hdu 5444(构造二叉树然后遍历)
Elven Postman
Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1286 Accepted Submission(s): 731
are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very
long time and their magical prowess are not something to be taken
lightly. Also, they live on trees. However, there is something about
them you may not know. Although delivering stuffs through magical
teleportation is extremely convenient (much like emails). They still
sometimes prefer other more “traditional” methods.
So, as a
elven postman, it is crucial to understand how to deliver the mail to
the correct room of the tree. The elven tree always branches into no
more than two paths upon intersection, either in the east direction or
the west. It coincidentally looks awfully like a binary tree we human
computer scientist know. Not only that, when numbering the rooms, they
always number the room number from the east-most position to the west.
For rooms in the east are usually more preferable and more expensive due
to they having the privilege to see the sunrise, which matters a lot in
elven culture.
Anyways, the elves usually wrote down all the
rooms in a sequence at the root of the tree so that the postman may know
how to deliver the mail. The sequence is written as follows, it will go
straight to visit the east-most room and write down every room it
encountered along the way. After the first room is reached, it will then
go to the next unvisited east-most room, writing down every unvisited
room on the way as well until all rooms are visited.
Your task is to determine how to reach a certain room given the sequence written on the root.
For instance, the sequence 2, 1, 4, 3 would be written on the root of the following tree.
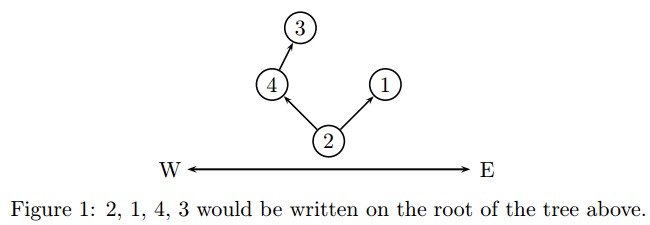
For each test case, there is a number n(n≤1000) on a line representing the number of rooms in this tree. n integers representing the sequence written at the root follow, respectively a1,...,an where a1,...,an∈{1,...,n}.
On the next line, there is a number q representing the number of mails to be sent. After that, there will be q integers x1,...,xq indicating the destination room number of each mail.
Note that for simplicity, we assume the postman always starts from the root regardless of the room he had just visited.
4
2 1 4 3
3
1 2 3
6
6 5 4 3 2 1
1
1
WE
EEEEE
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=;
struct btree
{
int left,right,val;
}tree[maxn];
int tot;
void init(int tot){
tree[tot].left = tree[tot].right = -;
}
void build(int root,int val){
if(tree[root].left!=-&&val<tree[root].val){ ///比根小并且左子树存在。
build(tree[root].left,val);
}else if(tree[root].right!=-&&val>tree[root].val){ ///比根大并且右子树存在。
build(tree[root].right,val);
}else {
init(tot);
tree[tot].val = val;
if(val<tree[root].val) tree[root].left = tot;
else tree[root].right = tot;
tot++;
}
}
void query(int root,int val){
if(tree[root].val==val){
printf("\n");
return;
}
if(val<tree[root].val){
printf("E");
query(tree[root].left,val); }
else {
printf("W");
query(tree[root].right,val); }
}
int v[maxn];
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
tot = ;
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&v[i]);
if(i==){ ///根节点
init(tot);
tree[tot].val = v[i];
tot++;
}
else build(,v[i]);
}
int q ;
scanf("%d",&q);
while(q--){
int val;
scanf("%d",&val);
query(,val);
}
}
return ;
}
法二:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std; const int maxn = ;
struct Node
{
int lson,rson;
}tree[maxn];
int n,q,cnt,pre[maxn];
char path[maxn][maxn],tmp[maxn]; void build(int l,int r)
{
if(l >= r) return;
int pos;
for(int i = l; i <= r; i++)
if(pre[cnt] == i)
{
pos = i;
break;
}
if(l != pos) ///这里要注意
tree[pos].lson = pre[++cnt];
build(l,pos-);
if(r != pos)
tree[pos].rson = pre[++cnt];
build(pos+,r);
} void dfs(int rt,int dep)
{
if(rt == ) return;
strcpy(path[rt],tmp);
tmp[dep] = 'E';
dfs(tree[rt].lson,dep+);
tmp[dep] = 'W';
dfs(tree[rt].rson,dep+);
tmp[dep] = ;
} int main()
{
int t,u;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
memset(tree,,sizeof(tree));
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d",&pre[i]);
cnt = ;
build(,n);
memset(tmp,,sizeof(tmp));
dfs(pre[],);
scanf("%d",&q);
while(q--)
{
scanf("%d",&u);
printf("%s\n",path[u]);
}
}
return ;
}
hdu 5444(构造二叉树然后遍历)的更多相关文章
- hdu 5444 构建二叉树,搜索二叉树
Elven Postman Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)T ...
- PYTHON实现算术表达式构造二叉树
LEETCOCE 224. Basic Calculator Implement a basic calculator to evaluate a simple expression string. ...
- lintcode :前序遍历和中序遍历树构造二叉树
解题 前序遍历和中序遍历树构造二叉树 根据前序遍历和中序遍历树构造二叉树. 样例 给出中序遍历:[1,2,3]和前序遍历:[2,1,3]. 返回如下的树: 2 / \ 1 3 注意 你可以假设树中不存 ...
- lintcode: 中序遍历和后序遍历树构造二叉树
题目 中序遍历和后序遍历树构造二叉树 根据中序遍历和后序遍历树构造二叉树 样例 给出树的中序遍历: [1,2,3] 和后序遍历: [1,3,2] 返回如下的树: 2 / \ 1 3 注意 你可 ...
- [Swift]LeetCode105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 | Construct Binary Tree from Preorder and Inorder Traversal
Given preorder and inorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree. Note:You may assume that ...
- [Swift]LeetCode106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 | Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
Given inorder and postorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree. Note:You may assume that ...
- 【2】【leetcode-105,106】 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树,从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 (没思路,典型记住思路好做) 根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树. 注意:你可以假设树中没有重复的元素. 例如,给出 前序遍历 preorder = [ ...
- LeetCode(106):从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
Medium! 题目描述: 根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树. 注意:你可以假设树中没有重复的元素. 例如,给出 中序遍历 inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] 后序遍历 posto ...
- LeetCode(105):从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
Medium! 题目描述: 根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树. 注意:你可以假设树中没有重复的元素. 例如,给出 前序遍历 preorder = [3,9,20,15,7] 中序遍历 inor ...
随机推荐
- 零拷贝详解 Java NIO学习笔记四(零拷贝详解)
转 https://blog.csdn.net/u013096088/article/details/79122671 Java NIO学习笔记四(零拷贝详解) 2018年01月21日 20:20:5 ...
- Redis的安装、服务配置
在网上找了很多资料,有些可以正常安装,有些安装会出毛病,仔细想了想,还是自己整理一份吧,仅仅为自己下次再用的时候,能够快速的定位到可以正常用的文章! 我使用的是VMware Workstation P ...
- python面试题之什么是lambda函数?
lambda表达式,通常是在需要一个函数,但是又不想费神去命名一个函数的场合下使用,也就是指匿名函数. lambda所表示的匿名函数的内容应该是很简单的,如果复杂的话,干脆就重新定义一个函数了,使用l ...
- poj-3009 curling2.0(搜索)
Curling 2.0 Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 26408 Accepted: 10546 Des ...
- 原生Ajax+springBoot实现用户登录
思路:用户输入登录信息——信息传到后台——数据库查询——比较查询结果——返回登录信息(成功/失败) html页面代码: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang=&quo ...
- debian卸载vmware
原因: 由于vagrant默认支持virtualbox,而要支持vmware需要一个商用付费的插件.所以卸载vmware,使用virtualbox 具体操作: $ sudo vmware-instal ...
- HDU 5614 Baby Ming and Matrix tree 树链剖分
题意: 给出一棵树,每个顶点上有个\(2 \times 2\)的矩阵,矩阵有两种操作: 顺时针旋转90°,花费是2 将一种矩阵替换为另一种矩阵,花费是10 树上有一种操作,将一条路经上的所有矩阵都变为 ...
- 修改const变量
看下面的一段代码 ; int * j=(int*)(&i); // 运行正确,j确为i的地址,但 int *j=&i; 编译错误 *j=; //确实改变了i的值 printf(&quo ...
- LSTM block和cell区别
LSTM的结构中每个时刻的隐层包含了多个memory blocks(一般我们采用一个block),每个block包含了包含一个Cell(有多个memory cell组成)和三个gate,一个基础的结构 ...
- 06-python进阶-多线程下载器练手
我们需要用python 写一个多线程的下载器 我们要先获取这个文件的大小 然后将其分片 然后启动多线程 分别去下载 然后将其拼接起来 #!/usr/bin/env python#coding:utf- ...
