java并发锁ReentrantReadWriteLock读写锁源码分析
public interface ReadWriteLock {
/**
* Returns the lock used for reading.
*
* @return the lock used for reading.
*/
Lock readLock();
/**
* Returns the lock used for writing.
*
* @return the lock used for writing.
*/
Lock writeLock();
}
/*
* Read vs write count extraction constants and functions.
* Lock state is logically divided into two unsigned shorts:
* The lower one representing the exclusive (writer) lock hold count,
* and the upper the shared (reader) hold count.
*/
static final int SHARED_SHIFT = 16;
static final int SHARED_UNIT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT);
static final int MAX_COUNT = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
static final int EXCLUSIVE_MASK = (1 << SHARED_SHIFT) - 1;
/** Returns the number of shared holds represented in count */
static int sharedCount(int c) { return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT; }
/** Returns the number of exclusive holds represented in count */
static int exclusiveCount(int c) { return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK; }
SHARED_SHIFT,表示读锁占用的位数,常量16
SHARED_UNIT, 增加一个读锁,按照上述设计,就相当于增加 SHARED_UNIT;
MAX_COUNT ,表示申请读锁最大的线程数量,为65535
EXCLUSIVE_MASK :表示计算写锁的具体值时,该值为 15个1,用 getState & EXCLUSIVE_MASK算出写锁的线程数,大于1表示重入。
static int sharedCount(int c) { return c >>> SHARED_SHIFT; }
static int exclusiveCount(int c) { return c & EXCLUSIVE_MASK; }
/**
* The number of reentrant read locks held by current thread.
* Initialized only in constructor and readObject.
* Removed whenever a thread's read hold count drops to 0.
*/
private transient ThreadLocalHoldCounter readHolds;
/**
* The hold count of the last thread to successfully acquire
* readLock. This saves ThreadLocal lookup in the common case
* where the next thread to release is the last one to
* acquire. This is non-volatile since it is just used
* as a heuristic, and would be great for threads to cache.
*
* <p>Can outlive the Thread for which it is caching the read
* hold count, but avoids garbage retention by not retaining a
* reference to the Thread.
*
* <p>Accessed via a benign data race; relies on the memory
* model's final field and out-of-thin-air guarantees.
*/
private transient HoldCounter cachedHoldCounter;
/**
* firstReader is the first thread to have acquired the read lock.
* firstReaderHoldCount is firstReader's hold count.
*
* <p>More precisely, firstReader is the unique thread that last
* changed the shared count from 0 to 1, and has not released the
* read lock since then; null if there is no such thread.
*
* <p>Cannot cause garbage retention unless the thread terminated
* without relinquishing its read locks, since tryReleaseShared
* sets it to null.
*
* <p>Accessed via a benign data race; relies on the memory
* model's out-of-thin-air guarantees for references.
*
* <p>This allows tracking of read holds for uncontended read
* locks to be very cheap.
*/
private transient Thread firstReader = null;
private transient int firstReaderHoldCount;
上述这4个变量,其实就是完成一件事情,将获取读锁的线程放入线程本地变量(ThreadLocal),方便从整个上 下文,根据当前线程获取持有锁的次数信息。其实 firstReader,firstReaderHoldCount ,cachedHoldCounter 这三个变量就是为readHolds变量服务的,是一个优化手段,尽量减少直接使用readHolds.get方法的次数,firstReader与firstReadHoldCount保存第一个获取读锁的线程,也就是readHolds中并不会保存第一个获取读锁的线程;cachedHoldCounter 缓存的是最后一个获取线程的HolderCount信息,该变量主要是在如果当前线程多次获取读锁时,减少从readHolds中获取HoldCounter的次数。请结合如下代码理解上述观点:
if (r == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != current.getId())
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
}
2、ReentrantReadWriterLock源码分析
大家可以点击加群【JAVA架构知识学习讨论群】473984645,(如多你想跳槽换工作,但是技术又不够,或者工作遇到了瓶颈,我这里有一个Java的免费直播课程,讲的是高端的知识点,只要有1-5年的开发工作经验可以加群找我要课堂链接。)注意:是免费的 没有开发经验的误入。
2.1 ReadLock 源码分析
2.1.1 lock方法
/**
* Acquires the read lock.
*
* <p>Acquires the read lock if the write lock is not held by
* another thread and returns immediately.
*
* <p>If the write lock is held by another thread then
* the current thread becomes disabled for thread scheduling
* purposes and lies dormant until the read lock has been acquired.
*/
public void lock() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
sync.acquireShared方法存在于AbstractQueuedSynchronizer类中,
/**
* Acquires in shared mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented by
* first invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquireShared},
* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly
* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link
* #tryAcquireShared} until success.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryAcquireShared} but is otherwise uninterpreted
* and can represent anything you like.
*/
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) //@1
doAcquireShared(arg); //@2
}
根据常识,具体获取锁的过程在子类中实现,果不其然,tryAcquireShared方法在ReentrantReadWriterLock的Sync类中实现
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If write lock held by another thread, fail.
* 2. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for
* lock wrt state, so ask if it should block
* because of queue policy. If not, try
* to grant by CASing state and updating count.
* Note that step does not check for reentrant
* acquires, which is postponed to full version
* to avoid having to check hold count in
* the more typical non-reentrant case.
* 3. If step 2 fails either because thread
* apparently not eligible or CAS fails or count
* saturated, chain to version with full retry loop.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); //@1 start
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1; // @1 end
int r = sharedCount(c);
if (!readerShouldBlock() &&
r < MAX_COUNT &&
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { // @2
if (r == 0) { //@21
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) { //@22
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else { // @23
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != current.getId())
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
}
return 1;
}
return fullTryAcquireShared(current); // @3
}
final boolean readerShouldBlock() {
/* As a heuristic to avoid indefinite writer starvation,
* block if the thread that momentarily appears to be head
* of queue, if one exists, is a waiting writer. This is
* only a probabilistic effect since a new reader will not
* block if there is a waiting writer behind other enabled
* readers that have not yet drained from the queue.
*/
return apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive(); //该方法,具体又是在 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer中
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if the apparent first queued thread, if one
* exists, is waiting in exclusive mode. If this method returns
* {@code true}, and the current thread is attempting to acquire in
* shared mode (that is, this method is invoked from {@link
* #tryAcquireShared}) then it is guaranteed that the current thread
* is not the first queued thread. Used only as a heuristic in
* ReentrantReadWriteLock.
*/
final boolean apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive() {
Node h, s;
return (h = head) != null &&
(s = h.next) != null &&
!s.isShared() &&
s.thread != null;
}
当前线程占有写锁,并且没有有其他写锁在当前线程的下一个节点等待获取写锁。;其实如果是这种情况,除非当前线程占有锁的下个线程取消,否则进入fullTryAcquireShared方法也无法获取锁。
/**
* Full version of acquire for reads, that handles CAS misses
* and reentrant reads not dealt with in tryAcquireShared.
*/
final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {
/*
* This code is in part redundant with that in
* tryAcquireShared but is simpler overall by not
* complicating tryAcquireShared with interactions between
* retries and lazily reading hold counts.
*/
HoldCounter rh = null;
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) { //@31
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
// else we hold the exclusive lock; blocking here
// would cause deadlock.
} else if (readerShouldBlock()) { //@32
// Make sure we're not acquiring read lock reentrantly
if (firstReader == current) { //@33
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
} else { //@34
if (rh == null) {
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != current.getId()) {
rh = readHolds.get();
if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.remove();
}
}
if (rh.count == 0)
return -1;
}
}
if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) { // @35
if (sharedCount(c) == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
if (rh == null)
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != current.getId())
rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release
}
return 1;
}
}
}
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) //@1
doAcquireShared(arg); //@2
}
/**
* Acquires in shared uninterruptible mode.
* @param arg the acquire argument
*/
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED); //@1
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) { // @2,开始自旋重试
final Node p = node.predecessor(); // @3
if (p == head) { // @4
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r); //@5
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt()) // @6
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
/**
* Sets head of queue, and checks if successor may be waiting
* in shared mode, if so propagating if either propagate > 0 or
* PROPAGATE status was set.
*
* @param node the node
* @param propagate the return value from a tryAcquireShared
*/
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head; // Record old head for check below
setHead(node);
/*
* Try to signal next queued node if:
* Propagation was indicated by caller,
* or was recorded (as h.waitStatus) by a previous operation
* (note: this uses sign-check of waitStatus because
* PROPAGATE status may transition to SIGNAL.)
* and
* The next node is waiting in shared mode,
* or we don't know, because it appears null
*
* The conservatism in both of these checks may cause
* unnecessary wake-ups, but only when there are multiple
* racing acquires/releases, so most need signals now or soon
* anyway.
*/
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0) { // @1
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.isShared()) // @2
doReleaseShared(); //@3
}
}
/**
* Sets head of queue to be node, thus dequeuing. Called only by
* acquire methods. Also nulls out unused fields for sake of GC
* and to suppress unnecessary signals and traversals.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void setHead(Node node) {
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
/**
* Release action for shared mode -- signal successor and ensure
* propagation. (Note: For exclusive mode, release just amounts
* to calling unparkSuccessor of head if it needs signal.)
*/
private void doReleaseShared() {
/*
* Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other
* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual
* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs
* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to
* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.
* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added
* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of
* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status
* fails, if so rechecking.
*/
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) { //@4
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) { //@5
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE)) //@6
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed //@7
break;
}
}
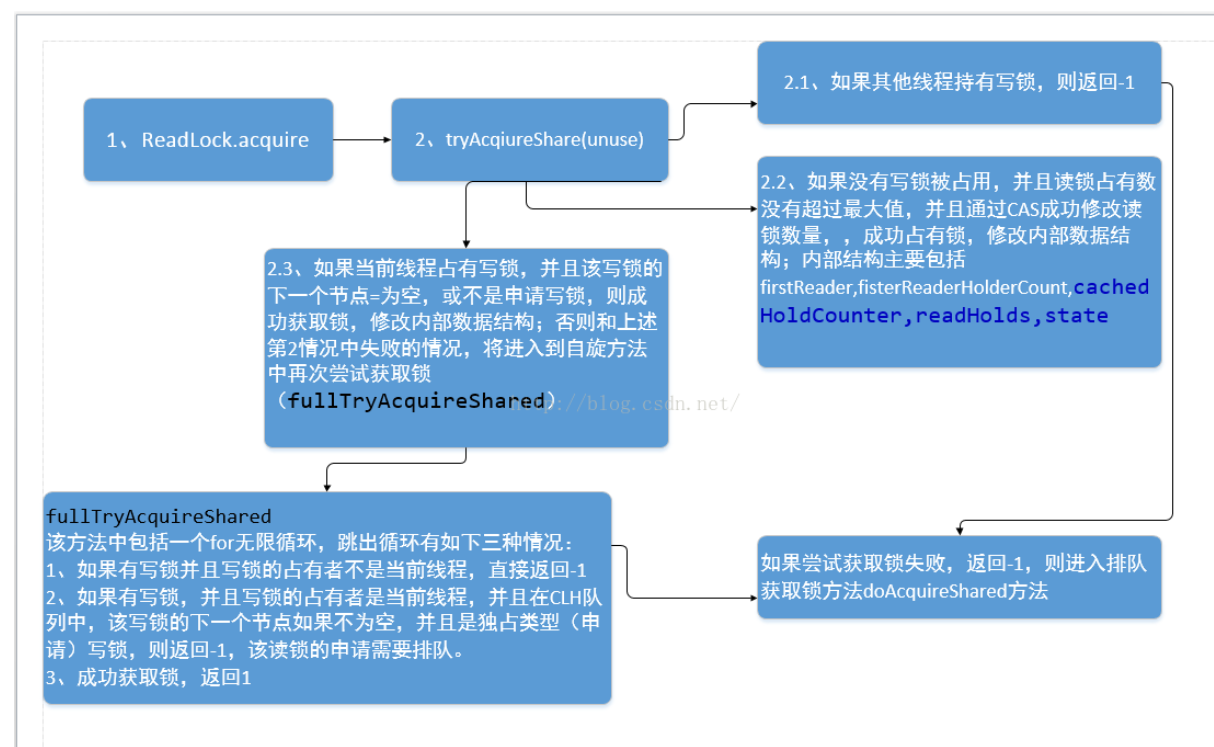
尝试获取读锁过程
从队列中获取读锁的流程如下:
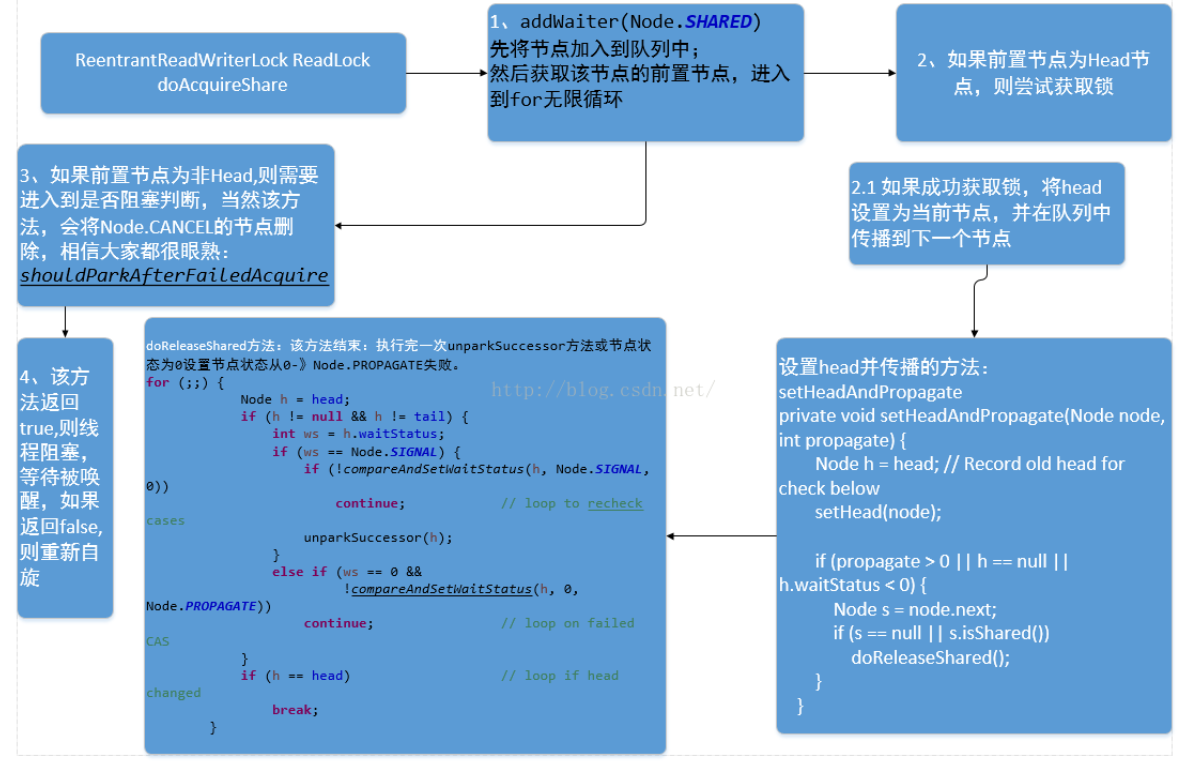
2.1.2 ReadLock 的 unlock方法详解
public void unlock() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
//AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的 realseShared方法
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ReentrantReadWriterLock.Sync tryReleaseShared
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (firstReader == current) { // @1 start
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
firstReader = null;
else
firstReaderHoldCount--;
} else {
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != current.getId())
rh = readHolds.get();
int count = rh.count;
if (count <= 1) {
readHolds.remove();
if (count <= 0)
throw unmatchedUnlockException();
}
--rh.count; // @1 end
}
for (;;) { // @2
int c = getState();
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
// Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,
// but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if
// both read and write locks are now free.
return nextc == 0;
}
}
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的doReleaseShared
/**
* Release action for shared mode -- signal successor and ensure
* propagation. (Note: For exclusive mode, release just amounts
* to calling unparkSuccessor of head if it needs signal.)
*/
private void doReleaseShared() {
/*
* Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other
* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual
* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs
* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to
* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.
* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added
* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of
* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status
* fails, if so rechecking.
*/
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
对上述代码是不是似曾相识,对了,在学习ReentrantLock时候,看到的一样,acquire是在AbstractQueuedSynchronizer中,关键是在 tryAcquire方法,是在不同的子类中实现的。那我们将目光移到ReentrantReadWriterLock.Sync中
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If read count nonzero or write count nonzero
* and owner is a different thread, fail.
* 2. If count would saturate, fail. (This can only
* happen if count is already nonzero.)
* 3. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for lock if
* it is either a reentrant acquire or
* queue policy allows it. If so, update state
* and set owner.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
if (c != 0) { // @1
// (Note: if c != 0 and w == 0 then shared count != 0)
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) //@2
return false;
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// Reentrant acquire
setState(c + acquires); //@3
return true;
}
if (writerShouldBlock() ||
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires)) //@4
return false;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); //@5
return true;
}


java并发锁ReentrantReadWriteLock读写锁源码分析的更多相关文章
- 多线程高并发编程(4) -- ReentrantReadWriteLock读写锁源码分析
背景: ReentrantReadWriteLock把锁进行了细化,分为了写锁和读锁,即独占锁和共享锁.独占锁即当前所有线程只有一个可以成功获取到锁对资源进行修改操作,共享锁是可以一起对资源信息进行查 ...
- java读写锁源码分析(ReentrantReadWriteLock)
读锁的调用,最终委派给其内部类 Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer /** * 获取读锁,如果写锁不是由其他线程持有,则获取并立即返回: * 如果写锁被其他 ...
- Java并发编程笔记之ReentrantLock源码分析
ReentrantLock是可重入的独占锁,同时只能有一个线程可以获取该锁,其他获取该锁的线程会被阻塞后放入该锁的AQS阻塞队列里面. 首先我们先看一下ReentrantLock的类图结构,如下图所示 ...
- Java并发编程笔记之AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析
为什么要说AbstractQueuedSynchronizer呢? 因为AbstractQueuedSynchronizer是JUC并发包中锁的底层支持,AbstractQueuedSynchroni ...
- Java并发编程笔记之CopyOnWriteArrayList源码分析
并发包中并发List只有CopyOnWriteArrayList这一个,CopyOnWriteArrayList是一个线程安全的ArrayList,对其进行修改操作和元素迭代操作都是在底层创建一个拷贝 ...
- Java并发编程笔记之ThreadLocal源码分析
多线程的线程安全问题是微妙而且出乎意料的,因为在没有进行适当同步的情况下多线程中各个操作的顺序是不可预期的,多线程访问同一个共享变量特别容易出现并发问题,特别是多个线程需要对一个共享变量进行写入时候, ...
- Java并发编程中线程池源码分析及使用
当Java处理高并发的时候,线程数量特别的多的时候,而且每个线程都是执行很短的时间就结束了,频繁创建线程和销毁线程需要占用很多系统的资源和时间,会降低系统的工作效率. 参考http://www.cnb ...
- Java并发编程笔记之CyclicBarrier源码分析
JUC 中 回环屏障 CyclicBarrier 的使用与分析,它也可以实现像 CountDownLatch 一样让一组线程全部到达一个状态后再全部同时执行,但是 CyclicBarrier 可以被复 ...
- Java并发编程笔记之PriorityBlockingQueue源码分析
JDK 中无界优先级队列PriorityBlockingQueue 内部使用堆算法保证每次出队都是优先级最高的元素,元素入队时候是如何建堆的,元素出队后如何调整堆的平衡的? PriorityBlock ...
随机推荐
- RSTP生成树
一.实验目的 二.实验拓扑图 三.实验编址 四.实验步骤 1.基本步骤 配置PC机IP 配置完成,开启所有设备,测试主机之间连通性 2.配置RSTP基本功能 在四台交换机上修改生成树模式:配置完成后, ...
- ELK+filebeat+redis 日志分析平台
一.简介 ELK Stack是软件集合Elasticsearch.Logstash.Kibana的简称,由这三个软件及其相关的组件可以打造大规模日志实时处理系统. 其中,Elasticsearch 是 ...
- Codeforces 500D New Year Santa Network(树 + 计数)
D. New Year Santa Network time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input st ...
- 发送xml数据
- 数组Array的十种使用方法
第一种方法 array toString () 将数组的元素全部转换为字符串; 第二种方法 array join ("这里是分隔符") 这种方法可以把数组的元素转换为字符串,并把分 ...
- python 发送请求
data = {"a":1,"b":2} urllib2 get: get_data = urllib.urlencode(data) req_url = UR ...
- eclipse中服务器找不到项目怎么解决
在我们运行项目前,都需要将项目部署到tomcat上,但是有时我们会遇到这种情况:项目明明存在,但是eclipse中tomcat的add and remove找不到项目,无法部署,那么这个问题该如何解决 ...
- C++ 排序(未完)
参考: 快速排序 堆排序 各类排序 #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <time.h> #include ...
- boost库:智能指针
1. C98里的智能指针 std::auto_ptr ,本质上是一个普通的指针,通过地址来访问你一个动态分配的对象,初始化时需要传递一个由new操作符返回的对象地址. std::auto_ptr的析构 ...
- qt学习(二):启动画面
打开一个软件,都会有启动画面. 现在去体验如何实现启动画面:输入图,装载,延时,下一张主部件图 在main.Cpp中实现启动时桌面图片. #include <QtGui/QApplication ...
