.dll')
GetStdHandle = kernel32.GetStdHandle
SetConsoleTextAttribute = kernel32.SetConsoleTextAttribute
GetStdHandle.argtypes = [ ctypes.c_uint32 ]
GetStdHandle.restype = ctypes.c_size_t
SetConsoleTextAttribute.argtypes = [ ctypes.c_size_t, ctypes.c_uint16 ]
SetConsoleTextAttribute.restype = ctypes.c_long
handle = GetStdHandle(0xfffffff5)
if color < 0: color = 7
result = 0
if (color & 1): result |= 4
if (color & 2): result |= 2
if (color & 4): result |= 1
if (color & 8): result |= 8
if (color & 16): result |= 64
if (color & 32): result |= 32
if (color & 64): result |= 16
if (color & 128): result |= 128
SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle, result)
else:
if color >= 0:
foreground = color & 7
background = (color >> 4) & 7
bold = color & 8
sys.stdout.write(" \033[%s3%d;4%dm"%(bold and "01;" or "", foreground, background))
sys.stdout.flush()
else:
sys.stdout.write(" \033[0m")
sys.stdout.flush()
return 0 # 彩色输出
def show (self):
print ' A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O'
mark = ('. ', 'O ', 'X ')
nrow = 0
self.check()
color1 = 10
color2 = 13
for row in xrange(15):
print chr(ord('A') + row),
for col in xrange(15):
ch = self.__board[row][col]
if ch == 0:
self.console(-1)
print '.',
elif ch == 1:
if (row, col) in self.won:
self.console(9)
else:
self.console(10)
print 'O',
#self.console(-1)
elif ch == 2:
if (row, col) in self.won:
self.console(9)
else:
self.console(13)
print 'X',
#self.console(-1)
self.console(-1)
print ''
return 0 #----------------------------------------------------------------------
# evaluation: 棋盘评估类,给当前棋盘打分用
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
class evaluation (object): def __init__ (self):
self.POS = []
for i in xrange(15):
row = [ (7 - max(abs(i - 7), abs(j - 7))) for j in xrange(15) ]
self.POS.append(tuple(row))
self.POS = tuple(self.POS)
self.STWO = 1 # 冲二
self.STHREE = 2 # 冲三
self.SFOUR = 3 # 冲四
self.TWO = 4 # 活二
self.THREE = 5 # 活三
self.FOUR = 6 # 活四
self.FIVE = 7 # 活五
self.DFOUR = 8 # 双四
self.FOURT = 9 # 四三
self.DTHREE = 10 # 双三
self.NOTYPE = 11
self.ANALYSED = 255 # 已经分析过
self.TODO = 0 # 没有分析过
self.result = [ 0 for i in xrange(30) ] # 保存当前直线分析值
self.line = [ 0 for i in xrange(30) ] # 当前直线数据
self.record = [] # 全盘分析结果 [row][col][方向]
for i in xrange(15):
self.record.append([])
self.record[i] = []
for j in xrange(15):
self.record[i].append([ 0, 0, 0, 0])
self.count = [] # 每种棋局的个数:count[黑棋/白棋][模式]
for i in xrange(3):
data = [ 0 for i in xrange(20) ]
self.count.append(data)
self.reset() # 复位数据
def reset (self):
TODO = self.TODO
count = self.count
for i in xrange(15):
line = self.record[i]
for j in xrange(15):
line[j][0] = TODO
line[j][1] = TODO
line[j][2] = TODO
line[j][3] = TODO
for i in xrange(20):
count[0][i] = 0
count[1][i] = 0
count[2][i] = 0
return 0 # 四个方向(水平,垂直,左斜,右斜)分析评估棋盘,然后根据分析结果打分
def evaluate (self, board, turn):
score = self.__evaluate(board, turn)
count = self.count
if score < -9000:
stone = turn == 1 and 2 or 1
for i in xrange(20):
if count[stone][i] > 0:
score -= i
elif score > 9000:
stone = turn == 1 and 2 or 1
for i in xrange(20):
if count[turn][i] > 0:
score += i
return score # 四个方向(水平,垂直,左斜,右斜)分析评估棋盘,然后根据分析结果打分
def __evaluate (self, board, turn):
record, count = self.record, self.count
TODO, ANALYSED = self.TODO, self.ANALYSED
self.reset()
# 四个方向分析
for i in xrange(15):
boardrow = board[i]
recordrow = record[i]
for j in xrange(15):
if boardrow[j] != 0:
if recordrow[j][0] == TODO: # 水平没有分析过?
self.__analysis_horizon(board, i, j)
if recordrow[j][1] == TODO: # 垂直没有分析过?
self.__analysis_vertical(board, i, j)
if recordrow[j][2] == TODO: # 左斜没有分析过?
self.__analysis_left(board, i, j)
if recordrow[j][3] == TODO: # 右斜没有分析过
self.__analysis_right(board, i, j) FIVE, FOUR, THREE, TWO = self.FIVE, self.FOUR, self.THREE, self.TWO
SFOUR, STHREE, STWO = self.SFOUR, self.STHREE, self.STWO
check = {} # 分别对白棋黑棋计算:FIVE, FOUR, THREE, TWO等出现的次数
for c in (FIVE, FOUR, SFOUR, THREE, STHREE, TWO, STWO):
check[c] = 1
for i in xrange(15):
for j in xrange(15):
stone = board[i][j]
if stone != 0:
for k in xrange(4):
ch = record[i][j][k]
if ch in check:
count[stone][ch] += 1 # 如果有五连则马上返回分数
BLACK, WHITE = 1, 2
if turn == WHITE: # 当前是白棋
if count[BLACK][FIVE]:
return -9999
if count[WHITE][FIVE]:
return 9999
else: # 当前是黑棋
if count[WHITE][FIVE]:
return -9999
if count[BLACK][FIVE]:
return 9999 # 如果存在两个冲四,则相当于有一个活四
if count[WHITE][SFOUR] >= 2:
count[WHITE][FOUR] += 1
if count[BLACK][SFOUR] >= 2:
count[BLACK][FOUR] += 1 # 具体打分
wvalue, bvalue, win = 0, 0, 0
if turn == WHITE:
if count[WHITE][FOUR] > 0: return 9990
if count[WHITE][SFOUR] > 0: return 9980
if count[BLACK][FOUR] > 0: return -9970
if count[BLACK][SFOUR] and count[BLACK][THREE]:
return -9960
if count[WHITE][THREE] and count[BLACK][SFOUR] == 0:
return 9950
if count[BLACK][THREE] > 1 and \
count[WHITE][SFOUR] == 0 and \
count[WHITE][THREE] == 0 and \
count[WHITE][STHREE] == 0:
return -9940
if count[WHITE][THREE] > 1:
wvalue += 2000
elif count[WHITE][THREE]:
wvalue += 200
if count[BLACK][THREE] > 1:
bvalue += 500
elif count[BLACK][THREE]:
bvalue += 100
if count[WHITE][STHREE]:
wvalue += count[WHITE][STHREE] * 10
if count[BLACK][STHREE]:
bvalue += count[BLACK][STHREE] * 10
if count[WHITE][TWO]:
wvalue += count[WHITE][TWO] * 4
if count[BLACK][TWO]:
bvalue += count[BLACK][TWO] * 4
if count[WHITE][STWO]:
wvalue += count[WHITE][STWO]
if count[BLACK][STWO]:
bvalue += count[BLACK][STWO]
else:
if count[BLACK][FOUR] > 0: return 9990
if count[BLACK][SFOUR] > 0: return 9980
if count[WHITE][FOUR] > 0: return -9970
if count[WHITE][SFOUR] and count[WHITE][THREE]:
return -9960
if count[BLACK][THREE] and count[WHITE][SFOUR] == 0:
return 9950
if count[WHITE][THREE] > 1 and \
count[BLACK][SFOUR] == 0 and \
count[BLACK][THREE] == 0 and \
count[BLACK][STHREE] == 0:
return -9940
if count[BLACK][THREE] > 1:
bvalue += 2000
elif count[BLACK][THREE]:
bvalue += 200
if count[WHITE][THREE] > 1:
wvalue += 500
elif count[WHITE][THREE]:
wvalue += 100
if count[BLACK][STHREE]:
bvalue += count[BLACK][STHREE] * 10
if count[WHITE][STHREE]:
wvalue += count[WHITE][STHREE] * 10
if count[BLACK][TWO]:
bvalue += count[BLACK][TWO] * 4
if count[WHITE][TWO]:
wvalue += count[WHITE][TWO] * 4
if count[BLACK][STWO]:
bvalue += count[BLACK][STWO]
if count[WHITE][STWO]:
wvalue += count[WHITE][STWO] # 加上位置权值,棋盘最中心点权值是7,往外一格-1,最外圈是0
wc, bc = 0, 0
for i in xrange(15):
for j in xrange(15):
stone = board[i][j]
if stone != 0:
if stone == WHITE:
wc += self.POS[i][j]
else:
bc += self.POS[i][j]
wvalue += wc
bvalue += bc if turn == WHITE:
return wvalue - bvalue return bvalue - wvalue # 分析横向
def __analysis_horizon (self, board, i, j):
line, result, record = self.line, self.result, self.record
TODO = self.TODO
for x in xrange(15):
line[x] = board[i][x]
self.analysis_line(line, result, 15, j)
for x in xrange(15):
if result[x] != TODO:
record[i][x][0] = result[x]
return record[i][j][0] # 分析横向
def __analysis_vertical (self, board, i, j):
line, result, record = self.line, self.result, self.record
TODO = self.TODO
for x in xrange(15):
line[x] = board[x][j]
self.analysis_line(line, result, 15, i)
for x in xrange(15):
if result[x] != TODO:
record[x][j][1] = result[x]
return record[i][j][1] # 分析左斜
def __analysis_left (self, board, i, j):
line, result, record = self.line, self.result, self.record
TODO = self.TODO
if i < j: x, y = j - i, 0
else: x, y = 0, i - j
k = 0
while k < 15:
if x + k > 14 or y + k > 14:
break
line[k] = board[y + k][x + k]
k += 1
self.analysis_line(line, result, k, j - x)
for s in xrange(k):
if result[s] != TODO:
record[y + s][x + s][2] = result[s]
return record[i][j][2] # 分析右斜
def __analysis_right (self, board, i, j):
line, result, record = self.line, self.result, self.record
TODO = self.TODO
if 14 - i < j: x, y, realnum = j - 14 + i, 14, 14 - i
else: x, y, realnum = 0, i + j, j
k = 0
while k < 15:
if x + k > 14 or y - k < 0:
break
line[k] = board[y - k][x + k]
k += 1
self.analysis_line(line, result, k, j - x)
for s in xrange(k):
if result[s] != TODO:
record[y - s][x + s][3] = result[s]
return record[i][j][3] def test (self, board):
self.reset()
record = self.record
TODO = self.TODO
for i in xrange(15):
for j in xrange(15):
if board[i][j] != 0 and 1:
if self.record[i][j][0] == TODO:
self.__analysis_horizon(board, i, j)
pass
if self.record[i][j][1] == TODO:
self.__analysis_vertical(board, i, j)
pass
if self.record[i][j][2] == TODO:
self.__analysis_left(board, i, j)
pass
if self.record[i][j][3] == TODO:
self.__analysis_right(board, i, j)
pass
return 0 # 分析一条线:五四三二等棋型
def analysis_line (self, line, record, num, pos):
TODO, ANALYSED = self.TODO, self.ANALYSED
THREE, STHREE = self.THREE, self.STHREE
FOUR, SFOUR = self.FOUR, self.SFOUR
while len(line) < 30: line.append(0xf)
while len(record) < 30: record.append(TODO)
for i in xrange(num, 30):
line[i] = 0xf
for i in xrange(num):
record[i] = TODO
if num < 5:
for i in xrange(num):
record[i] = ANALYSED
return 0
stone = line[pos]
inverse = (0, 2, 1)[stone]
num -= 1
xl = pos
xr = pos
while xl > 0: # 探索左边界
if line[xl - 1] != stone: break
xl -= 1
while xr < num: # 探索右边界
if line[xr + 1] != stone: break
xr += 1
left_range = xl
right_range = xr
while left_range > 0: # 探索左边范围(非对方棋子的格子坐标)
if line[left_range - 1] == inverse: break
left_range -= 1
while right_range < num: # 探索右边范围(非对方棋子的格子坐标)
if line[right_range + 1] == inverse: break
right_range += 1 # 如果该直线范围小于 5,则直接返回
if right_range - left_range < 4:
for k in xrange(left_range, right_range + 1):
record[k] = ANALYSED
return 0 # 设置已经分析过
for k in xrange(xl, xr + 1):
record[k] = ANALYSED srange = xr - xl # 如果是 5连
if srange >= 4:
record[pos] = self.FIVE
return self.FIVE # 如果是 4连
if srange == 3:
leftfour = False # 是否左边是空格
if xl > 0:
if line[xl - 1] == 0: # 活四
leftfour = True
if xr < num:
if line[xr + 1] == 0:
if leftfour:
record[pos] = self.FOUR # 活四
else:
record[pos] = self.SFOUR # 冲四
else:
if leftfour:
record[pos] = self.SFOUR # 冲四
else:
if leftfour:
record[pos] = self.SFOUR # 冲四
return record[pos] # 如果是 3连
if srange == 2: # 三连
left3 = False # 是否左边是空格
if xl > 0:
if line[xl - 1] == 0: # 左边有气
if xl > 1 and line[xl - 2] == stone:
record[xl] = SFOUR
record[xl - 2] = ANALYSED
else:
left3 = True
elif xr == num or line[xr + 1] != 0:
return 0
if xr < num:
if line[xr + 1] == 0: # 右边有气
if xr < num - 1 and line[xr + 2] == stone:
record[xr] = SFOUR # XXX-X 相当于冲四
record[xr + 2] = ANALYSED
elif left3:
record[xr] = THREE
else:
record[xr] = STHREE
elif record[xl] == SFOUR:
return record[xl]
elif left3:
record[pos] = STHREE
else:
if record[xl] == SFOUR:
return record[xl]
if left3:
record[pos] = STHREE
return record[pos] # 如果是 2连
if srange == 1: # 两连
left2 = False
if xl > 2:
if line[xl - 1] == 0: # 左边有气
if line[xl - 2] == stone:
if line[xl - 3] == stone:
record[xl - 3] = ANALYSED
record[xl - 2] = ANALYSED
record[xl] = SFOUR
elif line[xl - 3] == 0:
record[xl - 2] = ANALYSED
record[xl] = STHREE
else:
left2 = True
if xr < num:
if line[xr + 1] == 0: # 左边有气
if xr < num - 2 and line[xr + 2] == stone:
if line[xr + 3] == stone:
record[xr + 3] = ANALYSED
record[xr + 2] = ANALYSED
record[xr] = SFOUR
elif line[xr + 3] == 0:
record[xr + 2] = ANALYSED
record[xr] = left2 and THREE or STHREE
else:
if record[xl] == SFOUR:
return record[xl]
if record[xl] == STHREE:
record[xl] = THREE
return record[xl]
if left2:
record[pos] = self.TWO
else:
record[pos] = self.STWO
else:
if record[xl] == SFOUR:
return record[xl]
if left2:
record[pos] = self.STWO
return record[pos]
return 0
def textrec (self, direction = 0):
text = []
for i in xrange(15):
line = ''
for j in xrange(15):
line += '%x '%(self.record[i][j][direction] & 0xf)
text.append(line)
return '\n'.join(text) #----------------------------------------------------------------------
# DFS: 博弈树搜索
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
class searcher (object): # 初始化
def __init__ (self):
self.evaluator = evaluation()
self.board = [ [ 0 for n in xrange(15) ] for i in xrange(15) ]
self.gameover = 0
self.overvalue = 0
self.maxdepth = 3 # 产生当前棋局的走法
def genmove (self, turn):
moves = []
board = self.board
POSES = self.evaluator.POS
for i in xrange(15):
for j in xrange(15):
if board[i][j] == 0:
score = POSES[i][j]
moves.append((score, i, j))
moves.sort()
moves.reverse()
return moves # 递归搜索:返回最佳分数
def __search (self, turn, depth, alpha = -0x7fffffff, beta = 0x7fffffff): # 深度为零则评估棋盘并返回
if depth <= 0:
score = self.evaluator.evaluate(self.board, turn)
return score # 如果游戏结束则立马返回
score = self.evaluator.evaluate(self.board, turn)
if abs(score) >= 9999 and depth < self.maxdepth:
return score # 产生新的走法
moves = self.genmove(turn)
bestmove = None # 枚举当前所有走法
for score, row, col in moves: # 标记当前走法到棋盘
self.board[row][col] = turn # 计算下一回合该谁走
nturn = turn == 1 and 2 or 1 # 深度优先搜索,返回评分,走的行和走的列
score = - self.__search(nturn, depth - 1, -beta, -alpha) # 棋盘上清除当前走法
self.board[row][col] = 0 # 计算最好分值的走法
# alpha/beta 剪枝
if score > alpha:
alpha = score
bestmove = (row, col)
if alpha >= beta:
break # 如果是第一层则记录最好的走法
if depth == self.maxdepth and bestmove:
self.bestmove = bestmove # 返回当前最好的分数,和该分数的对应走法
return alpha # 具体搜索:传入当前是该谁走(turn=1/2),以及搜索深度(depth)
def search (self, turn, depth = 3):
self.maxdepth = depth
self.bestmove = None
score = self.__search(turn, depth)
if abs(score) > 8000:
self.maxdepth = depth
score = self.__search(turn, 1)
row, col = self.bestmove
return score, row, col #----------------------------------------------------------------------
# psyco speedup
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
def psyco_speedup ():
try:
import psyco
psyco.bind(chessboard)
psyco.bind(evaluation)
except:
pass
return 0 psyco_speedup() #----------------------------------------------------------------------
# main game
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
def gamemain():
b = chessboard()
s = searcher()
s.board = b.board() opening = [
'1:HH 2:II',
#'2:IG 2:GI 1:HH',
'1:IH 2:GI',
'1:HG 2:HI',
#'2:HG 2:HI 1:HH',
#'1:HH 2:IH 2:GI',
#'1:HH 2:IH 2:HI',
#'1:HH 2:IH 2:HJ',
#'1:HG 2:HH 2:HI',
#'1:GH 2:HH 2:HI',
] import random
openid = random.randint(0, len(opening) - 1)
b.loads(opening[openid])
turn = 2
history = []
undo = False # 设置难度
DEPTH = 1 if len(sys.argv) > 1:
if sys.argv[1].lower() == 'hard':
DEPTH = 2 while 1:
print ''
while 1:
print '<ROUND %d>'%(len(history) + 1)
b.show()
print 'Your move (u:undo, q:quit):',
text = raw_input().strip('\r\n\t ')
if len(text) == 2:
tr = ord(text[0].upper()) - ord('A')
tc = ord(text[1].upper()) - ord('A')
if tr >= 0 and tc >= 0 and tr < 15 and tc < 15:
if b[tr][tc] == 0:
row, col = tr, tc
break
else:
print 'can not move there'
else:
print 'bad position'
elif text.upper() == 'U':
undo = True
break
elif text.upper() == 'Q':
print b.dumps()
return 0 if undo == True:
undo = False
if len(history) == 0:
print 'no history to undo'
else:
print 'rollback from history ...'
move = history.pop()
b.loads(move)
else:
history.append(b.dumps())
b[row][col] = 1 if b.check() == 1:
b.show()
print b.dumps()
print ''
print 'YOU WIN !!'
return 0 print 'robot is thinking now ...'
score, row, col = s.search(2, DEPTH)
cord = '%s%s'%(chr(ord('A') + row), chr(ord('A') + col))
print 'robot move to %s (%d)'%(cord, score)
b[row][col] = 2 if b.check() == 2:
b.show()
print b.dumps()
print ''
print 'YOU LOSE.'
return 0 return 0 #----------------------------------------------------------------------
# testing case
#----------------------------------------------------------------------
if __name__ == '__main__':
def test1():
b = chessboard()
b[10][10] = 1
b[11][11] = 2
for i in xrange(4):
b[5 + i][2 + i] = 2
for i in xrange(4):
b[7 - 0][3 + i] = 2
print b
print 'check', b.check()
return 0
def test2():
b = chessboard()
b[7][7] = 1
b[8][8] = 2
b[7][9] = 1
eva = evaluation()
for l in eva.POS: print l
return 0
def test3():
e = evaluation()
line = [ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]
record = []
e.analysis_line(line, record, len(line), 6)
print record[:10]
return 0
def test4():
b = chessboard()
b.loads('2:DF 1:EG 2:FG 1:FH 2:FJ 2:GG 1:GH 1:GI 2:HG 1:HH 1:IG 2:IH 1:JF 2:JI 1:KE')
b.loads('2:CE 2:CK 1:DF 1:DK 2:DL 1:EG 1:EI 1:EK 2:FG 1:FH 1:FI 1:FJ 1:FK 2:FL 1:GD 2:GE 2:GF 2:GG 2:GH 1:GI 1:GK 2:HG 1:HH 2:HJ 2:HK 2:IG 1:JG 2:AA')
eva = evaluation()
print b
score = 0
t = time.time()
for i in xrange(10000):
score = eva.evaluate(b.board(), 2)
#eva.test(b.board())
t = time.time() - t
print score, t
print eva.textrec(3)
return 0
def test5():
import profile
profile.run("test4()", "prof.txt")
import pstats
p = pstats.Stats("prof.txt")
p.sort_stats("time").print_stats()
def test6():
b = chessboard()
b.loads('1:CJ 2:DJ 1:dk 1:DL 1:EH 1:EI 2:EJ 2:EK 2:FH 2:FI 2:FJ 1:FK 2:FL 1:FM 2:GF 1:GG 2:GH 2:GI 2:GJ 1:GK 1:GL 2:GM 1:HE 2:HF 2:HG 2:HH 2:HI 1:HJ 2:HK 2:HL 1:IF 1:IG 1:IH 2:II 1:IJ 2:IL 2:JG 1:JH 1:JI 1:JJ 1:JK 2:JL 1:JM 1:KI 2:KJ 1:KL 1:LJ 2:MK')
#b.loads('1:HH,1:HI,1:HJ,1:HK')
s = searcher()
s.board = b.board()
t = time.time()
score, row, col = s.search(2, 3)
t = time.time() - t
b[row][col] = 2
print b
print score, t
print chr(ord('A') + row) + chr(ord('A') + col)
def test7():
b = chessboard()
s = searcher()
s.board = b.board()
b.loads('2:HH 1:JF')
turn = 2
while 1:
score, row, col = s.search(2, 2)
print 'robot move %s%s (%d)'%(chr(ord('A') + row), chr(ord('A') + col), score)
b[row][col] = 2
if b.check() == 2:
print b
print b.dumps()
print 'you lose !!'
return 0
while 1:
print b
print 'your move (pos):',
text = raw_input().strip('\r\n\t ')
if len(text) == 2:
tr = ord(text[0].upper()) - ord('A')
tc = ord(text[1].upper()) - ord('A')
if tr >= 0 and tc >= 0 and tr < 15 and tc < 15:
if b[tr][tc] == 0:
row, col = tr, tc
break
else:
print 'can not move there'
else:
print 'bad position'
elif text.upper() == 'Q':
print b.dumps()
return 0
b[row][col] = 1
if b.check() == 1:
print b
print b.dumps()
print 'you win !!'
return 0
return 0
#test6()
gamemain()
https://study.163.com/provider/400000000398149/index.htm?share=2&shareId=400000000398149(博主视频教学主页)
python 五子棋的更多相关文章
- python五子棋
以后不更新了,把以前的一些东西发出来. 这是一个命令行环境的五子棋程序.使用了minimax算法. 除了百度各个棋型的打分方式,所有代码皆为本人所撸.本程序结构与之前的井字棋.黑白棋一模一样. 有一点 ...
- Python五子棋的小程序
代码是在开源中国上看到的,源代码网址:http://www.oschina.net/code/snippet_2365439_48010 需要安装graphics模块,下载地址:http://mcsp ...
- 【转】Python实现智能五子棋
前言 棋需要一步一步下,人生需要一步一步走.千里之行,始于足下,九层之台,起于累土. 用Python五子棋小游戏. 基本环境配置 版本:Python3 相关模块: 本文所做工作如下: (1) 五子棋界 ...
- Python:游戏:五子棋之人机对战
本文代码基于 python3.6 和 pygame1.9.4. 五子棋比起我之前写的几款游戏来说,难度提高了不少.如果是人与人对战,那么,电脑只需要判断是否赢了就可以.如果是人机对战,那你还得让电脑知 ...
- Python小项目之五子棋
1.项目简介 在刚刚学习完python套接字的时候做的一个五子棋小游戏,可以在局域网内双人对战,也可以和电脑对战 2.实现思路 局域网对战 对于局域网功能来说,首先建立连接(tcp),然后每次下棋时将 ...
- Python开发五子棋游戏【新手必学】
五子棋源码,原创代码,仅供 python 开源项目学习.目前电脑走法笨笨的,下一期版本会提高电脑算法ps:另外很多人在学习Python的过程中,往往因为遇问题解决不了或者没好的教程从而导致自己放弃,为 ...
- Python双人五子棋
这篇文章旨在介绍一个双人的五子棋程序.再次重申,本人不擅长对代码的可读性进行优化,所以可能有些杂乱(在所难免). 先瞅一眼效果图: 请注意,这个棋子--是这么圆润立体!本程序不需任何素材图片,完全用代 ...
- python控制台简单实现五子棋
#棋盘#落子#规则import randomclass chess: def __init__(self): print('#---------------棋盘----------------#') ...
- 进击的Python【第六章】:Python的高级应用(三)面向对象编程
Python的高级应用(三)面向对象编程 本章学习要点: 面向对象编程介绍 面向对象与面向过程编程的区别 为什么要用面向对象编程思想 面向对象的相关概念 一.面向对象编程介绍 面向对象程序设计(英语: ...
随机推荐
- C++ new失败的处理
我们都知道,使用 malloc/calloc 等分配内存的函数时,一定要检查其返回值是否为“空指针”(亦即检查分配内存的操作是否成功),这是良好的编程习惯,也是编写可靠程序所必需的.但是,如果你简单地 ...
- linux中级-JAVA企业级应用TOMCAT实战
1. Tomcat简介 Tomcat是Apache软件基金会(Apache Software Foundation)的Jakarta 项目中的一个核心项目,由Apache.Sun和其他一些公司及个人共 ...
- 你需要知道的MySQL开源存储引擎TokuDB
在四月份的Percona Live MySQL会议上, TokuDB庆祝自己成为开源存储引擎整一周年.我现在仍能记得一年前它刚创建时的官方声明与对它的期望.当时的情况非常有意思,因为它拥有帮助MySQ ...
- SharedPrefernces使用实例讲解
activity_main.xml <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android&qu ...
- [转] ServletContext 与application的异同
相同:其实servletContext和application 是一样的,就相当于一个类创建了两个不同名称的变量.在 servlet中ServletContext就是application对象.大家只 ...
- 【CodeVS 1163】访问艺术馆
http://codevs.cn/submission/2367697/ loli蜜汁(面向高一)树形dp是这道题的改编. 改编后的题目中每个展览厅的有多个不同的画,偷画的时间和画的价值也不同,求最大 ...
- JAVA1种C++3种继承方式
JAVA中只有一种public继承
- iOS 下ARC的内存管理机制
本文来源于我个人的ARC学习笔记,旨在通过简明扼要的方式总结出iOS开发中ARC(Automatic Reference Counting,自动引用计数)内存管理技术的要点,所以不会涉及全部细节.这篇 ...
- Mysql 中 iddata1的缩小步骤
原因就不多说了,,,, 直接上干货. 1. 备份数据库 mysqldump -q -uroot -ppassword --add-drop-table --all-databases >all1 ...
- python 学习笔记6(数据库 sqlite)
26. SQLite 轻量级的关系型数据库 SQLite是python自带的数据库,可以搭配python存储数据,开发网站等. 标准库中的 sqlite3 提供该数据库的接口. 1. 基本语法如下 c ...
