Executor框架(一)
类继承关系
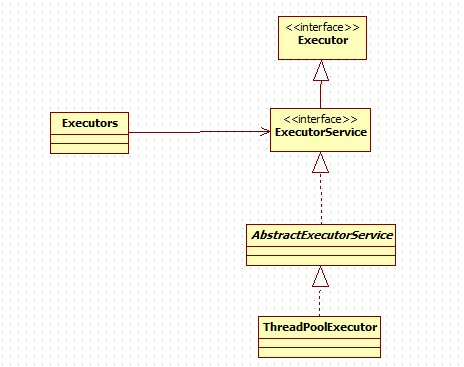
更详细的继承关系:
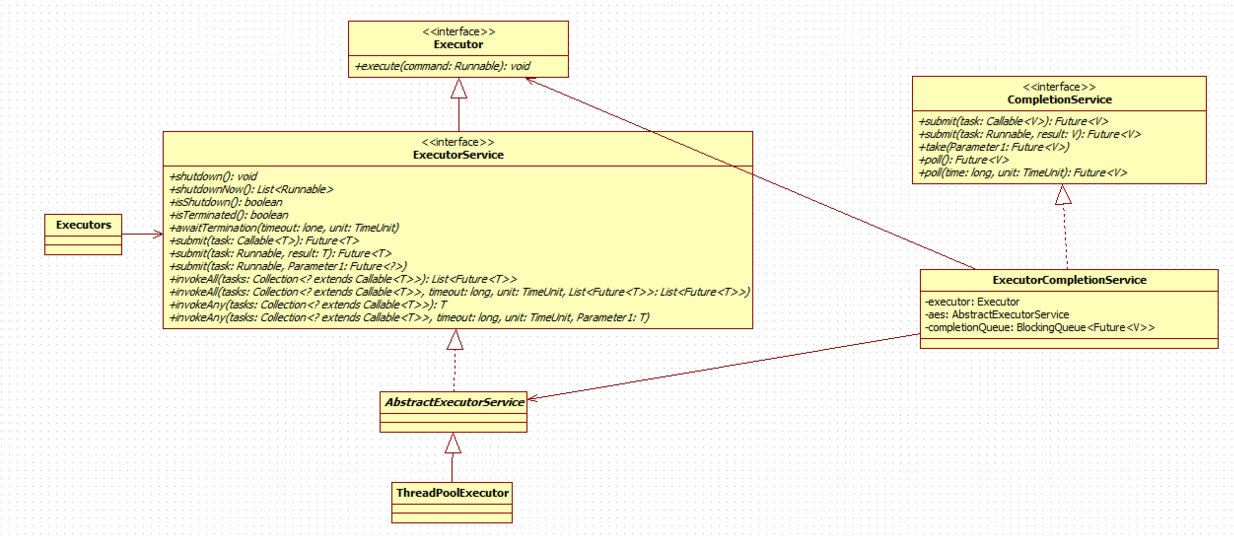
ExecutorComplitionService类
在说Executor接口及实现类之前,先聊聊ExecutorComplitionService。
成员变量
private final Executor executor;
private final AbstractExecutorService aes;
private final BlockingQueue<Future<V>> completionQueue;
executor
执行器,需要对象创建者提供,任务是通过该执行器执行的。
aes
暂时未领会到这个成员变量的精髓在哪里。
completionQueue
已执行完任务队列。
QueueingFuture内部类
private class QueueingFuture extends FutureTask<Void> {
QueueingFuture(RunnableFuture<V> task) {
super(task, null);
this.task = task;
}
protected void done() { completionQueue.add(task); }
private final Future<V> task;
}
QueueingFuture继承自FutureTask类,主要是为了实现done()方法,在FutureTask类中,done()方法是一个空方法。在FutureTask类中,不管任务是执行成功还是执行失败抛出异常,其run()方法的调用链都会调用到done()方法。QueueingFuture 类的done方法是把执行完的task添加到completionQueue队列中。
newTaskFor方法
只是创建新的FutureTask对象。
private RunnableFuture<V> newTaskFor(Callable<V> task) {
if (aes == null)
return new FutureTask<V>(task);
else
return aes.newTaskFor(task);
}
private RunnableFuture<V> newTaskFor(Runnable task, V result) {
if (aes == null)
return new FutureTask<V>(task, result);
else
return aes.newTaskFor(task, result);
}
构造方法
public ExecutorCompletionService(Executor executor) {
if (executor == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.executor = executor;
this.aes = (executor instanceof AbstractExecutorService) ?
(AbstractExecutorService) executor : null;
this.completionQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Future<V>>();
}
public ExecutorCompletionService(Executor executor,
BlockingQueue<Future<V>> completionQueue) {
if (executor == null || completionQueue == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.executor = executor;
this.aes = (executor instanceof AbstractExecutorService) ?
(AbstractExecutorService) executor : null;
this.completionQueue = completionQueue;
}
两个构造方法大同小异,差别在是否使用创建者提供的阻塞队列。
submit方法
public Future<V> submit(Callable<V> task) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<V> f = newTaskFor(task);
executor.execute(new QueueingFuture(f));
return f;
}
public Future<V> submit(Runnable task, V result) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<V> f = newTaskFor(task, result);
executor.execute(new QueueingFuture(f));
return f;
}
两个方法功能相同,只不过分别针对Callable和Runnable提供的。
take和poll
public Future<V> take() throws InterruptedException {
return completionQueue.take();
}
public Future<V> poll() {
return completionQueue.poll();
}
public Future<V> poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return completionQueue.poll(timeout, unit);
}
从已完成队列中取出任务结果。
Executor接口
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}
ExecutorService接口
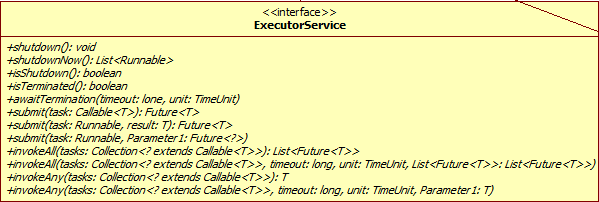
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
void shutdown();
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
boolean isShutdown();
boolean isTerminated();
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException;
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
AbstractExecutorService抽象类
public abstract class AbstractExecutorService implements ExecutorService {
......
}
newTaskFor方法
创建FutureTask任务。
protected <T> RunnableFuture<T> newTaskFor(Runnable runnable, T value) {
return new FutureTask<T>(runnable, value);
}
protected <T> RunnableFuture<T> newTaskFor(Callable<T> callable) {
return new FutureTask<T>(callable);
}
submit方法
提交任务。
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<Void> ftask = newTaskFor(task, null);
execute(ftask);
return ftask;
}
public <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task, result);
execute(ftask);
return ftask;
}
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
if (task == null) throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableFuture<T> ftask = newTaskFor(task);
execute(ftask);
return ftask;
}
AbstractExecutorService抽象类中并没有实现execute(ftask)方法,该方法在各个实现类中实现。
doInvokeAny方法
doInvokeAny方法被下面的invokeAny调用。
private <T> T doInvokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (tasks == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int ntasks = tasks.size();
if (ntasks == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
ArrayList<Future<T>> futures = new ArrayList<Future<T>>(ntasks);
ExecutorCompletionService<T> ecs =
new ExecutorCompletionService<T>(this);
try {
ExecutionException ee = null;
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
Iterator<? extends Callable<T>> it = tasks.iterator();
futures.add(ecs.submit(it.next()));
--ntasks;
int active = 1;
for (;;) {
/*只有任务已经执行完了(包括成功和抛出异常),这里的poll返回的才不是null*/
Future<T> f = ecs.poll();
if (f == null) {
if (ntasks > 0) {
--ntasks;
futures.add(ecs.submit(it.next()));
++active;
}
else if (active == 0)
break;
else if (timed) {
f = ecs.poll(nanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
if (f == null)
throw new TimeoutException();
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
else
f = ecs.take();
}
if (f != null) {
--active;
try {
return f.get();
} catch (ExecutionException eex) {
ee = eex;
} catch (RuntimeException rex) {
ee = new ExecutionException(rex);
}
}
}
if (ee == null)
ee = new ExecutionException();
throw ee;
} finally {
for (int i = 0, size = futures.size(); i < size; i++)
futures.get(i).cancel(true);
}
}
doInvokeAny不断的提交任务,直到有任务执行成功或者任务都提交了。提交的任务如果抛出了异常,先记录,如果最后任务都失败了,再把记录的异常重新抛出。如果是所有的任务都提交完了之后才有任务结束,那么状态就取决于这个最先完成的任务状态。在退出前,会取消掉所有任务的执行(对于那些执行完或者执行中已经抛出异常的任务,cancel没有任何效果)。
invokeAny方法
public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
try {
return doInvokeAny(tasks, false, 0);
} catch (TimeoutException cannotHappen) {
assert false;
return null;
}
}
public <T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
return doInvokeAny(tasks, true, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
invokeAny的主要逻辑都在doInvokeAny中。
invokeAll方法
public <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException {
if (tasks == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
ArrayList<Future<T>> futures = new ArrayList<Future<T>>(tasks.size());
boolean done = false;
try {
for (Callable<T> t : tasks) {
RunnableFuture<T> f = newTaskFor(t);
futures.add(f);
execute(f);
}
for (int i = 0, size = futures.size(); i < size; i++) {
Future<T> f = futures.get(i);
if (!f.isDone()) {
try {
f.get();
} catch (CancellationException ignore) {
} catch (ExecutionException ignore) {
}
}
}
done = true;
return futures;
} finally {
if (!done)
for (int i = 0, size = futures.size(); i < size; i++)
futures.get(i).cancel(true);
}
}
public <T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
if (tasks == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
ArrayList<Future<T>> futures = new ArrayList<Future<T>>(tasks.size());
boolean done = false;
try {
for (Callable<T> t : tasks)
futures.add(newTaskFor(t));
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanos;
final int size = futures.size();
// Interleave time checks and calls to execute in case
// executor doesn't have any/much parallelism.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
execute((Runnable)futures.get(i));
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L)
return futures;
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Future<T> f = futures.get(i);
if (!f.isDone()) {
if (nanos <= 0L)
return futures;
try {
f.get(nanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
} catch (CancellationException ignore) {
} catch (ExecutionException ignore) {
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
return futures;
}
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
}
done = true;
return futures;
} finally {
if (!done)
for (int i = 0, size = futures.size(); i < size; i++)
futures.get(i).cancel(true);
}
}
}
invokeAll也很好理解,执行所有的任务。如果最后由于抛出异常退出,那就取消各个任务的执行。注意,两个方法会吞下CancellationException 和ExecutionException 异常。
Executor框架(一)的更多相关文章
- java并发编程(十七)Executor框架和线程池
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/17465497 Executor框架简介 在Java 5之后,并发编程引入了一堆新的启动 ...
- Executor框架(转载)
Executor框架是指java 5中引入的一系列并发库中与executor相关的一些功能类,其中包括线程池,Executor,Executors,ExecutorService,Completion ...
- Java并发和多线程(二)Executor框架
Executor框架 1.Task?Thread? 很多人在学习多线程这部分知识的时候,容易搞混两个概念:任务(task)和线程(thread). 并发编程可以使我们的程序可以划分为多个分离的.独立运 ...
- java并发编程-Executor框架
Executor框架是指java 5中引入的一系列并发库中与executor相关的一些功能类,其中包括线程池,Executor,Executors,ExecutorService,Completion ...
- 戏(细)说Executor框架线程池任务执行全过程(上)
一.前言 1.5后引入的Executor框架的最大优点是把任务的提交和执行解耦.要执行任务的人只需把Task描述清楚,然后提交即可.这个Task是怎么被执行的,被谁执行的,什么时候执行的,提交的人就不 ...
- 戏(细)说Executor框架线程池任务执行全过程(下)
上一篇文章中通过引入的一个例子介绍了在Executor框架下,提交一个任务的过程,这个过程就像我们老大的老大要找个老大来执行一个任务那样简单.并通过剖析ExecutorService的一种经典实现Th ...
- Java并发——线程池Executor框架
线程池 无限制的创建线程 若采用"为每个任务分配一个线程"的方式会存在一些缺陷,尤其是当需要创建大量线程时: 线程生命周期的开销非常高 资源消耗 稳定性 引入线程池 任务是一组逻辑 ...
- Java Executor 框架学习总结
大多数并发都是通过任务执行的方式来实现的.一般有两种方式执行任务:串行和并行. class SingleThreadWebServer { public static void main(String ...
- Executor框架
Executor框架是指java5中引入的一系列并发库中与executor相关的功能类,包括Executor.Executors.ExecutorService.CompletionService. ...
- Java Executor 框架
Java Executor 框架 Executor框架是指java5中引入的一系列并发库中与executor相关的功能类,包括Executor.Executors. ExecutorService.C ...
随机推荐
- pageshow和pagehide事件
Firefox和opera有一个特性,往返缓存:可以在用户使用浏览器的后退和前进按钮时加快页面的转换速度,这个缓存不仅保存了页面的数据,还有DOM和JavaScript的状态. 为了更形象的说明bfc ...
- Check the NativeLink log file
今天用Quartus ii16.1仿真Cyclone IV的IP核DDR2,总是报上面的错误 .网上都说是modelsim路径的问题, 但我确定不是.最后用QaurtusII 12.1可以通道仿真. ...
- verilog中的多维数组
reg arrayb [7:0] [0:255] ;//二维数组.
- python_day1_python简单介绍
一.python解释器的种类 我们都知道python是一种解释型的语言,那python在执行的过程中必须要通过解释器来执行,那python的解释器到底分为哪些呢? 1.Cpython CPython是 ...
- 1129 Recommendation System
1129 Recommendation System (25 分) Recommendation system predicts the preference that a user would gi ...
- Video Processing and Communications:(视频处理和通信)
https://max.book118.com/html/2017/1010/136711526.shtm Application of (GAN) of AI faceswap in Music V ...
- web-day11
第11章WEB11-Cookie&Session篇 今日任务 显示用户的上次访问时间 登录系统以后显示商品浏览记录 购买商品将商品添加到购物车 系统登录的验证码的校验 教学导航 教学目标 了解 ...
- hdu 2642 Stars 【二维树状数组】
题目 题目大意:Yifenfei是一个浪漫的人,他喜欢数天上的星星.为了使问题变得更容易,我们假设天空是一个二维平面,上面的星星有时会亮,有时会发暗.最开始,没有明亮的星星在天空中,然后将给出一些信息 ...
- 马士兵hibernate(原始笔记)
马士兵hibernate(原始笔记) 课程内容 1 HelloWorld a) Xml b) annotation 2 Hibernate原理模拟 - 什么是O/R ...
- 转:Ubuntu 10.10 安装后上不了网的原因
最近新装了个Ubuntu10.10 发现上不了网,折腾了很久,在网上找了很多办法都不行,最后试了一招居然管用了.特此总结下Ubuntu了网的原因及对策分析. 环境:Ubuntu 10.10网络: 通过 ...
