3,LinkedList
一,LinkedList简介
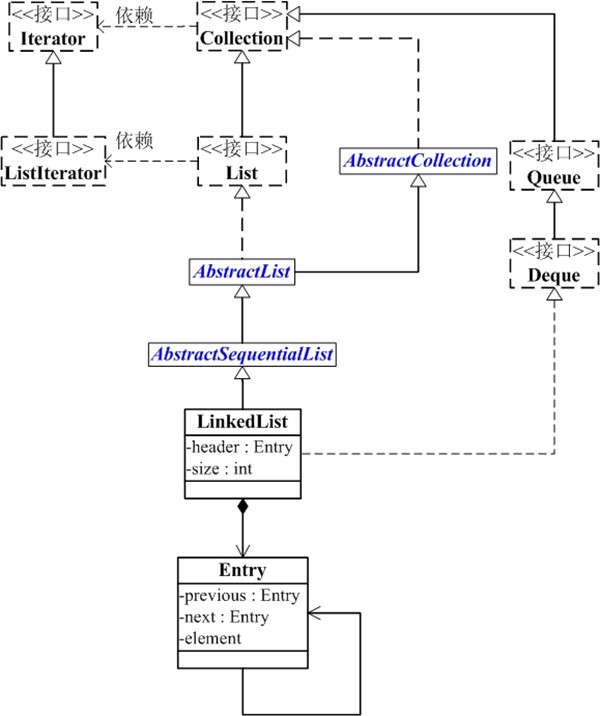
1,LinkedList 是一个继承于AbstractSequentialList的双向链表。它也可以被当作堆栈、队列或双端队列进行操作。
2,LinkedList 实现List 接口,能对它进行队列操作。
3,LinkedList 实现Deque 接口,即能将LinkedList当作双端队列使用。
4,LinkedList 实现Cloneable接口,即覆盖了函数clone(),能克隆。
5,LinkedList 实现Serializable接口,说明ArrayList支持序列化。
二,数据结构
LinkedList的数据结构如下:
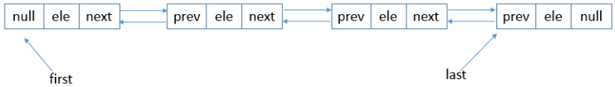
底层使用的双向链表结构,有一个头结点和一个尾结点,双向链表意味着我们可以从头开始正向遍历,或者是从尾开始逆向遍历,并且可以针对头部和尾部进行相应的操作。LinkedList实际上是通过双向链表去实现的。既然是双向链表,那么它的顺序访问会非常高效,而随机访问效率比较低。
三,LinkedList源码
1,LinkedList结构
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
// 实际元素个数
transient int size = 0;
// 头结点
transient Node<E> first;
// 尾结点
transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> {
E item; // 数据域
Node<E> next; // 后继
Node<E> prev; // 前驱
// 构造函数,负责赋值前驱后继。
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
} 省略......
}
1.1,Node内部类
Node就是实际的结点,用于存放实际元素的地方。
1.2,size
实际元素个数。
1.3,first、last
first表示一个头结点、last表示一个尾结点。注意,头结点、尾结点都有transient关键字修饰,这也意味着在序列化时该域是不会序列化的。
2,构造函数
ArrayList提供了二种方式的构造器,如下:
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 调用无参构造函数
this();
// 添加集合中所有的元素
addAll(c);
}
3,部分函数
3.1,add()函数
public boolean add(E e) {
// 添加到末尾
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
add()函数用于向LinkedList中添加一个元素,并且添加到链表尾部。具体添加到尾部的逻辑是由linkLast函数完成的,具体代码如下:
void linkLast(E e) {
// 保存尾结点,l为final类型,不可更改
final Node<E> l = last;
// 新生成结点的前驱为l,后继为null
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
// 重新赋值尾结点
last = newNode;
if (l == null) // 尾结点为空
first = newNode; // 赋值头结点
else // 尾结点不为空
l.next = newNode; // 尾结点的后继为新生成的结点
// 大小加1
size++;
// 结构性修改加1
modCount++;
}
3.2,addAll()函数
//添加指定集合的元素到列表,默认从最后开始添加
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);//size表示最后一个位置,可以理解为元素的位置分别为1~size
}
//从指定位置(而不是下标!下标即索引从0开始,位置可以看做从1开始,其实也是0)后面添加指定集合的元素到列表中,只要有至少一次添加就会返回true
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index); //检查索引是否正确(0<=index<=size)
Object[] a = c.toArray(); //得到元素数组
int numNew = a.length; //得到元素个数
if (numNew == 0) //若没有元素要添加,直接返回false
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ; //succ后节点,pred前节点
if (index == size) { //如果是在末尾开始添加,当前节点后一个节点初始化为null,前一个节点为尾节点
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else { //如果不是从末尾开始添加,当前位置的节点为指定位置的节点,前一个节点为要添加的节点的前一个节点
succ = node(index); //获取指定位置的节点
pred = succ.prev; //这里依然是node(index-1)
}
//遍历数组并添加到列表中
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);//创建一个节点,向前指向上面得到的前节点
if (pred == null)
first = newNode; //若果前节点为null,则新加的节点为首节点
else
pred.next = newNode;//如果存在前节点,前节点会向后指向新加的节点
pred = newNode; //新加的节点成为前一个节点
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred; //如果是从最后开始添加的,则最后添加的节点成为尾节点
} else {
pred.next = succ; //如果不是从最后开始添加的,则最后添加的节点向后指向之前得到的后续第一个节点
succ.prev = pred; //当前,后续的第一个节点也应改为向前指向最后一个添加的节点
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
四,LinkedList遍历方式
LinkedList支持7种遍历方式。
1,迭代器遍历。即通过Iterator去遍历。
for (Iterator<String> iter = linkedList.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
iter.next();
}
2,通过快速随机访问遍历LinkedList
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) {
linkedList.get(i);
}
3,通过for循环来遍历LinkedList
String tString;
for (String string : linkedList) {
tString = string;
}
4,通过pollFirst()来遍历LinkedList
while(linkedList.pollFirst() != null)
;
5,通过pollLast()来遍历LinkedList
while(linkedList.pollLast() != null)
;
6,通过removeFirst()来遍历LinkedList
while(linkedList.removeFirst() != null)
;
7,通过removeLast()来遍历LinkedList
while(linkedList.removeLast() != null)
;
下面通过一个实例,比较这7种方式的效率,代码如下:
public class TestLinkedList {
static long startTime = 0;
static long endTime = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
linkedList.add(i + "");
}
TestLinkedList.loopLinkedList_For(getLinkedList());
TestLinkedList.loopLinkedList_Indexes(getLinkedList());
TestLinkedList.loopLinkedList_Iterator(getLinkedList());
TestLinkedList.loopLinkedList_pollFirst(getLinkedList());
TestLinkedList.loopLinkedList_pollLast(getLinkedList());
TestLinkedList.loopLinkedList_removeFirst(getLinkedList());
TestLinkedList.loopLinkedList_removeLast(getLinkedList());
}
private static LinkedList<String> getLinkedList() {
LinkedList<String> llist = new LinkedList<String>();
for (int i=0; i<100000; i++)
llist.addLast(i + "");
return llist;
}
//快速随机访问遍历LinkedList
public static void loopLinkedList_Indexes(LinkedList<String> linkedList){
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) {
linkedList.get(i);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("快速随机访问遍历LinkedList(loopLinkedList_Indexes):" + interval + " ms");
}
//通过迭代器遍历。即通过Iterator去遍历。
public static void loopLinkedList_Iterator(LinkedList<String> linkedList){
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (Iterator<String> iter = linkedList.iterator(); iter.hasNext();) {
iter.next();
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("通过迭代器遍历(loopLinkedList_Iterator):" + interval + " ms");
}
//通过for循环遍历LinkedList
public static void loopLinkedList_For(LinkedList<String> linkedList){
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
String tString;
for (String string : linkedList) {
tString = string;
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("通过for循环遍历(loopLinkedList_For):" + interval + " ms");
}
//通过pollFirst()来遍历LinkedList
public static void loopLinkedList_pollFirst(LinkedList<String> linkedList){
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while(linkedList.pollFirst() != null)
;
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("通过pollFirst()来遍历(loopLinkedList_pollFirst):" + interval + " ms");
}
//通过pollLast()来遍历LinkedList
public static void loopLinkedList_pollLast(LinkedList<String> linkedList){
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
while(linkedList.pollLast() != null)
;
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = endTime - startTime;
System.out.println("通过pollLast()来遍历(loopLinkedList_pollLast):" + interval + " ms");
}
//通过removeFirst()来遍历LinkedList
public static void loopLinkedList_removeFirst(LinkedList<String> linkedList) {
if (linkedList == null)
return ;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
while(linkedList.removeFirst() != null)
;
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = end - start;
System.out.println("通过removeFirst()来遍历(loopLinkedList_removeFirst):" + interval + " ms");
}
//通过removeLast()来遍历LinkedList
public static void loopLinkedList_removeLast(LinkedList<String> linkedList) {
if (linkedList == null)
return ;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
while(linkedList.removeLast() != null)
;
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long interval = end - start;
System.out.println("通过removeLast()来遍历(loopLinkedList_removeLast):" + interval + " ms");
}
}
运行结果:
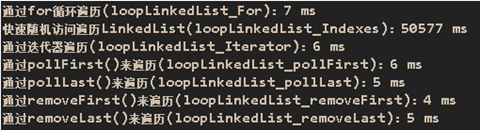
由此可见,遍历LinkedList时,使用removeFist()或removeLast()效率最高(删除原始数据)。不建议随机访问遍历LinkedList。
五,LinkedList应用举例
public class TestLinkedList2 {
static long startTime = 0;
static long endTime = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestLinkedList2.test();
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
TestLinkedList2.likeStack();
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
TestLinkedList2.likeQueue();
}
public static void test(){
LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<String>();
linkedList.add("ZenderA");
linkedList.add("ZenderB");
linkedList.add("ZenderC");
linkedList.add("ZenderD");
linkedList.add("ZenderE");
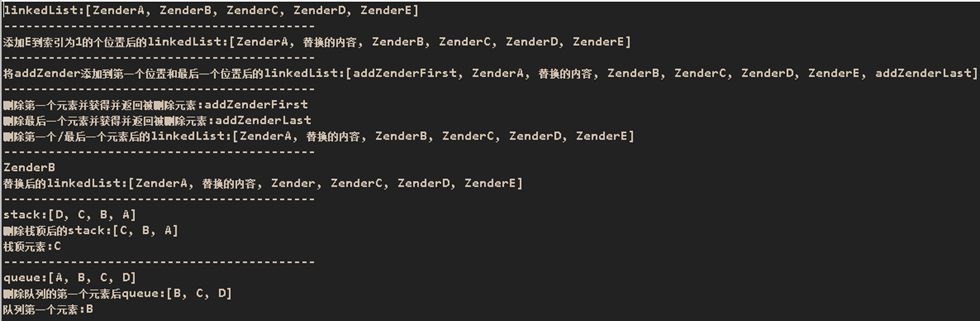
System.out.println("linkedList:" + linkedList);
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
// 将“替换的内容”添加到第索引为1的个位置
linkedList.add(1, "替换的内容");
//linkedList.addFirst("替换的内容");同样的效果
System.out.println("添加E到索引为1的个位置后的linkedList:" + linkedList);
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
//将“addZender”添加到第一个位置。 返回true。
linkedList.offerFirst("addZenderFirst");
//将“addZender”添加到最后一个位置。 返回true。
linkedList.offerLast("addZenderLast");
System.out.println("将addZender添加到第一个位置和最后一个位置后的linkedList:" + linkedList);
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
//删除第一个元素/删除最后一个元素并获得并返回被删除元素
System.out.println("删除第一个元素并获得并返回被删除元素:" + linkedList.removeFirst());
System.out.println("删除最后一个元素并获得并返回被删除元素:" + linkedList.removeLast());
System.out.println("删除第一个/最后一个元素后的linkedList:" + linkedList);
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
// 将第3个元素设置Zender,并返回旧值。
String text = linkedList.set(2, "Zender");
System.out.println(text);
System.out.println("替换后的linkedList:" + linkedList);
}
//将LinkedList作为栈(先进后出)使用
public static void likeStack() {
LinkedList<String> stack = new LinkedList<String>();
//向栈中添加元素
stack.push("A");
stack.push("B");
stack.push("C");
stack.push("D");
System.out.println("stack:"+stack);
stack.pop() ;// 删除“栈顶元素”
System.out.println("删除栈顶后的stack:"+stack);
System.out.println("栈顶元素:"+stack.peek()); // 取出栈顶
}
//将LinkedList作为队列(先进先出)使用
public static void likeQueue() {
LinkedList<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
//向队列中添加元素
queue.add("A");
queue.add("B");
queue.add("C");
queue.add("D");
System.out.println("queue:"+queue);
queue.remove() ;//删除队列的第一个元素
System.out.println("删除队列的第一个元素后queue:"+queue);
System.out.println("队列第一个元素:"+queue.element()); // 读取队列的第一个元素
}
}
运行结果:
六,常用函数
//在指定节点前插入节点,节点succ不能为空
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;//获取前一个节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);//使用参数创建新的节点,向前指向前一个节点,向后指向当前节点
succ.prev = newNode;//当前节点指向新的节点
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;//如果前一个节点为null,新的节点就是首节点
else
pred.next = newNode;//如果存在前节点,那么前节点的向后指向新节点
size++;
modCount++;
}
//删除首节点并返回删除前首节点的值,内部使用
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
final E element = f.item;//获取首节点的值
final Node<E> next = f.next;//得到下一个节点
f.item = null;
f.next = null; //便于垃圾回收期清理
first = next; //首节点的下一个节点成为新的首节点
if (next == null)
last = null; //如果不存在下一个节点,则首尾都为null(空表)
else
next.prev = null;//如果存在下一个节点,那它向前指向null
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//删除尾节点并返回删除前尾节点的值,内部使用
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
final E element = l.item;//获取值
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;//获取尾节点前一个节点
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; //便于垃圾回收期清理
last = prev; //前一个节点成为新的尾节点
if (prev == null)
first = null; //如果前一个节点不存在,则首尾都为null(空表)
else
prev.next = null;//如果前一个节点存在,先后指向null
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//删除指定节点并返回被删除的元素值
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
//获取当前值和前后节点
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next; //如果前一个节点为空(如当前节点为首节点),后一个节点成为新的首节点
} else {
prev.next = next;//如果前一个节点不为空,那么他先后指向当前的下一个节点
x.prev = null; //方便gc回收
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev; //如果后一个节点为空(如当前节点为尾节点),当前节点前一个成为新的尾节点
} else {
next.prev = prev;//如果后一个节点不为空,后一个节点向前指向当前的前一个节点
x.next = null; //方便gc回收
}
x.item = null; //方便gc回收
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//获取第一个元素
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;//得到首节点
if (f == null) //如果为空,抛出异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
//获取最后一个元素
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;//得到尾节点
if (l == null) //如果为空,抛出异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
//删除第一个元素并返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;//得到第一个节点
if (f == null) //如果为空,抛出异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
//删除最后一个元素并返回删除的值
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;//得到最后一个节点
if (l == null) //如果为空,抛出异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
//添加元素作为第一个元素
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
//店家元素作为最后一个元素
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
//检查是否包含某个元素,返回bool
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;//返回指定元素的索引位置,不存在就返回-1,然后比较返回bool值
}
//返回列表长度
public int size() {
return size;
}
//添加一个元素,默认添加到末尾作为最后一个元素
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//删除指定元素,默认从first节点开始,删除第一次出现的那个元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
//会根据是否为null分开处理。若值不是null,会用到对象的equals()方法
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//添加指定集合的元素到列表,默认从最后开始添加
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);//size表示最后一个位置,可以理解为元素的位置分别为1~size
}
//从指定位置(而不是下标!下标即索引从0开始,位置可以看做从1开始,其实也是0)后面添加指定集合的元素到列表中,只要有至少一次添加就会返回true
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index); //检查索引是否正确(0<=index<=size)
Object[] a = c.toArray(); //得到元素数组
int numNew = a.length; //得到元素个数
if (numNew == 0) //若没有元素要添加,直接返回false
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ; //succ后节点,pred前节点
if (index == size) { //如果是在末尾开始添加,当前节点后一个节点初始化为null,前一个节点为尾节点
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else { //如果不是从末尾开始添加,当前位置的节点为指定位置的节点,前一个节点为要添加的节点的前一个节点
succ = node(index); //获取指定位置的节点
pred = succ.prev; //这里依然是node(index-1)
}
//遍历数组并添加到列表中
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);//创建一个节点,向前指向上面得到的前节点
if (pred == null)
first = newNode; //若果前节点为null,则新加的节点为首节点
else
pred.next = newNode;//如果存在前节点,前节点会向后指向新加的节点
pred = newNode; //新加的节点成为前一个节点
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred; //如果是从最后开始添加的,则最后添加的节点成为尾节点
} else {
pred.next = succ; //如果不是从最后开始添加的,则最后添加的节点向后指向之前得到的后续第一个节点
succ.prev = pred; //当前,后续的第一个节点也应改为向前指向最后一个添加的节点
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
//清空表
public void clear() {
//方便gc回收垃圾
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) {
Node<E> next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
//获取指定索引的节点的值
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
//修改指定索引的值并返回之前的值
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
//指定位置后面(即索引为这个值的元素的前面)添加元素
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element); //如果指定位置为最后,则添加到链表最后
else //如果指定位置不是最后,则添加到指定位置前
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
//删除指定位置的元素,
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
//检查索引是否超出范围,因为元素索引是0~size-1的,所以index必须满足0<=index<size
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
//检查位置是否超出范围,index必须在index~size之间(含),如果超出,返回false
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
//异常详情
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
//检查元素索引是否超出范围,若已超出,就抛出异常
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
//检查位置是否超出范围,若已超出,就抛出异常
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
//获取指定位置的节点
Node<E> node(int index) {
//如果位置索引小于列表长度的一半(或一半减一),从前面开始遍历;否则,从后面开始遍历
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;//index==0时不会循环,直接返回first
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
//获取指定元素从first开始的索引位置,不存在就返回-1
//不能按条件双向找了,所以通常根据索引获得元素的速度比通过元素获得索引的速度快
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
//获取指定元素从first开始最后出现的索引,不存在就返回-1
//但实际查找是从last开始的
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
//提供普通队列和双向队列的功能,当然,也可以实现栈,FIFO,FILO
//出队(从前端),获得第一个元素,不存在会返回null,不会删除元素(节点)
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
//出队(从前端),不删除元素,若为null会抛出异常而不是返回null
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
//出队(从前端),如果不存在会返回null,存在的话会返回值并移除这个元素(节点)
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
//出队(从前端),如果不存在会抛出异常而不是返回null,存在的话会返回值并移除这个元素(节点)
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
//入队(从后端),始终返回true
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
//入队(从前端),始终返回true
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
//入队(从后端),始终返回true
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);//linkLast(e)
return true;
}
//出队(从前端),获得第一个元素,不存在会返回null,不会删除元素(节点)
public E peekFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
//出队(从后端),获得最后一个元素,不存在会返回null,不会删除元素(节点)
public E peekLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
//出队(从前端),获得第一个元素,不存在会返回null,会删除元素(节点)
public E pollFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
//出队(从后端),获得最后一个元素,不存在会返回null,会删除元素(节点)
public E pollLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
//入栈,从前面添加
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
//出栈,返回栈顶元素,从前面移除(会删除)
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
//节点的数据结构,包含前后节点的引用和当前节点
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
//返回迭代器
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
//因为采用链表实现,所以迭代器很简单
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
常用函数注释
3,LinkedList的更多相关文章
- ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector,Stack之间的区别
一,线程安全性 Vector.Stack:线程安全 ArrayList.LinkedList:非线程安全 二,实现方式 LinkedList:双向链表 ArrayList,Vector,Stack:数 ...
- 泛型,迭代器,LinkedList<E>
1 <e>里面只能填类,不能用基本数据类型,不过integer 这样的的也行 2在模板类(泛型类中)class demo<e>由于不知道e是那个,所有通常都是重写大家都有的to ...
- JAVA之旅(十九)——ListIterator列表迭代器,List的三个子类对象,Vector的枚举,LinkedList,ArrayList和LinkedList的小练习
JAVA之旅(十九)--ListIterator列表迭代器,List的三个子类对象,Vector的枚举,LinkedList,ArrayList和LinkedList的小练习 关于数据结构,所讲的知识 ...
- Hastable和Dictionary以及ArrayList和(List,LinkedList,数组)的区别
Hastable和Dictionary的区别:(键值对) 1:单线程程序中推荐使用 Dictionary, 有泛型优势, 且读取速度较快, 容量利用更充分. 2:多线程程序中推荐使用 Hashtabl ...
- List集合总结,对比分析ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList
前面已经写了三篇关于Java集合的文章,包括: Java集合 ArrayList原理及使用 再说Java集合,subList之于ArrayList Java集合 LinkedList的原理及使用 关于 ...
- Java ArrayList,LinkedList使用
1.ArrayList底层采用数组实现,当使用不带参数的构造方法生成ArrayList对象时,实际上回在底层生成一个长度为10的Object类型数组. 2.如果增加的元素个数超过10个,那么Array ...
- ArrayList,Vector ,LinkedList的存储性能和特性
ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList : 两者都采用数组元素方式存储数据,此数组元素数大于实际存储的数据(以便于增加和插入元素),允许直接按照序号索引元素,但是插入元素涉及数组元素移 ...
- Stack,ArrayDeque,LinkedList的区别
本文首发于cartoon的博客 转载请注明出处:https://cartoonyu.github.io/cartoon-blog 这段时间把疯狂JAVA再看了一遍,发现Stac ...
- 【转载】Java的Vector,ArrayList,LinkedList
首先看这两类都实现List接口,而List接口一共有三个实现类,分别是ArrayList.Vector和LinkedList.List用于存放多个元素,能够维护元素的次序,并且允许元素的重复.3个具体 ...
随机推荐
- 【cs231n作业笔记】一:KNN分类器
安装anaconda,下载assignment作业代码 作业代码数据集等2018版基于python3.6 下载提取码4put 本课程内容参考: cs231n官方笔记地址 贺完结!CS231n官方笔记授 ...
- Powershell 邮件发送
目录 目录 前言 Send-MailMessage NETMail 使用OutLook发送邮件 前言 最近领导想在winServer2012上搞个自动发送邮件的计划任务,下面有几种发送邮件的方式. 如 ...
- 解决旋转屏幕闪退在androidManifest.template.xml里,activity项添加:
解决旋转屏幕闪退在androidManifest.template.xml里,activity项添加:android:configChanges="orientation|keyboard ...
- 分布式ID生成 - 雪花算法
雪花算法是一种生成分布式全局唯一ID的经典算法,关于雪花算法的解读网上多如牛毛,大多抄来抄去,这里请参考耕耘的小象大神的博客ID生成器,Twitter的雪花算法(Java) 网上的教程一般存在两个问题 ...
- android window(四)WindowToken
在WindowManagerService中有两种常见的Token,WindowToken,和AppWindowToken. WindowToken http://androidxref.com/6. ...
- c# 对象相等性和同一性
一:对象相等性和同一性 System.Object提供了名为Equals的虚方法,作用是在两个对象包含相同值的前提下返回true,内部实现 public class Object { public v ...
- Java容器框架总结(一)
本篇根据<Java编程思想> 第11章 持有对象 整理,总结Java容器框架中常用集合类及接口的特点及使用场景. (一)总结 1)数组将数字与对象联系起来:可以保存基本类型的数据:一旦生成 ...
- HackGame2 writeup
网址:http://hackgame.blackbap.org/ 第一关 突破客户端:无论输入什么密码都会提示"密码不能为空",使用浏览器检查网页元素会发现提交时会触发 javas ...
- Linux 与 Unix 到底有啥区别和联系?
原文:https://opensource.com/article/18/5/differences-between-linux-and-unix 来源:开源中国社区,译者:Tocy, LinuxTe ...
- docker网络 macvlan
docker 还开发了另一个支持跨主机容器网络的 driver:macvlan. macvlan 本身是 linxu kernel 模块,其功能是允许在同一个物理网卡上配置多个 MAC 地址,即多个 ...
