Opentracing + Uber Jaeger 全链路灰度调用链,Nepxion Discovery
当网关和服务在实施全链路分布式灰度发布和路由时候,我们需要一款追踪系统来监控网关和服务走的是哪个灰度组,哪个灰度版本,哪个灰度区域,甚至监控从Http Header头部全程传递的灰度规则和路由策略。这个功能意义在于:
- 不仅可以监控全链路中基本的调用信息,也可以监控额外的灰度信息,有助于我们判断灰度发布和路由是否执行准确,一旦有问题,也可以快速定位
- 可以监控流量何时切换到新版本,或者新的区域,或者新的机器上
- 可以监控灰度规则和路由策略是否配置准确
- 可以监控网关和服务灰度上下级树状关系
- 可以监控全链路流量拓扑图
笔者尝试调研了一系列分布式追踪系统和中间件,包括Opentracing、Uber Jaeger、Twitter Zipkin、Apache Skywalking、Pinpoint、CAT等,最后决定采用Opentracing + Uber Jaeger方式来实现,重要原因除了易用性和可扩展性外,Opentracing支持WebMvc和WebFlux两种方式,业界的追踪系统能支持WebFlux相对较少
[OpenTracing] OpenTracing已进入CNCF,正在为全球的分布式追踪系统提供统一的概念、规范、架构和数据标准。它通过提供平台无关、厂商无关的API,使得开发人员能够方便的添加(或更换)追踪系统的实现。对于存在多样化的技术栈共存的调用链中,Opentracing适配Java、C、Go和.Net等技术栈,实现全链路分布式追踪功能。迄今为止,Uber Jaeger、Twitter Zipkin和Apache Skywalking已经适配了Opentracing规范
笔者以Nepxion社区的Discovery开源框架(对该开源框架感兴趣的同学,请访问如下链接)为例子展开整合
源码主页,请访问
https://github.com/Nepxion/Discovery
指南主页,请访问
https://github.com/Nepxion/DiscoveryGuide
文档主页,请访问
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1i57rXaNKPuhGRqZ2MONZOA#list/path=%2FNepxion
整合的效果图



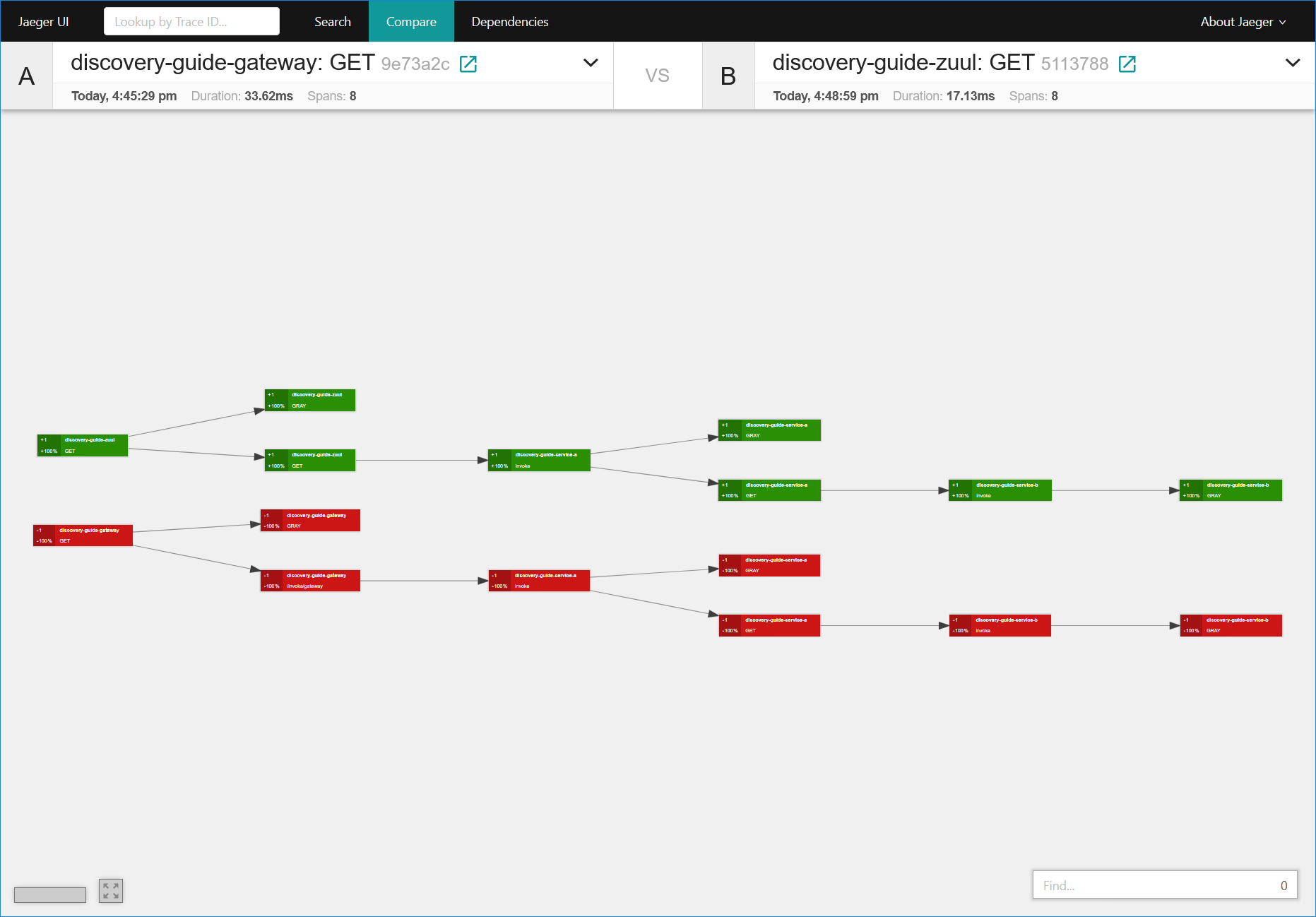
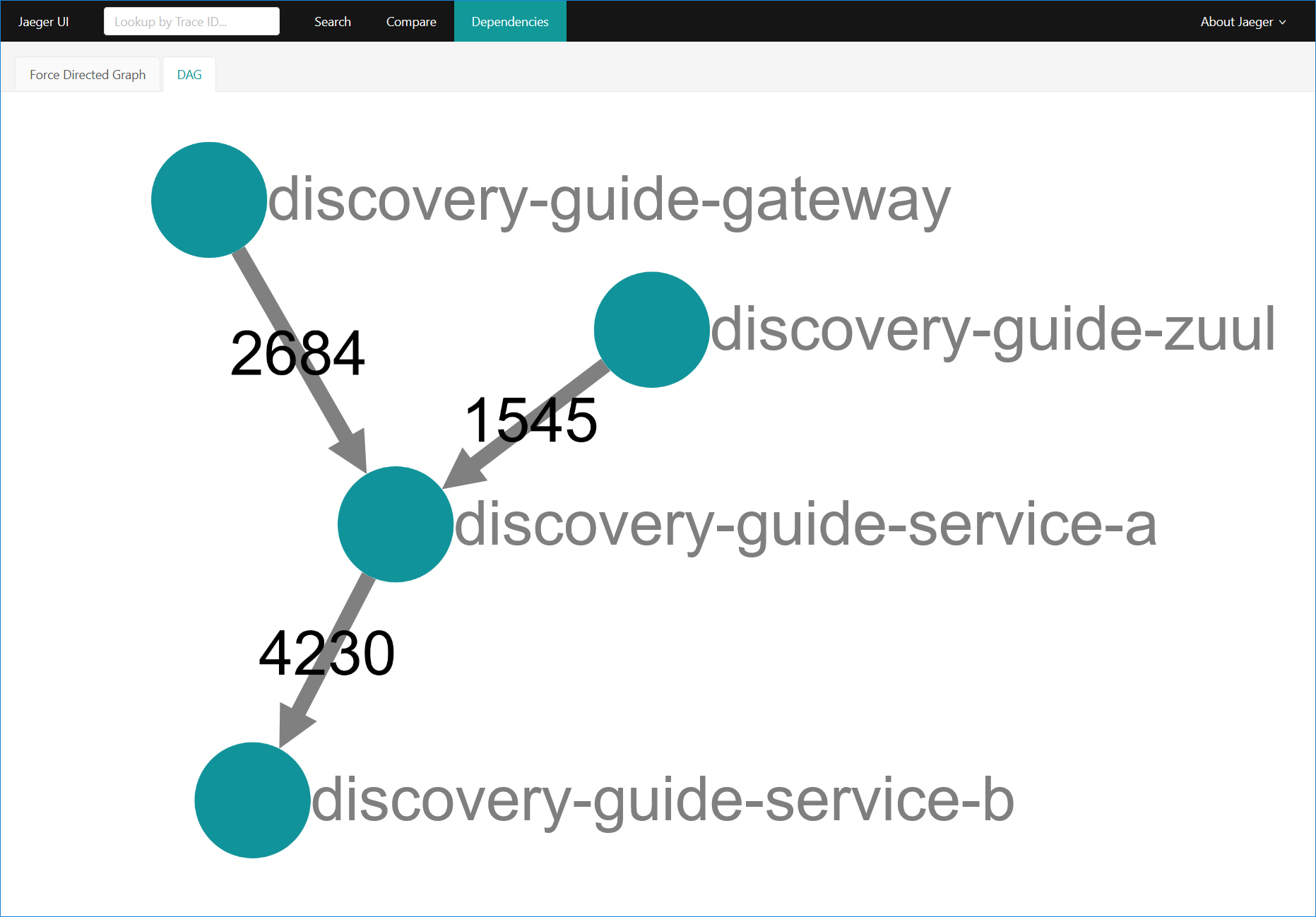
基本概念
灰度调用链主要包括如下11个参数。使用者可以自行定义要传递的调用链参数,例如:traceId, spanId等;也可以自行定义要传递的业务调用链参数,例如:mobile, user等
1. n-d-service-group - 服务所属组或者应用
2. n-d-service-type - 服务类型,分为“网关”和“服务”
3. n-d-service-id - 服务ID
4. n-d-service-address - 服务地址,包括Host和Port
5. n-d-service-version - 服务版本
6. n-d-service-region - 服务所属区域
7. n-d-version - 版本路由值
8. n-d-region - 区域路由值
9. n-d-address - 地址路由值
10. n-d-version-weight - 版本权重路由值
11. n-d-region-weight - 区域权重路由值
核心实现
Opentracing通用模块
源码参考
https://github.com/Nepxion/Discovery/tree/master/discovery-plugin-strategy-opentracing
由于OpenTracing扩展需要兼顾到Spring Cloud Gateway、Zuul和服务,它的核心逻辑存在着一定的可封装性,所以笔者抽取出一个公共模块discovery-plugin-strategy-opentracing,包含configuration、operation、context等模块,着重阐述operation模块,其它比较简单,不一一赘述了
在阐述前,笔者需要解释一个配置,该配置将决定核心实现以及终端界面的显示
- 如果开启,灰度信息输出到独立的Span节点中,意味着在界面显示中,灰度信息通过独立的GRAY Span节点来显示。优点是信息简洁明了,缺点是Span节点会增长一倍。我们可以称呼它为【模式A】
- 如果关闭,灰度信息输出到原生的Span节点中,意味着在界面显示中,灰度信息会和原生Span节点的调用信息、协议信息等混在一起,缺点是信息庞杂混合,优点是Span节点数不会增长。我们可以称呼它为【模式B】
# 启动和关闭调用链的灰度信息在Opentracing中以独立的Span节点输出,如果关闭,则灰度信息输出到原生的Span节点中。缺失则默认为true
spring.application.strategy.trace.opentracing.separate.span.enabled=true
Opentracing公共操作类 - StrategyOpentracingOperation.java
- 装配注入Opentracing的Tracer对象
- opentracingInitialize方法,提供给网关和服务的Span节点初始化
- 【模式A】下,tracer.buildSpan(...).start()实现新建一个Span,并把它放置到存储上下文的StrategyOpentracingContext的ThreadLocal里
- 【模式B】下,不需要做任何工作
- opentracingHeader方法,提供给网关的灰度调用链输出
- 【模式A】下,首先从StrategyOpentracingContext的ThreadLocal里获取Span对象,其次把customizationMap(自定义的调用链参数)的元素都放入到Tag中,最后把灰度调用链主11个参数(通过strategyContextHolder.getHeader(...)获取)和更多上下文信息放入到Tag中
- 【模式B】下,跟【模式A】类似,唯一区别的是Tags.COMPONENT的处理,由于原生的Span节点已经带有该信息,所以不需要放入到Tag中
- opentracingLocal方法,提供给服务的灰度调用链输出
- 【模式A】下,首先从StrategyOpentracingContext的ThreadLocal里获取Span对象,其次把customizationMap(自定义的调用链参数)的元素都放入到Tag中,最后把灰度调用链主11个参数(通过pluginAdapter.getXXX()获取)和更多上下文信息放入到Tag中
- 【模式B】下,跟【模式A】类似,唯一区别的是Tags.COMPONENT的处理,由于原生的Span节点已经带有该信息,所以不需要放入到Tag中
- opentracingError方法,提供给服务的灰度调用链异常输出
- 【模式A】下,首先从StrategyOpentracingContext的ThreadLocal里获取Span对象,其次span.log(...)方法实现异常输出
- 【模式B】下,不需要做任何工作
- opentracingClear方法,灰度调用链的Span上报和清除
- 【模式A】下,首先从StrategyOpentracingContext的ThreadLocal里获取Span对象,其次span.finish()方法实现Span上报,最后StrategyOpentracingContext.clearCurrentContext()方法实现Span清除
- 【模式B】下,不需要做任何工作
- getCurrentSpan方法
- 【模式A】下,返回StrategyOpentracingContext.getCurrentContext().getSpan(),即opentracingInitialize新建的Span对象
- 【模式B】下,返回tracer.activeSpan(),即原生的Span对象
public class StrategyOpentracingOperation {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StrategyOpentracingOperation.class);
@Autowired
protected PluginAdapter pluginAdapter;
@Autowired
protected StrategyContextHolder strategyContextHolder;
@Autowired
private Tracer tracer;
@Value("${" + StrategyOpentracingConstant.SPRING_APPLICATION_STRATEGY_TRACE_OPENTRACING_ENABLED + ":false}")
protected Boolean traceOpentracingEnabled;
@Value("${" + StrategyOpentracingConstant.SPRING_APPLICATION_STRATEGY_TRACE_OPENTRACING_SEPARATE_SPAN_ENABLED + ":true}")
protected Boolean traceOpentracingSeparateSpanEnabled;
public void opentracingInitialize() {
if (!traceOpentracingEnabled) {
return;
}
if (!traceOpentracingSeparateSpanEnabled) {
return;
}
Span span = tracer.buildSpan(DiscoveryConstant.SPAN_VALUE).start();
StrategyOpentracingContext.getCurrentContext().setSpan(span);
LOG.debug("Trace chain for Opentracing initialized...");
}
public void opentracingHeader(Map<String, String> customizationMap) {
if (!traceOpentracingEnabled) {
return;
}
Span span = getCurrentSpan();
if (span == null) {
LOG.error("Span not found in context to opentracing header");
return;
}
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(customizationMap)) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : customizationMap.entrySet()) {
span.setTag(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
if (traceOpentracingSeparateSpanEnabled) {
span.setTag(Tags.COMPONENT.getKey(), DiscoveryConstant.TAG_COMPONENT_VALUE);
}
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.PLUGIN, DiscoveryConstant.PLUGIN_VALUE);
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.TRACE_ID, span.context().toTraceId());
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.SPAN_ID, span.context().toSpanId());
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_GROUP, strategyContextHolder.getHeader(DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_GROUP));
...
String routeVersion = strategyContextHolder.getHeader(DiscoveryConstant.N_D_VERSION);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(routeVersion)) {
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.N_D_VERSION, routeVersion);
}
...
LOG.debug("Trace chain information outputs to Opentracing...");
}
public void opentracingLocal(String className, String methodName, Map<String, String> customizationMap) {
if (!traceOpentracingEnabled) {
return;
}
Span span = getCurrentSpan();
if (span == null) {
LOG.error("Span not found in context to opentracing local");
return;
}
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(customizationMap)) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : customizationMap.entrySet()) {
span.setTag(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
if (traceOpentracingSeparateSpanEnabled) {
span.setTag(Tags.COMPONENT.getKey(), DiscoveryConstant.TAG_COMPONENT_VALUE);
}
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.PLUGIN, DiscoveryConstant.PLUGIN_VALUE);
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.CLASS, className);
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.METHOD, methodName);
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.TRACE_ID, span.context().toTraceId());
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.SPAN_ID, span.context().toSpanId());
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.N_D_SERVICE_GROUP, pluginAdapter.getGroup());
...
String routeVersion = strategyContextHolder.getHeader(DiscoveryConstant.N_D_VERSION);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(routeVersion)) {
span.setTag(DiscoveryConstant.N_D_VERSION, routeVersion);
}
...
LOG.debug("Trace chain information outputs to Opentracing...");
}
public void opentracingError(String className, String methodName, Throwable e) {
if (!traceOpentracingEnabled) {
return;
}
if (!traceOpentracingSeparateSpanEnabled) {
return;
}
Span span = getCurrentSpan();
if (span == null) {
LOG.error("Span not found in context to opentracing error");
return;
}
span.log(new ImmutableMap.Builder<String, Object>()
.put(DiscoveryConstant.CLASS, className)
.put(DiscoveryConstant.METHOD, methodName)
.put(DiscoveryConstant.EVENT, Tags.ERROR.getKey())
.put(DiscoveryConstant.ERROR_OBJECT, e)
.build());
LOG.debug("Trace chain error outputs to Opentracing...");
}
public void opentracingClear() {
if (!traceOpentracingEnabled) {
return;
}
if (!traceOpentracingSeparateSpanEnabled) {
return;
}
Span span = getCurrentSpan();
if (span != null) {
span.finish();
} else {
LOG.error("Span not found in context to opentracing clear");
}
StrategyOpentracingContext.clearCurrentContext();
LOG.debug("Trace chain context of Opentracing cleared...");
}
public Span getCurrentSpan() {
return traceOpentracingSeparateSpanEnabled ? StrategyOpentracingContext.getCurrentContext().getSpan() : tracer.activeSpan();
}
public String getTraceId() {
if (!traceOpentracingEnabled) {
return null;
}
Span span = getCurrentSpan();
if (span != null) {
return span.context().toTraceId();
}
return null;
}
public String getSpanId() {
if (!traceOpentracingEnabled) {
return null;
}
Span span = getCurrentSpan();
if (span != null) {
return span.context().toSpanId();
}
return null;
}
}
Opentracing Service模块
实现OpenTracing对服务的扩展,包含configuration、tracer等模块,着重阐述tracer模块,其它比较简单,不一一赘述了
Opentracing的服务追踪类 - DefaultServiceStrategyOpentracingTracer.java
- 继承DefaultServiceStrategyTracer,并注入StrategyOpentracingOperation
- trace方法里先执行opentracingInitialize初始化Span,这样可以让后面的逻辑都可以从Span中拿到traceId和spanId,执行opentracingLocal实现服务的灰度调用链输出
- error方法里执行opentracingError实现服务的灰度调用链异常输出
- release方法里执行opentracingClear实现灰度调用链的Span上报和清除
public class DefaultServiceStrategyOpentracingTracer extends DefaultServiceStrategyTracer {
@Autowired
private StrategyOpentracingOperation strategyOpentracingOperation;
@Override
public void trace(ServiceStrategyTracerInterceptor interceptor, MethodInvocation invocation) {
strategyOpentracingOperation.opentracingInitialize();
super.trace(interceptor, invocation);
strategyOpentracingOperation.opentracingLocal(interceptor.getMethod(invocation).getDeclaringClass().getName(), interceptor.getMethodName(invocation), getCustomizationMap());
}
@Override
public void error(ServiceStrategyTracerInterceptor interceptor, MethodInvocation invocation, Throwable e) {
super.error(interceptor, invocation, e);
strategyOpentracingOperation.opentracingError(interceptor.getMethod(invocation).getDeclaringClass().getName(), interceptor.getMethodName(invocation), e);
}
@Override
public void release(ServiceStrategyTracerInterceptor interceptor, MethodInvocation invocation) {
super.release(interceptor, invocation);
strategyOpentracingOperation.opentracingClear();
}
@Override
public String getTraceId() {
return strategyOpentracingOperation.getTraceId();
}
@Override
public String getSpanId() {
return strategyOpentracingOperation.getSpanId();
}
}
Opentracing Spring Cloud Gateway模块
实现OpenTracing对Spring Cloud Gateway的扩展,跟discovery-plugin-strategy-starter-service-opentracing模块类似,不一一赘述了
Opentracing Zuul模块
源码参考
https://github.com/Nepxion/Discovery/tree/master/discovery-plugin-strategy-starter-zuul-opentracing
实现OpenTracing对Zuul的扩展,跟discovery-plugin-strategy-starter-service-opentracing模块类似,不一一赘述了
使用说明
示例参考
https://github.com/Nepxion/DiscoveryGuide
使用方式
Opentracing输出方式以Uber Jaeger为例来说明,步骤非常简单
- 从https://pan.baidu.com/s/1i57rXaNKPuhGRqZ2MONZOA#list/path=%2FNepxion获取Jaeger-1.14.0.zip,Windows操作系统下解压后运行jaeger.bat,Mac和Lunix操作系统请自行研究
- 执行Postman调用后,访问http://localhost:16686查看灰度调用链
- 灰度调用链支持WebMvc和WebFlux两种方式,以GRAY字样的标记来标识
开关控制
对于Opentracing调用链功能的开启和关闭,需要通过如下开关做控制:
# 启动和关闭调用链。缺失则默认为false
spring.application.strategy.trace.enabled=true
# 启动和关闭调用链的Opentracing输出,支持F版或更高版本的配置,其它版本不需要该行配置。缺失则默认为false
spring.application.strategy.trace.opentracing.enabled=true
# 启动和关闭调用链的灰度信息在Opentracing中以独立的Span节点输出,如果关闭,则灰度信息输出到原生的Span节点中。缺失则默认为true
spring.application.strategy.trace.opentracing.separate.span.enabled=true
可选功能
自定义调用链上下文参数的创建(该类不是必须的),继承DefaultStrategyTracerAdapter
// 自定义调用链上下文参数的创建
// 对于getTraceId和getSpanId方法,在Opentracing等调用链中间件引入的情况下,由调用链中间件决定,在这里定义不会起作用;在Opentracing等调用链中间件未引入的情况下,在这里定义才有效,下面代码中表示从Http Header中获取,并全链路传递
// 对于getCustomizationMap方法,表示输出到调用链中的定制化业务参数,可以同时输出到日志和Opentracing等调用链中间件,下面代码中表示从Http Header中获取,并全链路传递
public class MyStrategyTracerAdapter extends DefaultStrategyTracerAdapter {
@Override
public String getTraceId() {
return StringUtils.isNotEmpty(strategyContextHolder.getHeader(DiscoveryConstant.TRACE_ID)) ? strategyContextHolder.getHeader(DiscoveryConstant.TRACE_ID) : StringUtils.EMPTY;
}
@Override
public String getSpanId() {
return StringUtils.isNotEmpty(strategyContextHolder.getHeader(DiscoveryConstant.SPAN_ID)) ? strategyContextHolder.getHeader(DiscoveryConstant.SPAN_ID) : StringUtils.EMPTY;
}
@Override
public Map<String, String> getCustomizationMap() {
return new ImmutableMap.Builder<String, String>()
.put("mobile", StringUtils.isNotEmpty(strategyContextHolder.getHeader("mobile")) ? strategyContextHolder.getHeader("mobile") : StringUtils.EMPTY)
.put("user", StringUtils.isNotEmpty(strategyContextHolder.getHeader("user")) ? strategyContextHolder.getHeader("user") : StringUtils.EMPTY)
.build();
}
}
在配置类里@Bean方式进行调用链类创建,覆盖框架内置的调用链类
@Bean
public StrategyTracerAdapter strategyTracerAdapter() {
return new MyStrategyTracerAdapter();
}
本文作者
任浩军, 10 多年开源经历,Github ID:@HaojunRen,Nepxion 开源社区创始人,Nacos Group Member,Spring Cloud Alibaba & Nacos & Sentinel Committer
请联系我
微信、公众号和文档



转载,请保留原文地址,谢谢 ~
Opentracing + Uber Jaeger 全链路灰度调用链,Nepxion Discovery的更多相关文章
- 基于Opentracing+Jaeger全链路灰度调用链
当网关和服务在实施全链路分布式灰度发布和路由时候,我们需要一款追踪系统来监控网关和服务走的是哪个灰度组,哪个灰度版本,哪个灰度区域,甚至监控从Http Header头部全程传递的灰度规则和路由策略.这 ...
- 基于 Istio 的全链路灰度方案探索和实践
作者|曾宇星(宇曾) 审核&校对:曾宇星(宇曾) 编辑&排版:雯燕 背景 微服务软件架构下,业务新功能上线前搭建完整的一套测试系统进行验证是相当费人费时的事,随着所拆分出微服务数量的不 ...
- Spring Cloud灰度发布之Nepxion Discovery
<蓝绿部署.红黑部署.AB测试.灰度发布.金丝雀发布.滚动发布的概念与区别> 最近公司项目在做架构升级,升级为 Spring Cloud,我们希望能够做到服务的灰度发布,根据访问量逐渐切换 ...
- 使用Skyworking 作全链路api调用监控,Integration of Skyworking, auditing the whole chain circuit.
Applicable scenario: Structure Map ~ Skywalking uses elasticsearch to store data, don't mistake elas ...
- zipkin:调用链显示分析
为什么使用了httpclient,客户端没有向zipkin server发送日志? 因为我实在main方法中调用的,完事后这个线程就没了:httpclient用的还是异步的发送日志方式:所以没发日志. ...
- 调用链系列三、基于zipkin调用链封装starter实现springmvc、dubbo、restTemplate等实现全链路跟踪
一.实现思路 1.过滤器实现思路 所有调用链数据都通过过滤器实现埋点并收集.同一条链共享一个traceId.每个节点有唯一的spanId. 2.共享传递方式 1.rpc调用:通过隐式传参.dubbo有 ...
- 分布式调用链跟踪工具Jaeger?两分钟极速体验
欢迎访问我的GitHub https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java.Docker.Kubernetes.DevOPS ...
- springboot 项目添加jaeger调用链监控
1.添加maven依赖<dependency> <groupId>io.opentracing.contrib</groupId> <artifactId&g ...
- istio分布式调用链Jaeger
1.安装 kubectl apply -n istio-system -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jaegertracing/jaeger-kuberne ...
随机推荐
- node项目的基本目录结构
1.public目录: 项目公共目录,存放静态资源(img.js.css)和公共资源,404错误提示页面: 2.routor目录: 路由控制器目录,存放路由文件,将所有的业务逻辑都都写在这里: 3.v ...
- 将maven项目到入到idea中
一,前言 在文章将maven项目导入到eclipse中中我将新建的项目到入到了eclipse中了,因为最近也在尝试idea,那么就顺便也到入idea中. maven项目的话,我就使用在文章使用命令行创 ...
- 将SpringBoot部署在外部tomcat中
一,前言 在文章SpringBoot之简单入门中提到了,SpringBoot是内置一个tomcat容器的,但是如果要将SpringBoot部署在一个外部的tomcat,要怎么办呢?这就是本篇文章的目的 ...
- git分支操作笔记
git常用的基本操作 远程仓库只有一个master分支,创建dev分支并上传 # 创建本地dev分支 git checkout -b dev master # 推送dev分支到远程仓库 git pus ...
- tomcat下c3p0连接池配置问题
一.首先如果要使用这个连接池,就需要导入c3p0-0.9.2-pre1.jar架包和支持架包mchange-commons-0.2.jar, 我这里测试使用的是msql数据库 当然也需要导入mysql ...
- 将CDH中的hive和hbase相互整合使用
一..hbase与hive的兼容版本: hive0.90与hbase0.92是兼容的,早期的hive版本与hbase0.89/0.90兼容,不需要自己编译. hive1.x与hbase0.98.x或则 ...
- .Net Core 跨平台:一个简单程序的多平台(windows、Linux、osx)发布
.Net Core 跨平台:一个简单程序的多平台(windows.Linux.osx)发布 .Net Core 3.0 已于2019年9月23日发布了,包含了一些新特性,具体参见Announcing ...
- linux服务器创建虚拟路径解决文件上传路径隔离问题
需求环境 图片上传最简单的就是上传web项目下,这样图片与项目不可分离会产生很多不必要的影响.例如:重新部署项目需要把所有上传的图片再copy一份等. 图片与项目分离有好几种方式: 方式一.在linu ...
- 阿里云服务器ecs配置之安装redis服务
一.介绍 Redis是当前比较热门的NOSQL系统之一,它是一个key-value存储系统.和Memcache类似,但很大程度补偿了Memcache的不足,它支持存储的value类型相对更多,包括st ...
- 并发编程之多线程(Java)
一.线程与进程区别 每个正在系统上运行的程序都是一个进程.每个进程包含一到多个线程.线程是一组指令的集合,或者是程序的特殊段,它可以在程序里独立执行.也可以把它理解为代码运行的上下文.所以线程基本上是 ...
