hystrix(3) 熔断器
讲完metrics我们就来了解一下熔断器的执行情况,熔断器的判断取决metrics数据。
hystrix在执行命令前需要经过熔断器判断,如果服务被熔断,则执行fallback流程,熔断判断逻辑如下:
- 如果强制未开启,返回true(未熔断)。
- 如果强制开启,返回false(熔断)。
- 判断熔断标识
- 如果未熔断则返回true。
- 如果half_open,返回false(熔断)。
- 如果熔断,判断当前时间是否超过短路窗口期,
- 如果没有超过,返回false。
- 如果超过则返回true。 并设置熔断状态为half_open。
命令执行失败后逻辑如下:
如果熔断标识为half_open,并重新计算短路窗口期(记录当前时间)。
如果熔断标识为close,通过命令metric组件,获取命令指定窗口时间内执行总错误数和错误率。如果实际错误率或错误数高于配置错误率或错误数,则设置熔断标识为熔断。
命令执行成功后逻辑如下:
只有在熔断状态为half_open状态下,才能解除熔断。
如果请求执行成功,解除熔断。
熔断器还会监听metrics数据流,当错误比率或者请求量大于配置的值时,就会设置熔断标识为熔断。每个commandkey都会对应一个熔断器。
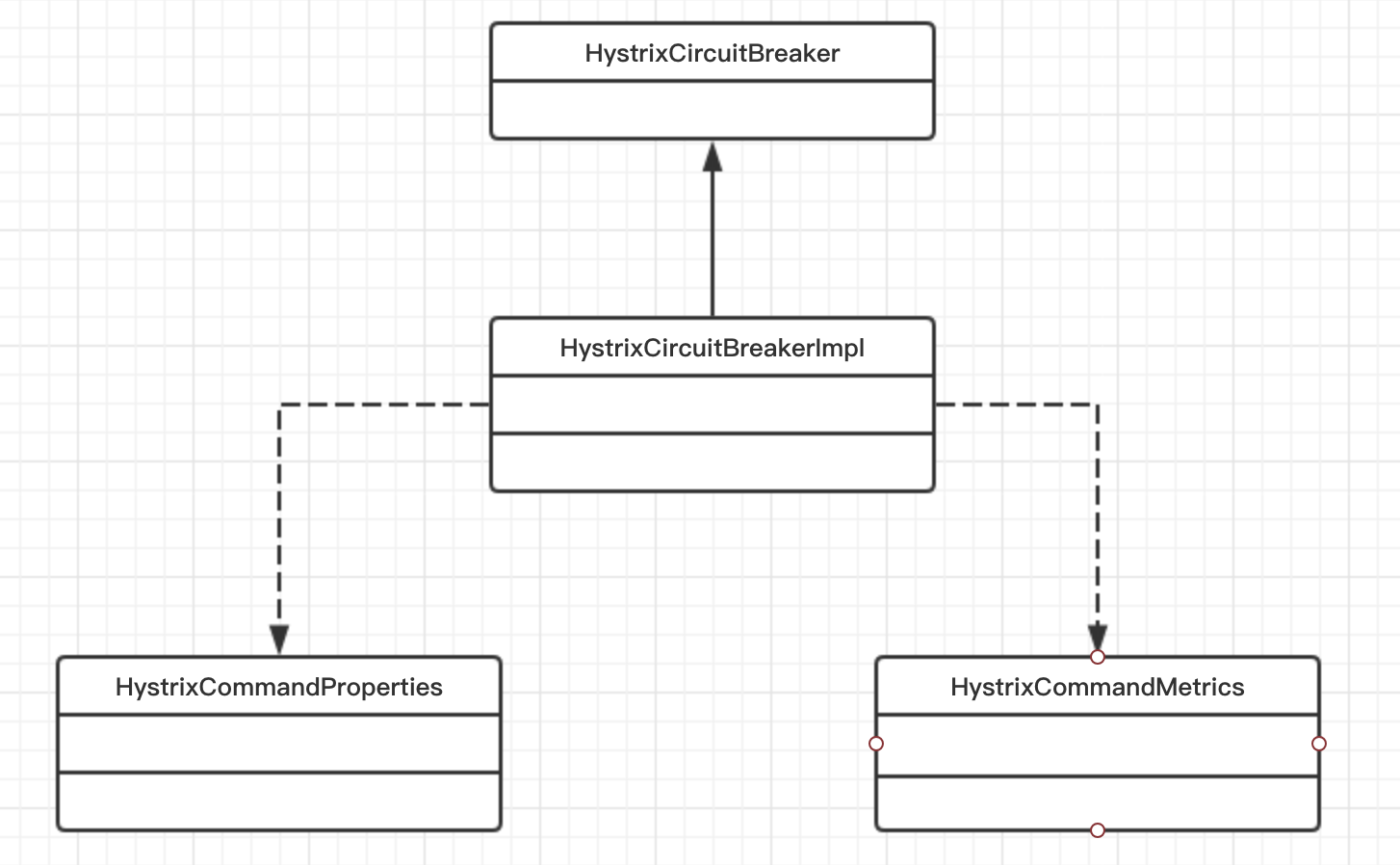
熔断器判断
private Observable<R> applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) {
...
if (circuitBreaker.allowRequest()) {
...
return executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd)
.doOnError(markExceptionThrown)
.doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease)
.doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease);
...
} else {
return handleShortCircuitViaFallback();
}
}
熔断器逻辑
static class HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl implements HystrixCircuitBreaker {
private final HystrixCommandProperties properties;
private final HystrixCommandMetrics metrics;
/* track whether this circuit is open/closed at any given point in time (default to false==closed) */
private AtomicBoolean circuitOpen = new AtomicBoolean(false);
/* when the circuit was marked open or was last allowed to try a 'singleTest' */
private AtomicLong circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime = new AtomicLong();
protected HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl(HystrixCommandKey key, HystrixCommandGroupKey commandGroup, HystrixCommandProperties properties, HystrixCommandMetrics metrics) {
this.properties = properties;
this.metrics = metrics;
}
public void markSuccess() {
if (circuitOpen.get()) {
if (circuitOpen.compareAndSet(true, false)) {
//win the thread race to reset metrics
//Unsubscribe from the current stream to reset the health counts stream. This only affects the health counts view,
//and all other metric consumers are unaffected by the reset
metrics.resetStream();
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean allowRequest() {
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceOpen().get()) {
// properties have asked us to force the circuit open so we will allow NO requests
return false;
}
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceClosed().get()) {
// we still want to allow isOpen() to perform it's calculations so we simulate normal behavior
isOpen();
// properties have asked us to ignore errors so we will ignore the results of isOpen and just allow all traffic through
return true;
}
return !isOpen() || allowSingleTest();
}
public boolean allowSingleTest() {
long timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested = circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.get();
// 1) if the circuit is open
// 2) and it's been longer than 'sleepWindow' since we opened the circuit
if (circuitOpen.get() && System.currentTimeMillis() > timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested + properties.circuitBreakerSleepWindowInMilliseconds().get()) {
// We push the 'circuitOpenedTime' ahead by 'sleepWindow' since we have allowed one request to try.
// If it succeeds the circuit will be closed, otherwise another singleTest will be allowed at the end of the 'sleepWindow'.
if (circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.compareAndSet(timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested, System.currentTimeMillis())) {
// if this returns true that means we set the time so we'll return true to allow the singleTest
// if it returned false it means another thread raced us and allowed the singleTest before we did
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isOpen() {
if (circuitOpen.get()) {
// if we're open we immediately return true and don't bother attempting to 'close' ourself as that is left to allowSingleTest and a subsequent successful test to close
return true;
}
// we're closed, so let's see if errors have made us so we should trip the circuit open
HealthCounts health = metrics.getHealthCounts();
// check if we are past the statisticalWindowVolumeThreshold
if (health.getTotalRequests() < properties.circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold().get()) {
// we are not past the minimum volume threshold for the statisticalWindow so we'll return false immediately and not calculate anything
return false;
}
if (health.getErrorPercentage() < properties.circuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage().get()) {
return false;
} else {
// our failure rate is too high, trip the circuit
if (circuitOpen.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// if the previousValue was false then we want to set the currentTime
circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
return true;
} else {
// How could previousValue be true? If another thread was going through this code at the same time a race-condition could have
// caused another thread to set it to true already even though we were in the process of doing the same
// In this case, we know the circuit is open, so let the other thread set the currentTime and report back that the circuit is open
return true;
}
}
}
}
hystrix(3) 熔断器的更多相关文章
- 分布式RPC框架Dubbo实现服务治理:集成Kryo实现高速序列化,集成Hystrix实现熔断器
Dubbo+Kryo实现高速序列化 Dubbo RPC是Dubbo体系中最核心的一种高性能,高吞吐量的远程调用方式,是一种多路复用的TCP长连接调用: 长连接: 避免每次调用新建TCP连接,提高调用的 ...
- Spring Cloud Hystrix Dashboard熔断器-Turbine集群监控(六)
序言 上一篇说啦hystrix的使用方法与配置还有工作流程及为何存在,我去,上一篇这么屌,去看看吧,没这么屌的话,我贴的有官方文档,好好仔细看看 hystrix除啦基本的熔断器功能之外,还可以对接口的 ...
- Hystrix核心熔断器
在深入研究熔断器之前,我们需要先看一下Hystrix的几个重要的默认配置,这几个配置在HystrixCommandProperties 中 //时间窗(ms) static final Integer ...
- SpringCloud学习笔记:熔断器Hystrix(5)
1. Hystrix简介 在分布式系统中,服务与服务之间相互依赖,一种不可避免的情况是某些服务会出现故障,导致依赖于它们的其他服务出现远程调度的线程阻塞. Hystrix提供熔断器功能,能够阻止分布式 ...
- 熔断器---Hystrix
Hystrix:熔断器,容错管理工具,旨在通过熔断机制控制服务和第三方库的节点,从而对延迟和故障提供更强大的容错能力. 说到熔断器,先要引入另外一个词,雪崩效应. 雪崩效应,百度百科的解释是这样的: ...
- 6、Spring Cloud -熔断器Hystrix
6.1.什么是Hystrix 在分布式系统中.服务与服务之间的依赖错综复杂,一种不可避免的情况就是某些服务 出现故障,导致依赖于它们的其他服务出现远程调度的线程阻塞. Hystrix是Netfli ...
- spring boot 2.0.3+spring cloud (Finchley)4、熔断器Hystrix
在分布式系统中服务与服务之间的依赖错综复杂,一种不可避免的情况就是某些服务会出现故障,导致依赖于他们的其他服务出现远程调度的线程阻塞.某个服务的单个点的请求故障会导致用户的请求处于阻塞状态,最终的结果 ...
- Spring-Cloud之Hystrix熔断器-5
一.在分布式系统中,服务与服务之间的依赖错综复杂,一种不可避免的情况就是某些服务会出现故障,导致依赖于它们的其他服务出现远程调度的线程阻塞 Hystrix是Netflix 公司开源的一个项目,它提供了 ...
- springCloud四:熔断器ribbon--Hystrix
注:前文概念部分摘抄自博客园 纯洁的微笑 熔断器 雪崩效应 在微服务架构中通常会有多个服务层调用,基础服务的故障可能会导致级联故障,进而造成整个系统不可用的情况,这种现象被称为服务雪崩效应.服务雪崩 ...
随机推荐
- 10.oracle分页
oracle的分页一共有三种方式 方法一 根据rowid来分 SELECT * FROM EMP WHERE ROWID IN (SELECT RID FROM (SELECT ROWNUM RN, ...
- Linux系统修改服务器系统时间
修改Linux系统时间,需要执行两个命令,如下: 第一条指令:date –s '2017-07-12 10:22:30' 第二条指令:clock –w //将日期写入CMOS
- Synergy--跨平台的键鼠共享工具
目前的状态,Windows并没有彻底放弃使用,现在一个电脑桌上摆放了一台Mac pro 一台Windows,两个笔记本都是15寸的,如果想要方便的使用外设鼠标键盘,整个桌子会异常的臃肿,鼠标键盘太占地 ...
- MYSQL经典练习题,熟悉DQL
MYSQL经典练习题 (本练习题可让你熟悉DQL,快速的上手DQL) 首先,先在数据库中建立基本数据库以及表项: DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS `test`; CREATE DATA ...
- 前端系列-CS与BS的区别
现在的系统架构有B/S与C/S之分. C/S,即Client/Server(客户端/服务器).我们一般使用的软件架构都是C/S架构,比如各个系统版本中的软件如qq管家.腾讯qq.office等.C/S ...
- python os库的使用方法 + 自动化安装第三方库脚本
一.os库基本介绍 os库提供通用的.基本的操作系统交互功能,包括windows.Mac os.linux os库是python标准库,包含几百个函数 常用路径操作.进程管理.环境参数等几类 路径操作 ...
- Unity Prefab关联
Unity3D研究院之Prefab里面的Prefab关联问题http://www.xuanyusong.com/archives/3042
- ParticleSystem 介绍
ParticleSystem 介绍 http://gad.qq.com/article/detail/31724
- 【学习中】Unity Schedule
章节 内容 签到 第一课:界面介绍 第一讲 编辑器工作区 4月27日 第二课:资源管理 第二讲 资源及资源类型 4月27日 第三讲 资源管理:模型和角色动画的输出设置(上) 4月27日 第四讲 资源管 ...
- Git在windows上的设置详解
这几天在学习使用Git版本管理工具,发现期间的各种配置还是挺繁琐的,而且好多命令的确记不住,于是写个blog记录下来,方便以后查阅. 1. 首先到GitHub官网上下载最新的Git,然后装上,装的过程 ...
