【C++】map容器的用法
检测map容器是否为空:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include<map>
3 #include<string>
4 using namespace std;
5 int main()
6 {
7 //检测容器是否为空
8 map<string, string>mapText;
9 if (mapText.empty())
10 {
11 cout << "mapText为空" << endl;
12 }
13 else
14 {
15 cout << "mapText不为空" << endl;
16 }
17
18 //向容器中添加元素
19 mapText["小A"] = "A"; //赋值
20 mapText["小B"] = "B"; //赋值
21 mapText["小C"] = "C"; //赋值
22
23 if (mapText.empty())
24 {
25 cout << "mapText为空" << endl;
26 }
27 else
28 {
29 cout << "mapText不为空" << endl;
30 }
31
32 system("pause");
33 return 0;
34 }

重复赋值,值被替换:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include<map>
3 #include<string>
4 using namespace std;
5 int main()
6 {
7 map<string, string>mapText;
8 mapText["小A"] = "A"; //赋值
9 mapText["小A"] = "B"; //重复赋值
10 cout << mapText["小A"] << endl;
11
12 system("pause");
13 return 0;
14 }
判断键是否存在,如果不存在再赋值:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include<map>
3 #include<string>
4 using namespace std;
5 int main()
6 {
7 map<string, string>mapText;
8 mapText["小A"] = "A"; //赋值
9 //先检测键是否存在,如果存在则不赋值
10 if (mapText.count("小A") == 0) //count==0不存在 count==1存在
11 {
12 mapText["小A"] = "B"; //重复赋值
13 }
14 cout << mapText["小A"] << endl;
15
16 system("pause");
17 return 0;
18 }
map循环遍历:
map.begin()指向map的第一个元素
map.end()指向map的最后一个元素之后的地址
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include<map>
3 #include<string>
4 using namespace std;
5 int main()
6 {
7 map<string, string>mapText;
8 mapText["小A"] = "A"; //赋值
9 mapText["小B"] = "B"; //赋值
10 mapText["小C1"] = "C"; //赋值
11 mapText["小C2"] = "C"; //赋值
12 for (map<string, string>::iterator itor = mapText.begin(); itor != mapText.end(); ++itor)
13 {
14 cout << "key = " << itor->first << ", value = " << itor->second << endl;
15
16 }
17 system("pause");
18 return 0;
19 }

map 通过“键”删除键值对:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include<map>
3 #include<string>
4 using namespace std;
5 int main()
6 {
7 map<string, string>mapText;
8 mapText["小A"] = "A"; //赋值
9 mapText["小B"] = "B"; //赋值
10 mapText["小C1"] = "C"; //赋值
11 mapText["小C2"] = "C"; //赋值
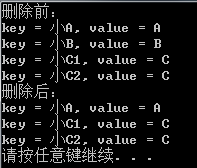
12 cout << "删除前:" << endl;
13 for (map<string, string>::iterator itor = mapText.begin(); itor != mapText.end(); ++itor)
14 {
15 cout << "key = " << itor->first << ", value = " << itor->second << endl;
16
17 }
18 //删除小B
19 mapText.erase("小B");
20 cout << "删除后:" << endl;
21 for (map<string, string>::iterator itor = mapText.begin(); itor != mapText.end(); ++itor)
22 {
23 cout << "key = " << itor->first << ", value = " << itor->second << endl;
24
25 }
26 mapText.erase("小B"); //小B不存在,erase也不会报错
27 system("pause");
28 return 0;
29 }
map 通过“值”删除键值对,先写一个错误用法,这里要注意:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include<map>
3 #include<string>
4 using namespace std;
5 int main()
6 {
7 map<string, string>mapText;
8 mapText["小A"] = "A"; //赋值
9 mapText["小B"] = "B"; //赋值
10 mapText["小C1"] = "C"; //赋值
11 mapText["小C2"] = "C"; //赋值
12 cout << "删除前:" << endl;
13 for (map<string, string>::iterator itor = mapText.begin(); itor != mapText.end(); ++itor)
14 {
15 cout << "key = " << itor->first << ", value = " << itor->second << endl;
16
17 }
18 //删除值为C的元素
19 //错误用法:
20 for (map<string, string>::iterator itor = mapText.begin(); itor != mapText.end(); ++itor)
21 {
22 if ((itor->second) == "C")
23 {
24 mapText.erase(itor);
25 }
26 }
27
28 cout << "删除后:" << endl;
29 for (map<string, string>::iterator itor = mapText.begin(); itor != mapText.end(); ++itor)
30 {
31 cout << "key = " << itor->first << ", value = " << itor->second << endl;
32
33 }
34 system("pause");
35 return 0;
36 }
错误原因:itor指针在元素被删除后失效了,回到for语句中与mapText.end()进行比较出现错误。
map 通过“值”删除键值对,正确的用法:
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include<map>
3 #include<string>
4 using namespace std;
5 int main()
6 {
7 map<string, string>mapText;
8 mapText["小A"] = "A"; //赋值
9 mapText["小B"] = "B"; //赋值
10 mapText["小C1"] = "C"; //赋值
11 mapText["小C2"] = "C"; //赋值
12 cout << "删除前:" << endl;
13 for (map<string, string>::iterator itor = mapText.begin(); itor != mapText.end(); ++itor)
14 {
15 cout << "key = " << itor->first << ", value = " << itor->second << endl;
16
17 }
18 //删除值为C的元素
19 //正确用法:
20 for (map<string, string>::iterator itor = mapText.begin(); itor != mapText.end(); /*++itor*/)
21 {
22 if ((itor->second) == "C")
23 {
24 itor = mapText.erase(itor);
25 }
26 else
27 {
28 ++itor;
29 }
30 }
31
32
33 cout << "删除后:" << endl;
34 for (map<string, string>::iterator itor = mapText.begin(); itor != mapText.end(); ++itor)
35 {
36 cout << "key = " << itor->first << ", value = " << itor->second << endl;
37
38 }
39 system("pause");
40 return 0;
41 }

删除map的第一个元素
mapText.erase(mapText.begin());
【C++】map容器的用法的更多相关文章
- 蓝桥杯 算法提高 9-3摩尔斯电码 _c++ Map容器用法
//****|*|*-**|*-**|--- #include <iostream> #include <map> #include <vector> #inclu ...
- 详解C++ STL map 容器
详解C++ STL map 容器 本篇随笔简单讲解一下\(C++STL\)中的\(map\)容器的使用方法和使用技巧. map容器的概念 \(map\)的英语释义是"地图",但\( ...
- map的详细用法
map是STL的一个关联容器,它提供一对一(其中第一个可以称为关键字,每个关键字只能在map中出现一次,第二个可能称为该关键字的值)的数据处理能力,由于这个特性,它完成有可能在我们处理一对一数据的时 ...
- stl之map容器的原理及应用
容器的数据结构同样是采用红黑树进行管理,插入的元素健位不允许重复,所使用的节点元素的比较函数,只对元素的健值进行比较,元素的各项数据可通过健值检索出来.map容器是一种关联容器,实现了SortedAs ...
- STL——map/unordered_map基础用法
map /multimap map是STL里重要容器之一. 它的特性总结来讲就是:所有元素都会根据元素的键值key自动排序(也可根据自定义的仿函数进行自定义排序),其中的每个元素都是<key, ...
- map的详细用法 (转
map的详细用法: map是STL的一个关联容器,它提供一对一(其中第一个可以称为关键字,每个关键字只能在map中出现一次,第二个可能称为该关键字的值)的数据处理能 力,由于这个特性,它完成有可能在我 ...
- C++ STL 中 map 容器
C++ STL 中 map 容器 Map是STL的一个关联容器,它提供一对一(其中第一个可以称为关键字,每个关键字只能在map中出现一次,第二个可能称为该关键字的值)的数据 处理能力,由于这个特性,它 ...
- map的常见用法
map的常见用法 map 是什么? map是一组键值对的组合,通俗理解类似一种特殊的数组,a[key]=val,只不过数组元素的下标是任意一种类型,而且数组的元素的值也是任意一种类型.有点类似pyth ...
- map 容器的使用
C++中map容器提供一个键值对容器,map与multimap差别仅仅在于multiple允许一个键对应多个值. 一.map的说明 1 头文件 #include <map> ...
随机推荐
- .NET之默认依赖注入
介绍 不要依赖于具体的实现,应该依赖于抽象,高层模块不应该依赖于底层模块,二者应该依赖于抽象.简单的说就是为了更好的解耦.而控制反转(Ioc)就是这样的原则的其中一个实现思路, 这个思路的其中一种实现 ...
- 解决docker镜像无法删除的问题
发现问题 来自守护进程的错误响应:冲突:无法删除050f26b6caca(必须强制) - 映像在多个存储库中被引用 Error response from daemon: conflict: unab ...
- Python协程与JavaScript协程的对比
前言 以前没怎么接触前端对JavaScript 的异步操作不了解,现在有了点了解一查,发现 python 和 JavaScript 的协程发展史简直就是一毛一样! 这里大致做下横向对比和总结,便于对这 ...
- JVM垃圾回收器总结
常见七种垃圾回收器以及使用的垃圾回收算法总结:
- 头文件string.h,cstring与string
string.h string.h是一个C标准头文件,所有的C标准头文件都形如name.h的形式,通过#include <string.h>可以导入此头文件.之后我们就可以在程序中使用st ...
- Java并发编程(二)如何保证线程同时/交替执行
第一篇文章中,我用如何保证线程顺序执行的例子作为Java并发系列的开胃菜.本篇我们依然不会有源码分析,而是用另外两个多线程的例子来引出Java.util.concurrent中的几个并发工具的用法. ...
- [Python] 地图API
请求位置信息 https://restapi.amap.com/v3/place/text?keywords=北京大学&city=beijing&output=xml&offs ...
- [Java] Git
版本控制 VCS(Version Control System):版本控制系统 主要功能:版本控制.主动提交.中央仓库 中央仓库功能:保存版本历史.同步团队代码 DVCS(Distributed VC ...
- 查看 swappiness 值
Swap的使用频率 发表于 2017-06-02 | 分类于 Linux | 评论数: 通过调整swappiness的值, 可以调整系统使用 swap 的频率 该值越小, 表示越大限度的使用物理 ...
- Docker Swarm(九)资源限制
资源限制 docker run 針對限制容器資源有許多設置選項,但Swarm中的 docker service 是另一回事,目前只有cpu和memory的選項可以操作. 如果 docker 找不到足夠 ...
