mybatis 动态SQL 源码解析
摘要
mybatis是个人最新喜欢的半自动ORM框架,它实现了SQL和业务逻辑的完美分割,今天我们来讨论一个问题,mybatis 是如何动态生成SQL
SqlSessionManager sqlSessionManager;
DataSource dataSource = new PooledDataSource(driver,url,username,pass);
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = new JdbcTransactionFactory();
Environment environment = new Environment("development", transactionFactory, dataSource);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(environment);
//设定解析mpper.xml位置
String resource = "mybatis/ApplicationMapper.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
// 解析 ****mapper.xml中SQL入口(这里偷懒懒,直接组装好configuration啦)
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(configuration);
// 执行SQL的入口方法 步骤①:获取参数,②:拼接SQL,③:执行
BizApp bizApp = sqlSessionFactory.openSession().getMapper(ApplicationMapper.class).queryByAppid("1000002715");
mybatis 解析mpper.xml中内容,动态生成SQL由2部分组成
①:解析动态SQL 解析xml 保存各种信息到XMLMapperBuilder和Configuration属性中,主要xml 节点保存在以下属性中
sql 解析 保存位置XmlMapperBuilderMap<String, XNode> sqlFragments
resultMap 解析 保存位置 XmlMapperBuilder类属性Configuration Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<ResultMap>("Result Maps collection");
select/update/insert/delete 解析 保存位置 XmlMapperBuilder类属性Configuration Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection");
②:执行前,拼接动态SQL
听起来很简单,但是mybatis源码看起来还是相当复杂的,很佩服mybatis 的源码开发人员(膜拜)
mybatis解析方法
mybatis 中之所以存在动态SQL,最主要的原因是因为,mybatis给大家提供了动态标签,这个给大家使用Mybatis 带来了很大的便利,但是这个也大大提高了解析xml中SQL的难度
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
- trim (where, set)
- foreach
mybatis 主要采用OGNL+组合模式来完成解析的,我们直接上手源码看一下
如:解析以下ApplicationMapper.xml中的SQL,mybatis流程什么样的 ???
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
id,biz_code,appid,appname,domain,sort,isactive, inserttime, updatetime
</sql>
//要解析的SQL SQL_TEST 开始
<select id="queryByAppid" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="Base_Column_List"/>
from application
where isactive=1
<if test="appid!=null">
and appid=#{appid}
</if>
</select>
//SQL_TEST 结束
//解析ApplicationMapper.xml入口方法
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(InputStream inputStream)
--->parser.parse()
--->parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"))
--->mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
--->mapperParser.parse();
--->configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
//最终解析ApplicationMapper.xml方法处
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
//动态标签解析处,最终调用方法parseStatementNode
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
实际代码解析处
public void parseStatementNode() {
省略.....
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
/**
重点代码,
①:调用XMLLanguageDriver的createSqlSource
②:builder.parseScriptNode(); 解析具体SQL内容,具体请看下面分析
**/
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
省略......
}
解析XML内容,并分解SQL
XMLScriptBuilder builder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
builder.parseScriptNode();
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
//这句话就是解析上面SQL_TEST结果
//后面拼接完整SQL就靠它啦,具体怎么玩,后面分析
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);

SqlSource sqlSource = null;
if (isDynamic) {
//只要XML中有动态标签就选择DynamicSqlSource
//DynamicSqlSource和RawSqlSource 不同点在于只有在执行前才知道完整预编译的SQL
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}
以上是mybatis解析动态SQL完整流程,只将动态SQL分解啦,其他什么都没做
下面是执行前拼接动态SQL的完整流程
//执行方法,sqlSessionFactory.openSession().getMapper(ApplicationMapper.class).queryByAppid("1000002715","appName");
//执行上述方法,其实这是一个动态代理的过程,最终调用MapperProxy.invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
//参数名称解析
//主要如何定义参数名称和设置值,方法queryByAppid("1000002715","appName");
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//方法执行
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
//参数名称源码分析
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
} public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
} public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
//省略....
//重点代码
this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method);
} //最终解析方法名处
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
//参数数组
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
//每个参数前注解数组
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
//参数名存放地点
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// get names from @Param annotations
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
// skip special parameters
continue;
}
String name = null;
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
//如果参数前有有Param注解,参数名为注解中value值
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
hasParamAnnotation = true;
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
if (name == null) {
// @Param was not specified.
// 木有@Param注解,则参数名为arg0,arg1......
if (config.isUseActualParamName()) {
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
if (name == null) {
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// gcode issue #71
name = String.valueOf(map.size());
}
}
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}
最终效果类似如下:names 中存放的值,key:参数位置,value:参数名称
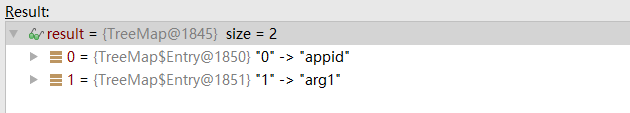
//方法执源码分析
//①将参数名和参数值对应起来,
//②动态拼接SQL,
//③SQL执行
mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
省略.....
}
case UPDATE: {
省略.....
}
case DELETE: {
省略.....
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
//将参数名和参数值对应起来,效果如下,param 存放的值

Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//具体拼接SQL和执行SQL,底层调用的BaseExecutor.query方法
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
//BaseExecutor.query方法
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//具体拼接SQL
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
} public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
省略.....
return boundSql;
} //这里调用的是DynamicSqlSource.getBoundSql,因为xmL中有动态标签
//这里采用经典组合模式+OGNL完成标签解析和拼接完整SQL,终于大结局啦
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
//组合模式,并将SQL拼接结果存放到context中
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : context.getBindings().entrySet()) {
boundSql.setAdditionalParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
return boundSql;
}
这里的SQL 拼接,解释一下,首先这个rootSqlNode 为MixedSqlNode 类型,(不知道说的是啥,看前面的分解SQL内容贴的debug调试图)
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
for (SqlNode sqlNode : contents) {
sqlNode.apply(context);
}
return true;
}
MixedSqlNode 这个类有一个集合属性List<SqlNode> contents,apply 就是遍历它,普通的文本为StaticTextSqlNode在组合模式中这个就是叶子节点,不需要任何转换直接拼接SQL
我们XML有IF动态标签,所以它会调用IfSqlNode.apply 方法
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
//调用OGNL解析if标签,test文本,是否满足条件<if test="appid!=null">
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
//符合条件,向下遍历
contents.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
总结
mybatis动态SQL生成,它主要是通过遍历XML中每行语句(某个具体的语句),遇到纯文本,直接封装成StaticTextSqlNode节点(普通文本,叶子节点,可直接拼接SQL)
遇到动态标签,直接封装成IfSqlNode,TrimSqlNode......(树枝节点,需要靠OGNL来解析文本,视解析结果来拼接SQL),以及包含上述所有的节点的根节点
(MixedSqlNode),拼接SQL时,只要从根节点向下遍历即可拼接出完整SQL
//SQL_TEST 结束
StaticTextSqlNode
mybatis 动态SQL 源码解析的更多相关文章
- Spark SQL源码解析(三)Analysis阶段分析
Spark SQL原理解析前言: Spark SQL源码剖析(一)SQL解析框架Catalyst流程概述 Spark SQL源码解析(二)Antlr4解析Sql并生成树 Analysis阶段概述 首先 ...
- Spark SQL源码解析(四)Optimization和Physical Planning阶段解析
Spark SQL原理解析前言: Spark SQL源码剖析(一)SQL解析框架Catalyst流程概述 Spark SQL源码解析(二)Antlr4解析Sql并生成树 Spark SQL源码解析(三 ...
- Spark SQL源码解析(五)SparkPlan准备和执行阶段
Spark SQL原理解析前言: Spark SQL源码剖析(一)SQL解析框架Catalyst流程概述 Spark SQL源码解析(二)Antlr4解析Sql并生成树 Spark SQL源码解析(三 ...
- Spark SQL源码解析(二)Antlr4解析Sql并生成树
Spark SQL原理解析前言: Spark SQL源码剖析(一)SQL解析框架Catalyst流程概述 这一次要开始真正介绍Spark解析SQL的流程,首先是从Sql Parse阶段开始,简单点说, ...
- mybatis通用mapper源码解析(二)
1.javabean的属性值生成sql /** * 获取所有查询列,如id,name,code... * * @param entityClass * @return */ public static ...
- drupal sql 源码解析query.inc 文件
query.inc 文件: sql语句: $this->condition($field);1707 line public function condition($field, $value ...
- mybatis通用mapper源码解析(一)
1.配置JavaBean与数据库表字段映射关系 /** * 字段转换方式 */ public enum Style { normal, //原值 camelhump, //驼峰转下划线 upperca ...
- MyBatis源码解析之数据源(含数据库连接池简析)
一.概述: 常见的数据源组件都实现了javax.sql.DataSource接口: MyBatis不但要能集成第三方的数据源组件,自身也提供了数据源的实现: 一般情况下,数据源的初始化过程参数较多,比 ...
- Spring源码解析系列汇总
相信我,你会收藏这篇文章的 本篇文章是这段时间撸出来的Spring源码解析系列文章的汇总,总共包含以下专题.喜欢的同学可以收藏起来以备不时之需 SpringIOC源码解析(上) 本篇文章搭建了IOC源 ...
随机推荐
- Google Cayley图数据库使用方法
最近在用Golang做流程引擎,对于流程图的存储,我看到了Google的Cayley图数据库,感觉它可能会比较适合我的应用,于是便拿来用了用. 项目地址在这里:https://github.com/g ...
- Jmeter CSV数据文件设置使用之一
第一步: 在Jmeter 里,新建CSV数据文件设置,选择对应的文件,变量名称根据需要自己取,如bug,test,如下图所示: 第二步: 配置Jmetet 数据源,参数对应的名称要与CSV数据文件设置 ...
- [Luogu P2387] [NOI2014]魔法森林 (LCT维护边权)
题面 传送门:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P2387 Solution 这题的思想挺好的. 对于这种最大值最小类的问题,很自然的可以想到二分答案.很不幸 ...
- hadoop使用实例
一.词频统计 1.下载喜欢的电子书或大量文本数据,并保存在本地文本文件中 2.编写map与reduce函数 3.本地测试map与reduce 4.将文本数据上传至HDFS上 5.用hadoop str ...
- 浅谈Linux桌面(发行版及桌面环境)
Part I: 前言 笔者2018年接触Linux(当时还是学校机房的Ubuntu 14.04 LTS),至今已经有4个年头了. 折腾了至少十几个Linux发行版,包括但不限于: ubuntu.Deb ...
- Java进阶专题(十六) 数据结构与算法的应用(上)
前言 学习算法,我们不需要死记硬背那些冗长复杂的背景知识.底层原理.指令语法--需要做的是领悟算法思想.理解算法对内存空间和性能的影响,以及开动脑筋去寻求解决问题的最佳方案.相比编程领域的其他技术 ...
- Elasticsearch 注册windows服务后,服务启动失败,意外终止
直接双击elasticsearch.bat可以成功启动,注册成服务后就启动失败 从网上查找问题,发现是jdk版本的问题,用ES自带的jdk就可以启动成功. 默认ES会先找JAVA_HOME环境变量,如 ...
- [阿里DIN] 从模型源码梳理TensorFlow的乘法相关概念
[阿里DIN] 从模型源码梳理TensorFlow的乘法相关概念 目录 [阿里DIN] 从模型源码梳理TensorFlow的乘法相关概念 0x00 摘要 0x01 矩阵乘积 1.1 matmul pr ...
- Python如何快速复制序列?
1 基本用法 把序列乘以一个整数,就会产生一个新序列.这个新序列是原始序列复制了整数份,然后再拼接起来的结果. l=[1,2,3] l2=l * 3 logging.info('l2 -> %s ...
- [MIT6.006] 23. Computational Complexity 计算复杂度
这节课主要讲的计算复杂度,一般有三种表达不同程度的计算复杂度,如下图所示: P:多项式时间: EXP:指数时间: R:有限时间内. 上图还给了一些问题的计算复杂度的对应结果,关于一些细节例如NP, N ...
