ArrayList和LinkedList、Vector的优缺点?
一般在面试中可能会被问到ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector三者相关的区别!
一般来说我想大概都会回答如下的这些:
ArrayList底层是数组结构,查询快,增删慢,线程不安全,效率高。
LinkedList底层是链表数据结构,查询慢,增删快,线程不安全,效率高。
Vector底层是数组结构,查询快,增删慢,线程安全,效率低。
以上就是最基本的一个优缺点,但是他们的内部结构,具体怎么实现添加查询这一块的,我想应该有一部分人还是不太清楚。
下面我将带领一起去集合的内部看一看具体的代码实现。
ArrayList:
首先是ArrayList的一个实例化,java提供了一个有参构造和无参构造。下面一起查看代码:
- /**
- * Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
构造具有指定初始容量的空列表。- *
- * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list 初始容量列表的初始容量
- * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity 如果指定的初始容量为负,则抛出IllegalArgumentException
- * is negative
- */
- public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
- if (initialCapacity > 0) {
- this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
- } else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
- this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
- } else {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
- initialCapacity);
- }
- }
通过上述我们可以看到,这是ArrayList的有参构造,可以自定义集合的初始化长度,否则如果输入的是0那么就使用ArrayList自带的默认的数组缓存区。
- /**
- * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. 构造初始容量为10的空列表。
- */
- public ArrayList() {
- this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
- }
使用无参构造,将会创建一个默认长度的数组。初始长度为10。
- /**
- * Default initial capacity. 默认初始容量
- */
- private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
- /**
- * Shared empty array instance used for empty instances. 用于空实例的共享空数组实例
- */
- private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
* 解析add添加方法的全过程,下面的add方法相关的所有源代码,
- /**
- * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. 将指定的元素追加到列表的末尾
- *
- * @param e element to be appended to this list 将追加到此列表中的e元素
- * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
- */
- public boolean add(E e) {
// 调用自动扩容存储机制,确保自动数组有存储新元素的能力。- ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
- // 自动扩容存储机制处理后,将元素添加到集合的末尾
- elementData[size++] = e;
- return true;
- }
- private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
// 判断该数组是否是一个新创建的实例对象- if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
// 如果是,就设置数组的长度为默认长度 10- minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
- }
- // 确保能够有储存能力
- ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
- }
- private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 保存这个列表在结构上被修改的次数。- modCount++;
- // overflow-conscious code
// 如果默认的长度减去实际数组的长度大于0,那么就调用grow()方法
- if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
- grow(minCapacity);
- }
- private void grow(int minCapacity) {
- // overflow-conscious code
- int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 获取数组原始的长度
- int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 获取新的数组的长度 (0 + 0/2)
- if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) // 如果新的值 - 最小值小于0 (0-10)
- newCapacity = minCapacity; // 将默认值 10 赋值给 新的值
- if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) // 如果新的值 - 最大长度 大于 0 (0 - 2147483639) > 0
- newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 调用方法
- // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
- elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); // 复制原本的数组,定义长度,赋值给自己,来达到自动扩容
- }
* 总结以上,在ArrayList被无参实例化的时候就会被创建一个空的数组,在添加第一个值时,ArrayList底层的自动扩容机制将会被执行,也就是private void grow(int minCapacity)这个方法会被调用,给内部的elementData数组定义初始长度为10,然后再将值添加到数组的末尾。这里面主要就是牵涉到一个自动扩容机制,在每一次添加之前,都会去判断,当前数组长度是否有实际的存储能力,如果没有那么自动扩容机制就会根据当前数组长度+当前长度/2来计算的方式,对当前数组进行扩容。
linkedList:
* 链接内部结构图
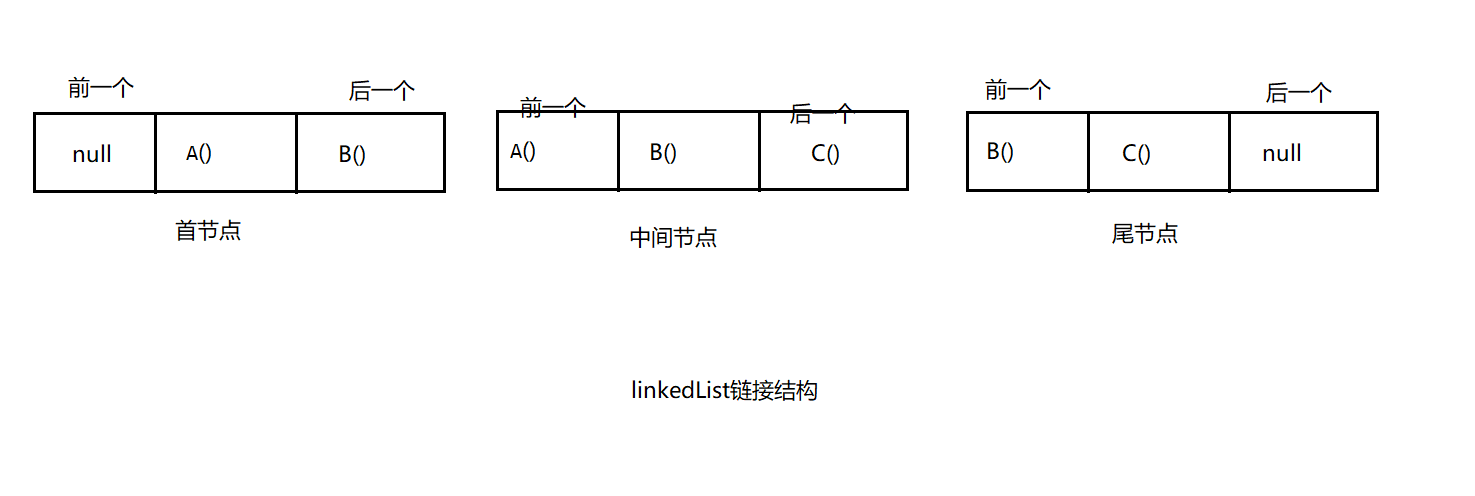
* 查看linkedList的无参构造和有参构造
* 无参构造
- /**
- * Constructs an empty list. // 构造一个空列表
- */
- public LinkedList() {
- }
* 有参构造
- /**
- * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified 构造包含指定元素的列表
- * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's 集合,按照集合返回的顺序
- * iterator. 迭代器
- *
- * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
- * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
- */
- public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
- this();
- addAll(c);
- }
* 解析add添加方法:
- /**
- * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. 将指定的元素追加到列表的末尾
- *
- * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
- *
- * @param e element to be appended to this list
- * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
- */
- public boolean add(E e) {
- linkLast(e);
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * Links e as last element. 链接做为最后一个元素
- */
- void linkLast(E e) {
// 将最后一个节点临时存储起来- final Node<E> l = last;
- // 创建一个新的节点,设置新的节点的上一个节点和当前节点的值
- final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
- // 将新创建的节点重新存储到专门用于保存最后一个节点的值的对象
- last = newNode;
- // 判断是否是第一次添加,如果是第一次添加值,那么上一个值一定是null,否则就会一个值
- if (l == null)
// 如果是第一次添加,那么我们就要将新创建的节点保存到链表的头first- first = newNode;
- else
- // 否则就设置l的下一个节点为新的节点
l.next = newNode;- // 长度增加
- size++;
// 修改次数- modCount++;
- }
* 总结以上:从源代码上我们可以看到,linkedList内部采用的实际上是通过多个节点来保存值,每个节点对象中对它的上一个节点和下一个节点继续记录,以此将所有的节点串联起来,就形成了链表。
Vector:
vector其实本质上和ArrayList是一样的,底层都是使用了数组来完成,只是vector是从jdk1.0版本开始,ArrayList是1.2版本开始,可以理解的是ArrayList其实就是用来代替Vector的。Vector和ArrayList最大的区别就是一个是线程安全,一个是线程不安全的。这个我们可以通过查看底层代码来得知。
* 解析add代码
- /**
- * Appends the specified element to the end of this Vector. 将指定的元素附加到这个向量的末尾
- *
- * @param e element to be appended to this Vector
- * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
- * @since 1.2
- */
- public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
- modCount++;
- ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
- elementData[elementCount++] = e;
- return true;
- }
* 总结上述可得知:相比较ArrayList的add方法,我们可以看出,Vector的add方法添加的同步锁。
------------------------------------------------------ 分割 -------------------------------------------------------------------
学无止境,永远不要轻言放弃。
ArrayList和LinkedList、Vector的优缺点?的更多相关文章
- ArrayList LinkedList Vector
ArrayList是基于数组实现的,没有容量的限制. 在删除元素的时候,并不会减少数组的容量大小,可以调用ArrayList的trimeToSize()来缩小数组的容量. ArrayList, Lin ...
- 数组Array和列表集合ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector的区别
一.ArrayList和Vector的区别 ArrayList与Vector主要从以下方面来说. 1.同步性: Vector是线程安全的,也就是说是同步的,而ArrayList是线程序不安全的,不是同 ...
- Java集合类学习-LinkedList, ArrayList, Stack, Queue, Vector
Collection List 在Collection的基础上引入了有序的概念,位置精确:允许相同元素.在列表上迭代通常优于索引遍历.特殊的ListIterator迭代器允许元素插入.替换,双向访问, ...
- ArrayList vs LinkedList vs Vector
List概览 List,正如它的名字,表明其是有顺序的.当讨论List的时候,最好拿它跟Set作比较,Set中的元素是无序且唯一:下面是一张类层次结构图,从这张图中,我们可以大致了解java集合类的整 ...
- 集合中list、ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector的区别、Collection接口的共性方法以及数据结构的总结
List (链表|线性表) 特点: 接口,可存放重复元素,元素存取是有序的,允许在指定位置插入元素,并通过索引来访问元素 1.创建一个用指定可视行数初始化的新滚动列表.默认情况下,不允许进行多项选择. ...
- ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector的区别
Arraylist和Vector是采用数组方式存储数据,此数组元素数大于实际存储的数据以便增加插入元素,都允许直接序号索引元素,但是插入数据要涉及到数组元素移动等内存操作,所以插入数据慢,查找有下标, ...
- ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector,Stack之间的区别
一,线程安全性 Vector.Stack:线程安全 ArrayList.LinkedList:非线程安全 二,实现方式 LinkedList:双向链表 ArrayList,Vector,Stack:数 ...
- java的List接口的实现类 ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector 的区别
Java的List接口有3个实现类,分别是ArrayList.LinkedList.Vector,他们用于存放多个元素,维护元素的次序,而且允许元素重复. 3个具体实现类的区别如下: 1. Array ...
- HashMap、HashTable、ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector区别
HashTable和HashMap区别 ①继承不同. public class Hashtable extends Dictionary implements Map public class Has ...
随机推荐
- FastStone Capture 截图工具
主要功能介绍 截屏 包括了全屏截取,当前活动窗口截取,截取选定区域,多边形截取和截取滚动页面等,基本上常用的都有了.特别是滚动截取,许多朋友为了这个功能,不惜安装各种重量级的截屏软件,甚至四处下载各种 ...
- 质因数分解(0)<P2012_1>
质因数分解 (prime.cpp/c/pas) [问题描述] 已知正整数n是两个不同的质数的乘积,试求出较大的那个质数. [输入] 输入文件名为prime.in. 输入只有一行,包含一个正整数n. [ ...
- ssh访问ubuntu13.10
步骤: 首先确保网络连接是ok,网络连接方式"桥接“,手动配置 ip 192.168.1.9,和主机是同一网段 1.检查当前有没有安装openssh-server(已安装) 2. 安装ope ...
- 3 CSS 定位&浮动&水平对齐&组合选择符&伪类&伪元素
CSS Position(定位):元素的定位与文档流无关 static定位: HTML元素的默认值, 没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中 静态定位的元素不会受到top,bottom,left,right影 ...
- Spring Boot 概括
Spring Boot 简介 简化Spring应用开发的一个框架: 整个Spring技术栈的一个大整合: J2EE开发的一站式解决方案: 微服务 2014,martin fowler 微服务:架构风格 ...
- Java基础 -4.6
循环嵌套 乘法口诀表 public static void main(String[] args) { for(int x =1;x<10;x++) { for(int y=1;y<=x; ...
- gcd && exgcd算法
目录 欧几里德算法与扩展欧几里德算法 1.欧几里德算法 2.扩展欧几里德算法 欧几里德算法与扩展欧几里德算法 1.欧几里德算法 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using ...
- Linux命令:top命令
top命令是Linux下常用的性能分析工具,能够实时显示系统中各个进程的资源占用状况,类似于Windows的任务管理器.下面详细介绍它的使用方法.top是一个动态显示过程,即可以通过用户按键来不断刷新 ...
- 列表推导式、生成器表达式以及zip()max()max()/min()sum()sort()map()filter()的用法
列表推导式: 基本格式: variable = [out_exp_res for out_exp in input_list if out_exp == 2] #out_exp_res: 列表生成元素 ...
- 130、Java面向对象之static关键字二(在没有实例化对象产生时直接操作static属性)
01.代码如下: package TIANPAN; class Book { // 描述的是同一个出版社的信息 private String title; // 普通属性 private double ...
