基础分类网络VGG
vgg16是牛津大学视觉几何组(Oxford Visual Geometry Group)2014年提出的一个模型. vgg模型也得名于此.
2014年,vgg16拿了Imagenet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2014 (ILSVRC2014)
比赛的冠军.
论文连接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556
http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/research/very_deep/牛津大学视觉研究小组在这里放出了他们在ImageNet比赛训练得到的模型文件.
网上有很多vgg16的实现,下面
https://github.com/machrisaa/tensorflow-vgg/blob/master/vgg16.py
这个是推理的实现,即加载权重文件,实现图像预测https://github.com/ppplinday/tensorflow-vgg16-train-and-test/blob/master/train_vgg.py
这个是训练的实现,即如何得到权重文件
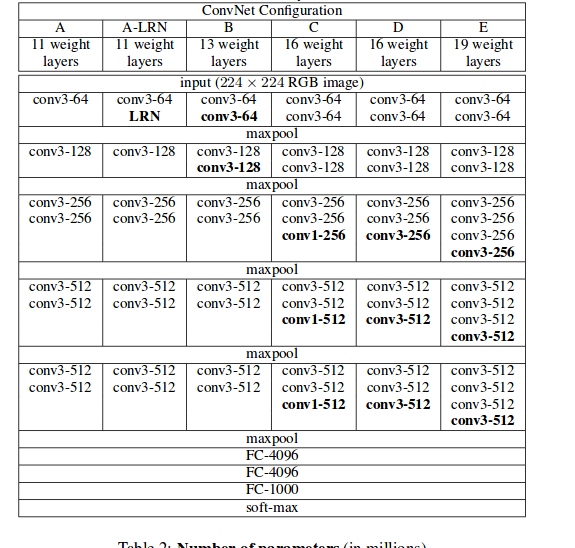
vgg的模型结构如下:
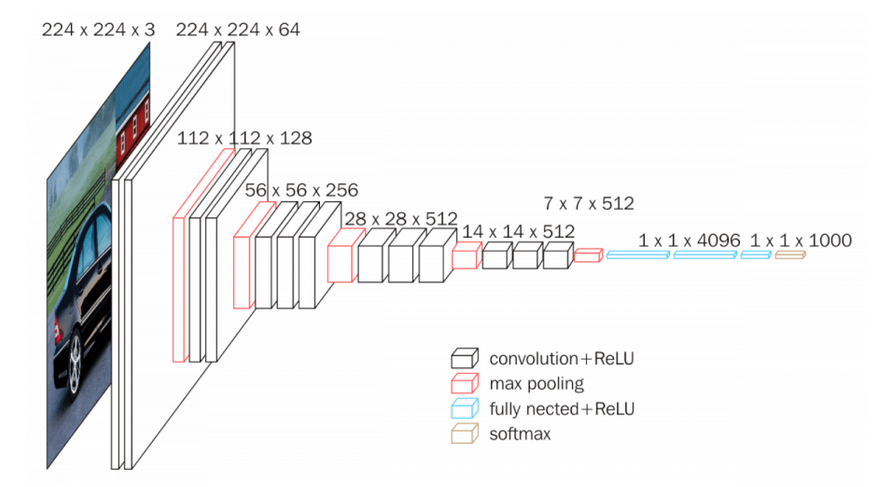
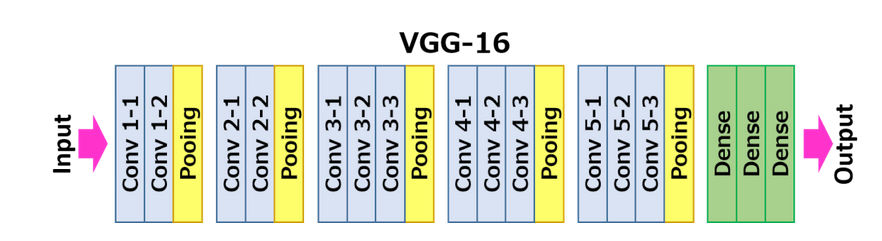
每一层的卷积核的大小都是3*3.
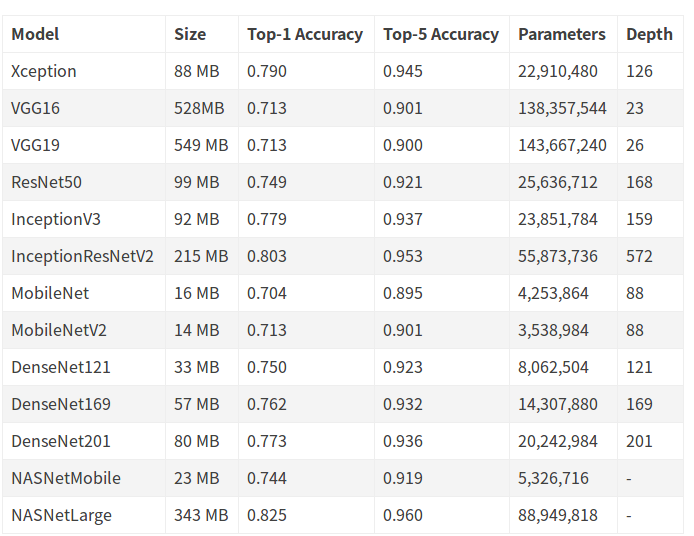
现在的keras里已经集成了很多模型,具体可以参考keras的文档.
https://keras.io/applications/#models-for-image-classification-with-weights-trained-on-imagenet
下面是keras_applications/vgg16.py的实现.比tensorflow的代码更易于理解.
"""VGG16 model for Keras.
# Reference
- [Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition](
https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556) (ICLR 2015)
"""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import os
from . import get_submodules_from_kwargs
from . import imagenet_utils
from .imagenet_utils import decode_predictions
from .imagenet_utils import _obtain_input_shape
preprocess_input = imagenet_utils.preprocess_input
WEIGHTS_PATH = ('https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-models/'
'releases/download/v0.1/'
'vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels.h5')
WEIGHTS_PATH_NO_TOP = ('https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-models/'
'releases/download/v0.1/'
'vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5')
def VGG16(include_top=True,
weights='imagenet',
input_tensor=None,
input_shape=None,
pooling=None,
classes=1000,
**kwargs):
"""Instantiates the VGG16 architecture.
Optionally loads weights pre-trained on ImageNet.
Note that the data format convention used by the model is
the one specified in your Keras config at `~/.keras/keras.json`.
# Arguments
include_top: whether to include the 3 fully-connected
layers at the top of the network.
weights: one of `None` (random initialization),
'imagenet' (pre-training on ImageNet),
or the path to the weights file to be loaded.
input_tensor: optional Keras tensor
(i.e. output of `layers.Input()`)
to use as image input for the model.
input_shape: optional shape tuple, only to be specified
if `include_top` is False (otherwise the input shape
has to be `(224, 224, 3)`
(with `channels_last` data format)
or `(3, 224, 224)` (with `channels_first` data format).
It should have exactly 3 input channels,
and width and height should be no smaller than 32.
E.g. `(200, 200, 3)` would be one valid value.
pooling: Optional pooling mode for feature extraction
when `include_top` is `False`.
- `None` means that the output of the model will be
the 4D tensor output of the
last convolutional block.
- `avg` means that global average pooling
will be applied to the output of the
last convolutional block, and thus
the output of the model will be a 2D tensor.
- `max` means that global max pooling will
be applied.
classes: optional number of classes to classify images
into, only to be specified if `include_top` is True, and
if no `weights` argument is specified.
# Returns
A Keras model instance.
# Raises
ValueError: in case of invalid argument for `weights`,
or invalid input shape.
"""
backend, layers, models, keras_utils = get_submodules_from_kwargs(kwargs)
if not (weights in {'imagenet', None} or os.path.exists(weights)):
raise ValueError('The `weights` argument should be either '
'`None` (random initialization), `imagenet` '
'(pre-training on ImageNet), '
'or the path to the weights file to be loaded.')
if weights == 'imagenet' and include_top and classes != 1000:
raise ValueError('If using `weights` as `"imagenet"` with `include_top`'
' as true, `classes` should be 1000')
# Determine proper input shape
input_shape = _obtain_input_shape(input_shape,
default_size=224,
min_size=32,
data_format=backend.image_data_format(),
require_flatten=include_top,
weights=weights)
if input_tensor is None:
img_input = layers.Input(shape=input_shape)
else:
if not backend.is_keras_tensor(input_tensor):
img_input = layers.Input(tensor=input_tensor, shape=input_shape)
else:
img_input = input_tensor
# Block 1
x = layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block1_conv1')(img_input)
x = layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block1_conv2')(x)
x = layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name='block1_pool')(x)
# Block 2
x = layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block2_conv1')(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block2_conv2')(x)
x = layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name='block2_pool')(x)
# Block 3
x = layers.Conv2D(256, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block3_conv1')(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(256, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block3_conv2')(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(256, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block3_conv3')(x)
x = layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name='block3_pool')(x)
# Block 4
x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block4_conv1')(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block4_conv2')(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block4_conv3')(x)
x = layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name='block4_pool')(x)
# Block 5
x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block5_conv1')(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block5_conv2')(x)
x = layers.Conv2D(512, (3, 3),
activation='relu',
padding='same',
name='block5_conv3')(x)
x = layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2), strides=(2, 2), name='block5_pool')(x)
if include_top:
# Classification block
x = layers.Flatten(name='flatten')(x)
x = layers.Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='fc1')(x)
x = layers.Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='fc2')(x)
x = layers.Dense(classes, activation='softmax', name='predictions')(x)
else:
if pooling == 'avg':
x = layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
elif pooling == 'max':
x = layers.GlobalMaxPooling2D()(x)
# Ensure that the model takes into account
# any potential predecessors of `input_tensor`.
if input_tensor is not None:
inputs = keras_utils.get_source_inputs(input_tensor)
else:
inputs = img_input
# Create model.
model = models.Model(inputs, x, name='vgg16')
# Load weights.
if weights == 'imagenet':
if include_top:
weights_path = keras_utils.get_file(
'vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels.h5',
WEIGHTS_PATH,
cache_subdir='models',
file_hash='64373286793e3c8b2b4e3219cbf3544b')
else:
weights_path = keras_utils.get_file(
'vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5',
WEIGHTS_PATH_NO_TOP,
cache_subdir='models',
file_hash='6d6bbae143d832006294945121d1f1fc')
model.load_weights(weights_path)
if backend.backend() == 'theano':
keras_utils.convert_all_kernels_in_model(model)
elif weights is not None:
model.load_weights(weights)
return model
可以清楚地看出来,所用的卷积核全部是3*3的.
用keras做预测也很简单,
from keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16
model = VGG16()
print(model.summary())
上面代码会把权重文件下载到
这里贴一段网上找的代码
from keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16, preprocess_input, decode_predictions
from keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array
import numpy as np
# VGG-16 instance
model = VGG16(weights='imagenet', include_top=True)
image = load_img('C:/Pictures/Pictures/test_imgs/golden.jpg', target_size=(224, 224))
image_data = img_to_array(image)
# reshape it into the specific format
image_data = image_data.reshape((1,) + image_data.shape)
print(image_data.shape)
# prepare the image data for VGG
image_data = preprocess_input(image_data)
# using the pre-trained model to predict
prediction = model.predict(image_data)
# decode the prediction results
results = decode_predictions(prediction, top=3)
print(results)
很简单
- 加载模型
- 加载图片,预处理
- 前向传播
- 解释输出tensor
vgg19和vgg16结构基本一致的,就是多了几个卷积层.
基础分类网络VGG的更多相关文章
- TCP/IP协议(一)网络基础知识 网络七层协议
参考书籍为<图解tcp/ip>-第五版.这篇随笔,主要内容还是TCP/IP所必备的基础知识,包括计算机与网络发展的历史及标准化过程(简述).OSI参考模型.网络概念的本质.网络构建的设备等 ...
- Python黑客编程基础3网络数据监听和过滤
网络数据监听和过滤 课程的实验环境如下: • 操作系统:kali Linux 2.0 • 编程工具:Wing IDE • Python版本:2.7.9 • 涉及 ...
- 黑马程序员:Java基础总结----网络编程
黑马程序员:Java基础总结 网络编程 ASP.Net+Android+IO开发 . .Net培训 .期待与您交流! 网络编程 网络通讯要素 . IP地址 . 网络中设备的标识 . 不易记忆,可用 ...
- 网络编程基础:网络基础之网络协议、socket模块
操作系统(简称OS)基础: 应用软件不能直接操作硬件,能直接操作硬件的只有操作系统:所以,应用软件可以通过操作系统来间接操作硬件 网络基础之网络协议: 网络通讯原理: 连接两台计算机之间的Intern ...
- GO学习-(19) Go语言基础之网络编程
Go语言基础之网络编程 现在我们几乎每天都在使用互联网,我们前面已经学习了如何编写Go语言程序,但是如何才能让我们的程序通过网络互相通信呢?本章我们就一起来学习下Go语言中的网络编程. 关于网络编程其 ...
- python渗透测试入门——基础的网络编程工具
<Python黑帽子--黑客与渗透测试编程之道学习>这本书是我在学习安全的过程中发现的在我看来十分优秀的一本书,业内也拥有很高的评价,所以在这里将自己的学习内容分享出来. 1.基础的网络编 ...
- 转 经典分类网络Googlenet
转自https://my.oschina.net/u/876354/blog/1637819 2014年,GoogLeNet和VGG是当年ImageNet挑战赛(ILSVRC14)的双雄,GoogLe ...
- 【深度学习系列】用PaddlePaddle和Tensorflow实现经典CNN网络Vgg
上周我们讲了经典CNN网络AlexNet对图像分类的效果,2014年,在AlexNet出来的两年后,牛津大学提出了Vgg网络,并在ILSVRC 2014中的classification项目的比赛中取得 ...
- 周末班:Python基础之网络编程
一.楔子 你现在已经学会了写python代码,假如你写了两个python文件a.py和b.py,分别去运行,你就会发现,这两个python的文件分别运行的很好.但是如果这两个程序之间想要传递一个数据, ...
随机推荐
- ASP.NET Core Web API 跨域(CORS) Cookie问题
身为一个Web API,处理来自跨域不同源的请求,是一件十分合理的事情. 先上已有的文章,快速复制粘贴,启用CORS: Microsoft:启用 ASP.NET Core 中的跨域请求 (CORS) ...
- [Inno Setup]写入注册表时32位系统和64位系统的路由
昨天下午组内一位同事跟说,他想在Inno Setup的安装包中写入一个注册表.目标位置是HKLM:\Software\下面创建自己的注册表项.然后说尝试了好几次都不行, 但是往HKCU下面写入却是OK ...
- java多线程基础(一)--sleep和wait的区别
sleep和wait的区别有: 1.这两个方法来自不同的类分别是Thread和Object: 2.最主要是sleep方法没有释放锁,而wait方法释放了锁,使得线程可以使用同步控制块或者方法: 3.w ...
- MVP架构下解决 RxJava 自动解绑问题
背景 MVP 模式下使用 RxJava 处理网络访问的回调,当数据返回时 Presenter 调用绑定的 View 的方法. 定义 BasePresenter 如下: public class Bas ...
- python 列表的增删改查
列表 有序可变的,索引 作用:存储数据的,支持很多种数据类型 定义方式: lst = [1,"alex",True,('a','b')]增 append() # 追加 extend ...
- java120经典面试题
经典面试题 -----version 1.0 题注:以下答案仅限本人个人见解,若有错误和建议请多多指教.QQ:1807812486 题目来源 1.什么是Java虚拟机?为什么Java被称作是" ...
- C#表达式树浅析
一.前言 在我们日常开发中Lamba 表达式经常会使用,如List.Where(n=>Name="abc") 使用起来非常的方便,代码也很简洁,总之一个字就是“爽”.在之前我 ...
- Qt无边框窗体-最大化时支持拖拽还原
目录 一.概述 二.效果展示 三.demo制作 1.设计窗体 2.双击放大 四.拖拽 五.相关文章 原文链接:Markdown模板 一.概述 用Qt进行开发界面时,既想要实现友好的用户交互又想界面漂亮 ...
- NNs(Neural Networks,神经网络)和Polynomial Regression(多项式回归)等价性之思考,以及深度模型可解释性原理研究与案例
1. Main Point 0x1:行文框架 第二章:我们会分别介绍NNs神经网络和PR多项式回归各自的定义和应用场景. 第三章:讨论NNs和PR在数学公式上的等价性,NNs和PR是两个等价的理论方法 ...
- egret之一维,二维数组
一维数组转换成二维数组下标公式: 行=下标/二维数组列数 列=下标%二维数组列数+1 ] + ); ] + ); 二维数组转一维数组: 下标=(二维数当前行-1)*列数+二维数当前列-1: let i ...
