python复杂网络分析库NetworkX
NetworkX是一个用Python语言开发的图论与复杂网络建模工具,内置了常用的图与复杂网络分析算法,可以方便的进行复杂网络数据分析、仿真建模等工作。networkx支持创建简单无向图、有向图和多重图(multigraph);内置许多标准的图论算法,节点可为任意数据;支持任意的边值维度,功能丰富,简单易用。
引入模块
import networkx as nx
print nx
无向图
例1:
#!-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt G = nx.Graph() #建立一个空的无向图G
G.add_node(1) #添加一个节点1
G.add_edge(2,3) #添加一条边2-3(隐含着添加了两个节点2、3)
G.add_edge(3,2) #对于无向图,边3-2与边2-3被认为是一条边
print "nodes:", G.nodes() #输出全部的节点: [1, 2, 3]
print "edges:", G.edges() #输出全部的边:[(2, 3)]
print "number of edges:", G.number_of_edges() #输出边的数量:1
nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("wuxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
输出
nodes: [1, 2, 3]
edges: [(2, 3)]
number of edges: 1
例2:
#-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
G = nx.DiGraph()
G.add_node(1)
G.add_node(2) #加点
G.add_nodes_from([3,4,5,6]) #加点集合
G.add_cycle([1,2,3,4]) #加环
G.add_edge(1,3)
G.add_edges_from([(3,5),(3,6),(6,7)]) #加边集合
nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("youxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
有向图
例1:
#!-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt G = nx.DiGraph()
G.add_node(1)
G.add_node(2)
G.add_nodes_from([3,4,5,6])
G.add_cycle([1,2,3,4])
G.add_edge(1,3)
G.add_edges_from([(3,5),(3,6),(6,7)])
nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("youxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
注:有向图和无向图可以互相转换,使用函数:
- Graph.to_undirected()
- Graph.to_directed()
例2,例子中把有向图转化为无向图:
#!-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt G = nx.DiGraph()
G.add_node(1)
G.add_node(2)
G.add_nodes_from([3,4,5,6])
G.add_cycle([1,2,3,4])
G.add_edge(1,3)
G.add_edges_from([(3,5),(3,6),(6,7)])
G = G.to_undirected()
nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("wuxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
注意区分以下2例
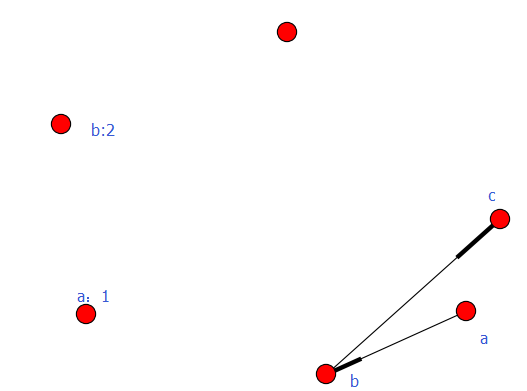
例3-1
#-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt G = nx.DiGraph() road_nodes = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
#road_nodes = {'a':{1:1}, 'b':{2:2}, 'c':{3:3}}
road_edges = [('a', 'b'), ('b', 'c')] G.add_nodes_from(road_nodes.iteritems())
G.add_edges_from(road_edges) nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("youxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
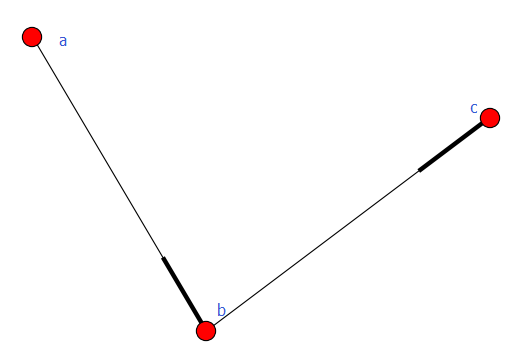
例3-2
#-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt G = nx.DiGraph() #road_nodes = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
road_nodes = {'a':{1:1}, 'b':{2:2}, 'c':{3:3}}
road_edges = [('a', 'b'), ('b', 'c')] G.add_nodes_from(road_nodes.iteritems())
G.add_edges_from(road_edges) nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("youxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
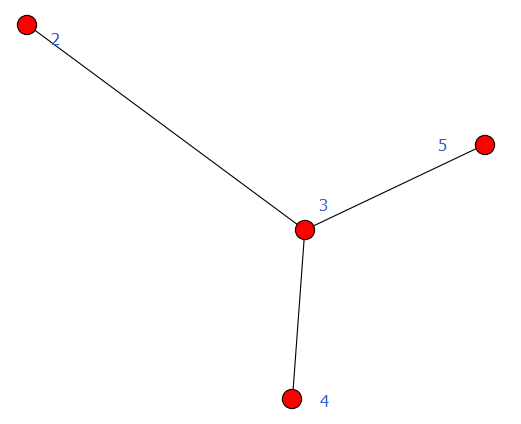
加权图
有向图和无向图都可以给边赋予权重,用到的方法是add_weighted_edges_from,它接受1个或多个三元组[u,v,w]作为参数,其中u是起点,v是终点,w是权重。
例1:
#!-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
G = nx.Graph() #建立一个空的无向图G
G.add_edge(2,3) #添加一条边2-3(隐含着添加了两个节点2、3)
G.add_weighted_edges_from([(3, 4, 3.5),(3, 5, 7.0)]) #对于无向图,边3-2与边2-3被认为是一条边 print G.get_edge_data(2, 3)
print G.get_edge_data(3, 4)
print G.get_edge_data(3, 5) nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("wuxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
输出
{}
{'weight': 3.5}
{'weight': 7.0}
经典图论算法计算
计算1:求无向图的任意两点间的最短路径
# -*- coding: cp936 -*-
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #计算1:求无向图的任意两点间的最短路径
G = nx.Graph()
G.add_edges_from([(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(1,5),(4,5),(4,6),(5,6)])
path = nx.all_pairs_shortest_path(G)
print path[1]
计算2:找图中两个点的最短路径
import networkx as nx
G=nx.Graph()
G.add_nodes_from([1,2,3,4])
G.add_edge(1,2)
G.add_edge(3,4)
try:
n=nx.shortest_path_length(G,1,4)
print n
except nx.NetworkXNoPath:
print 'No path'
强连通、弱连通
- 强连通:有向图中任意两点v1、v2间存在v1到v2的路径(path)及v2到v1的路径。
- 弱联通:将有向图的所有的有向边替换为无向边,所得到的图称为原图的基图。如果一个有向图的基图是连通图,则有向图是弱连通图。
距离
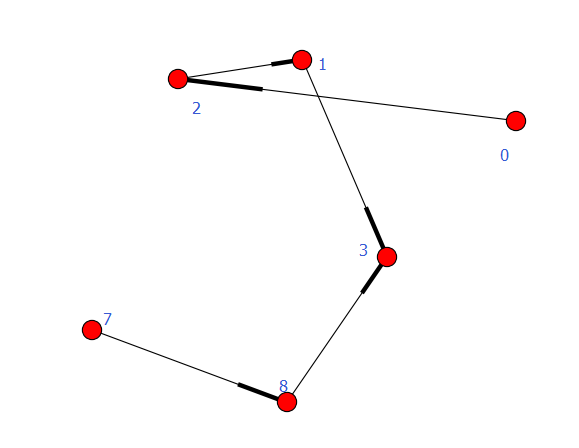
例1:弱连通
#-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#G = nx.path_graph(4, create_using=nx.Graph())
#0 1 2 3
G = nx.path_graph(4, create_using=nx.DiGraph()) #默认生成节点0 1 2 3,生成有向变0->1,1->2,2->3
G.add_path([7, 8, 3]) #生成有向边:7->8->3 for c in nx.weakly_connected_components(G):
print c print [len(c) for c in sorted(nx.weakly_connected_components(G), key=len, reverse=True)] nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("youxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
执行结果
set([0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 8])
[6]
例2:强连通
#-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#G = nx.path_graph(4, create_using=nx.Graph())
#0 1 2 3
G = nx.path_graph(4, create_using=nx.DiGraph())
G.add_path([3, 8, 1]) #for c in nx.strongly_connected_components(G):
# print c
#
#print [len(c) for c in sorted(nx.strongly_connected_components(G), key=len, reverse=True)] con = nx.strongly_connected_components(G)
print con
print type(con)
print list(con) nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("youxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
执行结果
<generator object strongly_connected_components at 0x0000000008AA1D80>
<type 'generator'>
[set([8, 1, 2, 3]), set([0])]
子图
#-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
G = nx.DiGraph()
G.add_path([5, 6, 7, 8])
sub_graph = G.subgraph([5, 6, 8])
#sub_graph = G.subgraph((5, 6, 8)) #ok 一样 nx.draw(sub_graph)
plt.savefig("youxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
条件过滤
#原图
#-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
G = nx.DiGraph() road_nodes = {'a':{'id':1}, 'b':{'id':1}, 'c':{'id':3}, 'd':{'id':4}}
road_edges = [('a', 'b'), ('a', 'c'), ('a', 'd'), ('b', 'd')] G.add_nodes_from(road_nodes)
G.add_edges_from(road_edges) nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("youxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
图
#过滤函数
#-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
G = nx.DiGraph()
def flt_func_draw():
flt_func = lambda d: d['id'] != 1
return flt_func road_nodes = {'a':{'id':1}, 'b':{'id':1}, 'c':{'id':3}, 'd':{'id':4}}
road_edges = [('a', 'b'), ('a', 'c'), ('a', 'd'), ('b', 'd')] G.add_nodes_from(road_nodes.iteritems())
G.add_edges_from(road_edges) flt_func = flt_func_draw()
part_G = G.subgraph(n for n, d in G.nodes_iter(data=True) if flt_func(d))
nx.draw(part_G)
plt.savefig("youxiangtu.png")
plt.show()
图
pred,succ
#-*- coding:utf8-*- import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
G = nx.DiGraph() road_nodes = {'a':{'id':}, 'b':{'id':}, 'c':{'id':}}
road_edges = [('a', 'b'), ('a', 'c'), ('c', 'd')] G.add_nodes_from(road_nodes.iteritems())
G.add_edges_from(road_edges) print G.nodes()
print G.edges() print "a's pred ", G.pred['a']
print "b's pred ", G.pred['b']
print "c's pred ", G.pred['c']
print "d's pred ", G.pred['d'] print "a's succ ", G.succ['a']
print "b's succ ", G.succ['b']
print "c's succ ", G.succ['c']
print "d's succ ", G.succ['d'] nx.draw(G)
plt.savefig("wuxiangtu.png")
plt.draw()
结果
['a', 'c', 'b', 'd']
[('a', 'c'), ('a', 'b'), ('c', 'd')] a's pred {}
b's pred {'a': {}}
c's pred {'a': {}}
d's pred {'c': {}} a's succ {'c': {}, 'b': {}}
b's succ {}
c's succ {'d': {}}
d's succ {}
python复杂网络分析库NetworkX的更多相关文章
- python复杂网络库networkx:基础
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/49839251 其它复杂网络绘图库 [SNAP for python] [ArcGIS,Python,网 ...
- python复杂网络库networkx:算法
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/54020333 Networks算法Algorithms 最短路径Shortest Paths shor ...
- python复杂网络库networkx:绘图draw
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/54291831 networkx使用matplotlib绘制函数 draw(G[, pos, ax, h ...
- python 各种开源库
测试开发 来源:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ea6f7fb69501 Web UI测试自动化 splinter - web UI测试工具,基于selnium封装. 链接 sel ...
- Python常用的库简单介绍一下
Python常用的库简单介绍一下fuzzywuzzy ,字符串模糊匹配. esmre ,正则表达式的加速器. colorama 主要用来给文本添加各种颜色,并且非常简单易用. Prettytable ...
- Python的常用库
读者您好.今天我将介绍20个属于我常用工具的Python库,我相信你看完之后也会觉得离不开它们.他们是: Requests.Kenneth Reitz写的最富盛名的http库.每个Python程序员都 ...
- Python底层socket库
Python底层socket库将Unix关于网络通信的系统调用对象化处理,是底层函数的高级封装,socket()函数返回一个套接字,它的方法实现了各种套接字系统调用.read与write与Python ...
- 【C++实现python字符串函数库】strip、lstrip、rstrip方法
[C++实现python字符串函数库]strip.lstrip.rstrip方法 这三个方法用于删除字符串首尾处指定的字符,默认删除空白符(包括'\n', '\r', '\t', ' '). s.st ...
- 【C++实现python字符串函数库】二:字符串匹配函数startswith与endswith
[C++实现python字符串函数库]字符串匹配函数startswith与endswith 这两个函数用于匹配字符串的开头或末尾,判断是否包含另一个字符串,它们返回bool值.startswith() ...
随机推荐
- FZU 1025 状压dp 摆砖块
云峰菌曾经提到过的黄老师过去讲课时的摆砖块 那时百度了一下题目 想了想并没有想好怎么dp 就扔了 这两天想补动态规划知识 就去FZU做专题 然后又碰到了 就认真的想并且去做了 dp思想都在代码注释里 ...
- sql order by+字段,指定按照哪个字段来排序
1.我们就可以使用 MySQL 的 ORDER BY 子句来设定你想按哪个字段哪中方式来进行排序,再返回搜索结果. 2.SELECT field1, field2,...fieldN table_na ...
- java list<int>报错
请问一下在java中的List<int> list=new List<int>();这条语句的两个int处会报错,请问为什么? 答: 两处错误:第一:List是接口,需要实现类 ...
- 判断返回数据是否为 null
判断是否为null //尖括号 if ([regeocode.city isEqual:[NSNull class]]) { NSL ...
- PHP函数库(other)
PHP函数库(other) Session函数: session_abort — Discard session array changes and finish session session_ab ...
- ExtJS笔记2 Class System
For the first time in its history, Ext JS went through a huge refactoring from the ground up with th ...
- 实用Javascript代码片段
清除select下拉选项,添加并选择特点选项 $('#mySelect') .find('option') .remove() .end() .append('<option value=&qu ...
- 时间函数 date strtotime
date_default_timezone_set('Asia/Shanghai');echo strtotime('Today');echo strtotime(date('Y-m-d')); 获取 ...
- Java中常用的内存区域
在Java中主要存在4块内存空间,这些内存空间的名称及作用如下. 1. 栈内存空间: 保存所有对象名称(更准确的说是保存了引用的堆内存空间的地址). 2. 堆内存空间: 保存每个对象的具体属性内容 ...
- 迷宫bfs POJ3984
#include<stdio.h> int map[5][5]={0,1,0,0,0, 0,1,0,1,0, 0,0,0,0,0, 0,1,1,1,0, ...
