201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十七周学习总结
第十七周学习总结
1. 程序是一段静态的代码,它是应用程序执行的蓝本。进程是程序的一次动态执行,它对应了从代码加载、执行至执行完毕的一个完整过程。操作系统为每个进程分配一段独立的内存空间和系统资源,包括:代码数据以及堆栈等资源。每一个进程的内部数据和状态都是完全独立的。多任务操作系统中,进程切换对CPU资源消耗较大。
2. 多线程是进程执行过程中产生的多条执行线索。线程是比进程执行更小的单位。线程不能独立存在,必须存在于进程中,同一进程的各线程间共享进程空间的数据。每个线程有它自身的产生、存在和消亡的过程,是一个动态的概念。多线程意味着一个程序的多行语句可以看上去几乎在同一时间内同时运行。线程创建、销毁和切换的负荷远小于进程,又称为轻量级进程。
3. Java实现多线程有两种途径:创建Thread类的子类;在程序中定义实现Runnable接口的类。
4. 用Thread类的子类创建线程:首先需从Thread类派生出一个子类,在该子类中重写run()方法。然后用创建该子类的对象Lefthand left=new Lefthand(); Righthand right=new Righthand();最后用start()方法启动线程 left.start(); right.start();
5. 用Thread类的子类创建多线程的关键性操作:定义Thread类的子类并实现用户线程操作,即run()方法的实现。在适当的时候启动线程。由于Java只支持单重继承,用这种方法定义的类不可再继承其他父类。
6.用Runnable()接口实现线程:首先设计一个实现Runnable接口的类;然后在类中根据需要重写run方法;再创建该类对象,以此对象为参数建立Thread 类的对象;调用Thread类对象的start方法启动线程,将 CPU执行权转交到run方法。
7.Thread(Runnable r):创建一个新线程,它调用r的run(), r是一个实现了Runnable接口的类的实例。
8.线程两种创建方法比较:实现Runnable接口的优势:符合OO设计的思想;便于用extends继承其它类。采用继承Thread类方法的优点:代码简单。
9. 线程的终止:当线程的run方法执行方法体中最后一条语句后,或者出现了在run方法中没有捕获的异常时,线程将终止,让出CPU使用权。调用interrupt()方法也可终止线程。 void interrupt() :向一个线程发送一个中断请求,同时把这个线程的“interrupted”状态置为true。若该线程处于 blocked 状 态,会抛出 InterruptedException。
10. 测试线程是否被中断的方法:static boolean interrupted() :检测当前线程是否已被中断,并重置状态 “interrupted”值为false。 boolean isInterrupted() :检测当前线程是否已被中断 , 不改变状态 “interrupted”值 利用各线程的状态变换,可以控制各个线程轮流 使用CPU,体现多线程的并行性特征。
11. 线程有如下7种状态:New (新建);Runnable (可运行);Running(运行) ;Blocked (被阻塞) ;Waiting (等待) ;Timed waiting (计时等待) ; Terminated (被终止)。
new(新建):线程对象刚刚创建,还没有启动,此时线程还处于不可运行状态。例如: Thread thread=new Thread(r); 此时线程thread处于新建状态,有了相应的内存空间以及其它资源。
runnable(可运行状态):此时线程已经启动,处于线程的run()方法之中。此时的线程可能运行,也可能不运行,只要 CPU一空闲,马上就会运行。调用线程的start()方法可使线程处于“可运行”状态。例如: thread.start();
12. blocked (被阻塞):一个正在执行的线程因特殊原因,被暂停执行,进入阻塞状态。阻塞时线程不能进入队列排队,必须等到引起阻塞的原因消除,才可重新进入排队队列。引起阻塞的原因很多,不同原因要用不同的方法解除。sleep(),wait()是两个常用引起线程阻塞的方法。
13. 线程阻塞的三种情况:等待阻塞:通过调用线程的wait()方法,让线程等待某工作的完成。同步阻塞:线程在获取synchronized同步锁失败(因为锁被其它线程所占用),它会进入同步阻 塞状态。 其他阻塞:通过调用线程的sleep()或join() 或发出了I/O请求时,线程会进入到阻塞状态。当 sleep()状态超时、join()等待线程终止或者超时、或者I/O处理完毕时,线程重新转入就绪状态。
14. Terminated (被终止) :线程被终止的原因有二:一是run()方法中最后一个语句执行完毕而自 然死亡。二是因为一个没有捕获的异常终止了run方法而意外死亡。可以调用线程的 stop 方法杀死一个线程(thread.stop();),但是,stop方法已过时,不要在自己的代码中调用它。
15. Java 的线程调度采用优先级策略:优先级高的先执行,优先级低的后执行;多线程系统会自动为每个线程分配一个优先级,缺省时,继承其父类的优先级; 任务紧急的线程,其优先级较高; 同优先级的线程按“先进先出”的队列原则。
16.Thread类有三个与线程优先级有关的静态量: MAX_PRIORITY:最大优先权,值为10; MIN_PRIORITY:最小优先权,值为1; NORM _PRIORITY:默认优先权,值为5。
调用setPriority(int a)重置当前线程的优先级,a取值可以是前述的三个静态量。调用getPriority()获得当前线程优先级。
17.下面几种情况下,当前运行线程会放弃CPU:线程调用了yield() 或sleep() 方法;抢先式系统下,有高优先级的线程参与调度;由于当前线程进行I/O访问、外存读写、等待用 户输入等操作导致线程阻塞;或者是为等候一个条件变量,以及线程调用wait() 方法。
18.守护线程的惟一用途是为其他线程提供服务。例如计时线程。在一个线程启动之前,调用setDaemon方法可将线程转换为守护线程。例如:setDaemon(true);
19.多线程并发执行中的问题:多个线程相对执行的顺序是不确定的。线程执行顺序的不确定性会产生执行结果的不确定性。在多线程对共享数据操作时常常会产生这种不确定性
2.多线程并发运行不确定性问题解决方案:引入线程同步机制,使得另一线程要使用该方法,就只能等待。
21. 在Java中解决多线程同步问题的方法有两种:J ava SE 5.0中引入ReentrantLock类。 在共享内存的类方法前加synchronized修饰符。
22.有关锁对象和条件对象的关键要点:锁用来保护代码片段,保证任何时刻只能有一个线程执行被保护的代码。锁管理试图进入被保护代码段的线程。锁可拥有一个或多个相关条件对象。每个条件对象管理那些已经进入被保护的代码 段但还不能运行的线程。
23.synchronized关键字作用: 某个类内方法用synchronized 修饰后,该方法被称为同步方法;只要某个线程正在访问同步方法,其他线程欲要访问同步方法就被阻塞,直至线程从同 步方法返回前唤醒被阻塞线程,其他线程方可能进入同步方法。
24.在同步方法中使用wait()、notify 和notifyAll()方法:一个线程在使用的同步方法中时,可能根据问题的需要,必须使用wait()方法使本线程等待,暂时让出CPU的使用权,并允许其它线程使用这个同步方法。线程如果用完同步方法,应当执行notifyAll()方 法通知所有由于使用这个同步方法而处于等待的 线程结束等待
实验十七 线程同步控制
实验时间 2018-12-10
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握线程同步的概念及实现技术;
(2) 线程综合编程练习
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1:
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材651页程序14-7,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握利用锁对象和条件对象实现的多线程同步技术。
- package synch;
- import java.util.*;
- import java.util.concurrent.locks.*;
- /**
- * A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses locks for serializing access.
- * @version 1.30 2004-08-01
- * @author Cay Horstmann
- */
- public class Bank
- {
- private final double[] accounts;
- private Lock bankLock;
- private Condition sufficientFunds;
- /**
- * Constructs the bank.
- * @param n the number of accounts
- * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account
- */
- public Bank(int n, double initialBalance)
- {
- accounts = new double[n];
- Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance);
- bankLock = new ReentrantLock();
- sufficientFunds = bankLock.newCondition();
- }
- /**
- * Transfers money from one account to another.
- * @param from the account to transfer from
- * @param to the account to transfer to
- * @param amount the amount to transfer
- */
- public void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException
- {
- //加锁;
- bankLock.lock();
- try//临界区互斥访问;
- {
- while (accounts[from] < amount)
- sufficientFunds.await();//将线程放到条件的等待等待;有两个以上使得临界区代码执行不下去的原因,针对每个原因设置一个条件对象;
- System.out.print(Thread.currentThread());
- accounts[from] -= amount;
- System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to);
- accounts[to] += amount;
- System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance());
- //sufficientFunds.signalAll();
- sufficientFunds.signal();//唤醒所有线程,由阻塞状态进入运行;
- }
- finally
- {
- bankLock.unlock();//解锁,放在finally语句中,以是得出现异常时其他线程能正常使用临界区;
- }
- }
- /**
- * Gets the sum of all account balances.
- * @return the total balance
- */
- public double getTotalBalance()
- {
- bankLock.lock();//加锁;
- try
- {
- double sum = 0;
- for (double a : accounts)
- sum += a;
- return sum;
- }
- finally
- {
- bankLock.unlock();//解锁;
- }
- }
- /**
- * Gets the number of accounts in the bank.
- * @return the number of accounts
- */
- public int size()
- {
- return accounts.length;
- }
- }
- package synch;
- /**
- * This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure.
- * @version 1.31 2015-06-21
- * @author Cay Horstmann
- */
- public class SynchBankTest
- {
- public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100;
- public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000;
- public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000;
- public static final int DELAY = 10;
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE);
- for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++)
- {
- int fromAccount = i;
- Runnable r = () -> {
- try
- {
- while (true)
- {
- int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random());
- double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random();
- bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount);
- Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random()));
- }
- }
- catch (InterruptedException e)
- {
- }
- };
- Thread t = new Thread(r);
- t.start();
- }
- }
- }

 什么条件下需要设置条件对象?
什么条件下需要设置条件对象?有两个以上使得临界区代码执行不下去的原因,针对每个原因设置一个条件对象

测试程序2:
l 在Elipse环境下调试教材655页程序14-8,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握synchronized在多线程同步中的应用。
- package synch2;
- import java.util.*;
- /**
- * A bank with a number of bank accounts that uses synchronization primitives.
- * @version 1.30 2004-08-01
- * @author Cay Horstmann
- */
- public class Bank
- {
- private final double[] accounts;
- /**
- * Constructs the bank.
- * @param n the number of accounts
- * @param initialBalance the initial balance for each account
- */
- public Bank(int n, double initialBalance)
- {
- accounts = new double[n];
- Arrays.fill(accounts, initialBalance);
- }
- /**
- * Transfers money from one account to another.
- * @param from the account to transfer from
- * @param to the account to transfer to
- * @param amount the amount to transfer
- */
- public synchronized void transfer(int from, int to, double amount) throws InterruptedException
- {//同步方法;
- while (accounts[from] < amount)
- wait();//导致线程进入等待状态直到他被通知;容许其他线程使用这个同步方法;如果当前线程不是对象锁的持有者,该方法抛出InterruptedException异常;
- System.out.print(Thread.currentThread());
- accounts[from] -= amount;
- System.out.printf(" %10.2f from %d to %d", amount, from, to);
- accounts[to] += amount;
- System.out.printf(" Total Balance: %10.2f%n", getTotalBalance());
- notifyAll();//解除那些在该对象上调用方法的线程的阻塞状态,如果当前线程不是对象锁的持有者,该方法抛出InterruptedException异常;
- }
- /**
- * Gets the sum of all account balances.
- * @return the total balance
- */
- public synchronized double getTotalBalance()
- {
- double sum = 0;
- for (double a : accounts)
- sum += a;
- return sum;
- }
- /**
- * Gets the number of accounts in the bank.
- * @return the number of accounts
- */
- public int size()
- {
- return accounts.length;
- }
- }
- package synch2;
- /**
- * This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure,
- * using synchronized methods.
- * @version 1.31 2015-06-21
- * @author Cay Horstmann
- */
- public class SynchBankTest2
- {
- public static final int NACCOUNTS = 100;
- public static final double INITIAL_BALANCE = 1000;
- public static final double MAX_AMOUNT = 1000;
- public static final int DELAY = 10;
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Bank bank = new Bank(NACCOUNTS, INITIAL_BALANCE);
- for (int i = 0; i < NACCOUNTS; i++)
- {
- int fromAccount = i;
- Runnable r = () -> {
- try
- {
- while (true)
- {
- int toAccount = (int) (bank.size() * Math.random());
- double amount = MAX_AMOUNT * Math.random();
- bank.transfer(fromAccount, toAccount, amount);
- Thread.sleep((int) (DELAY * Math.random()));
- }
- }
- catch (InterruptedException e)
- {
- }
- };
- Thread t = new Thread(r);
- t.start();
- }
- }
- }

测试程序3:
l 在Elipse环境下运行以下程序,结合程序运行结果分析程序存在问题;
l 尝试解决程序中存在问题。
|
class Cbank { private static int s=2000; public static void sub(int m) { int temp=s; temp=temp-m; try { Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random())); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } s=temp; System.out.println("s="+s); } } class Customer extends Thread { public void run() { for( int i=1; i<=4; i++) Cbank.sub(100); } } public class Thread3 { public static void main(String args[]) { Customer customer1 = new Customer(); Customer customer2 = new Customer(); customer1.start(); customer2.start(); } } |
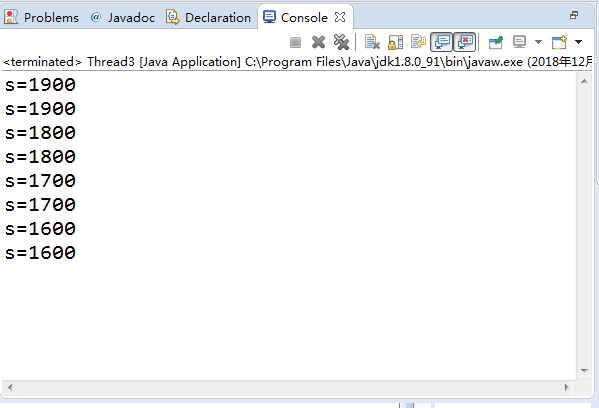
显示结果不合逻辑;
修改后:
- class Cbank
- {
- private static int s=2000;
- public synchronized static void sub(int m)
- {
- int temp=s;
- temp=temp-m;
- try {
- Thread.sleep((int)(1000*Math.random()));
- }
- catch (InterruptedException e) { }
- s=temp;
- System.out.println("s="+s);
- }
- }
- class Customer extends Thread
- {
- public void run()
- {
- for( int i=1; i<=4; i++)
- Cbank.sub(100);
- }
- }
- public class Thread3
- {
- public static void main(String args[])
- {
- Customer customer1 = new Customer();
- Customer customer2 = new Customer();
- customer1.start();
- customer2.start();
- }
- }
Cbank

实验2 编程练习
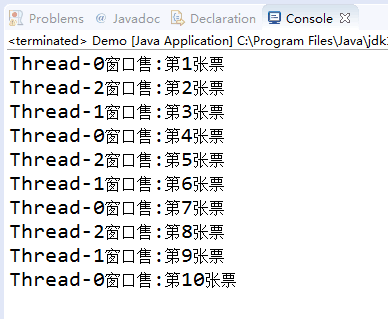
利用多线程及同步方法,编写一个程序模拟火车票售票系统,共3个窗口,卖10张票,程序输出结果类似(程序输出不唯一,可以是其他类似结果)。
Thread-0窗口售:第1张票
Thread-0窗口售:第2张票
Thread-1窗口售:第3张票
Thread-2窗口售:第4张票
Thread-2窗口售:第5张票
Thread-1窗口售:第6张票
Thread-0窗口售:第7张票
Thread-2窗口售:第8张票
Thread-1窗口售:第9张票
Thread-0窗口售:第10张票
- package xaincheng;
- import java.nio.charset.MalformedInputException;
- public class Demo {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- Mythread mythread= new Mythread();
- Thread t1 = new Thread(mythread);
- Thread t2 = new Thread(mythread);
- Thread t3 = new Thread(mythread);
- t1.start();
- t2.start();
- t3.start();
- }
- }
- class Mythread implements Runnable{
- int t=1;
- boolean flag=true;
- public void run() {
- while(flag) {
- try {
- Thread.sleep(500);
- }
- catch (InterruptedException e)
- {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- synchronized (this) {
- if(t<=10){
- System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"窗口售:第"+t+"张票");
- t++;
- }
- if(t>10){
- flag=false;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十七周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 马凯军201771010116《面向对象与程序设计Java》第九周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 异常.日志.断言和调试 1.异常:在程序的执行过程中所发生的异常事件,它中断指令的正常执行. 2.Java的异常处理机制可以控制程序从错误产生的位置转移到能够进行错误处理的位置. 3 ...
随机推荐
- 六、Python-字符串编码
最早的编码为ASCII码(包含0-9.A-Z.a-z.符号(空格.制表符等)),最多支持256个符号(每个符号占1字节) GBK/GB2312:我国制定的中文编码标准,一个字节表示因为字母,两个字 ...
- flink 学习
一.运行 SockWordCount例子 1.到官网上下载 flink-1.6.2-bin-hadoop27-scala_2.11.tgz 然后加压出来 2.cd flink-1.6.2 3.打开fl ...
- 渐进反馈式搜索技术助力运维工程师——Linux命令高效检索
日常生活工作中,我们通过搜索引擎查询相关资料时,经常遇到不知如何指定准确关键词的情况,仅仅根据指定大概范围的关键词时,搜索结果往往不能尽如人意. <信息导航>APP最新版本(Ver 1.1 ...
- Java的注解总结
java 1.5开始引入了注解和反射,正确的来说注解是反射的一部分,没有反射,注解无法正常使用,但离开注解,反射依旧可以使用.Java的注解详解和自定义注解: https://blog.csdn.ne ...
- ORM版学员管理系统 3
老师信息管理 思考 三种方式创建多对多外键方式及其优缺点. 通过外键创建 class Class(models.Model): id = models.AutoField(primary_key=Tr ...
- JSON Web Token(缩写 JWT) 目前最流行的跨域认证解决方案
一.跨域认证的问题 互联网服务离不开用户认证.一般流程是下面这样. 1.用户向服务器发送用户名和密码. 2.服务器验证通过后,在当前对话(session)里面保存相关数据,比如用户角色.登录时间等等. ...
- js数值大小判断的错误
1.js中定义一个变量i,判断i的取值在[1,3]中的错误写法 if(1<= i <= 3) 假设js的值为4,浏览器在解析js时会先将1与4比较 ,显然1<= 4,返回结果为1,然 ...
- 如何引入.graphql文件并优雅的使用fragment
你还在为代码中放入长长的模版字符串所苦恼吗,如下图代码片段: ps:这个是grqphql client在nodejs后端项目的实践,如果你是在前端使用graphql,并使用了webpack,那么这些问 ...
- 同时安装 Python 2 与Python 3 的方法及pip模块的下载安装
Python虽然功能强大,上手容易,但版本问题却是个烦人的问题. Python 2.x 和 Python 3.x 版本之间存在很大的不兼容. 同时安装Python2.x和Python3.x 1. 在P ...
- RFCN配置参数
最近一直被人问这个,索性画张图,省得一遍一遍解释.
