利用tensorflow训练简单的生成对抗网络GAN
对抗网络是14年Goodfellow Ian在论文Generative Adversarial Nets中提出来的。 原理方面,对抗网络可以简单归纳为一个生成器(generator)和一个判断器(discriminator)之间博弈的过程。整个网络训练的过程中,
两个模块的分工
- 判断网络,直观来看就是一个简单的神经网络结构,输入就是一副图像,输出就是一个概率值,用于判断真假使用(概率值大于0.5那就是真,小于0.5那就是假)
- 生成网络,同样也可以看成是一个神经网络模型,输入是一组随机数Z,输出是一个图像。
两个模块的训练目的
- 判别网络的目的:就是能判别出来属于的一张图它是来自真实样本集还是假样本集。假如输入的是真样本,网络输出就接近1,输入的是假样本,网络输出接近0,那么很完美,达到了很好判别的目的。
- 生成网络的目的:生成网络是造样本的,它的目的就是使得自己造样本的能力尽可能强,强到判别网络没法判断是真样本还是假样本。
GAN的训练
需要注意的是生成模型与对抗模型可以说是完全独立的两个模型,好比就是完全独立的两个神经网络模型,他们之间没有什么联系。
那么训练这样的两个模型的大方法就是:单独交替迭代训练。因为是2个网络,不好一起训练,所以才去交替迭代训练,我们一一来看。
首先我们先随机产生一个生成网络模型(当然可能不是最好的生成网络),那么给一堆随机数组,就会得到一堆假的样本集(因为不是最终的生成模型,那么现在生成网络可能就处于劣势,导致生成的样本很糟糕,可能很容易就被判别网络判别出来了说这货是假冒的),但是先不管这个,假设我们现在有了这样的假样本集,真样本集一直都有,现在我们人为的定义真假样本集的标签,因为我们希望真样本集的输出尽可能为1,假样本集为0,很明显这里我们就已经默认真样本集所有的类标签都为1,而假样本集的所有类标签都为0.
对于生成网络,回想下我们的目标,是生成尽可能逼真的样本。那么原始的生成网络生成的样本你怎么知道它真不真呢?就是送到判别网络中,所以在训练生成网络的时候,我们需要联合判别网络一起才能达到训练的目的。就是如果我们单单只用生成网络,那么想想我们怎么去训练?误差来源在哪里?细想一下没有,但是如果我们把刚才的判别网络串接在生成网络的后面,这样我们就知道真假了,也就有了误差了。所以对于生成网络的训练其实是对生成-判别网络串接的训练,就像图中显示的那样。好了那么现在来分析一下样本,原始的噪声数组Z我们有,也就是生成了假样本我们有,此时很关键的一点来了,我们要把这些假样本的标签都设置为1,也就是认为这些假样本在生成网络训练的时候是真样本。这样才能起到迷惑判别器的目的,也才能使得生成的假样本逐渐逼近为正样本。
下面是代码部分,这里,我们利用训练的两个数据集分别是
- mnist
- Celeba
来生成手写数字以及人脸
首先是数据集的下载
import math
import os
import hashlib
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
import zipfile
import gzip
import shutil data_dir = './data' def download_extract(database_name, data_path):
"""
Download and extract database
:param database_name: Database name
"""
DATASET_CELEBA_NAME = 'celeba'
DATASET_MNIST_NAME = 'mnist' if database_name == DATASET_CELEBA_NAME:
url = 'https://s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/udacity-dlnfd/datasets/celeba.zip'
hash_code = '00d2c5bc6d35e252742224ab0c1e8fcb'
extract_path = os.path.join(data_path, 'img_align_celeba')
save_path = os.path.join(data_path, 'celeba.zip')
extract_fn = _unzip
elif database_name == DATASET_MNIST_NAME:
url = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz'
hash_code = 'f68b3c2dcbeaaa9fbdd348bbdeb94873'
extract_path = os.path.join(data_path, 'mnist')
save_path = os.path.join(data_path, 'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz')
extract_fn = _ungzip if os.path.exists(extract_path):
print('Found {} Data'.format(database_name))
return if not os.path.exists(data_path):
os.makedirs(data_path) if not os.path.exists(save_path):
with DLProgress(unit='B', unit_scale=True, miniters=1, desc='Downloading {}'.format(database_name)) as pbar:
urlretrieve(
url,
save_path,
pbar.hook) assert hashlib.md5(open(save_path, 'rb').read()).hexdigest() == hash_code, \
'{} file is corrupted. Remove the file and try again.'.format(save_path) os.makedirs(extract_path)
try:
extract_fn(save_path, extract_path, database_name, data_path)
except Exception as err:
shutil.rmtree(extract_path) # Remove extraction folder if there is an error
raise err # Remove compressed data
os.remove(save_path) # download mnist
download_extract('mnist', data_dir)
# download celeba
download_extract('celeba', data_dir
我们先看看我们的mnist还有celeba数据集是什么样子
# the number of images
show_n_images =16 %matplotlib inline
import os
from glob import glob
from matplotlib import pyplot def get_batch(image_files, width, height, mode):
data_batch = np.array(
[get_image(sample_file, width, height, mode) for sample_file in image_files]).astype(np.float32) # Make sure the images are in 4 dimensions
if len(data_batch.shape) < 4:
data_batch = data_batch.reshape(data_batch.shape + (1,)) return data_batch def images_square_grid(images, mode):
# Get maximum size for square grid of images
save_size = math.floor(np.sqrt(images.shape[0])) # Scale to 0-255
images = (((images - images.min()) * 255) / (images.max() - images.min())).astype(np.uint8) # Put images in a square arrangement
images_in_square = np.reshape(
images[:save_size*save_size],
(save_size, save_size, images.shape[1], images.shape[2], images.shape[3]))
if mode == 'L':
images_in_square = np.squeeze(images_in_square, 4) # Combine images to grid image
new_im = Image.new(mode, (images.shape[1] * save_size, images.shape[2] * save_size))
for col_i, col_images in enumerate(images_in_square):
for image_i, image in enumerate(col_images):
im = Image.fromarray(image, mode)
new_im.paste(im, (col_i * images.shape[1], image_i * images.shape[2])) return new_im mnist_images = get_batch(glob(os.path.join(data_dir, 'mnist/*.jpg'))[:show_n_images], 28, 28, 'L')
pyplot.imshow(images_square_grid(mnist_images, 'L'), cmap='gray')
mninst:

show_n_images = 9 mnist_images = get_batch(glob(os.path.join(data_dir, 'img_align_celeba/*.jpg'))[:show_n_images], 28, 28, 'RGB')
pyplot.imshow(images_square_grid(mnist_images, 'RGB'))
celeba

现在我们开始搭建网络
这里我建议用GPU来训练,tensorflow的版本最好是1.1.0
from distutils.version import LooseVersion
import warnings
import tensorflow as tf # Check TensorFlow Version
assert LooseVersion(tf.__version__) >= LooseVersion('1.0'), 'Please use TensorFlow version 1.0 or newer. You are using {}'.format(tf.__version__)
print('TensorFlow Version: {}'.format(tf.__version__)) # Check for a GPU
if not tf.test.gpu_device_name():
warnings.warn('No GPU found. Please use a GPU to train your neural network.')
else:
print('Default GPU Device: {}'.format(tf.test.gpu_device_name()))
接着我们要做的是构建输入
def model_inputs(image_width, image_height, image_channels, z_dim):
## Real imag
inputs_real = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,(None, image_width,image_height,image_channels), name = 'input_real') ## input z inputs_z = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,(None, z_dim), name='input_z') ## Learning rate
learning_rate = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name = 'lr') return inputs_real, inputs_z, learning_rate
构建Discriminator
def discriminator(images, reuse=False):
"""
Create the discriminator network
:param images: Tensor of input image(s)
:param reuse: Boolean if the weights should be reused
:return: Tuple of (tensor output of the discriminator, tensor logits of the discriminator)
"""
# TODO: Implement Function ## scope here with tf.variable_scope('discriminator', reuse=reuse): alpha = 0.2 ### leak relu coeff # drop out probability
keep_prob = 0.8 # input layer 28 * 28 * color channel
x1 = tf.layers.conv2d(images, 128, 5, strides=2, padding='same',
kernel_initializer= tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed=2))
## No batch norm here
## leak relu here / alpha = 0.2
relu1 = tf.maximum(alpha * x1, x1)
# applied drop out here
drop1 = tf.nn.dropout(relu1, keep_prob= keep_prob)
# 14 * 14 * 128 # Layer 2
x2 = tf.layers.conv2d(drop1, 256, 5, strides=2, padding='same',
kernel_initializer= tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed=2))
## employ batch norm here
bn2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x2, training=True)
## leak relu
relu2 = tf.maximum(alpha * bn2, bn2)
drop2 = tf.nn.dropout(relu2, keep_prob=keep_prob) # 7 * 7 * 256 # Layer3
x3 = tf.layers.conv2d(drop2, 512, 5, strides=2, padding='same',
kernel_initializer= tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(seed=2))
bn3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x3, training=True)
relu3 = tf.maximum(alpha * bn3, bn3)
drop3 = tf.nn.dropout(relu3, keep_prob=keep_prob)
# 4 * 4 * 512 # Output
# Flatten
flatten = tf.reshape(relu3, (-1, 4 * 4 * 512))
logits = tf.layers.dense(flatten,1)
# activation
out = tf.nn.sigmoid(logits) return out, logits
接着是 Generator
def generator(z, out_channel_dim, is_train=True):
"""
Create the generator network
:param z: Input z
:param out_channel_dim: The number of channels in the output image
:param is_train: Boolean if generator is being used for training
:return: The tensor output of the generator
"""
# TODO: Implement Function with tf.variable_scope('generator', reuse = not is_train):
# First Fully connect layer
x0 = tf.layers.dense(z, 4 * 4 * 512)
# Reshape
x0 = tf.reshape(x0,(-1,4,4,512))
# Use the batch norm
bn0 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x0, training= is_train)
# Leak relu
relu0 = tf.nn.relu(bn0)
# 4 * 4 * 512 # Conv transpose here
x1 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(relu0, 256, 4, strides=1, padding='valid')
bn1 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x1, training=is_train)
relu1 = tf.nn.relu(bn1)
# 7 * 7 * 256 x2 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(relu1, 128, 3, strides=2, padding='same')
bn2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x2, training=is_train)
relu2 = tf.nn.relu(bn2)
# 14 * 14 * 128 # Last cov
logits = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(relu2, out_channel_dim, 3, strides=2, padding='same')
## without batch norm here
out = tf.tanh(logits) return out
然后我们来定义loss,这里,加入了smoother
def model_loss(input_real, input_z, out_channel_dim):
"""
Get the loss for the discriminator and generator
:param input_real: Images from the real dataset
:param input_z: Z input
:param out_channel_dim: The number of channels in the output image
:return: A tuple of (discriminator loss, generator loss)
"""
# TODO: Implement Function g_model = generator(input_z, out_channel_dim, is_train=True) d_model_real, d_logits_real = discriminator(input_real, reuse = False) d_model_fake, d_logits_fake = discriminator(g_model, reuse= True) ## add smooth here smooth = 0.1
d_loss_real = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_real,
labels=tf.ones_like(d_model_real) * (1 - smooth))) d_loss_fake = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_fake, labels=tf.zeros_like(d_model_fake))) g_loss = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_fake,
labels= tf.ones_like(d_model_fake))) d_loss = d_loss_real + d_loss_fake return d_loss, g_loss
接着我们需要定义网络优化的过程,这里我们需要用到batch_normlisation, 不懂的话去搜下文档
def model_opt(d_loss, g_loss, learning_rate, beta1):
"""
Get optimization operations
:param d_loss: Discriminator loss Tensor
:param g_loss: Generator loss Tensor
:param learning_rate: Learning Rate Placeholder
:param beta1: The exponential decay rate for the 1st moment in the optimizer
:return: A tuple of (discriminator training operation, generator training operation)
""" t_vars = tf.trainable_variables()
d_vars = [var for var in t_vars if var.name.startswith('discriminator')]
g_vars = [var for var in t_vars if var.name.startswith('generator')] update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS) with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops):
d_train_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate,beta1=beta1).minimize(d_loss,var_list = d_vars)
g_train_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate,beta1=beta1).minimize(g_loss,var_list = g_vars) return d_train_opt, g_train_opt
现在,我们网络的模块,损失函数,以及优化的过程都定义好了,现在我们就要开始训练我们的网络了,我们的训练过程定义如下。
def train(epoch_count, batch_size, z_dim, learning_rate, beta1, get_batches, data_shape, data_image_mode):
"""
Train the GAN
:param epoch_count: Number of epochs
:param batch_size: Batch Size
:param z_dim: Z dimension
:param learning_rate: Learning Rate
:param beta1: The exponential decay rate for the 1st moment in the optimizer
:param get_batches: Function to get batches
:param data_shape: Shape of the data
:param data_image_mode: The image mode to use for images ("RGB" or "L")
"""
losses = []
samples = [] input_real, input_z, lr = model_inputs(data_shape[1], data_shape[2], data_shape[3], z_dim) d_loss, g_loss = model_loss(input_real,input_z,data_shape[-1]) d_opt, g_opt = model_opt(d_loss, g_loss, learning_rate, beta1) steps = 0 with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for epoch_i in range(epoch_count):
for batch_images in get_batches(batch_size):
# TODO: Train Model
steps += 1 # Reshape the image and pass to Discriminator
batch_images = batch_images.reshape(batch_size,
data_shape[1],
data_shape[2],
data_shape[3])
# Rescale the data to -1 and 1
batch_images = batch_images * 2 # Sample the noise
batch_z = np.random.uniform(-1,1,size = (batch_size, z_dim)) ## Run optimizer
_ = sess.run(d_opt, feed_dict = {input_real:batch_images,
input_z:batch_z,
lr:learning_rate
})
_ = sess.run(g_opt, feed_dict = {input_real:batch_images,
input_z:batch_z,
lr:learning_rate}) if steps % 10 == 0: train_loss_d = d_loss.eval({input_real:batch_images, input_z:batch_z})
train_loss_g = g_loss.eval({input_real:batch_images, input_z:batch_z}) losses.append((train_loss_d,train_loss_g)) print("Epoch {}/{}...".format(epoch_i+1, epochs),
"Discriminator Loss: {:.4f}...".format(train_loss_d),
"Generator Loss: {:.4f}".format(train_loss_g)) if steps % 100 == 0: show_generator_output(sess, 25, input_z, data_shape[-1], data_image_mode)
开始训练,超参数的设置
对于MNIST
batch_size = 64
z_dim = 100
learning_rate = 0.001
beta1 = 0.5
epochs = 2 mnist_dataset = helper.Dataset('mnist', glob(os.path.join(data_dir, 'mnist/*.jpg')))
with tf.Graph().as_default():
train(epochs, batch_size, z_dim, learning_rate, beta1, mnist_dataset.get_batches,
mnist_dataset.shape, mnist_dataset.image_mode)
训练效果如下
开始的时候,网络的参数很差,我们生成的手写数字的效果自然就不好
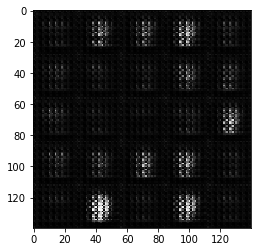
随着训练的进行,轮廓逐渐清晰,效果如下,到最后:
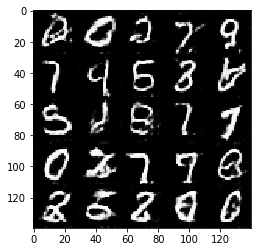
我们看到数字的轮廓基本是清晰可以辨认的,当然,这只是两个epoch的结果,如果有足够的时间经过更长时间的训练,效果会更好。
我们同样展示下对celeba人脸数据集的训练结果
batch_size = 32
z_dim = 100
learning_rate = 0.001
beta1 = 0.4
epochs = 1 celeba_dataset = helper.Dataset('celeba', glob(os.path.join(data_dir, 'img_align_celeba/*.jpg')))
with tf.Graph().as_default():
train(epochs, batch_size, z_dim, learning_rate, beta1, celeba_dataset.get_batches,
celeba_dataset.shape, celeba_dataset.image_mode)
训练开始:

经过一个epoch之后:

人脸的轮廓基本清晰了。
这里我们就是用了DCGAN最简单的方式来实现,原理过程说的不是很详细,同时,可能这个参数设置也不是很合理,训练的也不够成分,但是我想可以帮大家快速掌握实现一个简单的DCGAN的方法了。
利用tensorflow训练简单的生成对抗网络GAN的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow从1到2(十二)生成对抗网络GAN和图片自动生成
生成对抗网络的概念 上一篇中介绍的VAE自动编码器具备了一定程度的创造特征,能够"无中生有"的由一组随机数向量生成手写字符的图片. 这个"创造能力"我们在模型中 ...
- 人工智能中小样本问题相关的系列模型演变及学习笔记(二):生成对抗网络 GAN
[说在前面]本人博客新手一枚,象牙塔的老白,职业场的小白.以下内容仅为个人见解,欢迎批评指正,不喜勿喷![握手][握手] [再啰嗦一下]本文衔接上一个随笔:人工智能中小样本问题相关的系列模型演变及学习 ...
- 生成对抗网络GAN介绍
GAN原理 生成对抗网络GAN由生成器和判别器两部分组成: 判别器是常规的神经网络分类器,一半时间判别器接收来自训练数据中的真实图像,另一半时间收到来自生成器中的虚假图像.训练判别器使得对于真实图像, ...
- 用MXNet实现mnist的生成对抗网络(GAN)
用MXNet实现mnist的生成对抗网络(GAN) 生成式对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Network,简称GAN)由一个生成网络与一个判别网络组成.生成网络从潜在空间(la ...
- 深度学习框架PyTorch一书的学习-第七章-生成对抗网络(GAN)
参考:https://github.com/chenyuntc/pytorch-book/tree/v1.0/chapter7-GAN生成动漫头像 GAN解决了非监督学习中的著名问题:给定一批样本,训 ...
- 生成对抗网络(GAN)
基本思想 GAN全称生成对抗网络,是生成模型的一种,而他的训练则是处于一种对抗博弈状态中的. 譬如:我要升职加薪,你领导力还不行,我现在领导力有了要升职加薪,你执行力还不行,我现在执行力有了要升职加薪 ...
- 深度学习-生成对抗网络GAN笔记
生成对抗网络(GAN)由2个重要的部分构成: 生成器G(Generator):通过机器生成数据(大部分情况下是图像),目的是“骗过”判别器 判别器D(Discriminator):判断这张图像是真实的 ...
- 科普 | 生成对抗网络(GAN)的发展史
来源:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edmond_de_Belamy 五年前,Generative Adversarial Networks(GANs)在深度学习领域掀起 ...
- 在浏览器中进行深度学习:TensorFlow.js (八)生成对抗网络 (GAN
Generative Adversarial Network 是深度学习中非常有趣的一种方法.GAN最早源自Ian Goodfellow的这篇论文.LeCun对GAN给出了极高的评价: “There ...
随机推荐
- Android 获取ROOT权限原理解析
一. 概述 本文介绍了android中获取root权限的方法以及原理,让大家对android玩家中常说的“越狱”有一个更深层次的认识. 二. Root的介绍 1. Root 的目的 可以让 ...
- samtools 工具
软件地址: http://www.htslib.org/ 功能三大版块 : Samtools Reading/writing/editing/indexing/viewing SAM/BAM/CRAM ...
- MVC--SSM和SSH简介
- Python全栈2期 备忘
http://www.cnblogs.com/linhaifeng/ http://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/ http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/ ...
- HDU 3681 Prison Break (二分 + bfs + TSP)
题意:给定上一个 n * m的矩阵,你的出发点是 F,你初始有一个电量,每走一步就会少1,如果遇到G,那么就会加满,每个G只能第一次使用,问你把所有的Y都经过,初始电量最少是多少. 析:首先先预处理每 ...
- python 编码方式大全 fr = open(filename_r,encoding='cp852')
7.8.3. Standard Encodings Python comes with a number of codecs built-in, either implemented as C fun ...
- Object-C中方法
//方法 //方法分了两种 //1.类方法,类调用,方法以+开头 //2.实例方法,对象调用,方法以-开头 //类方法和实例方 ...
- OpenGL ES之GLFW窗口搭建
概述 本章节主要总结如何使用GLFW来创建Opengl窗口.主要包括如下内容: OpenGl窗口创建介绍 GLFW Window版编译介绍 GLFW简单工程源码介绍 OpenGL窗口创建介绍 能用于O ...
- UT源码+019
设计三角形问题的程序 输入三个整数a.b.c,分别作为三角形的三条边,现通过程序判断由三条边构成的三角形的类型为等边三角形.等腰三角形.一般三角形(特殊的还有直角三角形),以及不构成三角形.(等腰直角 ...
- Delphi for iOS开发指南(4):在iOS应用程序中使用不同风格的Button组件
http://blog.csdn.net/DelphiTeacher/article/details/8923481 在FireMonkey iOS应用程序中的按钮 FireMoneky定义了不同类型 ...
