深度学习之DCGAN
1、知识点
"""
DCGAN:相比GAN而言,使用了卷积网络替代全连接
卷积:256*256*3 --- > 28*28*14 -->结果 ,即H,W变小,特征图变多
反卷积(就是把卷积的前向和反向传播完全颠倒了) :4*4*1024 ---> 28 * 28 *1 -->结果 即H,W变大,特征图变少 特点:
1、判别模型:使用带步长的卷积(strided convolutions)取代了的空间池化(spatial pooling),容许网络学习自己的空间下采样(spatial downsampling)。
2、生成模型:使用微步幅卷积(fractional strided),容许它学习自己的空间上采样(spatial upsampling)。
3、激活函数: LeakyReLU
4、Batch Normalization 批标准化:解决因糟糕的初始化引起的训练问题,使得梯度能传播更深层次。 Batch Normalization证明了生成模型初始化的重要性,避免生成模型崩溃:生成的所有样本都在一个点上(样本相同),这是训练GANs经常遇到的失败现象。
简而言之,DCGAN是利用数据生成图片的过程
"""
2、代码
# coding: utf-8
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import pickle
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
get_ipython().run_line_magic('matplotlib', 'inline') from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('/MNIST_data/') # ## 获得数据 # In[4]: def get_inputs(noise_dim, image_height, image_width, image_depth): inputs_real = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, image_height, image_width, image_depth], name='inputs_real')
inputs_noise = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, noise_dim], name='inputs_noise') return inputs_real, inputs_noise # # 生成器 # In[5]: def get_generator(noise_img, output_dim, is_train=True, alpha=0.01): with tf.variable_scope("generator", reuse=(not is_train)):
# 100 x 1 to 4 x 4 x 512
# 全连接层
layer1 = tf.layers.dense(noise_img, 4*4*512)
layer1 = tf.reshape(layer1, [-1, 4, 4, 512])
# batch normalization
layer1 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(layer1, training=is_train)
# Leaky ReLU
layer1 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer1, layer1)
# dropout
layer1 = tf.nn.dropout(layer1, keep_prob=0.8) # 4 x 4 x 512 to 7 x 7 x 256
layer2 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(layer1, 256, 4, strides=1, padding='valid')
layer2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(layer2, training=is_train)
layer2 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer2, layer2)
layer2 = tf.nn.dropout(layer2, keep_prob=0.8) # 7 x 7 256 to 14 x 14 x 128
layer3 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(layer2, 128, 3, strides=2, padding='same')
layer3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(layer3, training=is_train)
layer3 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer3, layer3)
layer3 = tf.nn.dropout(layer3, keep_prob=0.8) # 14 x 14 x 128 to 28 x 28 x 1
logits = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(layer3, output_dim, 3, strides=2, padding='same')
# MNIST原始数据集的像素范围在0-1,这里的生成图片范围为(-1,1)
# 因此在训练时,记住要把MNIST像素范围进行resize
outputs = tf.tanh(logits) return outputs # ## 判别器 # In[6]: def get_discriminator(inputs_img, reuse=False, alpha=0.01): with tf.variable_scope("discriminator", reuse=reuse):
# 28 x 28 x 1 to 14 x 14 x 128
# 第一层不加入BN
layer1 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs_img, 128, 3, strides=2, padding='same')
layer1 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer1, layer1)
layer1 = tf.nn.dropout(layer1, keep_prob=0.8) # 14 x 14 x 128 to 7 x 7 x 256
layer2 = tf.layers.conv2d(layer1, 256, 3, strides=2, padding='same')
layer2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(layer2, training=True)
layer2 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer2, layer2)
layer2 = tf.nn.dropout(layer2, keep_prob=0.8) # 7 x 7 x 256 to 4 x 4 x 512
layer3 = tf.layers.conv2d(layer2, 512, 3, strides=2, padding='same')
layer3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(layer3, training=True)
layer3 = tf.maximum(alpha * layer3, layer3)
layer3 = tf.nn.dropout(layer3, keep_prob=0.8) # 4 x 4 x 512 to 4*4*512 x 1
flatten = tf.reshape(layer3, (-1, 4*4*512))
logits = tf.layers.dense(flatten, 1)
outputs = tf.sigmoid(logits) return logits, outputs # ## 目标函数 # In[7]: def get_loss(inputs_real, inputs_noise, image_depth, smooth=0.1): g_outputs = get_generator(inputs_noise, image_depth, is_train=True)
d_logits_real, d_outputs_real = get_discriminator(inputs_real)
d_logits_fake, d_outputs_fake = get_discriminator(g_outputs, reuse=True) # 计算Loss
g_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_fake,
labels=tf.ones_like(d_outputs_fake)*(1-smooth))) d_loss_real = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_real,
labels=tf.ones_like(d_outputs_real)*(1-smooth)))
d_loss_fake = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_fake,
labels=tf.zeros_like(d_outputs_fake)))
d_loss = tf.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake) return g_loss, d_loss # ## 优化器 # In[8]: def get_optimizer(g_loss, d_loss, beta1=0.4, learning_rate=0.001): train_vars = tf.trainable_variables() g_vars = [var for var in train_vars if var.name.startswith("generator")]
d_vars = [var for var in train_vars if var.name.startswith("discriminator")] # Optimizer
with tf.control_dependencies(tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)):
g_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(g_loss, var_list=g_vars)
d_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(d_loss, var_list=d_vars) return g_opt, d_opt # In[9]: def plot_images(samples):
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=25, sharex=True, sharey=True, figsize=(50,2))
for img, ax in zip(samples, axes):
ax.imshow(img.reshape((28, 28)), cmap='Greys_r')
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
fig.tight_layout(pad=0) # In[10]: def show_generator_output(sess, n_images, inputs_noise, output_dim): cmap = 'Greys_r'
noise_shape = inputs_noise.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
# 生成噪声图片
examples_noise = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, size=[n_images, noise_shape]) samples = sess.run(get_generator(inputs_noise, output_dim, False),
feed_dict={inputs_noise: examples_noise}) result = np.squeeze(samples, -1)
return result # ## 训练网络 # In[11]: # 定义参数
batch_size = 64
noise_size = 100
epochs = 5
n_samples = 25
learning_rate = 0.001 # In[12]: def train(noise_size, data_shape, batch_size, n_samples): # 存储loss
losses = []
steps = 0 inputs_real, inputs_noise = get_inputs(noise_size, data_shape[1], data_shape[2], data_shape[3])
g_loss, d_loss = get_loss(inputs_real, inputs_noise, data_shape[-1])
g_train_opt, d_train_opt = get_optimizer(g_loss, d_loss, beta1, learning_rate) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
# 迭代epoch
for e in range(epochs):
for batch_i in range(mnist.train.num_examples//batch_size):
steps += 1
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) batch_images = batch[0].reshape((batch_size, data_shape[1], data_shape[2], data_shape[3]))
# scale to -1, 1
batch_images = batch_images * 2 - 1 # noise
batch_noise = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, size=(batch_size, noise_size)) # run optimizer
_ = sess.run(g_train_opt, feed_dict={inputs_real: batch_images,
inputs_noise: batch_noise})
_ = sess.run(d_train_opt, feed_dict={inputs_real: batch_images,
inputs_noise: batch_noise}) if steps % 101 == 0:
train_loss_d = d_loss.eval({inputs_real: batch_images,
inputs_noise: batch_noise})
train_loss_g = g_loss.eval({inputs_real: batch_images,
inputs_noise: batch_noise})
losses.append((train_loss_d, train_loss_g))
# 显示图片
samples = show_generator_output(sess, n_samples, inputs_noise, data_shape[-1])
plot_images(samples)
print("Epoch {}/{}....".format(e+1, epochs),
"Discriminator Loss: {:.4f}....".format(train_loss_d),
"Generator Loss: {:.4f}....". format(train_loss_g)) # In[13]: with tf.Graph().as_default():
train(noise_size, [-1, 28, 28, 1], batch_size, n_samples)
3、结构图
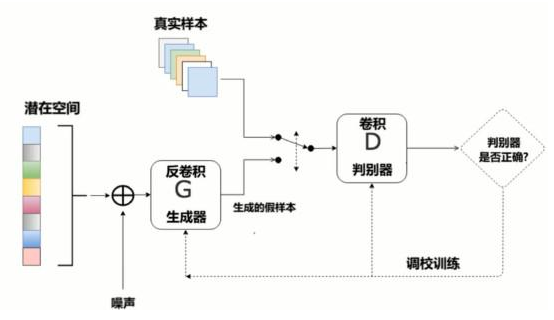
深度学习之DCGAN的更多相关文章
- 【神经网络与深度学习】DCGAN及其TensorFlow源码
上一节我们提到G和D由多层感知机定义.深度学习中对图像处理应用最好的模型是CNN,那么如何把CNN与GAN结合?DCGAN是这方面最好的尝试之一.源码:https://github.com/Newmu ...
- 【深度学习】--DCGAN从入门到实例应用
一.前述 DCGAN就是Deep Concolutions应用到GAN上,但是和传统的卷积应用还有一些区别,最大的区别就是没有池化层.本文将详细分析卷积在GAN上的应用. 二.具体 1.DCGAN和传 ...
- 深度学习算法 之DCGAN(写得不系统,后期再总结,大家可简单阅览一下)
目录 1.基本介绍 2.模型 3.优缺点/其他 参考 1.基本介绍 DCGAN是生成对抗网络GAN中一种常见的模型结构.其中的生成器和判别器都是神经网络模型. GAN是一种生成式对抗网络,即通过对抗的 ...
- GitHub 上 57 款最流行的开源深度学习项目
转载:https://www.oschina.net/news/79500/57-most-popular-deep-learning-project-at-github GitHub 上 57 款最 ...
- CNCC2017中的深度学习与跨媒体智能
CNCC2017中的深度学习与跨媒体智能 转载请注明作者:梦里茶 目录 机器学习与跨媒体智能 传统方法与深度学习 图像分割 小数据集下的深度学习 语音前沿技术 生成模型 基于贝叶斯的视觉信息编解码 珠 ...
- Hinton“深度学习之父”和“神经网络先驱”,新论文Capsule将推翻自己积累了30年的学术成果时
Hinton“深度学习之父”和“神经网络先驱”,新论文Capsule将推翻自己积累了30年的学术成果时 在论文中,Capsule被Hinton大神定义为这样一组神经元:其活动向量所表示的是特定实体类型 ...
- (zhuan) 126 篇殿堂级深度学习论文分类整理 从入门到应用
126 篇殿堂级深度学习论文分类整理 从入门到应用 | 干货 雷锋网 作者: 三川 2017-03-02 18:40:00 查看源网址 阅读数:66 如果你有非常大的决心从事深度学习,又不想在这一行打 ...
- (zhuan) 深度学习全网最全学习资料汇总之模型介绍篇
This blog from : http://weibo.com/ttarticle/p/show?id=2309351000224077630868614681&u=5070353058& ...
- Github上Stars最多的53个深度学习项目,TensorFlow遥遥领先
原文:https://github.com/aymericdamien/TopDeepLearning 项目名称 Stars 项目介绍 TensorFlow 29622 使用数据流图计算可扩展机器学习 ...
随机推荐
- 移动端设备管理平台 atx server2实践
目录 1.需求背景 2.初步调研 2.1.云测试平台 2.2.开源工具 2.3.VNC 2.4.企业内部自研云测试平台 3.ATX Server安装 依赖环境 安装rethinkdb 安装atx se ...
- Centos7安装dig命令
作者: jwj 时间: 2018-10-17 分类: 服务器 最近做一个项目,需要用到Gmail邮箱发送邮件,但发现发送不出去.排查问题时,需要用到dig命令,但使用时,却提醒我dig命令不存在~那就 ...
- 八:MVC初始化数据库
生成数据库策略: CreateDatabaseIfNotExists:方法会在没有数据库时创建一个,这是默认行为. DropCreateDatabaseIfModelChanges:如果我们在在模型改 ...
- 02_ Flume的安装部署及其简单使用
一.Flume的安装部署: Flume的安装非常简单,只需要解压即可,当然,前提是已有hadoop环境 安装包的下载地址为:http://www-us.apache.org/dist/flume/1. ...
- linux——在windows上搭建linux练习环境
程序员自己研究——java-linux-php——环境搭建 需要首选准备一个linux环境. 1,可用安装一个虚拟机:VMware虚拟机 2,安装一个VMware大约5分钟左右. 3,截止目前2019 ...
- C++ 内存泄露和内存越界
内存泄露:分配了内存而没有释放,逐渐耗尽内存资源,导致系统崩溃内存越界: 打个比方 就是你有一个500ml的水瓶,然后你倒在瓶里的水大于500ml 那个多余的就会流出来... 1. 原理分析经常有些新 ...
- “景驰科技杯”2018年华南理工大学程序设计竞赛 B. 一级棒!(并查集)
题目链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/94/B 题意:在一棵有 n 个节点的树上,有两种操作,一个是把 u 到 v 的路径走一遍,另一个是查询 u 到 f ...
- 第二个爬虫之爬取知乎用户回答和文章并将所有内容保存到txt文件中
自从这两天开始学爬虫,就一直想做个爬虫爬知乎.于是就开始动手了. 知乎用户动态采取的是动态加载的方式,也就是先加载一部分的动态,要一直滑道底才会加载另一部分的动态.要爬取全部的动态,就得先获取全部的u ...
- C++头文件中#pragma once与#ifndef……#define……#endif
两者功能一样,防止重复包含被多次编译.建议头文件加入#pragma once C++头文件开头的两句与结尾的一句#ifndef <标识>#define <标识>类代码#endi ...
- EMS命令
Tibco EMS 初级使用方法小结 http://blog.csdn.net/bincavin/article/details/8290905
