分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ的消息存储持久化
ActiveMQ的消息存储持久化
■概述
ActiveMQ不仅支持 persistent和 non-persistent两种方式,还支持消息的
恢复( recovery)方式
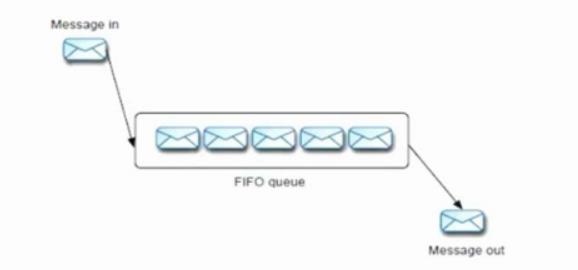
PTP
Queue的存储是很简单的,就是一个FIFO的 Queue
图1-1
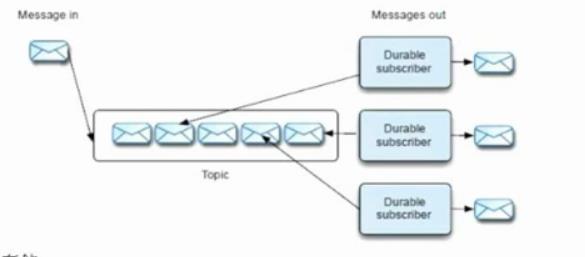
PUB/SUB
对于持久化订阅主题,每一个消费者将获得一个消息的复制
图1-2
有效的消息存储
ActiveMQ提供了一个插件式的消息存储,类似于消息的多点传播,主要实现了如下几种:
1:AMQ消息存储-基于文件的存储方式,是以前的默认消息存储
2: KahaDB消息存储-提供了容量的提升和恢复能力,是现在的默认存储方式
3:JDBC消息存储-消息基于JDBC存储的
4:Memory信息存储-基于内存的信息存储
KahaDB Message Store
概述
KahaDB是目前默认的存储方式,可用于任何场景,提高了性能和恢复能力。消息存储使用一个事
务日志和仅仅用一个索引文件来存储它所有的地址。
KahaDB是一个专门针对消息持久化的解决方案,它对典型的消息使用模式进行了优化。在Kaha
中,数据被追加到data logs中。当不再需要log文件中的数据的时候,log文件会被丢弃
KahaDB基本配置例子
<persistenceAdapter>
<kahaDB directory="{activemq.data}/kahadb"/>
</persistenceAdapter>
可用的属性有:
1: director: KahaDB存放的路径,默认值 activemq-data
2: indexWriteBatchsize:批量写入磁盘的索引page数量,默认值1000
3: indexCachesize:内存中缓存索引page的数量,默认值10000
4: enableIndexWriteAsync:是否异步写出索引,默认 false
5: journalMaxFileLength:设置每个消息data1og的大小,默认是32MB
6: enableJournalDiskSyncs:设置是否保证每个没有事务的内容,被同步写入磁盘,JMS持久化的时候需
要,默认为true
7: cleanupInterval: 在检查到不再使用的消息后,在具体删除消息前的时间,默认30000
8: checkpointInterval: checkpoint的间隔时间,默认5000
9: ignoreMissingJournalfiles:是否忽略丢失的消息日志文件,默认fa1se
10: checkForCorruptJournalFiles:在启动的时候,将会验证消息文件是否损坏,默认fa1se
11: checksumJournalFiles:是否为每个消息日志文件提供 checksum,默认 false
12: archiveDatalogs:是否移动文件到特定的路径,而不是删除它们,默认fa1se
13: directoryArchive:定义消息已经被消费过后,移动 data log到的路径,默认nu11
14: databaseLockedWailayDelay:获得数据库锁的等待时间( used by shared master/ slave),默认
10000
15: maxAsyncJobs:设置最大的可以存储的异步消息队列,默认值10000,可以和 concurrent
MessageProducers设置成一样的值
16: concurrentStoreAndDispatchTransactions:是否分发消息到客户端,同时事务存储消息,默认
true
17: concurrentstoreAndDispatchTopics:是否分发 Topic消息到客户端,同时进行存储,默认true
18: concurrentStoreAndDispatchQueues:是否分发 queue消息到客户端,同时进行存储,默认true
在Java中内嵌使用 Broker,使用 KahaDB的例子
package com.mq.test.activeMQ; import java.io.File; import org.apache.activemq.broker.BrokerService;
import org.apache.activemq.store.kahadb.KahaDBStore; public class KahaDB {
BrokerService createEmbeddedBroker() throws Exception {
BrokerService broker =new BrokerService();
File dataFileDir =new File( "target/amg-in-action/kahadb");
KahaDBStore kaha= new KahaDBStore();
kaha.setDirectory (dataFileDir);
// Using a bi gger journal file
kaha.setJournalMaxFileLength(*);
// small batch means more frequent and smaller writes
kaha.setIndexWriteBatchSize();
// do the Andex write in a separate thread
kaha.setEnableIndexWriteAsync(true);
broker.setPersistenceAdapter(kaha);
//create a transport connector
broker.addConnector("tcp://localhost:61616");
//start the broker
broker.start();
return broker;
}
}
AMQ Message Store概述
AMQ Message Store是 ActiveMQ5.0缺省的持久化存储,它是一个基于文件、事
务存储设计为快速消息存储的一个结构,该结构是以流的形式来进行消息交互的。
这种方式中, Messages被保存到 data logs中,同时被 reference store进行索
引以提高存取速度。 Date logs由一些单独的 data log文件组成,缺省的文件大小是
32M,如果某个消息的大小超过了 data log文件的大小,那么可以修改配置以增加
data log文件的大小。如果某个 data log文件中所有的消息都被成功消费了,那么这
个 data log文件将会被标记,以便在下一轮的清理中被删除或者归档。
AMQ Message Store配置示例
<broker brokerName=broker persistent=true useShutdownHook="false">
<persistenceAdapter>
<amqPersistenceAdapter directory="${activemq.basel/data" maxFileLength="32mb"/>
</persistenceAdapter>
</broker>
使用JDBC来持久化消息
ActiveMQ支持使用JDBC来持久化消息,预定义的表如下:
1:消息表,缺省表名为 ACTIVEMQ_MSGS, queue和 topic都存在里面i,结构如下:
图2-1
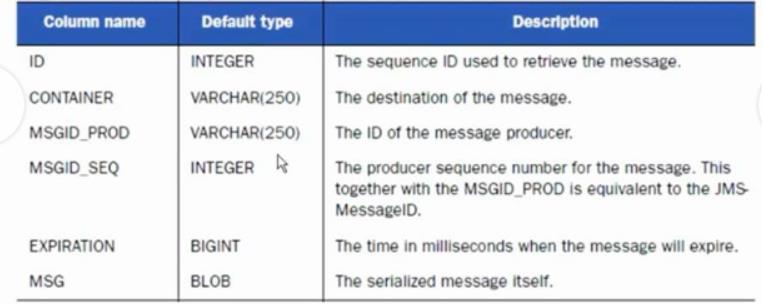
2: ACTIVEMQ_ACKS表存储持久订阅的信息和最后一个持久订阅接收的消息ID,结构如下
图2-2
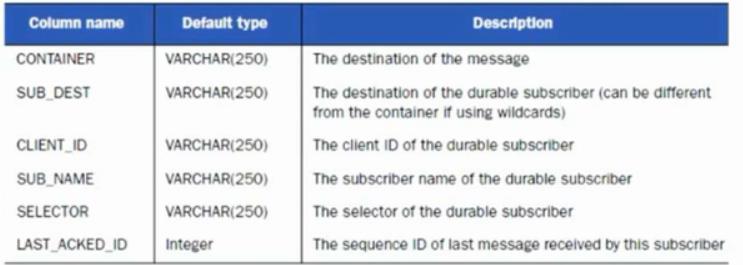
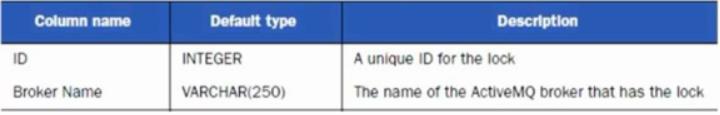
3:锁定表,缺省表名为 ACTIVEMQ_LOCK,用来确保在某一时刻,只能有一个
ActiveMQ broker实例来访问数据库,结构如下:
图2-3
■使用JDBC来持久化消息的配置示例
图2-4

代码如下:
<!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
<!-- START SNIPPET: example -->
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core/activemq-core.xsd"> <!-- Allows us to use system properties as variables in this configuration file -->
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>file:${activemq.conf}/credentials.properties</value>
</property>
</bean> <!-- Allows accessing the server log -->
<bean id="logQuery" class="io.fabric8.insight.log.log4j.Log4jLogQuery"
lazy-init="false" scope="singleton"
init-method="start" destroy-method="stop">
</bean> <!--
The <broker> element is used to configure the ActiveMQ broker.
-->
<broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" brokerName="localhost" dataDirectory="${activemq.data}"> <destinationPolicy>
<policyMap>
<policyEntries>
<policyEntry topic=">" >
<!-- The constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy is used to prevent
slow topic consumers to block producers and affect other consumers
by limiting the number of messages that are retained
For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/slow-consumer-handling.html -->
<pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
<constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy limit=""/>
</pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
</policyEntry>
</policyEntries>
</policyMap>
</destinationPolicy> <!--
The managementContext is used to configure how ActiveMQ is exposed in
JMX. By default, ActiveMQ uses the MBean server that is started by
the JVM. For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/jmx.html
-->
<managementContext>
<managementContext createConnector="false"/>
</managementContext> <!--
Configure message persistence for the broker. The default persistence
mechanism is the KahaDB store (identified by the kahaDB tag).
For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/persistence.html
-->
<persistenceAdapter>
<!--
<kahaDB directory="${activemq.data}/kahadb"/>
-->
<jdbcPersistenceAdapter dataSource="#mysql-ds" createTablesOnStartup="true"/>
</persistenceAdapter> <!--
The systemUsage controls the maximum amount of space the broker will
use before disabling caching and/or slowing down producers. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html
-->
<systemUsage>
<systemUsage>
<memoryUsage>
<memoryUsage percentOfJvmHeap="" />
</memoryUsage>
<storeUsage>
<storeUsage limit="100 gb"/>
</storeUsage>
<tempUsage>
<tempUsage limit="50 gb"/>
</tempUsage>
</systemUsage>
</systemUsage> <!--
The transport connectors expose ActiveMQ over a given protocol to
clients and other brokers. For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/configuring-transports.html
-->
<transportConnectors>
<!-- DOS protection, limit concurrent connections to and frame size to 100MB -->
<transportConnector name="openwire" uri="tcp://0.0.0.0:61616?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="amqp" uri="amqp://0.0.0.0:5673?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="stomp" uri="stomp://0.0.0.0:61613?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="mqtt" uri="mqtt://0.0.0.0:1883?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="ws" uri="ws://0.0.0.0:61614?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
</transportConnectors> <!-- destroy the spring context on shutdown to stop jetty -->
<shutdownHooks>
<bean xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" class="org.apache.activemq.hooks.SpringContextHook" />
</shutdownHooks> </broker>
<bean id="mysql-ds" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/activemq?relaxAutoCommit=true"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
<property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!--
Enable web consoles, REST and Ajax APIs and demos
The web consoles requires by default login, you can disable this in the jetty.xml file Take a look at ${ACTIVEMQ_HOME}/conf/jetty.xml for more details
-->
<import resource="jetty.xml"/> </beans>
<!-- END SNIPPET: example -->
问题:报org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource 找不到
解决:导入jar报lib中mysql-connector-java-5.1.35.jar
JDBC Message Store with ActiveMQ Journal
这种方式克服了 JDBC Store的不足,用快速的缓存写入技术,大大提高了性能。配置示例如下:
<!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
<!-- START SNIPPET: example -->
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core/activemq-core.xsd"> <!-- Allows us to use system properties as variables in this configuration file -->
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>file:${activemq.conf}/credentials.properties</value>
</property>
</bean> <!-- Allows accessing the server log -->
<bean id="logQuery" class="io.fabric8.insight.log.log4j.Log4jLogQuery"
lazy-init="false" scope="singleton"
init-method="start" destroy-method="stop">
</bean> <!--
The <broker> element is used to configure the ActiveMQ broker.
-->
<broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" brokerName="localhost" dataDirectory="${activemq.data}"> <destinationPolicy>
<policyMap>
<policyEntries>
<policyEntry topic=">" >
<!-- The constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy is used to prevent
slow topic consumers to block producers and affect other consumers
by limiting the number of messages that are retained
For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/slow-consumer-handling.html -->
<pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
<constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy limit=""/>
</pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
</policyEntry>
</policyEntries>
</policyMap>
</destinationPolicy> <!--
The managementContext is used to configure how ActiveMQ is exposed in
JMX. By default, ActiveMQ uses the MBean server that is started by
the JVM. For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/jmx.html
-->
<managementContext>
<managementContext createConnector="false"/>
</managementContext> <!--
Configure message persistence for the broker. The default persistence
mechanism is the KahaDB store (identified by the kahaDB tag).
For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/persistence.html
-->
<!--
<persistenceAdapter> <kahaDB directory="${activemq.data}/kahadb"/> <jdbcPersistenceAdapter dataSource="#mysql-ds" createTablesOnStartup="true"/> </persistenceAdapter>
-->
<persistenceFactory>
<journalPersistenceAdapterFactory
journalLogFiles=""
journalLogFileSize=""
useJournal="true"
useQuickJournal="true"
dataSource="#mysql-ds"
dataDirectory="activemq-data" />
</persistenceFactory>
<!--
The systemUsage controls the maximum amount of space the broker will
use before disabling caching and/or slowing down producers. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html
-->
<systemUsage>
<systemUsage>
<memoryUsage>
<memoryUsage percentOfJvmHeap="" />
</memoryUsage>
<storeUsage>
<storeUsage limit="100 gb"/>
</storeUsage>
<tempUsage>
<tempUsage limit="50 gb"/>
</tempUsage>
</systemUsage>
</systemUsage> <!--
The transport connectors expose ActiveMQ over a given protocol to
clients and other brokers. For more information, see: http://activemq.apache.org/configuring-transports.html
-->
<transportConnectors>
<!-- DOS protection, limit concurrent connections to and frame size to 100MB -->
<transportConnector name="openwire" uri="tcp://0.0.0.0:61616?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="amqp" uri="amqp://0.0.0.0:5673?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="stomp" uri="stomp://0.0.0.0:61613?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="mqtt" uri="mqtt://0.0.0.0:1883?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="ws" uri="ws://0.0.0.0:61614?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
</transportConnectors> <!-- destroy the spring context on shutdown to stop jetty -->
<shutdownHooks>
<bean xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" class="org.apache.activemq.hooks.SpringContextHook" />
</shutdownHooks> </broker>
<bean id="mysql-ds" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/activemq?relaxAutoCommit=true"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
<property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!--
Enable web consoles, REST and Ajax APIs and demos
The web consoles requires by default login, you can disable this in the jetty.xml file Take a look at ${ACTIVEMQ_HOME}/conf/jetty.xml for more details
-->
<import resource="jetty.xml"/> </beans>
<!-- END SNIPPET: example -->
JDBC Store和 JDBC Message Store with ActiveMQ Journal的区别
1: Jdbc with journal的性能优表jdbc
2:Jdbc用于 master/ slave模式的数据库分享
3: Jdbc with journal不能用于 master/ slave模式
4:一般情况下,推荐使用 jdbc with journal
Memory Message Store
内存游息存储主要是存储所有的持久化的消息在内存中,这里没有动态的缓存存在,所以
你必须注意设置你的 broker所在的JM和内存限制
Memory Message Store配置示例
<beans>
<broker brokerName="test-broker" persistent= "false" xmlns="http://activemq.apacheorg/schema/core">
<transportConnectors>
<ransport Connector uri="tcp: //localhost: 61635"/>
</transportConnectors>
<broker>
</beans>
在Java中内嵌使用 Broker,使用 Memory的例子
package test.mq.topic1; import java.net.URI; import org.apache.activemq.broker.BrokerFactory;
import org.apache.activemq.broker.BrokerService; public class InnerBroker {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BrokerService broker=new BrokerService();
broker.setPersistent(false);
broker.setUseJmx(true);
broker.addConnector("tcp://localhost:61616");
broker.start(); }
}
分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ的消息存储持久化的更多相关文章
- 分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ基础
ActiveMQ简介 ActiveMQ是什么ActiveMQ是Apache推出的,一款开源全支持JMS.1和J2EE1.4范的JMS Provider实现的信息中间件.(message oriente ...
- 分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ的Destination高级特性3
虚拟destination用来创建逻辑destination,客户端可以通过它来生产和消费消息,它会把消息映射到物理destination. ActiveMQ支持2种方式: 1:虚拟主题(Virtua ...
- 分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ的Message dispatch高级特性之(指针) Message cursors
Message dispatch高级特性之 Message cursors概述 ActiveMQ发送持久消息的典型处现方式是:当消息的消费者准备就绪时,消息发送系统把存储的 消息 ...
- 分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ的Destination高级特性2
使用filtered destinations,在xml配置如下: <destinationInterceptors> <virtualDestinationInterceptor& ...
- 分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ的Destination高级特性1
ActiveMQ的Destination高级特性 Destination高级特性----->Composite Destinations 组合队列Composite Destinations : ...
- 分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ的集群
ActiveMQ的集群Queue consumer clusters ActiveMQ支持 Consumer对消息高可靠性的负载平衡消费,如果一个 Consumer死掉,该消 ...
- 分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ静态网络连接的容错
容错的链接Failover Protocol 前面讲述的都是client配置链接到指定的 broker上.但是,如果 Broker的链接失败怎么办呢?此时, Client有两个选项:要么立刻死掉,要么 ...
- 分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ的动态网络链接
ActiveMQ的动态网络链接多播协议 multicast ActiveMQ使用 Multicast协议将一个 Service和其他的 Broker的 Service连接起来,IPmulticast是 ...
- 分布式-信息方式-ActiveMQ静态网络连接信息回流功能
“丢失”的消息 有这样的场景, broker1和 broker2通过 netwoskconnector连接,一些 consumers连接到 broker1,消费 broker2上的消息.消息先被 br ...
随机推荐
- 纯H5 AJAX文件上传加进度条功能
上传代码js部分 //包上传 $('.up_apk').change(function () { var obj = $(this); var form_data = new FormData(); ...
- linux增加swap大小
参考自:https://blog.csdn.net/ssrmygod/article/details/70157716 我在centos6.5上照着操作成功了首先查一下目前swap的大小: [root ...
- C数据结构排序算法——直接插入排序法用法总结(转http://blog.csdn.net/lg1259156776/)
声明:引用请注明出处http://blog.csdn.net/lg1259156776/ 排序相关的的基本概念 排序:将一组杂乱无章的数据按一定的规律顺次排列起来. 数据表( data list): ...
- es分数_score衰减函数
1.按日期衰变 GET news/doc/_search { "query" : { "function_score": { "query" ...
- Python标准库、第三方库和外部工具汇总
导读:Python数据工具箱涵盖从数据源到数据可视化的完整流程中涉及到的常用库.函数和外部工具.其中既有Python内置函数和标准库,又有第三方库和工具. 这些库可用于文件读写.网络抓取和解析.数据连 ...
- 新技能get,文件夹隐藏
attrib命令用来显示或更改文件属性. ATTRIB [+R | -R] [+A | -A ] [+S | -S] [+H | -H] [[drive:] [path] filename] [/S ...
- python cv2读取rtsp实时码流按时生成连续视频文件
代码实现 # coding: utf-8 import datetime import cv2 import os ip = '192.168.3.160'.replace("." ...
- PID应用详解
PID应用详解 阅读目录 1.PID介绍及原理2.常用四轴的两种PID算法讲解(单环PID.串级PID)3.常用PID算法的C语言实现5.常用的四轴飞行器PID算法 PID介绍及原理 PID介绍 在工 ...
- SQL Server里面如何导出包含数据的SQL脚本
通常情况下,SQL Server里面的生成SQL脚本,只会包含数据库及表的字段结构,而不会包含表的数据,也就是SQL脚本里面只有Create database,Create table 这样的语句,没 ...
- silverlight发布设置
HTTP头 - MIME类型.xap xapapplication/x-silverlight .xaml application/xaml+xml
