吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestRegressor回归模型
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def load_data_regression():
'''
加载用于回归问题的数据集
'''
#使用 scikit-learn 自带的一个糖尿病病人的数据集
diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes()
# 拆分成训练集和测试集,测试集大小为原始数据集大小的 1/4
return train_test_split(diabetes.data,diabetes.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0) #集成学习随机森林RandomForestRegressor回归模型
def test_RandomForestRegressor(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
regr=ensemble.RandomForestRegressor()
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
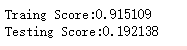
print("Traing Score:%f"%regr.score(X_train,y_train))
print("Testing Score:%f"%regr.score(X_test,y_test)) # 获取分类数据
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_regression()
# 调用 test_RandomForestRegressor
test_RandomForestRegressor(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
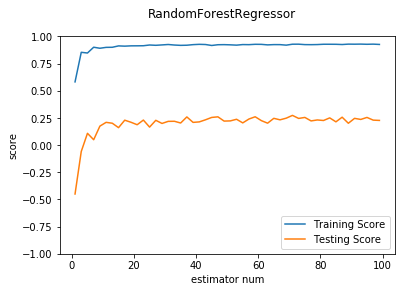
def test_RandomForestRegressor_num(*data):
'''
测试 RandomForestRegressor 的预测性能随 n_estimators 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
nums=np.arange(1,100,step=2)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for num in nums:
regr=ensemble.RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=num)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(-1,1)
plt.suptitle("RandomForestRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_RandomForestRegressor_num
test_RandomForestRegressor_num(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
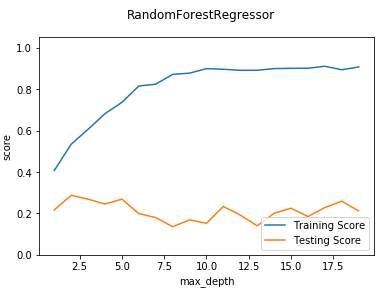
def test_RandomForestRegressor_max_depth(*data):
'''
测试 RandomForestRegressor 的预测性能随 max_depth 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
maxdepths=range(1,20)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for max_depth in maxdepths:
regr=ensemble.RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=max_depth)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(maxdepths,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(maxdepths,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("max_depth")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle("RandomForestRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_RandomForestRegressor_max_depth
test_RandomForestRegressor_max_depth(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
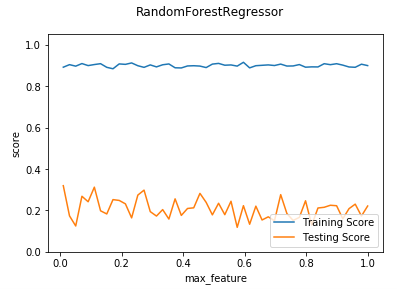
def test_RandomForestRegressor_max_features(*data):
'''
测试 RandomForestRegressor 的预测性能随 max_features 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
max_features=np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for max_feature in max_features:
regr=ensemble.RandomForestRegressor(max_features=max_feature)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(max_features,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(max_features,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("max_feature")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle("RandomForestRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_RandomForestRegressor_max_features
test_RandomForestRegressor_max_features(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestRegressor回归模型的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestClassifier分类模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法回归模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法分类模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 机器学习:集成学习:随机森林.GBDT
集成学习(Ensemble Learning) 集成学习的思想是将若干个学习器(分类器&回归器)组合之后产生一个新学习器.弱分类器(weak learner)指那些分类准确率只稍微好于随机猜测 ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——伯努利贝叶斯BernoulliNB模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,naive_bayes from skl ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——数据预处理过滤式特征选取SelectPercentile模型
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectPercentile,f_classif #数据预处理过滤式特征选取SelectPercentile模型 def ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——数据预处理过滤式特征选取VarianceThreshold模型
from sklearn.feature_selection import VarianceThreshold #数据预处理过滤式特征选取VarianceThreshold模型 def test_Va ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——数据预处理字典学习模型
from sklearn.decomposition import DictionaryLearning #数据预处理字典学习DictionaryLearning模型 def test_Diction ...
随机推荐
- python接口自动化-requests-toolbelt处理multipart/form-data
1.requests-toolbelt官方文档:https://pypi.org/project/requests-toolbelt/ 2.环境安装 pip install requests-tool ...
- java中类的构造方法出错点
大家请看下面的这个代码 package ppt_test; public class test1 { public static void main(String args[]) { Foo obj1 ...
- 解决并发问题的CAS思想及原理
全称为:Compare and swap(比较与交换),用来解决多线程并发情况下使用锁造成性能开销的一种机制: 原理思想:CAS(V,A,B),V为内存地址,A为预期原值,B为新值.如果内存地 ...
- LaTeX技巧011:LaTtex中如何产生直立体希腊字母?
%\usepackage{upgreek}\upmu \uppi
- Javascript 利用 switch 语句进行范围判断
; switch (true) { ): alert("less than five"); break; ): alert("between 5 and 8") ...
- 2020牛客寒假算法基础集训营5 B.牛牛战队的比赛地 (二分/三分)
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/3006/B 三分做法 #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f ...
- 简单的Spring1.0小配置
开始Spring AOP的小理解 拿一个小例子来说吧! 老师上课 这样的例子! 老师上课--就是一个核心的业务! 那么上课之前需要点名,天气太热,需要开空调! 这个时候,一个老 ...
- 巨杉Tech | SparkSQL+SequoiaDB 性能调优策略
当今时代,企业数据越发膨胀.数据是企业的价值,但数据处理也是一种技术挑战.在海量数据处理的场景,即使单机计算能力再强,也无法满足日益增长的数据处理需求.所以,分布式才是解决该类问题的根本解决方案.而在 ...
- HTML代码中<%%>、<%=%>
运行.获取后台代码或值.<%%>之间可以写服务器端代码,比如<%for(var i=0;i<10;i++){//执行循环体}%>又如<%for(var i=0;i& ...
- Error: Unexpected HTTP status 413 'Request Entity Too Large' on
由于nginx的client_max_body_size设置过小,默认上传的文件小于所要上传的文件大小,把这个值调大就可以了,我这里在配置文件的server下更改如下: server { client ...
