Spring 注解(二)注解工具类
本文转载自Spring 注解(二)注解工具类
导语
首先回顾一下 AnnotationUtils 和 AnnotatedElementUtils 这两个注解工具类的用法:
@Test
@GetMapping(value = "/GetMapping", consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public void test() throws NoSuchMethodException {
Method method = ReflectUtils.findDeclaredMethod(
AliasForTest.class, "test", null);
// AnnotationUtils 不支持注解属性覆盖
RequestMapping requestMappingAnn1 = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class);
Assert.assertEquals(new String[]{}, requestMappingAnn1.value());
Assert.assertEquals(new String[]{}, requestMappingAnn1.consumes());
// AnnotatedElementUtils 支持注解属性覆盖
RequestMapping requestMappingAnn2 = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class);
Assert.assertEquals(new String[]{"/GetMapping"}, requestMappingAnn2.value());
Assert.assertEquals(new String[]{MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE}, requestMappingAnn2.consumes());
}
AnnotationUtils 源码分析
AnnotationUtils 解决注解别名,包括显式别名、隐式别名、传递的隐式别名,还可以查的指定注解的属性信息。
AnnotationUtils 底层使用动态代理的方式处理注解别名的问题。
get* 系列注解查找
get 遵循 JDK 的注解查找语义,只是增加了一级元注解的查找。
public static <A extends Annotation> A getAnnotation(Annotation annotation, Class<A> annotationType) {
// 1. 直接查找本地注解
if (annotationType.isInstance(annotation)) {
return synthesizeAnnotation((A) annotation);
}
// 2. 元注解上查找,注意相对于 find* 而言,这里只查找一级元注解
Class<? extends Annotation> annotatedElement = annotation.annotationType();
try {
A metaAnn = annotatedElement.getAnnotation(annotationType);
return (metaAnn != null ? synthesizeAnnotation(metaAnn, annotatedElement) : null);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleIntrospectionFailure(annotatedElement, ex);
return null;
}
}
find* 系列注解查找
遵循 JDK 的注解查找语义,只是增加了多级元注解的查找。
// visited 表示已经查找的元素,Spring 的递归很多都用到了这个参数
private static <A extends Annotation> A findAnnotation(
AnnotatedElement annotatedElement, Class<A> annotationType, Set<Annotation> visited) {
try {
// 1. 本地注解查找
A annotation = annotatedElement.getDeclaredAnnotation(annotationType);
if (annotation != null) {
return annotation;
}
// 2. 元注解上查找
for (Annotation declaredAnn : getDeclaredAnnotations(annotatedElement)) {
Class<? extends Annotation> declaredType = declaredAnn.annotationType();
if (!isInJavaLangAnnotationPackage(declaredType) && visited.add(declaredAnn)) {
// 3. 元注解上递归查找
annotation = findAnnotation((AnnotatedElement) declaredType, annotationType, visited);
if (annotation != null) {
return annotation;
}
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleIntrospectionFailure(annotatedElement, ex);
}
return null;
}
synthesizeAnnotation 动态代理解决别名问题
static <A extends Annotation> A synthesizeAnnotation(A annotation, @Nullable Object annotatedElement) {
// 1. SynthesizedAnnotation 为一个标记,表示已经动态代理过了
// hasPlainJavaAnnotationsOnly 如果是 java 中的注解不可能有注解别名,直接返回
if (annotation instanceof SynthesizedAnnotation || hasPlainJavaAnnotationsOnly(annotatedElement)) {
return annotation;
}
// 2. 判断是否需要进行动态代理,即注解中存在别名,包括显示别名、隐式别名、传递的隐式别名
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType = annotation.annotationType();
if (!isSynthesizable(annotationType)) {
return annotation;
}
// 3. AnnotationAttributeExtractor 用于从注解 annotation 中提取属性的值
DefaultAnnotationAttributeExtractor attributeExtractor =
new DefaultAnnotationAttributeExtractor(annotation, annotatedElement);
// 4. SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler 动态代理的类
InvocationHandler handler = new SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler(attributeExtractor);
// 5. 接口中有 SynthesizedAnnotation,并返回动态代理的对象
Class<?>[] exposedInterfaces = new Class<?>[] {annotationType, SynthesizedAnnotation.class};
return (A) Proxy.newProxyInstance(annotation.getClass().getClassLoader(), exposedInterfaces, handler);
}
SynthesizedAnnotationInvocationHandler
下面主要看一下动态代理的 invoke 实现是怎么实现的。
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (ReflectionUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
return annotationEquals(args[0]);
}
if (ReflectionUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
return annotationHashCode();
}
if (ReflectionUtils.isToStringMethod(method)) {
return annotationToString();
}
// 注解的 annotationType 返回注解的 Class 类型
if (AnnotationUtils.isAnnotationTypeMethod(method)) {
return annotationType();
}
if (!AnnotationUtils.isAttributeMethod(method)) {
throw new AnnotationConfigurationException(String.format(
"Method [%s] is unsupported for synthesized annotation type [%s]", method, annotationType()));
}
// 真正获取注解的属性值
return getAttributeValue(method);
}
getAttributeValue 的核心其实就一句话 this.attributeExtractor.getAttributeValue(attributeMethod); 委托给了对应的 AnnotationAttributeExtractor 处理。
AnnotationAttributeExtractor
AbstractAliasAwareAnnotationAttributeExtractor(
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType, @Nullable Object annotatedElement, S source) {
Assert.notNull(annotationType, "annotationType must not be null");
Assert.notNull(source, "source must not be null");
this.annotationType = annotationType;
this.annotatedElement = annotatedElement;
this.source = source;
this.attributeAliasMap = AnnotationUtils.getAttributeAliasMap(annotationType);
}
在构造方法中有一个很重要的方法 AnnotationUtils.getAttributeAliasMap(annotationType) 用于获取其别名。
public final Object getAttributeValue(Method attributeMethod) {
String attributeName = attributeMethod.getName();
// attributeValue 表示属性的真实值
Object attributeValue = getRawAttributeValue(attributeMethod);
// 获取所有的别名
List<String> aliasNames = this.attributeAliasMap.get(attributeName);
if (aliasNames != null) {
// 属性的默认值,默认值肯定是一样的,因为在获取别名的时候已经校验了默认值
Object defaultValue = AnnotationUtils.getDefaultValue(this.annotationType, attributeName);
for (String aliasName : aliasNames) {
// 别名的真实值
Object aliasValue = getRawAttributeValue(aliasName);
// 如果两个别名的值不相等,且都不等于默认值,直接抛异常
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(attributeValue, aliasValue) &&
!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(attributeValue, defaultValue) &&
!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(aliasValue, defaultValue)) {
throw new AnnotationConfigurationException();
}
if (ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(attributeValue, defaultValue)) {
attributeValue = aliasValue;
}
}
}
return attributeValue;
}
AliasDescriptor
getAttributeAliasMap
在 AbstractAliasAwareAnnotationAttributeExtractor 的构造器中有一个很重要的方法 getAttributeAliasMap 获取注解中所有属性的别名。
static Map<String, List<String>> getAttributeAliasMap(@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (Method attribute : getAttributeMethods(annotationType)) {
List<String> aliasNames = getAttributeAliasNames(attribute);
if (!aliasNames.isEmpty()) {
map.put(attribute.getName(), aliasNames);
}
}
return map;
}
static List<String> getAttributeAliasNames(Method attribute) {
AliasDescriptor descriptor = AliasDescriptor.from(attribute);
return (descriptor != null ? descriptor.getAttributeAliasNames() : Collections.emptyList());
}
可以别名获取的所有的工作都是委托给了 AliasDescriptor 完成,这一小节我们就主要看一下这个类。
AliasDescriptor 构造及校验
public static AliasDescriptor from(Method attribute) {
AliasFor aliasFor = attribute.getAnnotation(AliasFor.class);
if (aliasFor == null) {
return null;
}
descriptor = new AliasDescriptor(attribute, aliasFor);
descriptor.validate();
return descriptor;
}
构建一个 AliasDescriptor 分为两步:一是获取注解信息(构造器),二是校验别名是否成立(validate)。@AliasFor 有以下的规约:
- 规约1:显示别名可以不用配置 annotation 属性
- 规约2:隐式别名默认和原注解属性名称一致,getAliasedAttributeName 中体现
- 规约3:隐式别名 @AliasFor 配置的注解必须出现在元注解中,可以是多级元注解
- 规约4:显示别名必须成对配置
- 规约5:别名必须配置默认值,且默认值一致。注意别名可以为数组类型,而原属性为数组的元素类型
private AliasDescriptor(Method sourceAttribute, AliasFor aliasFor) {
Class<?> declaringClass = sourceAttribute.getDeclaringClass();
// 1. 注解原字段的信息
this.sourceAttribute = sourceAttribute;
this.sourceAnnotationType = (Class<? extends Annotation>) declaringClass;
this.sourceAttributeName = sourceAttribute.getName();
// 2. @AliasFor 注解的信息
// 规约1:显示的别名可以不用配置 annotation 属性
// 规约2:隐式别名默认和原注解属性名称一致,getAliasedAttributeName 中体现
this.aliasedAnnotationType = (Annotation.class == aliasFor.annotation() ?
this.sourceAnnotationType : aliasFor.annotation());
this.aliasedAttributeName = getAliasedAttributeName(aliasFor, sourceAttribute);
if (this.aliasedAnnotationType == this.sourceAnnotationType &&
this.aliasedAttributeName.equals(this.sourceAttributeName)) {
throw new AnnotationConfigurationException(...);
}
try {
// @AliasFor 配置的别名不存在直接抛出异常
this.aliasedAttribute = this.aliasedAnnotationType.getDeclaredMethod(this.aliasedAttributeName);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new AnnotationConfigurationException(..., ex);
}
// 3. isAliasPair=true 表示就同一个注解内的显示别名
this.isAliasPair = (this.sourceAnnotationType == this.aliasedAnnotationType);
}
getAttributeAliasNames 获取别名
public List<String> getAttributeAliasNames() {
// 1. 显示别名,直接返回
if (this.isAliasPair) {
return Collections.singletonList(this.aliasedAttributeName);
}
// 2. 隐式别名,包括可传递的隐式别名
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>();
// 2.1 遍历注解中的其它属性,一一判断是否互为别名
// getOtherDescriptors 获取其它的所有属性
// isAliasFor 判断两个属性是否互为别名,会递归向上查找
for (AliasDescriptor otherDescriptor : getOtherDescriptors()) {
if (this.isAliasFor(otherDescriptor)) {
this.validateAgainst(otherDescriptor);
aliases.add(otherDescriptor.sourceAttributeName);
}
}
return aliases;
}
getAttributeOverrideName 获取当前属性在元注解中对应的别名
public String getAttributeOverrideName(Class<? extends Annotation> metaAnnotationType) {
// 递归向上查找别名,如果 sourceAnnotationType==metaAnnotationType 则查找到了
for (AliasDescriptor desc = this; desc != null; desc = desc.getAttributeOverrideDescriptor()) {
if (desc.isOverrideFor(metaAnnotationType)) {
return desc.aliasedAttributeName;
}
}
return null;
}
AnnotatedElementUtils 源码分析
Processor 对匹配的注解进行后置处理
Processor 对匹配的注解进行后置处理,可以通过 process 方法的返回值来控制查找的流程:返回 null 时继续查找,非 null 时直接返回。有一种情况例外就是 aggregates=true,这种情况要查找所有的注解,所以会继续查找。
接口
private interface Processor<T> {
// 两个作用:一是根据返回值是否为 null 控制查询的流程;二是对查询的注解进行处理,主要是用于获取该注解的属性值
T process(@Nullable AnnotatedElement annotatedElement, Annotation annotation, int metaDepth);
// 只有 MergedAnnotationAttributesProcessor 有效,用于处理元注解属性覆盖
// annotation 为当前注解,result 为元注解属性信息,annotation 会覆盖元注解中的属性信息
void postProcess(@Nullable AnnotatedElement annotatedElement, Annotation annotation, T result);
// 查询所有元注解时有效,不管是否匹配都要执行 process 方法
boolean alwaysProcesses();
// MergedAnnotationAttributesProcessor 查找所有的注解有效
boolean aggregates();
List<T> getAggregatedResults();
}
有两个方法要特别关注:
process(@Nullable AnnotatedElement annotatedElement, Annotation annotation, int metaDepth)有两个作用:一是根据返回值来控制查找的流程;二是 MergedAnnotationAttributesProcessor 的 process 方法返回查找到的注解信息 AnnotationAttributespostProcess(@Nullable AnnotatedElement element, Annotation annotation, AnnotationAttributes attributes)只有 MergedAnnotationAttributesProcessor 有效,用来处理元注解属性覆盖。其中 annotation 表示当前的注解,attributes 表示元注解的属性信息,执行时会用 annotation 覆盖 attributes。
类图
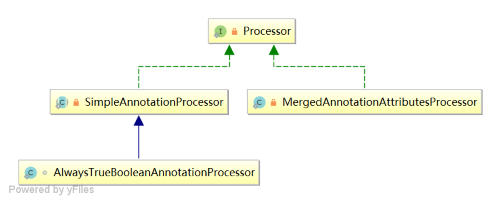
Processor 的有几个实现:SimpleAnnotationProcessor 相当于一个简单的适配器;AlwaysTrueBooleanAnnotationProcessor 的 process 方法永远返回 TRUE;MergedAnnotationAttributesProcessor 用于处理元注解属性覆盖。
常用的方法对应的 Processor 返回值如下:
getMetaAnnotationTypes获取指定注解上的所有元注解,所以 process 方法返回 null 且 alwaysProcesses=truehasMetaAnnotationTypes判断指定的注解上是否有元注解,所以 process 方法返回 metaDepth > 0 ? Boolean.TRUE : CONTINUE,即当 metaDepth>0 表示有元注解就停止查询isAnnotated是否存在指定的注解,所以只配匹配到 process 方法就返回 TRUE,使用 AlwaysTrueBooleanAnnotationProcessorgetMergedAnnotationAttributes元注解会进行属性覆盖,使用 MergedAnnotationAttributesProcessorgetAllMergedAnnotations查找所有的注解,使用 MergedAnnotationAttributesProcessor 且 aggregates=true
MergedAnnotationAttributesProcessor
// AnnotationUtils#retrieveAnnotationAttributes 方法获取当前注解的属性
public AnnotationAttributes process(@Nullable AnnotatedElement annotatedElement, Annotation annotation, int metaDepth) {
return AnnotationUtils.retrieveAnnotationAttributes(annotatedElement, annotation,
this.classValuesAsString, this.nestedAnnotationsAsMap);
}
// annotation 为当前注解,result 为元注解属性信息,这个元注解的属性信息是 process 方法提取的
// annotation 会覆盖元注解中的属性信息
public void postProcess(@Nullable AnnotatedElement element, Annotation annotation, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
annotation = AnnotationUtils.synthesizeAnnotation(annotation, element);
Class<? extends Annotation> targetAnnotationType = attributes.annotationType();
// 1. 已经解析过的属性,避免循环查找
Set<String> valuesAlreadyReplaced = new HashSet<>();
for (Method attributeMethod : AnnotationUtils.getAttributeMethods(annotation.annotationType())) {
String attributeName = attributeMethod.getName();
// 2. 查找 attributeMethod 属性到底覆盖了 targetAnnotationType 元注解的那个属性
String attributeOverrideName = AnnotationUtils.getAttributeOverrideName(attributeMethod, targetAnnotationType);
// 3 显示进行属性覆盖,通过 @AliasFor 注解
if (attributeOverrideName != null) {
if (valuesAlreadyReplaced.contains(attributeOverrideName)) {
continue;
}
List<String> targetAttributeNames = new ArrayList<>();
targetAttributeNames.add(attributeOverrideName);
valuesAlreadyReplaced.add(attributeOverrideName);
// 确保所有的别名都要进行属性覆盖 (SPR-14069)
List<String> aliases = AnnotationUtils.getAttributeAliasMap(targetAnnotationType).get(attributeOverrideName);
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
if (!valuesAlreadyReplaced.contains(alias)) {
targetAttributeNames.add(alias);
valuesAlreadyReplaced.add(alias);
}
}
}
// 将 targetAttributeNames 的属性值设置为 attributeName 的值
overrideAttributes(element, annotation, attributes, attributeName, targetAttributeNames);
}
// 3.2 隐式的进行属性覆盖,只要字段与元注解的属性字段一下致(规约)
else if (!AnnotationUtils.VALUE.equals(attributeName) && attributes.containsKey(attributeName)) {
overrideAttribute(element, annotation, attributes, attributeName, attributeName);
}
}
}
searchWithGetSemantics
searchWithGetSemantics 有 7 个参数:
- element 注解标注的 AnnotatedElement
- annotationTypes、annotationName、containerType 分别表示要查找的注解类型、注解名称、以及可重复注解的容器对象
- processor 后置的处理器,process 返回 null 继续查找,否则停止查找。aggregates=true 时例外,因为此时查找全部的注解。
- visited 已经查找的元素,避免重复查找。
- metaDepth 注解深度,普通注解为 0
// 用于查找 element 上的 annotationTypes、annotationName、containerType 类型注解
// 返回后置处理器对查找后的注解 process 后的值
private static <T> T searchWithGetSemantics(AnnotatedElement element,
Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> annotationTypes, @Nullable String annotationName,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation> containerType, Processor<T> processor,
Set<AnnotatedElement> visited, int metaDepth) {
if (visited.add(element)) {
try {
// 1. 本地注解查找 Start searching within locally declared annotations
List<Annotation> declaredAnnotations = Arrays.asList(AnnotationUtils.getDeclaredAnnotations(element));
T result = searchWithGetSemanticsInAnnotations(element, declaredAnnotations,
annotationTypes, annotationName, containerType, processor, visited, metaDepth);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
// 2. @Inherited 类型查找
if (element instanceof Class) { // otherwise getAnnotations doesn't return anything new
Class<?> superclass = ((Class<?>) element).getSuperclass();
if (superclass != null && superclass != Object.class) {
List<Annotation> inheritedAnnotations = new LinkedList<>();
for (Annotation annotation : element.getAnnotations()) {
if (!declaredAnnotations.contains(annotation)) {
inheritedAnnotations.add(annotation);
}
}
// Continue searching within inherited annotations
result = searchWithGetSemanticsInAnnotations(element, inheritedAnnotations,
annotationTypes, annotationName, containerType, processor, visited, metaDepth);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
AnnotationUtils.handleIntrospectionFailure(element, ex);
}
}
return null;
}
searchWithGetSemanticsInAnnotations 真正用于在指定的注解集合 annotations 中查找指定的注解。
private static <T> T searchWithGetSemanticsInAnnotations(@Nullable AnnotatedElement element,
List<Annotation> annotations, Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> annotationTypes,
@Nullable String annotationName, @Nullable Class<? extends Annotation> containerType,
Processor<T> processor, Set<AnnotatedElement> visited, int metaDepth) {
// 1. 直接匹配 Search in annotations
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
Class<? extends Annotation> currentAnnotationType = annotation.annotationType();
if (!AnnotationUtils.isInJavaLangAnnotationPackage(currentAnnotationType)) {
// 1.1 注解类型或注解名相同
if (annotationTypes.contains(currentAnnotationType) ||
currentAnnotationType.getName().equals(annotationName) ||
processor.alwaysProcesses()) {
T result = processor.process(element, annotation, metaDepth);
if (result != null) {
if (processor.aggregates() && metaDepth == 0) {
processor.getAggregatedResults().add(result);
}
else {
return result;
}
}
}
// 1.2 可重复注解,注意可重复注解不可能是组合注解 Repeatable annotations in container?
else if (currentAnnotationType == containerType) {
for (Annotation contained : getRawAnnotationsFromContainer(element, annotation)) {
T result = processor.process(element, contained, metaDepth);
if (result != null) {
processor.getAggregatedResults().add(result);
}
}
}
}
}
// 2. 递归查找元注解 Recursively search in meta-annotations
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
Class<? extends Annotation> currentAnnotationType = annotation.annotationType();
if (!AnnotationUtils.hasPlainJavaAnnotationsOnly(currentAnnotationType)) {
T result = searchWithGetSemantics(currentAnnotationType, annotationTypes,
annotationName, containerType, processor, visited, metaDepth + 1);
if (result != null) {
// MergedAnnotationAttributesProcessor 用于元注解属性覆盖
// annotation 表示当前的注解,attributes 表示元注解的属性信息,annotation 会覆盖 attributes。
processor.postProcess(element, annotation, result);
if (processor.aggregates() && metaDepth == 0) {
processor.getAggregatedResults().add(result);
} else {
return result;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
参考
- 《spring注解工具类AnnotatedElementUtils和AnnotationUtils》:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_22845447/article/details/83210559
Spring 注解(二)注解工具类的更多相关文章
- 获取Spring容器Bean对象工具类
在开发中,总是能碰到用注解注入不了Spring容器里面bean对象的问题.为了解决这个问题,我们需要一个工具类来直接获取Spring容器中的bean.因此就写了这个工具类,在此记录一下,方便后续查阅. ...
- Spring统一返回Json工具类,带分页信息
前言: 项目做前后端分离时,我们会经常提供Json数据给前端,如果有一个统一的Json格式返回工具类,那么将大大提高开发效率和减低沟通成本. 此Json响应工具类,支持带分页信息,支持泛型,支持Htt ...
- Spring 常用的一些工具类
学习Java的人,或者开发很多项目,都需要使用到Spring 这个框架,这个框架对于java程序员来说.学好spring 就不怕找不到工作.我们时常会写一些工具类,但是有些时候 我们不清楚,我们些的工 ...
- Spring boot中普通工具类不能使用@Value注入yml文件中的自定义参数的问题
在写一个工具类的时候,因为要用到yml中的自定义参数,使用@Value发现值不能正常注入,都显示为null: yml文件中的自定义格式 调用工具类的时候不能new的方式 要使用@Autowired的方 ...
- Maven基础&&Spring框架阶段常用工具类整理
常用工具类 1.密码加密工具类: package com.itheima.utils; import java.security.MessageDigest; import sun.misc.BASE ...
- Thymeleaf+Spring使用自己的工具类
第一种.提供思路,继承SpringStandardDialect,重写getExpressionObjectFactory方法,设置expressionObjectFactory的实际对象,并在Tem ...
- 获取spring上下文的bean 工具类
有些场景我们不属于controller,service,dao,但是我们需要从spring中得到spring容器里面的bean.这时候我们需要一个类继承 ApplicationContextAware ...
- Android Studio 插件开发详解二:工具类
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/article/details/78112856 本文出自[赵彦军的博客] 在插件开发过程中,我们按照开发一个正式的项 ...
- nodejs Async详解之二:工具类
Async中提供了几个工具类,给我们提供一些小便利: memoize unmemoize log dir noConflict 1. memoize(fn, [hasher]) 有一些方法比较耗时,且 ...
- spring util包 StringUtils工具类中的isEmpty() 方法解析
今天在公司看到同事写的代码,无意发现在判断字符串类型时,使用的是StringUtils工具类中的isEmpty()去判断如下所示 @RequestMapping(value = "/pub/ ...
随机推荐
- Linux-处理用户输入
Linux-处理用户输入 1.命令行参数 1.2读取参数 1.3 读取脚本名 1.4测试参数 2.特殊参数变量 2.1 参数统计 2.2抓取所有的数据 3.移动变量 4.处理选项 5.选项标准化 6. ...
- VMware Workstation Pro下载
VMware Workstation Pro 下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1XXhFFh0Fx0vzvcd1A543Yg,提取码:2o19(下载得到的压缩包中含有 VMw ...
- ness使用-漏扫
1.登录nessus后,会自动弹出目标输入弹框: 输入目标IP,可通过CIDR表示法(192.168.0.0/80),范围(192.168.0.1-192.168.0.255),或逗号分隔(192.1 ...
- c++nullptr(空指针常量)、constexpr(常量表达式)
总述 又来更新了,今天带来的是nullptr空指针常量.constexpr(常量表达式)C++的两个用法.Result result_fun = nullptr;constexpr stati ...
- Scala数据结构(数组,Map和Tuple)
package com.zy import scala.collection.mutable import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer object te ...
- 【uva 10954】Add All(算法效率--Huffman编码+优先队列)
题意:有N个数,每次选2个数合并为1个数,操作的开销就是这个新的数.直到只剩下1个数,问最小总开销. 解法:合并的操作可以转化为二叉树上的操作[建模],每次选两棵根树合并成一棵新树,新树的根权值等于两 ...
- Codeforces Round #641 (Div. 2) D. Orac and Medians (贪心)
题意:有一个长度为\(n\)的数组,问能否通过多次使某个区间的所有元素变成这个区间的中位数,来使整个数组变成题目所给定的\(k\). 题解:首先这个\(k\)一定要在数组中存在,然后我们对中位数进行考 ...
- Jpress小程序
首页轮播.首页公告.首页宫格.个人中心页面均支持在PC后台设置内容 首页列表.分类列表页.搜索列表的文章展示页均支持后台设置,拥有三种风格 所有分类展示支持两种风格 用户中心授权登陆,查看个人数据 J ...
- TextCNN论文解读
引言 本文是对<Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification>的原理解读,简称TextCNN. 作者提出了一种基于CN ...
- MySQL 字符集及校验规则
字符集 Mysql 的字符集有4个级别的默认设置:服务器级,数据库级,表级和字段级,客户端交互时,也可以指定字符集 # 字符集:是一个系统支持的所有抽象字符的集合.字符是各种文字和符号的总称,包括各国 ...
