spring-第八篇之容器中的bean的生命周期
1、容器中的bean的生命周期
spring容器可以管理singleton作用域的bean的生命周期,包括bean何时被创建、何时初始化完成、何时被销毁。客户端代码不能控制该类型bean的销毁。spring容器可以管理该类型bean在实例化结束之后和销毁之前的行为。
prototype作用域类型的bean则完全交由客户端代码管理,spring容器仅仅是负责创建bean。spring容器无法管理该类型的bean。
管理bean的生命周期行为的主要时机有以下两个:
1》注入依赖关系之后
2》即将销毁bean之前
2、依赖关系注入之后的行为
spring提供两种方式在bean全部属性设置成功后执行特定的行为:
1》使用init-method属性,指定某方法在在bean全部属性(即包括依赖)设置成功后执行特定行为。
2》实现InitializingBean接口,并实现该接口的void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception方法。
举个例子:

Chinese.java
package com.lfy.bean; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; public class Chinese implements InitializingBean,BeanNameAware,ApplicationContextAware { private ApplicationContext ctx;
private String beanName;
private String personName; public Chinese() { System.out.println("=========调用无参构造器Chinese()=========");
} @Override
public void setBeanName(String beanName) { this.beanName=beanName;
System.out.println("=========setBeanName()=========");
} @Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext arg0) throws BeansException { this.ctx=arg0;
System.out.println("=========setApplicationContext()=========");
} /**
* 生命周期方法
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("=========初始化bean方法afterPropertiesSet()=========");
} /**
* 将被设为生命周期方法
*/
public void init() { System.out.println("=========初始化bean方法init()=========");
} public void setPersonName(String name) { this.personName=name;
System.out.println("=========setPersonName()执行setter方法注入personName========="+personName);
} public void info() { System.out.println("Chinese实现类"+",部署该bean时指定的id为:"+beanName);
} }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- spring配置文件的根元素,使用spring-beans-4.0.xsd语义约束 -->
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <bean id="chinese" class="com.lfy.bean.Chinese" init-method="init">
<property name="personName" value="至尊宝"/>
</bean>
</beans>
SpringTest.java
package com.lfy.main; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.lfy.bean.Chinese; /**
* 获得bean本身的id
* @author lfy
*
*/
public class SpringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); Chinese chin=ctx.getBean("chinese", Chinese.class);
} }
运行结果:
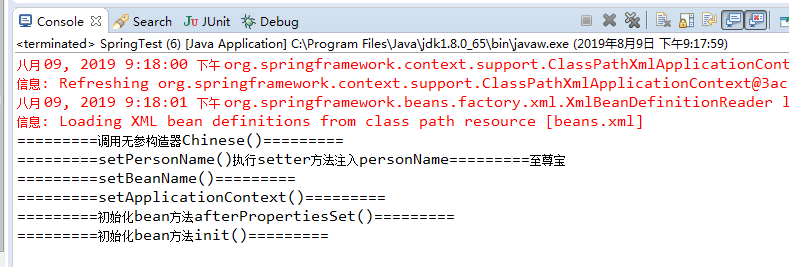
总结:上面的例子,两种方式都同时实现了,注意它们执行的顺序。afterPropertiesSet()方法先于init()方法得到执行。
3、bean销毁之前的行为
spring提供两种方式在bean实例销毁之前执行特定的行为:
1》使用destroy-method属性,指定某方法在在bean实例销毁之前执行特定行为。
2》实现DisposableBean接口,并实现该接口的void destroy() throws Exception方法。
举个例子:对前面的例子做一些修改
Chinese.java
package com.lfy.bean; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; public class Chinese implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean,BeanNameAware,ApplicationContextAware { private ApplicationContext ctx;
private String beanName;
private String personName; public Chinese() { System.out.println("=========调用无参构造器Chinese()=========");
} @Override
public void setBeanName(String beanName) { this.beanName=beanName;
System.out.println("=========setBeanName()=========");
} @Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext arg0) throws BeansException { this.ctx=arg0;
System.out.println("=========setApplicationContext()=========");
} /**
* 生命周期方法
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("=========初始化bean方法afterPropertiesSet()=========");
} /**
* 将被设为生命周期方法
*/
public void init() { System.out.println("=========初始化bean方法init()=========");
} /**
* 生命周期方法
*/
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("=========结束bean前执行方法destroy()=========");
} /**
* 将被设为生命周期方法
*/
public void close() { System.out.println("=========结束bean前执行方法close()=========");
} public void setPersonName(String name) { this.personName=name;
System.out.println("=========setPersonName()执行setter方法注入personName========="+personName);
} public void info() { System.out.println("Chinese实现类"+",部署该bean时指定的id为:"+beanName);
} }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- spring配置文件的根元素,使用spring-beans-4.0.xsd语义约束 -->
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 遇到了个问题,偶尔出现destory-method="close"不能出现在<bean.../>,暂未明白原因 -->
<bean id="chinese" class="com.lfy.bean.Chinese" init-method="init" destory-method="close">
<property name="personName" value="至尊宝"/>
</bean>
</beans>
SpringTest.java
package com.lfy.main; import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.lfy.bean.Chinese; /**
* 获得bean本身的id
* @author lfy
*
*/
public class SpringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { AbstractApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); Chinese chin=ctx.getBean("chinese", Chinese.class); ctx.registerShutdownHook();
} }
运行结果:

总结:由于xml解析发生了些问题未能找到原因,一开始destory-method方法没能演示效果。后来突然又好了,可能是eclipse的问题。在非Web应用上,使用registerShutdownHook()能够正确的关闭spring容器。并且注意destory()方法先于close()方法执行。
4、此外协调作用域不同步的bean:
singleton作用域的bean依赖于prototype作用域的bean,但singleton bean只有一次初始化的机会,在初始化单例bean的时候,会先创建prototype作用域的bean,然后再初始化单例bean。这将导致以后无论什么时候通过单例bean访问prototype bean都会是同一个bean,相当于单例bean变相的将prototype bean单例化了。
为了解决这种生命周期与预期不同步的问题,有两种解决思路:
1》 放弃依赖注入:单例bean每次需要prototype bean时,主动向容器请求新的bean实例。
2》利用方法注入:通常使用lookup方法注入。使用lookup方法注入可以让spring容器重写容器中bean的抽象或者具体方法,返回查找容器中其他bean的结果。spring通过使用JDK动态代理或cglib库修改客户端的二进制代码,从而实现上述需求。
使用lookup方法注入,大致的步骤有:
1》将调用者bean的实现类定义为抽象类,并定义一个抽象方法来获取被依赖的bean。
2》在<bean.../>元素中添加<lookup-method.../>子元素让spring为调用者bean的实现类实现指定的抽象方法。
3》使用<lookup-method.../>元素需要指定如下两个元素:
name:指定需要让spring实现的方法。
bean:指定spring实现该方法的返回值。
举个例子:

Dog.java
package com.lfy.bean;
public interface Dog {
public String run();
}
GunDog.java
package com.lfy.impl;
import com.lfy.bean.Dog;
public class GunDog implements Dog {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
@Override
public String run() {
return "我是一只叫"+this.name+"的猎犬,奔跑迅速...";
}
}
Chinese.java
package com.lfy.bean;
public abstract class Chinese {
//private Dog dog;留作动态注入一个Dog的实例
// 定义抽象方法,该方法用于获取被依赖的bean
public abstract Dog getDog();
public void hunt() {
System.out.println("我带着:"+getDog()+"出去打猎");
System.out.println(getDog().run());
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- spring配置文件的根元素,使用spring-beans-4.0.xsd语义约束 -->
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> <!-- chinese依赖于gunDog,并且为单例bean依赖prototype实例。
spring检测到lookup-method元素,会自动为该元素的name属性
指定的方法提供实现体
-->
<bean id="chinese" class="com.lfy.bean.Chinese">
<lookup-method name="getDog" bean="gunDog"/>
</bean> <!-- 指定bean的作用域为prototype,希望每次都是新的bean -->
<bean id="gunDog" class="com.lfy.impl.GunDog" scope="prototype">
<property name="name" value="旺财"/>
</bean>
</beans>
SpringTest.java
package com.lfy.main; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.lfy.bean.Chinese; /**
* 获得bean本身的id
* @author lfy
*
*/
public class SpringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); Chinese p1=ctx.getBean("chinese", Chinese.class);
Chinese p2=ctx.getBean("chinese", Chinese.class);
System.out.println("是否还是同一个Chinese猎人:"+(p1 == p2));
p1.hunt();
p2.hunt();
} }
运行结果:
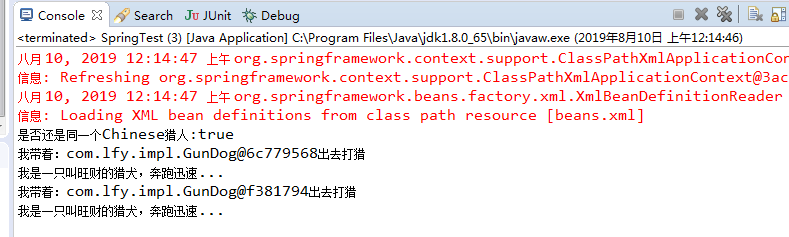
总结:我们的Chinese类是一个抽象类,它不能实例化。我们通过给它添加<lookup-method.../>元素,告诉spring需要实现哪个抽象方法spring容器为抽象方法提供实体后,抽象方法变成类的具体方法,这个类也就变成了具体类,接下来spring就可以创建该bean的实例了。
spring会采用运行时动态增强的方式来实现<lookup-method.../>元素所指定的抽象方法:如果目标抽象类实现过接口,spring会采用JDK动态代理来实现该抽象类,并为之实现抽象方法;如果目标抽象类没有实现过接口,spring会采用cglib实现该抽象类,并为之实现抽象方法。spring-4.0.4已经在核心包中集成了cglib类库,无需额外添加cglib的jar包。
spring-第八篇之容器中的bean的生命周期的更多相关文章
- SpringBean容器启动流程+Bean的生命周期【附源码】
如果对SpringIoc与Aop的源码感兴趣,可以访问参考:https://javadoop.com/,十分详细. 目录 Spring容器的启动全流程 Spring容器关闭流程 Bean 的生命周期 ...
- Spring扩展:替换IOC容器中的Bean组件 -- @Replace注解
1.背景: 工作中是否有这样的场景?一个软件系统会同时有多个不同版本部署,比如我现在做的IM系统,同时又作为公司的技术输出给其他银行,不同的银行有自己的业务实现(比如登陆验证.用户信息查询等) ...
- spring中的bean的生命周期
bean的生命周期:bean的创建 —— 初始化 ——销毁的过程 容器管理bean的生命周期,我们可以自定义初始化和销毁方法,容器在bean进行到当前生命周期就会调用我们的方法 在xml配置文件中是在 ...
- Spring重点—— IOC 容器中 Bean 的生命周期
一.理解 Bean 的生命周期,对学习 Spring 的整个运行流程有极大的帮助. 二.在 IOC 容器中,Bean 的生命周期由 Spring IOC 容器进行管理. 三.在没有添加后置处理器的情况 ...
- Spring Bean的生命周期,《Spring 实战》书中的官方说法
连着两天的面试 ,都问到了 Spring 的Bean的生命周期,其中还包括 昨晚一波阿里的电话面试.这里找到了Spring 实战中的官方说法.希望各位要面试的小伙伴记住,以后有可能,或者是有时间 去看 ...
- 简:Spring中Bean的生命周期及代码示例
(重要:spring bean的生命周期. spring的bean周期,装配.看过spring 源码吗?(把容器启动过程说了一遍,xml解析,bean装载,bean缓存等)) 完整的生命周期概述(牢记 ...
- 【Spring】Spring中的Bean - 4、Bean的生命周期
Bean的生命周期 简单记录-Java EE企业级应用开发教程(Spring+Spring MVC+MyBatis)-Spring中的Bean 了解Spring中Bean的生命周期有何意义? 了解Sp ...
- Spring基础14——Bean的生命周期
1.IOC容器中的Bean的生命周期方法 SpringIOC容器可以管理Bean的生命周期,Spring允许在Bean生命周期的特定点执行定制的任务.SpringIOC容器对Bean的生命周期进行管理 ...
- Spring学习-- IOC 容器中 bean 的生命周期
Spring IOC 容器可以管理 bean 的生命周期 , Spring 允许在 bean 声明周期的特定点执行定制的任务. Spring IOC 容器对 bean 的生命周期进行管理的过程: 通过 ...
随机推荐
- Python 爬虫 校花网
爬虫:是一种按照一定的规则,自动地抓取万维网信息的程序或者脚本. 福利来了 校花网 ,首先说为什么要爬这个网站呢,第一这个网站简单爬起来容易,不会受到打击,第二呢 你懂得.... 1.第一步,需要下 ...
- MTCNN 人脸检测
demo.py import cv2 from detection.mtcnn import MTCNN # 检测图片中的人脸 def test_image(imgpath): mtcnn = MTC ...
- jvm监控和诊断工具
大牛写的Java的OOM Killer:https://www.jianshu.com/p/4645254be259 强烈推荐 总的参考链接:https://cloud.tencent.com/dev ...
- 修改 linux 默认字符集
[root@eric6 ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/i18n //查看 linux 默认的字符集,默认是 UTF-8 LANG="zh_CN.UTF-8" cp ...
- Tomcat部署虚拟主机
使用Tomcat部署加密虚拟主机,实现: a.使用www.a.com域名访问的页面根路径为/usr/local/tomcat/a/base b.使用www.b.com域名访问的页面根路径为/usr/l ...
- dict/json转xml
在json转xml时,首先传进来的一定是一个dict,如果不是需要转一下,然后开始迭代,遇到dict则递归,如果是list则循环递归,否则认为是文字,将其写入,逻辑不复杂,因为为了代码循环不是太频繁, ...
- python常用函数 U
update(dict) 字典合并,生成的为新的字典,新字典操作不会影响老字典. 例子:
- [Luogu2014]选课(树形dp)
[Luogu2014]选课 题目描述 在大学里每个学生,为了达到一定的学分,必须从很多课程里选择一些课程来学习,在课程里有些课程必须在某些课程之前学习,如高等数学总是在其它课程之前学习.现在有N门功课 ...
- div+css做出带三角的弹出框 和箭头
一.三角形 https://blog.csdn.net/Szu_AKer/article/details/51755821 notice:三角的那部分可以用图片作为背景,但是容易出现杂边.所以利用cs ...
- Java中最基本的集合接口:初识Collection
Collection接口 Collection是最基本的集合接口,一个Collection代表一组Object,即Collection的元素(Elements). 一些 Collection允许相同的 ...
