大数据入门第二十四天——SparkStreaming(一)入门与示例
一、概述
1.什么是spark streaming
Spark Streaming is an extension of the core Spark API that enables scalable, high-throughput, fault-tolerant stream processing of live data streams.
中文的简明介绍如下:
Spark Streaming类似于Apache Storm,用于流式数据的处理。根据其官方文档介绍,Spark Streaming有高吞吐量和容错能力强等特点。Spark Streaming支持的数据输入源很多,例如:Kafka、Flume、Twitter、ZeroMQ和简单的TCP套接字等等。数据输入后可以用Spark的高度抽象原语如:map、reduce、join、window等进行运算。而结果也能保存在很多地方,如HDFS,数据库等。另外Spark Streaming也能和MLlib(机器学习)以及Graphx完美融合。
从官网可以看到主要的特性与处理的流程:
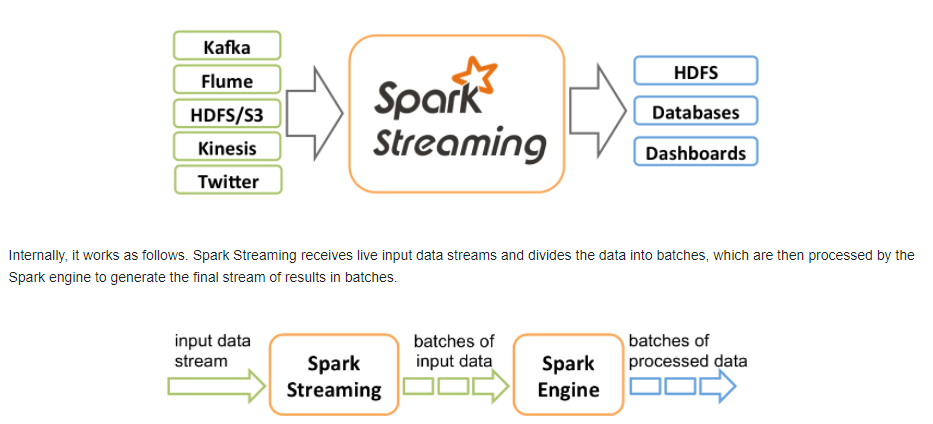
二、编程模型DStream
1.什么是DStream
Discretized Stream是Spark Streaming的基础抽象,代表持续性的数据流和经过各种Spark原语操作后的结果数据流。在内部实现上,DStream是一系列连续的RDD来表示。每个RDD含有一段时间间隔内的数据,如下图:
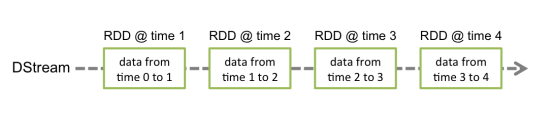
2.DStream的相关操作
DStream上的原语与RDD的类似,分为Transformations(转换)和Output Operations(输出)两种,此外转换操作中还有一些比较特殊的原语,如:updateStateByKey()、transform()以及各种Window相关的原语。
常见操作如下:
|
Transformation |
Meaning |
|
map(func) |
Return a new DStream by passing each element of the source DStream through a function func. |
|
flatMap(func) |
Similar to map, but each input item can be mapped to 0 or more output items. |
|
filter(func) |
Return a new DStream by selecting only the records of the source DStream on which func returns true. |
|
repartition(numPartitions) |
Changes the level of parallelism in this DStream by creating more or fewer partitions. |
|
union(otherStream) |
Return a new DStream that contains the union of the elements in the source DStream and otherDStream. |
|
count() |
Return a new DStream of single-element RDDs by counting the number of elements in each RDD of the source DStream. |
|
reduce(func) |
Return a new DStream of single-element RDDs by aggregating the elements in each RDD of the source DStream using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). The function should be associative so that it can be computed in parallel. |
|
countByValue() |
When called on a DStream of elements of type K, return a new DStream of (K, Long) pairs where the value of each key is its frequency in each RDD of the source DStream. |
|
reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) |
When called on a DStream of (K, V) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, V) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given reduce function. Note: By default, this uses Spark's default number of parallel tasks (2 for local mode, and in cluster mode the number is determined by the config property spark.default.parallelism) to do the grouping. You can pass an optional numTasks argument to set a different number of tasks. |
|
join(otherStream, [numTasks]) |
When called on two DStreams of (K, V) and (K, W) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, (V, W)) pairs with all pairs of elements for each key. |
|
cogroup(otherStream, [numTasks]) |
When called on a DStream of (K, V) and (K, W) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, Seq[V], Seq[W]) tuples. |
|
transform(func) |
Return a new DStream by applying a RDD-to-RDD function to every RDD of the source DStream. This can be used to do arbitrary RDD operations on the DStream. |
|
updateStateByKey(func) |
Return a new "state" DStream where the state for each key is updated by applying the given function on the previous state of the key and the new values for the key. This can be used to maintain arbitrary state data for each key. |
|
Output Operation |
Meaning |
|
print() |
Prints the first ten elements of every batch of data in a DStream on the driver node running the streaming application. This is useful for development and debugging. |
|
saveAsTextFiles(prefix, [suffix]) |
Save this DStream's contents as text files. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix: "prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". |
|
saveAsObjectFiles(prefix, [suffix]) |
Save this DStream's contents as SequenceFiles of serialized Java objects. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix: "prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". |
|
saveAsHadoopFiles(prefix, [suffix]) |
Save this DStream's contents as Hadoop files. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix: "prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". |
|
foreachRDD(func) |
The most generic output operator that applies a function, func, to each RDD generated from the stream. This function should push the data in each RDD to an external system, such as saving the RDD to files, or writing it over the network to a database. Note that the function func is executed in the driver process running the streaming application, and will usually have RDD actions in it that will force the computation of the streaming RDDs. |
特殊的Transformations
1.UpdateStateByKey Operation
UpdateStateByKey原语用于记录历史记录,上文中Word Count示例中就用到了该特性。若不用UpdateStateByKey来更新状态,那么每次数据进来后分析完成后,结果输出后将不在保存
2.Transform Operation
Transform原语允许DStream上执行任意的RDD-to-RDD函数。通过该函数可以方便的扩展Spark API。此外,MLlib(机器学习)以及Graphx也是通过本函数来进行结合的。
3.Window Operations
Window Operations有点类似于Storm中的State,可以设置窗口的大小和滑动窗口的间隔来动态的获取当前Steaming的允许状态
完整请参考官网文档:http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/streaming-programming-guide.html#overview
三、Spark Streaming实战
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-streaming_2.10</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
// 依旧使用HelloSpark这个项目(注意scope,根据实际情况使用)
2.编写代码
package com.streaming
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
object wordCount {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 需要Spark Streaming Context
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("wc").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
// ssc需要sc以及时间间隔(参考streaming原理)来构造
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc, Seconds(5))
// 通过网络读取数据(存储级别采用默认的)
val ds = ssc.socketTextStream("192.168.137.128", 8888)
// 接下来操作DStream,和RDD是很类似的(除了一些特殊的),返回result
val result = ds.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)).reduceByKey(_+_)
// 打印结果
result.print()
// 启动
ssc.start()
// 等待停止
ssc.awaitTermination()
}
}
3.通过nc测试
安装并启动生成者
首先在一台Linux(ip:192.168.10.101)上用YUM安装nc工具
yum install -y nc
启动一个服务端并监听9999端口
nc -lk 9999
4.累加
结果每次在Linux段输入的单词次数都被正确的统计出来,但是结果不能累加!如果需要累加需要使用updateStateByKey(func)来更新状态,下面给出一个例子:
package com.streaming
import org.apache.spark.{HashPartitioner, SparkConf, SparkContext}
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
object StateFullWordCount {
/**
* String : 单词 hello
* Seq[Int] :单词在当前批次出现的次数(例如,(hello,Seq(1,1,1))
* Option[Int] : 历史结果(例如,(3))
*/
val updateFunc = (iter: Iterator[(String, Seq[Int], Option[Int])]) => {
//iter.flatMap(it=>Some(it._2.sum + it._3.getOrElse(0)).map(x=>(it._1,x)))
// 使用的是3个元素的模式匹配(已经确定是3个元素)
iter.flatMap { case (x, y, z) => Some(y.sum + z.getOrElse(0)).map(m => (x, m)) }
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 需要Spark Streaming Context
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("wc").setMaster("local[2]")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
// ssc需要sc以及时间间隔(参考streaming原理)来构造
val ssc = new StreamingContext(sc, Seconds(5))
// updateStateByKey必须设置checkPoint来恢复历史数据,只需设置dir即可(这里本地使用本地目录,集群中使用Linux目录)
sc.setCheckpointDir("F:/ck")
// 通过网络读取数据(存储级别采用默认的)
val ds = ssc.socketTextStream("192.168.137.128", 8888)
// 可以累加的操作,不通过reduceByKey,而是通过key来更新状态
ds.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1)).updateStateByKey(updateFunc, new HashPartitioner(ssc.sparkContext.defaultParallelism), true)
}
}
四、窗口函数
官网有相关的介绍:http://spark.apache.org/docs/1.6.0/streaming-programming-guide.html#window-operations
有关窗口函数的概念介绍,参考hive部分:http://www.cnblogs.com/jiangbei/p/8469528.html
小示例:(更多示例参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wisgood/article/details/55189656)
package cn.itcast.spark.day5 import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Milliseconds, Seconds, StreamingContext} /**
* Created by ZX on 2016/4/19.
*/
object WindowOpts { def main(args: Array[String]) {
LoggerLevels.setStreamingLogLevels()
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("WindowOpts").setMaster("local[2]")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Milliseconds(5000))
val lines = ssc.socketTextStream("172.16.0.11", 9999)
val pairs = lines.flatMap(_.split(" ")).map((_, 1))
val windowedWordCounts = pairs.reduceByKeyAndWindow((a:Int,b:Int) => (a + b), Seconds(15), Seconds(10))
//Map((hello, 5), (jerry, 2), (kitty, 3))
windowedWordCounts.print()
// val a = windowedWordCounts.map(_._2).reduce(_+_)
// a.foreachRDD(rdd => {
// println(rdd.take(0))
// })
// a.print()
// //windowedWordCounts.map(t => (t._1, t._2.toDouble / a.toD))
// windowedWordCounts.print()
// //result.print()
ssc.start()
ssc.awaitTermination()
} }
大数据入门第二十四天——SparkStreaming(一)入门与示例的更多相关文章
- 大数据入门第二十四天——SparkStreaming(二)与flume、kafka整合
前一篇中数据源采用的是从一个socket中拿数据,有点属于“旁门左道”,正经的是从kafka等消息队列中拿数据! 主要支持的source,由官网得知如下: 获取数据的形式包括推送push和拉取pull ...
- 大数据入门第十四天——Hbase详解(一)入门与安装配置
一.概述 1.什么是Hbase 根据官网:https://hbase.apache.org/ Apache HBase™ is the Hadoop database, a distributed, ...
- 大数据入门第十四天——Hbase详解(二)基本概念与命令、javaAPI
一.hbase数据模型 完整的官方文档的翻译,参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/simple-focus/p/6198329.html 1.rowkey 与nosql数据库们一样, ...
- 大数据入门第十四天——Hbase详解(三)hbase基本原理与MR操作Hbase
一.基本原理 1.hbase的位置 上图描述了Hadoop 2.0生态系统中的各层结构.其中HBase位于结构化存储层,HDFS为HBase提供了高可靠性的底层存储支持, MapReduce为HBas ...
- 大数据笔记(十四)——HBase的过滤器与Mapreduce
一. HBase过滤器 1.列值过滤器 2.列名前缀过滤器 3.多个列名前缀过滤器 4.行键过滤器5.组合过滤器 package demo; import javax.swing.RowFilter; ...
- Spring入门第二十四课
Spring对JDBC的支持 直接看代码: db.properties jdbc.user=root jdbc.password=logan123 jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql ...
- RabbitMQ入门教程(十四):RabbitMQ单机集群搭建
原文:RabbitMQ入门教程(十四):RabbitMQ单机集群搭建 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明. 本文链接:https://b ...
- NeHe OpenGL教程 第二十四课:扩展
转自[翻译]NeHe OpenGL 教程 前言 声明,此 NeHe OpenGL教程系列文章由51博客yarin翻译(2010-08-19),本博客为转载并稍加整理与修改.对NeHe的OpenGL管线 ...
- 孤荷凌寒自学python第二十四天python类中隐藏的私有方法探秘
孤荷凌寒自学python第二十四天python类中隐藏的私有方法探秘 (完整学习过程屏幕记录视频地址在文末,手写笔记在文末) 今天发现了python的类中隐藏着一些特殊的私有方法. 这些私有方法不管我 ...
随机推荐
- servlet和jsp页面过滤器Filter的作用及配置
刚刚有个朋友问我,Servlet的过滤器有什么作用? 现在发个帖子说明一下, 过滤器是一个对象,可以传输请求或修改响应.它可以在请求到达Servlet/JSP之前对其进行预处理, ...
- Docker相关概念
一.概念 ①云计算:是一种资源的服务模式,该模式可以实现随时随地,便捷按需地从可配置计算资源共享池中获取所需的资源(如网络.服务器.存储.应用及服务),资源能够快速供应并释放,大大减少了资源管理工作的 ...
- Mac日常使用问题
问题一: macbook如何关闭safari左侧书签栏? 方法1: 快捷键:control+command+1键 办法2: 把光标移到safari顶部, 菜单单出来后, 选择view-->sho ...
- Huawei vlan 配置及vlan 间通讯
Huawei Vlan配置及vlan 间通讯实例 组网需求:汇聚层交换机做为 PC 电脑的网关, PC3直连 SW2 属于 vlan 2,网关为 vlanif 2 接口地址192.168.2.1/24 ...
- unknown host www.baidu.com 解决方法
今晚一开机发现无法更新yum了,本机是连着wife的,咋无法更新呢,作为小白,一脸懵逼.于是ping了一下百度,网络不可达.... 于是我查看了一下DNS,发现设置了,于是看了一下物理机的DNS,发现 ...
- python基础学习16----模块
模块(Module)的引入 import 模块名 调用模块中的函数的方式为 模块名.函数名 这种方式引入会相当于将模块中代码执行一遍,所以如果引入的模块中有输出语句,那么只写import 模块名,运行 ...
- ES6+转ES5
npm init //创建package.json文件 下载转换babel库及其100+依赖 npm install babel-cli -D npm install babel-preset-env ...
- 【第一次玩Travis CI】终于弄好了我的马鸭
真是不容易,我都要哭了.熬了半天终于弄完了!! 终于可以坐这儿挺会小曲,写写感受了. 作为一个程序写的不咋滴的程序员,倒是特别喜欢写博客,也是绝了. 高三的时候,用OneNote,后来转到Lofter ...
- include_path='.;C:\php5\pear'解决方法
问题原因:路径中出现中文, 解决方法:你懂的,,
- 团队作业——Beta冲刺3
团队作业--Beta冲刺 冲刺任务安排 杨光海天 今日任务:浏览详情界面的开发 明日任务:浏览详情界面的开发 吴松青 今日任务:与队长一同进行图片详情的开发,接触了一些自己没接触过的知识点并向队友学习 ...
