ffmpeg 学习: 003-关键函数介绍
背景
了解一些关键函数对于开发的帮助比较大。
avformat_open_input
FFMPEG 打开媒体的过程开始于 avformat_open_input,因此该函数的重要性不可忽视。
在该函数中,FFMPEG 完成了:
1.输入输出结构体 AVIOContext 的初始化;
2.输入数据的协议(例如 RTMP,或者 file)的识别(通过一套评分机制):
A 判断文件名的后缀
B 读取文件头的 数据进行比对;
使用获得最高分的文件协议对应的 URLProtocol,通过函数指针的方式,与 FFMPEG 连接(非专业用词);
剩下的就是调用该 URLProtocol 的函数进行 open,read 等操作了
以下是通过 eclipse+MinGW 调试 FFMPEG 源代码获得的函数调用关系图 :
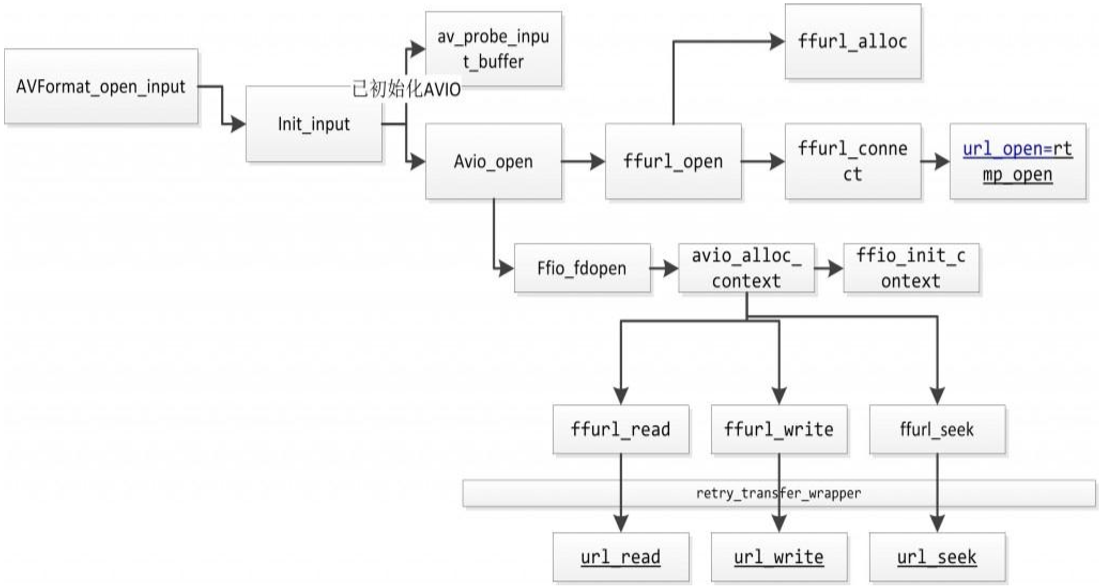
可见最终都调用了 URLProtocol 结构体中的函数指针。
URLProtocol 结构是一大堆函数指针的集合(avio.h 文件),数据结构 URLProtocol 的功能就是完成各种输入协议的读写等操作。
但输入协议种类繁多,它是怎样做到“大一统”的呢?
原来,每个具体的输入协议都有自己对应的 URLProtocol。
比如 file 协议(FFMPEG 把文件也当做一种特殊的协议)(*file.c 文件)URLProtocol ff_pipe_protocol = {
.name = "pipe",
.url_open = pipe_open,
.url_read = file_read,
.url_write = file_write,
.url_get_file_handle = file_get_handle,
.url_check = file_check,
}
或者 rtmp 协议(此处使用了 librtmp)( librtmp.c 文件)
URLProtocol ff_rtmp_protocol = {
.name = "rtmp",
.url_open = rtmp_open,
.url_read = rtmp_read,
.url_write = rtmp_write,
.url_close = rtmp_close,
.url_read_pause = rtmp_read_pause,
.url_read_seek = rtmp_read_seek,
.url_get_file_handle = rtmp_get_file_handle,
.priv_data_size = sizeof(RTMP),
.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};
可见它们把各自的函数指针都赋值给了 URLProtocol 结构体的函数指针。
因此 avformat_open_input 只需调用 url_open,url_read 这些函数就可以完成各种具体输入协议的 open,read 等操作了。
avcodec_register_all()
ffmpeg 注册复用器,编码器等的函数 av_register_all()。
该函数在所有基于 ffmpeg 的应用程序中几乎都是第一个被调用的。只有调用了该函数,才能使用复用器,编码器等。
void avcodec_register_all(void)
{
static AVOnce control = AV_ONCE_INIT;
ff_thread_once(&control, register_all);
}
...
static void register_all(void)
{
/* hardware accelerators */
REGISTER_HWACCEL(H263_VAAPI, h263_vaapi);
REGISTER_HWACCEL(H263_VIDEOTOOLBOX, h263_videotoolbox);
REGISTER_HWACCEL(H264_CUVID, h264_cuvid);
REGISTER_HWACCEL(H264_D3D11VA, h264_d3d11va);
REGISTER_HWACCEL(H264_D3D11VA2, h264_d3d11va2);
REGISTER_HWACCEL(H264_DXVA2, h264_dxva2);
...
}
可见解复用器注册都是用 REGISTER_DEMUXER (X,x)
例如: REGISTER_DEMUXER (AAC, aac)
可见复用器注册都是用 REGISTER_MUXER (X,x))
例如: REGISTER_MUXER (ADTS, adts)
既有解复用器又有复用器的话,可以用 REGISTER_MUXDEMUX (X,x));
例如: REGISTER_MUXDEMUX (AC3, ac3);
我们来看一下宏的定义,这里以解复用器为例:
#define REGISTER_DEMUXER(X,x) {
extern AVInputFormat ff_##x##_demuxer; \
if(CONFIG_##X##_DEMUXER) av_register_input_format(&ff_##x##_demuxer); }
注意:define 里面的##可能不太常见,它的含义就是拼接两个字符串,
比如 #define Conn(x,y) x##y 那么 int n = Conn(123,456); 结果就是 n=123456;
我们以 REGISTER_DEMUXER (AAC, aac)为例,则它等效于
extern AVInputFormat ff_aac_demuxer;
if(CONFIG_AAC_DEMUXER)
av_register_input_format(&ff_aac_demuxer);
从上面这段代码我们可以看出,真正注册的函数是 av_register_input_format(&ff_aac_demuxer),查看一下 av_register_input_format()的代码:
void av_register_input_format(AVInputFormat *format)
{
AVInputFormat **p;
p = &first_iformat;
while (*p != NULL) p = &(*p)->next;
*p = format;
format->next = NULL;
}
// libavformat/allformats.c
void av_register_input_format(AVInputFormat *format)
{
ff_thread_once(&av_format_next_init, av_format_init_next);
}
// libavutil/thread.h 根据不同的宏定义有不同的实现,但实际上都是为了让 routine 指针所指的函数只执行一次。
libavutil/thread.h:147:#define ff_thread_once(control, routine) pthread_once(control, routine)
libavutil/thread.h:162:static inline int ff_thread_once(char *control, void (*routine)(void))
static inline int ff_thread_once(char *control, void (*routine)(void))
{
if (!*control) {
routine();
*control = 1;
}
return 0;
}
实际上我并没有理解这段函数,因为这段函数其中没有使用到参数:format,我不知道ff_thread_once的内部到底执行了什么。但根据前人给出的结论:av_register_input_format()的含义,一句话概括就是:遍历链表并把当前的 Input Format 加到链 表的尾部,然后确定是不是已经初始化过了(initialized),如果没有,就调用 avcodec_register_all()注 册编解码器(这个先不分析),然后就是注册,注册,注册...直到完成所有注册。
av_read_frame()
ffmpeg 中的 av_read_frame()的作用是读取码流中的音频若干帧或者视频一帧。例如,解码视频的时候,每解码一个视频帧,需要先调用 av_read_frame()获得一帧视频的压缩数据,然后才能对该数据进行解码(例如 H.264 中 一帧压缩数据通常对应一个 NAL)。
通过 av_read_packet(***),读取一个包,需要说明的是此函数必须是包含整数帧的,不存在半帧的情况,以 ts 流为例,是读取一个完整的 PES 包(一个完整 pes 包包含若干视频或音频 es 包),读取完毕后,通过 av_parser_parse2(***) 分析出视频一帧(或音频若干帧),返回,下次进入循环的时候,如果上次的数据没有完全取完,则 st = s->cur_st;不会是 NULL,即再此进入 av_parser_parse2(***)流程,而不是下面的 av_read_packet(**)流程,这样就保证了,如果读取一次包含了 N 帧视频数据(以视频为例),则调用 av_read_frame(***)N 次都不会 去读数据,而是返回第一次读取的数据,直到全部解析完毕。
avcodec_decode_video2()
ffmpeg 中的 avcodec_decode_video2()的作用是解码一帧视频数据。输入一个压缩编码的结构体 AVPacket,输出一个 解码后的结构体 AVFrame。
transcode_init()
transcode_init()函数是在转换前做准备工作的.此处看一下它的真面目,不废话,看注释吧:
// 为转换过程做准备
static int transcode_init(void)
{
int ret = 0, i, j, k;
AVFormatContext *oc;
OutputStream *ost;
InputStream *ist;
char error[1024] = {0};
for (i = 0; i < nb_filtergraphs; i++) {
FilterGraph *fg = filtergraphs[i];
for (j = 0; j < fg->nb_outputs; j++) {
OutputFilter *ofilter = fg->outputs[j];
if (!ofilter->ost || ofilter->ost->source_index >= 0)
continue;
if (fg->nb_inputs != 1)
continue;
for (k = nb_input_streams-1; k >= 0 ; k--)
if (fg->inputs[0]->ist == input_streams[k])
break;
ofilter->ost->source_index = k;
}
}
/* init framerate emulation */
for (i = 0; i < nb_input_files; i++) {
InputFile *ifile = input_files[i];
if (ifile->rate_emu)
for (j = 0; j < ifile->nb_streams; j++)
input_streams[j + ifile->ist_index]->start = av_gettime_relative();
}
/* init input streams */
for (i = 0; i < nb_input_streams; i++)
if ((ret = init_input_stream(i, error, sizeof(error))) < 0) {
for (i = 0; i < nb_output_streams; i++) {
ost = output_streams[i];
avcodec_close(ost->enc_ctx);
}
goto dump_format;
}
/* open each encoder */
for (i = 0; i < nb_output_streams; i++) {
// skip streams fed from filtergraphs until we have a frame for them
if (output_streams[i]->filter)
continue;
ret = init_output_stream(output_streams[i], error, sizeof(error));
if (ret < 0)
goto dump_format;
}
/* discard unused programs */
for (i = 0; i < nb_input_files; i++) {
InputFile *ifile = input_files[i];
for (j = 0; j < ifile->ctx->nb_programs; j++) {
AVProgram *p = ifile->ctx->programs[j];
int discard = AVDISCARD_ALL;
for (k = 0; k < p->nb_stream_indexes; k++)
if (!input_streams[ifile->ist_index + p->stream_index[k]]->discard) {
discard = AVDISCARD_DEFAULT;
break;
}
p->discard = discard;
}
}
/* write headers for files with no streams */
for (i = 0; i < nb_output_files; i++) {
oc = output_files[i]->ctx;
if (oc->oformat->flags & AVFMT_NOSTREAMS && oc->nb_streams == 0) {
ret = check_init_output_file(output_files[i], i);
if (ret < 0)
goto dump_format;
}
}
dump_format:
/* dump the stream mapping */
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, "Stream mapping:\n");
for (i = 0; i < nb_input_streams; i++) {
ist = input_streams[i];
for (j = 0; j < ist->nb_filters; j++) {
if (!filtergraph_is_simple(ist->filters[j]->graph)) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, " Stream #%d:%d (%s) -> %s",
ist->file_index, ist->st->index, ist->dec ? ist->dec->name : "?",
ist->filters[j]->name);
if (nb_filtergraphs > 1)
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, " (graph %d)", ist->filters[j]->graph->index);
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, "\n");
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < nb_output_streams; i++) {
ost = output_streams[i];
if (ost->attachment_filename) {
/* an attached file */
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, " File %s -> Stream #%d:%d\n",
ost->attachment_filename, ost->file_index, ost->index);
continue;
}
if (ost->filter && !filtergraph_is_simple(ost->filter->graph)) {
/* output from a complex graph */
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, " %s", ost->filter->name);
if (nb_filtergraphs > 1)
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, " (graph %d)", ost->filter->graph->index);
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, " -> Stream #%d:%d (%s)\n", ost->file_index,
ost->index, ost->enc ? ost->enc->name : "?");
continue;
}
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, " Stream #%d:%d -> #%d:%d",
input_streams[ost->source_index]->file_index,
input_streams[ost->source_index]->st->index,
ost->file_index,
ost->index);
if (ost->sync_ist != input_streams[ost->source_index])
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, " [sync #%d:%d]",
ost->sync_ist->file_index,
ost->sync_ist->st->index);
if (ost->stream_copy)
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, " (copy)");
else {
const AVCodec *in_codec = input_streams[ost->source_index]->dec;
const AVCodec *out_codec = ost->enc;
const char *decoder_name = "?";
const char *in_codec_name = "?";
const char *encoder_name = "?";
const char *out_codec_name = "?";
const AVCodecDescriptor *desc;
if (in_codec) {
decoder_name = in_codec->name;
desc = avcodec_descriptor_get(in_codec->id);
if (desc)
in_codec_name = desc->name;
if (!strcmp(decoder_name, in_codec_name))
decoder_name = "native";
}
if (out_codec) {
encoder_name = out_codec->name;
desc = avcodec_descriptor_get(out_codec->id);
if (desc)
out_codec_name = desc->name;
if (!strcmp(encoder_name, out_codec_name))
encoder_name = "native";
}
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, " (%s (%s) -> %s (%s))",
in_codec_name, decoder_name,
out_codec_name, encoder_name);
}
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, "\n");
}
if (ret) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "%s\n", error);
return ret;
}
atomic_store(&transcode_init_done, 1);
return 0;
}
transcode()
static int transcode(
OutputFile *output_files,//输出文件数组
int nb_output_files,//输出文件的数量
InputFile *input_files,//输入文件数组
int nb_input_files)//输入文件的数量
{
int ret, i;
AVFormatContext *is, *os;
OutputStream *ost;
InputStream *ist;
uint8_t *no_packet;
int no_packet_count = 0; int64_t timer_start; int key; if (!(no_packet = av_mallocz(nb_input_files))) exit_program(1); //设置编码参数,打开所有输出流的编码器,打开所有输入流的解码器,写入所有输出文件的文件头,于是准备好了 ret = transcode_init(output_files, nb_output_files, input_files,nb_input_files); if (ret < 0) goto fail; if (!using_stdin){ av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_INFO, "Press [q] to stop, [?] for help\n"); } timer_start = av_gettime(); //循环,直到收到系统信号才退出 for (; received_sigterm == 0;) { int file_index, ist_index; AVPacket pkt; int64_t ipts_min; double opts_min; int64_t cur_time = av_gettime(); ipts_min = INT64_MAX; opts_min = 1e100; /* if 'q' pressed, exits */ if (!using_stdin) { //先查看用户按下了什么键,跟据键做出相应的反应 static int64_t last_time; if (received_nb_signals) break; /* read_key() returns 0 on EOF */ if (cur_time - last_time >= 100000 && !run_as_daemon){ key = read_key(); last_time = cur_time; }else{ }
/* select the stream that we must read now by looking at the smallest output pts */ //下面这个循环的目的是找一个最小的输出 pts(也就是离当前最近的)的输出流 file_index = -1; for (i = 0; i < nb_output_streams; i++){ OutputFile *of; int64_t ipts; double opts; ost = &output_streams[i];//循环每一个输出流 of = &output_files[ost->file_index];//输出流对应的输出文件 os = output_files[ost->file_index].ctx;//输出流对应的 FormatContext ist = &input_streams[ost->source_index];//输出流对应的输入流 if (ost->is_past_recording_time || //是否过了录制时间?(可能用户指定了一个录制时间段) no_packet[ist->file_index]|| //对应的输入流这个时间内没有数据? (os->pb && avio_tell(os->pb) >= of->limit_filesize))//是否超出了录制范围(也是用户指定的) continue;//是的,符合上面某一条,那么再看下一个输出流吧 //判断当前输入流所在的文件是否可以使用(我也不很明白) opts = ost->st->pts.val * av_q2d(ost->st->time_base); ipts = ist->pts; if (!input_files[ist->file_index].eof_reached) { if (ipts < ipts_min){ //每找到一个 pts 更小的输入流就记录下来,这样循环完所有的输出流时就找到了 //pts 最小的输入流,及输入文件的序号 ipts_min = ipts; if (input_sync) file_index = ist->file_index; } if (opts < opts_min){ opts_min = opts; if (!input_sync) file_index = ist->file_index; } } //难道下面这句话的意思是:如果当前的输出流已接收的帧数,超出用户指定的输出最大帧数时, //则当前输出流所属的输出文件对应的所有输出流,都算超过了录像时间? if (ost->frame_number >= ost->max_frames){ int j; for (j = 0; j < of->ctx->nb_streams; j++) output_streams[of->ost_index + j].is_past_recording_time = 1; continue;
} } /* if none, if is finished */ if (file_index < 0) { //如果没有找到合适的输入文件 if (no_packet_count){ //如果是因为有的输入文件暂时得不到数据,则还不算是结束 no_packet_count = 0; memset(no_packet, 0, nb_input_files); usleep(10000); continue; } //全部转换完成了,跳出大循环 break; } //从找到的输入文件中读出一帧(可能是音频也可能是视频),并放到 fifo 队列中 is = input_files[file_index].ctx; ret = av_read_frame(is, &pkt); if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN)) { //此时发生了暂时没数据的情况 no_packet[file_index] = 1; no_packet_count++; continue; } //下文判断是否有输入文件到最后了 if (ret < 0){ input_files[file_index].eof_reached = 1; if (opt_shortest) break; else continue; } no_packet_count = 0; memset(no_packet, 0, nb_input_files); if (do_pkt_dump){ av_pkt_dump_log2(NULL, AV_LOG_DEBUG, &pkt, do_hex_dump, is->streams[pkt.stream_index]); } /* the following test is needed in case new streams appear
dynamically in stream : we ignore them */ //如果在输入文件中遇到一个忽然冒出的流,那么我们不鸟它 if (pkt.stream_index >= input_files[file_index].nb_streams) goto discard_packet; //取得当前获得的帧对应的输入流 ist_index = input_files[file_index].ist_index + pkt.stream_index; ist = &input_streams[ist_index]; if (ist->discard) goto discard_packet; //重新鼓捣一下帧的时间戳 if (pkt.dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) pkt.dts += av_rescale_q(input_files[ist->file_index].ts_offset, AV_TIME_BASE_Q, ist->st->time_base); if (pkt.pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) pkt.pts += av_rescale_q(input_files[ist->file_index].ts_offset, AV_TIME_BASE_Q, ist->st->time_base); if (pkt.pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) pkt.pts *= ist->ts_scale; if (pkt.dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) pkt.dts *= ist->ts_scale; if (pkt.dts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE && ist->next_pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE && (is->iformat->flags & AVFMT_TS_DISCONT)) { int64_t pkt_dts = av_rescale_q(pkt.dts, ist->st->time_base, AV_TIME_BASE_Q); int64_t delta = pkt_dts - ist->next_pts; if ((delta < -1LL * dts_delta_threshold * AV_TIME_BASE || (delta > 1LL * dts_delta_threshold * AV_TIME_BASE && ist->st->codec->codec_type != AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE) || pkt_dts + 1 < ist->pts) && !copy_ts) { input_files[ist->file_index].ts_offset -= delta; av_log( NULL, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "timestamp discontinuity %"PRId64", new offset= %"PRId64"\n", delta, input_files[ist->file_index].ts_offset); pkt.dts -= av_rescale_q(delta, AV_TIME_BASE_Q, ist->st->time_base); if (pkt.pts != AV_NOPTS_VALUE) pkt.pts -= av_rescale_q(delta, AV_TIME_BASE_Q, ist->st->time_base);
} } //把这一帧转换并写入到输出文件中 if (output_packet(ist, output_streams, nb_output_streams, &pkt) < 0){ av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error while decoding stream #%d:%d\n", ist->file_index, ist->st->index); if (exit_on_error) exit_program(1); av_free_packet(&pkt); continue; } discard_packet: av_free_packet(&pkt); /* dump report by using the output first video and audio streams */ print_report(output_files, output_streams, nb_output_streams, 0, timer_start, cur_time); } //文件处理完了,把缓冲中剩余的数据写到输出文件中 for (i = 0; i < nb_input_streams; i++){ ist = &input_streams[i]; if (ist->decoding_needed){ output_packet(ist, output_streams, nb_output_streams, NULL); } } flush_encoders(output_streams, nb_output_streams); term_exit(); //为输出文件写文件尾(有的不需要). for (i = 0; i < nb_output_files; i++){ os = output_files[i].ctx; av_write_trailer(os); } /* dump report by using the first video and audio streams */ print_report(output_files, output_streams, nb_output_streams, 1, timer_start, av_gettime());
//关闭所有的编码器 for (i = 0; i < nb_output_streams; i++){ ost = &output_streams[i]; if (ost->encoding_needed){ av_freep(&ost->st->codec->stats_in); avcodec_close(ost->st->codec); } #if CONFIG_AVFILTER avfilter_graph_free(&ost->graph); #endif } //关闭所有的解码器 for (i = 0; i < nb_input_streams; i++){ ist = &input_streams[i]; if (ist->decoding_needed){ avcodec_close(ist->st->codec); } } /* finished ! */ ret = 0; fail: av_freep(&bit_buffer); av_freep(&no_packet); if (output_streams) { for (i = 0; i < nb_output_streams; i++) { ost = &output_streams[i]; if (ost) { if (ost->stream_copy) av_freep(&ost->st->codec->extradata); if (ost->logfile){ fclose(ost->logfile); ost->logfile = NULL; } av_fifo_free(ost->fifo); /* works even if fifo is not initialized but set to zero */ av_freep(&ost->st->codec->subtitle_header); av_free(ost->resample_frame.data[0]); av_free(ost->forced_kf_pts); if (ost->video_resample) sws_freeContext(ost->img_resample_ctx);
swr_free(&ost->swr); av_dict_free(&ost->opts); } } } return ret; }ffmpeg 学习: 003-关键函数介绍的更多相关文章
- ffmpeg结构体以及函数介绍(一)
本文对在使用ffmpeg进行音视频编解码时使用到的一些函数做一个简单介绍,我当前使用的ffmpeg版本为:0.8.5,因为本人发现在不同的版本中,有些函数名称会有点小改动,所以在此有必要说明下ffmp ...
- ffmpeg结构体以及函数介绍(二)
1 avcodec_find_decoder() /** * Find a registered decoder with a matching codec ID. * * @param id Cod ...
- FFmpeg AVPacket相关主要函数介绍
1.AVPacket相关函数介绍 操作AVPacket的函数大约有30个,主要分为:AVPacket的创建初始化,AVPacket中的data数据管理(clone,free,copy),AVPacke ...
- ffmpeg结构体以及函数介绍(三)
1 AVPacket typedef struct AVPacket { /** * Presentation timestamp in AVStream->time_base units; t ...
- FFmpeg 学习(五):FFmpeg 编解码 API 分析
在上一篇文章 FFmpeg学习(四):FFmpeg API 介绍与通用 API 分析 中,我们简单的讲解了一下FFmpeg 的API基本概念,并分析了一下通用API,本文我们将分析 FFmpeg 在编 ...
- FFmpeg学习5:多线程播放视音频
在前面的学习中,视频和音频的播放是分开进行的.这主要是为了学习的方便,经过一段时间的学习,对FFmpeg的也有了一定的了解,本文就介绍了 如何使用多线程同时播放音频和视频(未实现同步),并对前面的学习 ...
- Python开发【第三章】:Python函数介绍
一. 函数介绍 1.函数是什么? 在学习函数之前,一直遵循面向过程编程,即根据业务逻辑从上到下实现功能,其往往用一长段代码来实现指定功能,开发过程中最常见的操作就是粘贴复制,也就是将之前实现的代码块复 ...
- SQL函数介绍
http://www.cnblogs.com/moss_tan_jun/archive/2010/08/23/1806861.html 一旦成功地从表中检索出数据,就需要进一步操纵这些数据,以获得有用 ...
- Python开发【第三章】:函数介绍
一. 函数介绍 1.函数是什么? 在学习函数之前,一直遵循面向过程编程,即根据业务逻辑从上到下实现功能,其往往用一长段代码来实现指定功能,开发过程中最常见的操作就是粘贴复制,也就是将之前实现的代码块复 ...
随机推荐
- [ NLP ] CS224N 学习笔记
Lecture1 One-Hot 定义:用N位状态寄存器编码N个状态,每个状态都有独立的寄存器位,且这些寄存器位中只有一位有效,说白了就是只能有一个状态.即保证每个样本中的每个特征只有1位处于状态1, ...
- CSS阴影 box-shadow属性用法
box-shadow: 它可以设置一个或者多个下拉阴影的框 语法:box-shadow:h-shadow v-shadow blur spread color inset 注意:该属性把一个或者多个下 ...
- POJ 2104 主席树模板题
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> int const maxn = 200010 ...
- Java基础 -5.2
方法重载 当方法名称相同,参数的类型或者个数不同的时候 就会称为方法重载. public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(ad ...
- Python学习笔记006
算术运算符 加+ 减- 乘* 除/ 整除//,地板除 取余% 指数** ()区分 优先级 比较运算符 赋值 = 等于 == 不等于 != 大于等于 >= 小于等于 <=
- Windows对应的"Hello,world"程序
<Windows程序设计>(第五版)(美Charles Petzold著) https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/windows/desktop/apiinde ...
- 58按之字形顺序打印二叉树 +队列访问使用front和back,栈才是top
题目描述 请实现一个函数按照之字形打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右至左的顺序打印,第三行按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推. 思路:最暴力的方法就是使用队列进行层次遍 ...
- 「SPOJ10707」Count on a tree II
「SPOJ10707」Count on a tree II 传送门 树上莫队板子题. 锻炼基础,没什么好说的. 参考代码: #include <algorithm> #include &l ...
- 「AMPPZ2014」Petrol
传送门: 这是一道bzoj权限题 Luogu团队题链接 解题思路 首先对于每一个点 \(x\) 预处理出 \(nr[x]\) 和 \(dis[x]\),分别表示离 \(x\) 最近的加油站以及该段距离 ...
- CSP-S 2019 初赛游记
Day 0 上午考了一套毒瘤的数据结构题,考的我心态爆炸SB出题人 晚上考了一套初赛模拟,只考1h,然后我91分,感觉初赛完全没问题? 回寝室后一直在忙活,整理东西什么的,居然将近12点睡? Day ...
