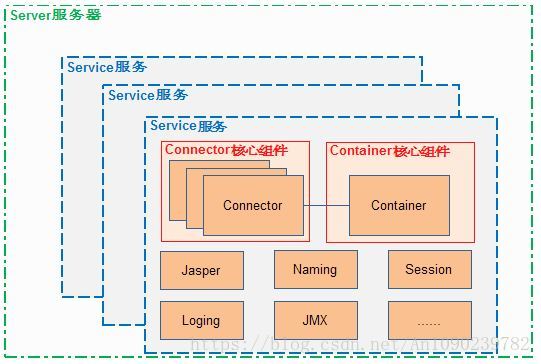
Tomcat 核心组件 Container容器相关
前言
Connector把封装了Request对象以及Response对象的Socket传递给了Container容器,那么在Contianer容器中又是怎么样的处理流程呢?在说Container容器之前,有必要对Container容器有一个简单的了解,Container容器是子容器的父接口,所有的子容器都必须实现这个接口,在Tomcat中Container容器的设计是典型的责任链设计模式,其有四个子容器:Engine、Host、Context和Wrapper。这四个容器之间是父子关系,Engine容器包含Host,Host包含Context,Context包含Wrapper。
我们在web项目中的一个Servlet类对应一个Wrapper,多个Servlet就对应多个Wrapper,当有多个Wrapper的时候就需要一个容器来管理这些Wrapper了,这就是Context容器了,Context容器对应一个工程,所以我们新部署一个工程到Tomcat中就会新创建一个Context容器。Container容器的处理过程也比较复杂,下面是一个大概的流程:
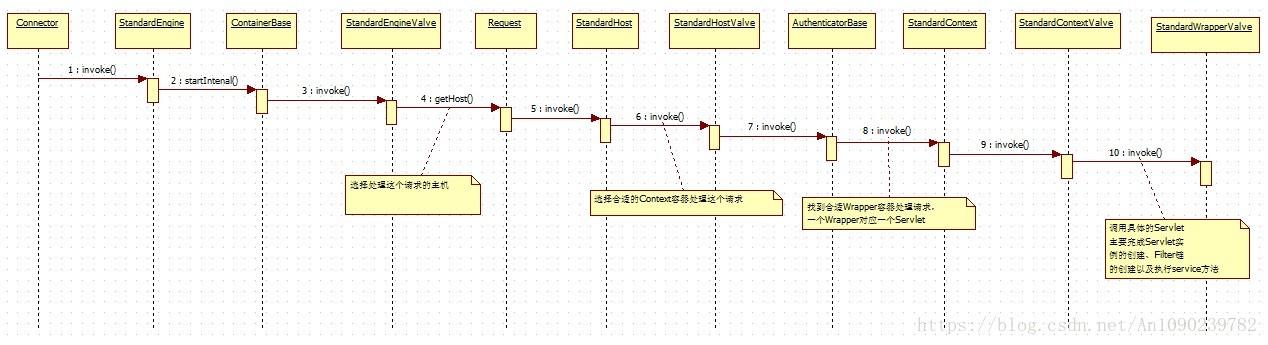
上面出现了Pipeline与Valve,这两个对象可以分别理解为管道与管道中闸门,当收到从Connector的请求后,这个请求要通过一个个管道以及管道中一个个的闸门,只有全部通过才能最终被具体的Servlet处理。要注意的是,每一个容器都有自己的管道和闸门,这些管道与闸门都是由容器自身老控制的,所以我们可以看到注入StandardEngineValve等类了。
下面就从Container容器的四个子容器入手,分析每一个容器是怎么样处理的:
Engine容器
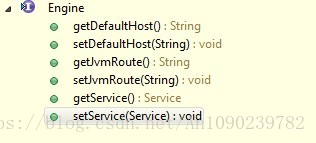
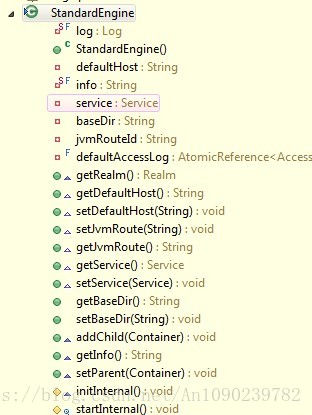
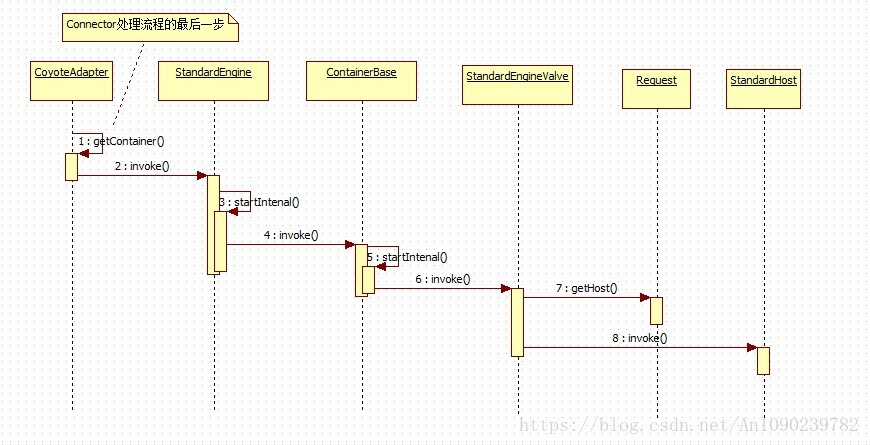
Engine容器包含Host容器,根据文章第一部分的架构图,可以知道其管理的容器是Host,Engine是一个接口,其标准实现类是StandardEngine,下面是其类结构图:
注意其中的addChild方法,其类型是Container,但是其实际管理的就是Host容器。Engine容器处理请求的流程可以简化如下:
在刚开始的流程图中调用了StandardEngineValve的invoke方法,这个方法的具体实现如何呢?
/**
* Select the appropriate child Host to process this request,
* based on the requested server name. If no matching Host can
* be found, return an appropriate HTTP error.
*
* @param request Request to be processed
* @param response Response to be produced
*
* @exception IOException if an input/output error occurred
* @exception ServletException if a servlet error occurred
*/
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Host to be used for this Request
Host host = request.getHost();
if (host == null) {
response.sendError
(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST,
sm.getString("standardEngine.noHost",
request.getServerName()));
return;
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
// Ask this Host to process this request
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}可以看到这个方法的任务就是选择可用的Host容器处理当前的请求,选择Host容器后,就调用其invoke方法,所以具体的处理就转移到了Host容器。
Host容器
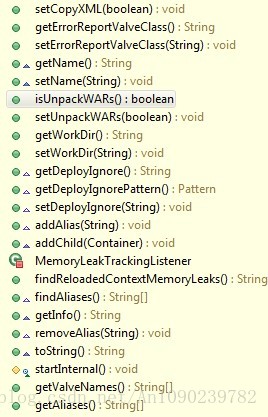
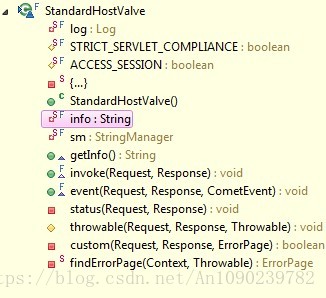
Host容器是Engine容器的子容器,上面也说到Host是受Engine容器管理的,就是指一个虚拟主机,比如我们在访问具体jsp页面URL中localhost就是一个虚拟主机,其作用是运行多个应用,并对这些应用进行管理,其子容器是Context,而且一个主机还保存了主机的相关信息。Host的标准实现类是StandardHost,其闸门实现是StandardHostValve,下面是StandardHost与StandardHostValve的类结构图:
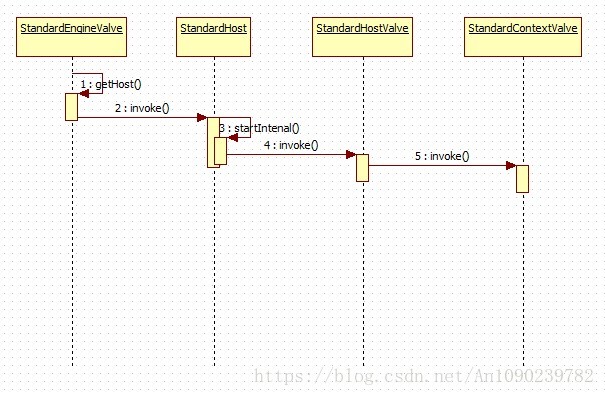
Host容器的处理流程可以简化如下:
接着我们回到Engine容器的invoke方法,下面是host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response)的方法源码:
@Override
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Select the Context to be used for this Request
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
response.sendError
(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR,
sm.getString("standardHost.noContext"));
return;
}
// Bind the context CL to the current thread
if( context.getLoader() != null ) {
// Not started - it should check for availability first
// This should eventually move to Engine, it's generic.
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction<Void> pa = new PrivilegedSetTccl(
context.getLoader().getClassLoader());
AccessController.doPrivileged(pa);
} else {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
(context.getLoader().getClassLoader());
}
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(context.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
// Don't fire listeners during async processing
// If a request init listener throws an exception, the request is
// aborted
boolean asyncAtStart = request.isAsync();
// An async error page may dispatch to another resource. This flag helps
// ensure an infinite error handling loop is not entered
boolean errorAtStart = response.isError();
if (asyncAtStart || context.fireRequestInitEvent(request)) {
// Ask this Context to process this request
try {
context.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
if (errorAtStart) {
container.getLogger().error("Exception Processing " +
request.getRequestURI(), t);
} else {
request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, t);
throwable(request, response, t);
}
}
// If the request was async at the start and an error occurred then
// the async error handling will kick-in and that will fire the
// request destroyed event *after* the error handling has taken
// place
if (!(request.isAsync() || (asyncAtStart &&
request.getAttribute(
RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION) != null))) {
// Protect against NPEs if context was destroyed during a
// long running request.
if (context.getState().isAvailable()) {
if (!errorAtStart) {
// Error page processing
response.setSuspended(false);
Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(
RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);
if (t != null) {
throwable(request, response, t);
} else {
status(request, response);
}
}
context.fireRequestDestroyEvent(request);
}
}
}
// Access a session (if present) to update last accessed time, based on a
// strict interpretation of the specification
if (ACCESS_SESSION) {
request.getSession(false);
}
// Restore the context classloader
if (Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction<Void> pa = new PrivilegedSetTccl(
StandardHostValve.class.getClassLoader());
AccessController.doPrivileged(pa);
} else {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
(StandardHostValve.class.getClassLoader());
}
}其处理过程可以总结如下:
- 为特定的请求URL选择一个Context容器
- 把Context容器绑定到线程中
- 判断是否是一个异步请求
- 让Context去处理这个请求
- Context执行invoke方法,进入管道中,由StandardContextValve(是ContextValve的标准实现类)处理
原文博主:rhwayfunn
Tomcat 核心组件 Container容器相关的更多相关文章
- Tomcat是什么:Tomcat与Java技、Tomcat与Web应用以及Tomcat基本框架及相关配置
1.Tomcat是什么 Apache Tomcat是由Apache Software Foundation(ASF)开发的一个开源Java WEB应用服务器. 类似功能的还有:Jetty. ...
- tomcat(5)servlet容器
[0]README 0.0)本文部分文字描写叙述转自:"深入剖析tomcat",旨在学习 tomcat(5)servlet容器 的基础知识. 0.1)intro to servle ...
- 带你走进EJB--那些跟EJB容器相关的那些Java概念
最近在对EJB的相关内容进行总结,在总结的过程中发现对容器的概念并不是很理解,因为EJB本身就是一个容器,但是容器到底是用来做什么的?它跟我们之前所了解的组件,框架,包,类等都有什么关系?接下来主要是 ...
- JSP学习 —— 开篇:JSP,servlet容器,Tomcat,servlet容器之间的关系
JSP(JAVA SERVER PAGE)的缩写,其本身就是servlet的简化,是一种动态网页标准,其特点是在HTML代码中嵌入JAVA代码,JSP标签或用户标签来生成网页.至于它为什么会出现,主要 ...
- Docker 0x01:Docker Container容器技术
目录 Docker Container容器技术 一句话回答什么是容器? 为什么要有容器? 容器技术的影响 容器技术浅谈原理,怎么实现的?为什么能够这样轻量级标准化 难点 容器的标准 花边 Docker ...
- Docker容器化【Docker镜像与容器相关命令】
# Docker 学习目标: 掌握Docker基础知识,能够理解Docker镜像与容器的概念 完成Docker安装与启动 掌握Docker镜像与容器相关命令 掌握Tomcat Nginx 等软件的常用 ...
- How tomcat works(深入剖析tomcat)servlet容器
How tomcat works (5)servlet容器阅读笔记 第四章阅读了tomcat默认连接器的实现,当时connector中的使用的容器是自定义的容器,也是非常之简单奥,一个人就干完了所有的 ...
- Tomcat 核心组件 Connector
Connector是Tomcat的连接器,其主要任务是负责处理浏览器发送过来的请求,并创建一个Request和Response的对象用于和浏览器交换数据,然后产生一个线程用于处理请求,Connecto ...
- Tomcat就是个容器,一种软件
1.tomcat就是一个容器而已,一个软件,运行在java虚拟机. 2.tomcat是一种能接收http协议的软件,java程序猿自己也可以写出http解析的服务器啊. 3.tomcat支持servl ...
随机推荐
- 实现连续登录X天送红包这个连续登录X天算法
实现用户只允许登录系统1次(1天无论登录N次算一次) //timeStamp%864000计算结果为当前时间在一天当中过了多少秒 //当天0点时间戳 long time=timeStamp-timeS ...
- TurtleBot 3 & 2i ROS开源实验平台
TurtleBot 3 & 2i ROS开源实验平台,全球更受欢迎的ROS平台. TurtleBot是ROS标准平台机器人,在全球开发人员和学生中深受欢迎.其有3个版本: TurtleBot1 ...
- Java利用VLC开发简易视屏播放器
1.环境配置 (1)下载VLC VlC官网http://www.videolan.org/ 各个版本的下载地址http://download.videolan.org/pub/videolan ...
- post传参数 传json格式参数
如下: const dataObject = JSON.stringify({ "base64str" ...
- Spring用了哪些设计模式?
设计模式是一套被反复使用的.多数人知晓的.经过分类编目的.代码设计经验的总结.总共有 23 种设计模式 使用设计模式是为了重用代码.让代码更容易被他人理解.保证代码可靠性. Spring用了哪些设计模 ...
- SQL注入之堆叠注入(堆查询注入)
Stached injection -- 堆叠注入 0x00 堆叠注入的定义 Stacked injection 汉语翻译过来后,称 为堆查询注入,也有称之为堆叠注入.堆叠注入为攻击者提供了很多的 ...
- 最新最简洁Spring Cloud Oauth2.0 Jwt 的Security方式
因为Spring Cloud 2020.0.0和Spring Boot2.4.1版本升级比较大,所以把我接入过程中的一些需要注意的地方告诉大家 我使用的版本是Spring boot 2.4.1+Spr ...
- 十四:SQL注入之类型及提交注入
简要明确参数类型 数字,字符,搜索,json等 简要明确请求方法 GET,POST,COOKIE,REQUEST,HTTP头 其中SQL语句干扰符号:' " % ) } 等,具体查看用法 非 ...
- 从一次生产消费者的bug看看线程池如何增加线程
0 背景 某个闲来无事的下午,看到旧有的项目中,有个任务调度的地方都是同步的操作,就是流程A的完成依赖流程B,流程B的完成依赖流程C,按此类推. 作为一名垃圾代码生产者,QA的噩梦.故障报告枪手的我来 ...
- 【Linux】添加硬盘不需要重启服务器
添加硬盘之后,不用重启服务器 执行下面的语句 ls /sys/class/scsi_host 查看下面有多少host 我这里有三个host 分别执行 echo "- - -" &g ...