23、matplotlib数据可视化、绘图库模块
matplotlib官方文档:https://matplotlib.org/contents.html?v=20190307135750
matplotlib是一个绘图库,它可以创建常用的统计图,包括条形图、箱型图、折线图、散点图、饼图和直方图。
一、条形图bar()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc') # 修改背景为条纹
plt.style.use('ggplot') classes = ['3班', '4班', '5班', '6班'] classes_index = range(len(classes))
print(list(classes_index))
# [0, 1, 2, 3] student_amounts = [66, 55, 45, 70] # 画布设置
fig = plt.figure()
# 1,1,1表示一张画布切割成1行1列共一张图的第1个;2,2,1表示一张画布切割成2行2列共4张图的第一个(左上角)
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax1.bar(classes_index, student_amounts, align='center', color='darkblue')
ax1.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax1.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left') plt.xticks(classes_index,
classes,
rotation=0,
fontsize=13,
fontproperties=font)
plt.xlabel('班级', fontproperties=font, fontsize=15)
plt.ylabel('学生人数', fontproperties=font, fontsize=15)
plt.title('班级-学生人数', fontproperties=font, fontsize=20)
# 保存图片,bbox_inches='tight'去掉图形四周的空白
# plt.savefig('classes_students.png?x-oss-process=style/watermark', dpi=400, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
二、直方图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc') # 修改背景为条纹
plt.style.use('ggplot')
mu1, mu2, sigma = 50, 100, 10 # 构造均值为50的符合正态分布的数据
x1 = mu1 + sigma * np.random.randn(10000)
print(x1)
# [59.00855949 43.16272141 48.77109774 ... 57.94645859 54.70312714
# 58.94125528] # 构造均值为100的符合正态分布的数据
x2 = mu2 + sigma * np.random.randn(10000)
print(x2)
# [115.19915511 82.09208214 110.88092454 ... 95.0872103 104.21549068
# 133.36025251] fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121)
# bins=50表示每个变量的值分成50份,即会有50根柱子
ax1.hist(x1, bins=50, color='darkgreen')ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
ax2.hist(x2, bins=50, color='orange') fig.suptitle('两个正态分布', fontproperties=font, fontweight='bold', fontsize=15)
ax1.set_title('绿色的正态分布', fontproperties=font)
ax2.set_title('橙色的正态分布', fontproperties=font)
plt.show()
三、折线图
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import randn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc') # 修改背景为条纹
plt.style.use('ggplot') np.random.seed(1) # 使用numpy的累加和,保证数据取值范围不会在(0,1)内波动
plot_data1 = randn(40).cumsum()
print(plot_data1)
# [ 1.62434536 1.01258895 0.4844172 -0.58855142 0.2768562 -2.02468249
# -0.27987073 -1.04107763 -0.72203853 -0.97140891 0.49069903 -1.56944168
# -1.89185888 -2.27591324 -1.1421438 -2.24203506 -2.41446327 -3.29232169
# -3.25010794 -2.66729273 -3.76791191 -2.6231882 -1.72159748 -1.21910314
# -0.31824719 -1.00197505 -1.12486527 -2.06063471 -2.32852279 -1.79816732
# -2.48982807 -2.8865816 -3.5737543 -4.41895994 -5.09020607 -5.10287067
# -6.22018102 -5.98576532 -4.32596314 -3.58391898] plot_data2 = randn(40).cumsum()
plot_data3 = randn(40).cumsum()
plot_data4 = randn(40).cumsum() plt.plot(plot_data1, marker='o', color='red', linestyle='-', label='红实线')
plt.plot(plot_data2, marker='x', color='orange', linestyle='--', label='橙虚线')
plt.plot(plot_data3, marker='*', color='yellow', linestyle='-.', label='黄点线')
plt.plot(plot_data4, marker='s', color='green', linestyle=':', label='绿点图') # loc='best'给label自动选择最好的位置
plt.legend(loc='best', prop=font)
plt.show()
四、散点图+直线图
import numpy as np
from numpy.random import randn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc') # 修改背景为条纹
plt.style.use('ggplot') x = np.arange(1, 20, 1)
print(x)
# [ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19] # 拟合一条水平散点线
np.random.seed(1)
y_linear = x + 10 * np.random.randn(19)
# print(y_linear)
# [ 17.24345364 -4.11756414 -2.28171752 -6.72968622 13.65407629
# -17.01538697 24.44811764 0.38793099 12.19039096 7.50629625
# 25.62107937 -8.60140709 9.77582796 10.15945645 26.33769442
# 5.00108733 15.27571792 9.22141582 19.42213747] # 拟合一条x²的散点线
y_quad = x**2 + 10 * np.random.randn(19)
print(y_quad)
# [ 6.82815214 -7.00619177 20.4472371 25.01590721 30.02494339
# 45.00855949 42.16272141 62.77109774 71.64230566 97.3211192
# 126.30355467 137.08339248 165.03246473 189.128273 216.54794359
# 249.28753869 288.87335401 312.82689651 363.34415698] # s是散点大小
fig = plt.figure()
ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121)
plt.scatter(x, y_linear, s=30, color='r', label='蓝点')
plt.scatter(x, y_quad, s=100, color='b', label='红点') ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
plt.plot(x, y_linear, color='r')
plt.plot(x, y_quad, color='b') # 限制x轴和y轴的范围取值
plt.xlim(min(x) - 1, max(x) + 1)
plt.ylim(min(y_quad) - 10, max(y_quad) + 10)
fig.suptitle('散点图+直线图', fontproperties=font, fontsize=20)
ax1.set_title('散点图', fontproperties=font)
ax1.legend(prop=font)
ax2.set_title('直线图', fontproperties=font)
plt.show()
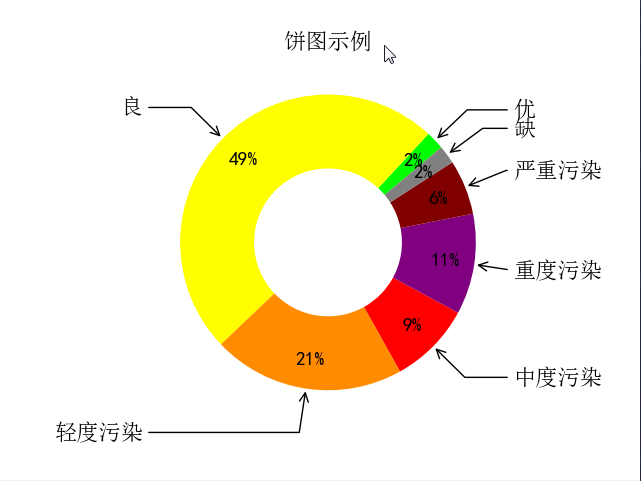
五、饼图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pylab import mpl
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc') mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw=dict(aspect="equal")) recipe = ['优', '良', '轻度污染', '中度污染', '重度污染', '严重污染', '缺'] data = [2, 49, 21, 9, 11, 6, 2]
colors = ['lime', 'yellow', 'darkorange', 'red', 'purple', 'maroon', 'grey']
wedges, texts, texts2 = ax.pie(data,
wedgeprops=dict(width=0.5),
startangle=40,
colors=colors,
autopct='%1.0f%%',
pctdistance=0.8)
plt.setp(texts2, size=14, weight="bold") bbox_props = dict(boxstyle="square,pad=0.3", fc="w", ec="k", lw=0.72)
kw = dict(xycoords='data',
textcoords='data',
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"),
bbox=None,
zorder=0,
va="center") for i, p in enumerate(wedges):
ang = (p.theta2 - p.theta1) / 2. + p.theta1
y = np.sin(np.deg2rad(ang))
x = np.cos(np.deg2rad(ang))
horizontalalignment = {-1: "right", 1: "left"}[int(np.sign(x))]
connectionstyle = "angle,angleA=0,angleB={}".format(ang)
kw["arrowprops"].update({"connectionstyle": connectionstyle})
ax.annotate(recipe[i],
xy=(x, y),
xytext=(1.25 * np.sign(x), 1.3 * y),
size=16,
horizontalalignment=horizontalalignment,
fontproperties=font,
**kw) ax.set_title("饼图示例", fontproperties=font) plt.show()
# plt.savefig('jiaopie2.png?x-oss-process=style/watermark')
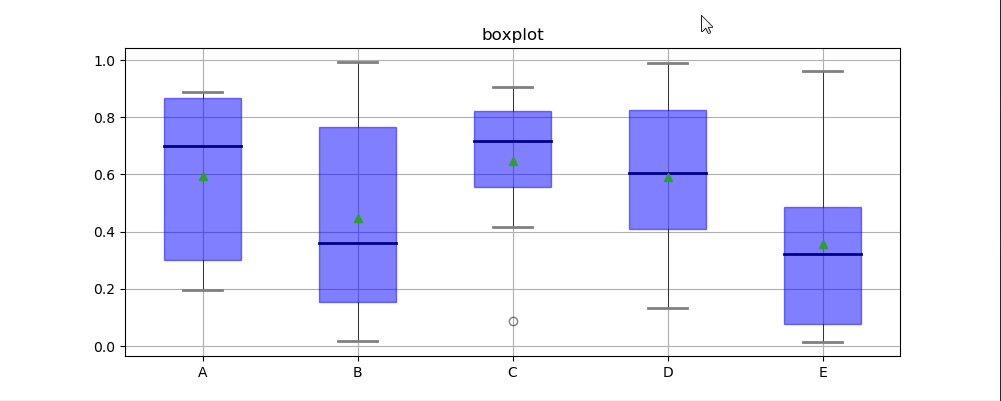
六、箱型图
箱型图:又称为盒须图、盒式图、盒状图或箱线图,是一种用作显示一组数据分散情况资料的统计图(在数据分析中常用在异常值检测)
包含一组数据的:最大值、最小值、中位数、上四分位数(Q3)、下四分位数(Q1)、异常值
- 中位数 → 一组数据平均分成两份,中间的数
- 上四分位数Q1 → 是将序列平均分成四份,计算(n+1)/4与(n-1)/4两种,一般使用(n+1)/4
- 下四分位数Q3 → 是将序列平均分成四份,计算(1+n)/4*3=6.75
- 内限 → T形的盒须就是内限,最大值区间Q3+1.5IQR,最小值区间Q1-1.5IQR (IQR=Q3-Q1)
- 外限 → T形的盒须就是内限,最大值区间Q3+3IQR,最小值区间Q1-3IQR (IQR=Q3-Q1)
- 异常值 → 内限之外 - 中度异常,外限之外 - 极度异常
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc')
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10, 5), columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'])
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))
# 创建图表、数据 f = df.boxplot(
sym='o', # 异常点形状,参考marker
vert=True, # 是否垂直
whis=1.5, # IQR,默认1.5,也可以设置区间比如[5,95],代表强制上下边缘为数据95%和5%位置
patch_artist=True, # 上下四分位框内是否填充,True为填充
meanline=False,
showmeans=True, # 是否有均值线及其形状
showbox=True, # 是否显示箱线
showcaps=True, # 是否显示边缘线
showfliers=True, # 是否显示异常值
notch=False, # 中间箱体是否缺口
return_type='dict' # 返回类型为字典
)
plt.title('boxplot') for box in f['boxes']:
box.set(color='b', linewidth=1) # 箱体边框颜色
box.set(facecolor='b', alpha=0.5) # 箱体内部填充颜色
for whisker in f['whiskers']:
whisker.set(color='k', linewidth=0.5, linestyle='-')
for cap in f['caps']:
cap.set(color='gray', linewidth=2)
for median in f['medians']:
median.set(color='DarkBlue', linewidth=2)
for flier in f['fliers']:
flier.set(marker='o', color='y', alpha=0.5)
# boxes, 箱线
# medians, 中位值的横线,
# whiskers, 从box到error bar之间的竖线.
# fliers, 异常值
# caps, error bar横线
# means, 均值的横线
plt.show()
七、plot函数参数
- 线型linestyle(-,-.,--,..)
- 点型marker(v,^,s,*,H,+,x,D,o,…)
- 颜色color(b,g,r,y,k,w,…)
八、图像标注参数
- 设置图像标题:plt.title()
- 设置x轴名称:plt.xlabel()
- 设置y轴名称:plt.ylabel()
- 设置X轴范围:plt.xlim()
- 设置Y轴范围:plt.ylim()
- 设置X轴刻度:plt.xticks()
- 设置Y轴刻度:plt.yticks()
- 设置曲线图例:plt.legend()
九、Matplolib应用
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
font = FontProperties(fname=r'c:\windows\fonts\simsun.ttc') header_list = ['方程组', '函数', '导数', '微积分', '线性代数', '概率论', '统计学']
py3_df = pd.read_excel('py3.xlsx', header=None, skiprows=[0, 1], names=header_list)
# 处理带有NaN的行
py3_df = py3_df.dropna(axis=0) #<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
print(py3_df) # 自定义映射
map_dict = {
'不会': 0,
'了解': 1,
'熟悉': 2,
'使用过': 3,
} for header in header_list:
py3_df[header] = py3_df[header].map(map_dict) unable_series = (py3_df == 0).sum(axis=0)
know_series = (py3_df == 1).sum(axis=0)
familiar_series = (py3_df == 2).sum(axis=0)
use_series = (py3_df == 3).sum(axis=0) unable_label = '不会'
know_label = '了解'
familiar_label = '熟悉'
use_label = '使用过'
for i in range(len(header_list)):
bottom = 0 # 描绘不会的条形图
plt.bar(x=header_list[i], height=unable_series[i], width=0.60, color='r', label=unable_label)
if unable_series[i] != 0:
plt.text(header_list[i], bottom, s=unable_series[i], ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=15, color='white')
bottom += unable_series[i] # 描绘了解的条形图
plt.bar(x=header_list[i], height=know_series[i], width=0.60, color='y', bottom=bottom, label=know_label)
if know_series[i] != 0:
plt.text(header_list[i], bottom, s=know_series[i], ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=15, color='white')
bottom += know_series[i] # 描绘熟悉的条形图
plt.bar(x=header_list[i], height=familiar_series[i], width=0.60, color='g', bottom=bottom, label=familiar_label)
if familiar_series[i] != 0:
plt.text(header_list[i], bottom, s=familiar_series[i], ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=15, color='white')
bottom += familiar_series[i] # 描绘使用过的条形图
plt.bar(x=header_list[i], height=use_series[i], width=0.60, color='b', bottom=bottom, label=use_label)
if use_series[i] != 0:
plt.text(header_list[i], bottom, s=use_series[i], ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=15, color='white') unable_label = know_label = familiar_label = use_label = '' plt.xticks(header_list, fontproperties=font)
plt.ylabel('人数', fontproperties=font)
plt.title('Python3期数学摸底可视化', fontproperties=font)
plt.legend(prop=font, loc='upper left')
plt.show()
方程组 函数 导数 微积分 线性代数 概率论 统计学
0 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 不会 不会
1 使用过 使用过 了解 不会 不会 不会 不会
2 使用过 使用过 熟悉 不会 不会 不会 不会
3 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 了解 了解 了解 了解
4 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过
5 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 了解
6 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 不会
7 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过
8 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 使用过
9 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 不会 使用过 使用过 不会
10 使用过 使用过 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉
11 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会
12 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过
13 使用过 使用过 了解 不会 不会 不会 不会
14 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会
15 使用过 使用过 熟悉 不会 不会 不会 不会
16 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会
17 使用过 使用过 使用过 了解 不会 不会 不会
18 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉
19 使用过 使用过 使用过 了解 不会 不会 不会
20 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过
21 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过
22 使用过 很了解 熟悉 了解一点,不会运用 了解一点,不会运用 了解 不会
23 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 熟悉 使用过 熟悉
24 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 不会 不会 不会
25 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过
26 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会
27 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 不会 不会
28 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 了解
29 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 了解 不会
30 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会
31 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 使用过 使用过
32 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会
33 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 熟悉 使用过 熟悉
34 熟悉 熟悉 熟悉 使用过 使用过 熟悉 不会
35 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过
36 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 了解
37 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会
38 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 不会
39 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 不会 不会
40 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会
41 使用过 使用过 熟悉 了解 了解 了解 不会
42 使用过 使用过 使用过 不会 不会 不会 不会
43 熟悉 使用过 了解 了解 不会 不会 不会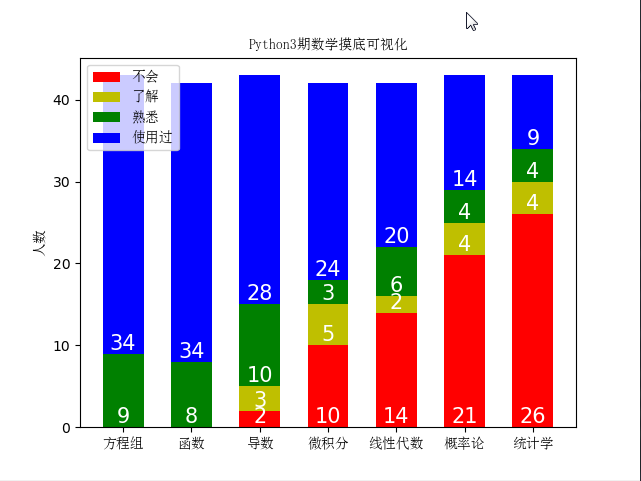
23、matplotlib数据可视化、绘图库模块的更多相关文章
- matplotlib python高级绘图库 一周总结
matplotlib python高级绘图库 一周总结 官网 http://matplotlib.org/ 是一个python科学作图库,可以快速的生成很多非常专业的图表. 只要你掌握要领,画图将变得 ...
- matplotlib 数据可视化
图的基本结构 通常,使用 numpy 组织数据, 使用 matplotlib API 进行数据图像绘制. 一幅数据图基本上包括如下结构: Data: 数据区,包括数据点.描绘形状 Axis: 坐标轴, ...
- 【Data Visual】一文搞懂matplotlib数据可视化
一文搞懂matplotlib数据可视化 作者:白宁超 2017年7月19日09:09:07 摘要:数据可视化主要旨在借助于图形化手段,清晰有效地传达与沟通信息.但是,这并不就意味着数据可视化就一定因为 ...
- Python - matplotlib 数据可视化
在许多实际问题中,经常要对给出的数据进行可视化,便于观察. 今天专门针对Python中的数据可视化模块--matplotlib这块内容系统的整理,方便查找使用. 本文来自于对<利用python进 ...
- Python第三方库matplotlib(2D绘图库)入门与进阶
Matplotlib 一 简介: 二 相关文档: 三 入门与进阶案例 1- 简单图形绘制 2- figure的简单使用 3- 设置坐标轴 4- 设置legend图例 5- 添加注解和绘制点以及在图形上 ...
- Matplotlib数据可视化(1):入门介绍
1 matplot入门指南¶ matplotlib是Python科学计算中使用最多的一个可视化库,功能丰富,提供了非常多的可视化方案,基本能够满足各种场景下的数据可视化需求.但功能丰富从另一方面来 ...
- Matplotlib数据可视化从入门到精通(持续更新)
目录 前言 如何添加标题-title 如何添加文字-text 如何添加注释-annotate 如何设置坐标轴名称-xlabel/ylabel 如何添加图例-legend 如何调整颜色-color 如何 ...
- Matplotlib数据可视化(2):三大容器对象与常用设置
上一篇博客中说到,matplotlib中所有画图元素(artist)分为两类:基本型和容器型.容器型元素包括三种:figure.axes.axis.一次画图的必经流程就是先创建好figure实例, ...
- python Matplotlib数据可视化神器安装与基本应用
Matplotlib Matplotlib 是一个非常强大的 Python 画图工具; 手中有很多数据, Matplotlib能帮你画出美丽的: 线图; 散点图; 等高线图; 条形图; 柱状图; 3D ...
随机推荐
- Linux内核device结构体分析
1.前言 Linux内核中的设备驱动模型,是建立在sysfs设备文件系统和kobject上的,由总线(bus).设备(device).驱动(driver)和类(class)所组成的关系结构,在底层,L ...
- C语言字节对齐分析
1.前言 什么是字节对齐呢?现代计算机中的内存空间都是按字节(byte)划分的,从理论上讲似乎任何类型的变量的访问都可以从任何地址开始,但是实际情况是在访问特定变量的时候经常需要在特定的内存地址进行访 ...
- C中关键字inline用法
一.什么是内联函数 在C语言中,如果一些函数被频繁的调用,不断地用函数入栈,即函数栈,则会造成栈空间或者栈内存的大量消耗,为了解决这个问题,特别的引入了inline关键字,表示为内联函数.栈空间指的是 ...
- 源码编译安装使用glusterfs+heketi安装使用
注:使用源码安装的原因主要是使用yum安装glusterfs服务端时出现一些依赖库问题 准备3台glusterfs服务器(官方也建议至少3台,防止发生脑裂),并在各个服务器的/etc/hosts下面添 ...
- 【转帖】 PM RD QA OP
From 百度知道 一.PM: Product Manager,产品经理,又称品牌经理(Brand Manager).举凡产品从创意到上市,所有相关的研发.调研.生产.编预算.广告.促销活动等等,都由 ...
- docker入门实例(转载)
1.Docker 是什么?Docker 是一个开源的应用容器引擎,让开发者可以打包他们的应用以及依赖包到一个可移植的镜像中,然后发布到任何流行的 Linux 或 Windows 机器上( 摘自百度 ) ...
- Java Mockito 笔记
Mockito 1 Overview 2 Maven 项目初始化 3 示例 3.1 第一个示例 3.2 自动 Mock 3.3 Mock 返回值 3.4 Mock 参数 3.5 自动注入 Mock 对 ...
- Angular复习笔记7-路由(上)
Angular复习笔记7-路由(上) 关于Angular路由的部分将分为上下两篇来介绍.这是第一篇. 概述 路由所要解决的核心问题是通过建立URL和页面的对应关系,使得不同的页面可以用不同的URL来表 ...
- App.config 分开文件
App.config 分开文件 分开文件里配置: <appSettings configSource="App_TestMachine.config"> App_Tes ...
- 使用Nexus3搭建Maven私服+上传第三方jar包到本地maven仓库
1.搭建Maven私服背景 公司还是按捺不住,要搭建一个自己的Maven本地仓库,可以让开发人员down架包,从内网还是快很多. 这样公司的maven本地仓库就是 开发人员自己电脑上的maven仓库 ...