利用ZYNQ SOC快速打开算法验证通路(3)——PS端DMA缓存数据到PS端DDR
上篇该系列博文中讲述W5500接收到上位机传输的数据,此后需要将数据缓存起来。当数据量较大或者其他数据带宽较高的情况下,片上缓存(OCM)已无法满足需求,这时需要将大量数据保存在外挂的DDR SDRAM中。
最简单的方式是使用Xilinx的读写地址库函数Xil_In32()和Xil_Out32(),当然不仅支持32bit位宽,还包括8 16和64bit。但这种方式每次读写都要占用CPU,无法在读写的同时接收后续数据或者对之前的数据进一步处理,也就无法形成类似FPGA逻辑设计中的“流水线结构”,此时前段数据缓存过程中,后段数据会被丢弃。所以,需要利用PS端CPU子系统内的专用硬件DMA完成高速的批量数据搬移工作。

在Xilinx SDK的system.mss页面下直接导入ps_dma示例工程。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sleep.h"
#include "xparameters.h"
#include "xil_types.h"
#include "xil_assert.h"
#include "xil_io.h"
#include "xil_exception.h"
#include "xil_cache.h"
#include "xil_printf.h"
#include "xscugic.h"
#include "xdmaps.h" /************************** Constant Definitions *****************************/
/*
* The following constants map to the XPAR parameters created in the
* xparameters.h file. They are defined here such that a user can easily
* change all the needed parameters in one place.
*/
#define DMA_DEVICE_ID XPAR_XDMAPS_1_DEVICE_ID
#define INTC_DEVICE_ID XPAR_SCUGIC_SINGLE_DEVICE_ID #define DMA_DONE_INTR_0 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_0
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_1 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_1
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_2 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_2
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_3 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_3
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_4 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_4
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_5 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_5
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_6 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_6
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_7 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_7
#define DMA_FAULT_INTR XPAR_XDMAPS_0_FAULT_INTR #define TEST_ROUNDS 1 /* Number of loops that the Dma transfers run.*/
#define DMA_LENGTH 1024 /* Length of the Dma Transfers */
#define TIMEOUT_LIMIT 0x2000 /* Loop count for timeout */ /**************************** Type Definitions *******************************/ /***************** Macros (Inline Functions) Definitions *********************/ /************************** Function Prototypes ******************************/ int XDmaPs_Example_W_Intr(XScuGic *GicPtr, u16 DeviceId);
int SetupInterruptSystem(XScuGic *GicPtr, XDmaPs *DmaPtr);
void DmaDoneHandler(unsigned int Channel, XDmaPs_Cmd *DmaCmd,
void *CallbackRef); /************************** Macro Definitions *****************************/ /************************** Variable Definitions *****************************/
#ifdef __ICCARM__
#pragma data_alignment=32
static int Src[DMA_LENGTH];
static int Dst[DMA_LENGTH];
#pragma data_alignment=4
#else
static int Src[DMA_LENGTH] __attribute__ ((aligned ()));
static int Dst[DMA_LENGTH] __attribute__ ((aligned ()));
#endif XDmaPs DmaInstance;
#ifndef TESTAPP_GEN
XScuGic GicInstance;
#endif /****************************************************************************/
/**
*
* This is the main function for the DmaPs interrupt example.
*
* @param None.
*
* @return XST_SUCCESS to indicate success, otherwise XST_FAILURE.
*
* @note None.
*
****************************************************************************/
#ifndef TESTAPP_GEN
int main(void)
{
int Status; Status = XDmaPs_Example_W_Intr(&GicInstance,DMA_DEVICE_ID);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("Error: XDMaPs_Example_W_Intr failed\r\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
} xil_printf("XDMaPs_Example_W_Intr passed\r\n");
return XST_SUCCESS; }
#endif /*****************************************************************************/
/**
*
* Interrupt Example to test the DMA.
*
* @param DeviceId is the Device ID of the DMA controller.
*
* @return XST_SUCCESS to indicate success, otherwise XST_FAILURE.
*
* @note None.
*
****************************************************************************/
int XDmaPs_Example_W_Intr(XScuGic *GicPtr, u16 DeviceId)
{
int Index;
unsigned int Channel = ;
int Status;
int TestStatus;
int TestRound;
int TimeOutCnt;
volatile int Checked[XDMAPS_CHANNELS_PER_DEV];
XDmaPs_Config *DmaCfg;
XDmaPs *DmaInst = &DmaInstance;
XDmaPs_Cmd DmaCmd; memset(&DmaCmd, , sizeof(XDmaPs_Cmd)); DmaCmd.ChanCtrl.SrcBurstSize = ;
DmaCmd.ChanCtrl.SrcBurstLen = ;
DmaCmd.ChanCtrl.SrcInc = ;
DmaCmd.ChanCtrl.DstBurstSize = ;
DmaCmd.ChanCtrl.DstBurstLen = ;
DmaCmd.ChanCtrl.DstInc = ;
DmaCmd.BD.SrcAddr = (u32) Src;
DmaCmd.BD.DstAddr = (u32) Dst;
DmaCmd.BD.Length = DMA_LENGTH * sizeof(int); /*
* Initialize the DMA Driver
*/
DmaCfg = XDmaPs_LookupConfig(DeviceId);
if (DmaCfg == NULL) {
return XST_FAILURE;
} Status = XDmaPs_CfgInitialize(DmaInst,
DmaCfg,
DmaCfg->BaseAddress);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
} /*
* Setup the interrupt system.
*/
Status = SetupInterruptSystem(GicPtr, DmaInst);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
} TestStatus = XST_SUCCESS; for (TestRound = ; TestRound < TEST_ROUNDS; TestRound++) {
xil_printf("Test round %d\r\n", TestRound);
for (Channel = ;
Channel < XDMAPS_CHANNELS_PER_DEV;
Channel++) { /* Initialize source */
for (Index = ; Index < DMA_LENGTH; Index++)
Src[Index] = DMA_LENGTH - Index; /* Clear destination */
for (Index = ; Index < DMA_LENGTH; Index++)
Dst[Index] = ; Checked[Channel] = ; /* Set the Done interrupt handler */
XDmaPs_SetDoneHandler(DmaInst,
Channel,
DmaDoneHandler,
(void *)Checked); Status = XDmaPs_Start(DmaInst, Channel, &DmaCmd, );
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
} TimeOutCnt = ; /* Now the DMA is done */
while (!Checked[Channel]
&& TimeOutCnt < TIMEOUT_LIMIT) {
TimeOutCnt++;
} if (TimeOutCnt >= TIMEOUT_LIMIT) {
TestStatus = XST_FAILURE;
} if (Checked[Channel] < ) {
/* DMA controller failed */
TestStatus = XST_FAILURE;
}
}
} return TestStatus; } /******************************************************************************/
/**
*
* This function connects the interrupt handler of the interrupt controller to
* the processor. This function is seperate to allow it to be customized for
* each application. Each processor or RTOS may require unique processing to
* connect the interrupt handler.
*
* @param GicPtr is the GIC instance pointer.
* @param DmaPtr is the DMA instance pointer.
*
* @return None.
*
* @note None.
*
****************************************************************************/
int SetupInterruptSystem(XScuGic *GicPtr, XDmaPs *DmaPtr)
{
int Status;
#ifndef TESTAPP_GEN
XScuGic_Config *GicConfig; Xil_ExceptionInit(); /*
* Initialize the interrupt controller driver so that it is ready to
* use.
*/
GicConfig = XScuGic_LookupConfig(INTC_DEVICE_ID);
if (NULL == GicConfig) {
return XST_FAILURE;
} Status = XScuGic_CfgInitialize(GicPtr, GicConfig,
GicConfig->CpuBaseAddress);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
} /*
* Connect the interrupt controller interrupt handler to the hardware
* interrupt handling logic in the processor.
*/
Xil_ExceptionRegisterHandler(XIL_EXCEPTION_ID_IRQ_INT,
(Xil_ExceptionHandler)XScuGic_InterruptHandler,
GicPtr);
#endif
/*
* Connect the device driver handlers that will be called when an interrupt
* for the device occurs, the device driver handler performs the specific
* interrupt processing for the device
*/ /*
* Connect the Fault ISR
*/
Status = XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_FAULT_INTR,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_FaultISR,
(void *)DmaPtr);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
} /*
* Connect the Done ISR for all 8 channels of DMA 0
*/
Status = XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_0,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_0,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_1,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_1,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_2,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_2,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_3,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_3,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_4,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_4,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_5,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_5,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_6,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_6,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_7,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_7,
(void *)DmaPtr); if (Status != XST_SUCCESS)
return XST_FAILURE; /*
* Enable the interrupts for the device
*/
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_0);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_1);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_2);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_3);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_4);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_5);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_6);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_7);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_FAULT_INTR); Xil_ExceptionEnable(); return XST_SUCCESS; } /*****************************************************************************/
/**
*
* DmaDoneHandler.
*
* @param Channel is the Channel number.
* @param DmaCmd is the Dma Command.
* @param CallbackRef is the callback reference data.
*
* @return None.
*
* @note None.
*
******************************************************************************/
void DmaDoneHandler(unsigned int Channel, XDmaPs_Cmd *DmaCmd, void *CallbackRef)
{ /* done handler */
volatile int *Checked = (volatile int *)CallbackRef;
int Index;
int Status = ;
int *Src;
int *Dst; Src = (int *)DmaCmd->BD.SrcAddr;
Dst = (int *)DmaCmd->BD.DstAddr; /* DMA successful */
/* compare the src and dst buffer */
for (Index = ; Index < DMA_LENGTH; Index++) {
if ((Src[Index] != Dst[Index]) ||
(Dst[Index] != DMA_LENGTH - Index)) {
Status = -XST_FAILURE;
}
} Checked[Channel] = Status;
}
ps_dma_demo
其实demo中做的操作非常简单,仅仅是定义了两个数组Src和Dst,之后利用PS_DMA将Src中数据搬移到Dst中,搬移完成后进入中断函数比较两部分地址数据是否一致。Xilinx的SDK软件代码有固定的套路,“上有政策,下有对策”,我们可以将其封装成固定格式的一个个子函数,方便今后调用。这里把整个工程分为:系统中断,PS_DMA专有中断以及主函数三个部分。
#include "xscugic.h"
#include "sys_intr.h" int sys_IntrInit(XScuGic *GicPtr)
{
XScuGic_Config *GicConfig;
/*
* Initialize the interrupt controller driver so that it is ready to
* use.
*/
int Status;
GicConfig = XScuGic_LookupConfig(INTC_DEVICE_ID);
if (NULL == GicConfig) {
return XST_FAILURE;
} Status = XScuGic_CfgInitialize(GicPtr, GicConfig,
GicConfig->CpuBaseAddress);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
return XST_SUCCESS;
} void setupIntrException(XScuGic *GicPtr)
{
Xil_ExceptionInit();
/*
* Connect the interrupt controller interrupt handler to the hardware
* interrupt handling logic in the processor.
*/
Xil_ExceptionRegisterHandler(XIL_EXCEPTION_ID_IRQ_INT,
(Xil_ExceptionHandler)XScuGic_InterruptHandler,
GicPtr);
Xil_ExceptionEnable();
}
sys_intr.c
#ifndef SRC_SYS_INTR_H_
#define SRC_SYS_INTR_H_ #define INTC_DEVICE_ID XPAR_SCUGIC_SINGLE_DEVICE_ID int sys_IntrInit(XScuGic *GicPtr);
void setupIntrException(XScuGic *GicPtr); #endif /* SRC_SYS_INTR_H_ */
sys_intr.h
#include "xil_types.h"
#include "xdmaps.h"
#include "xscugic.h"
#include "psdma_intr.h" int PS_DMA_IntrInit(XDmaPs *DmaInst,u16 DeviceId)
{
/*
* Initialize the DMA Driver
*/
int Status;
XDmaPs_Config *DmaCfg = NULL;
DmaCfg = XDmaPs_LookupConfig(DeviceId);
if (DmaCfg == NULL) {
return XST_FAILURE;
} Status = XDmaPs_CfgInitialize(DmaInst,
DmaCfg,
DmaCfg->BaseAddress);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
}
return XST_SUCCESS;
} int PS_DMA_SetupIntr(XScuGic *GicPtr,XDmaPs *DmaPtr,unsigned Channel)
{
int Status;
/*
* Connect the device driver handlers that will be called when an interrupt
* for the device occurs, the device driver handler performs the specific
* interrupt processing for the device
*/ /*
* Connect the Fault ISR
*/
Status = XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_FAULT_INTR,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_FaultISR,
(void *)DmaPtr);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
return XST_FAILURE;
} /*
* Connect the Done ISR for all 8 channels of DMA 0
*/
Status = XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_0,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_0,
(void *)DmaPtr);
/*Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_1,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_1,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_2,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_2,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_3,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_3,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_4,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_4,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_5,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_5,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_6,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_6,
(void *)DmaPtr);
Status |= XScuGic_Connect(GicPtr,
DMA_DONE_INTR_7,
(Xil_InterruptHandler)XDmaPs_DoneISR_7,
(void *)DmaPtr);*/ if (Status != XST_SUCCESS)
return XST_FAILURE; /* Set the Done interrupt handler */
XDmaPs_SetDoneHandler(DmaPtr,
Channel,//Channel
DmaDoneHandler,//真正的中断函数
(void *)Checked); /*
* Enable the interrupts for the device
*/
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_0);
/*
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_1);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_2);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_3);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_4);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_5);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_6);
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_DONE_INTR_7);*/
XScuGic_Enable(GicPtr, DMA_FAULT_INTR); return XST_SUCCESS;
} void DmaDoneHandler(unsigned int Channel, XDmaPs_Cmd *DmaCmd, void *CallbackRef)
{ /* done handler */
volatile int *Checked = (volatile int *)CallbackRef;
//int Index;
int Status = ; xil_printf("Enter into the interrupt\n");
Checked[Channel] = Status;
} void PS_DMA_InitPara(XDmaPs_Cmd* DmaCmd)
{ memset(DmaCmd, , sizeof(XDmaPs_Cmd)); DmaCmd->ChanCtrl.SrcBurstSize = ;
DmaCmd->ChanCtrl.SrcBurstLen = ;
DmaCmd->ChanCtrl.SrcInc = ;
DmaCmd->ChanCtrl.DstBurstSize = ;
DmaCmd->ChanCtrl.DstBurstLen = ;
DmaCmd->ChanCtrl.DstInc = ;
DmaCmd->BD.SrcAddr = (u32) Src;
DmaCmd->BD.DstAddr = (u32) DDR_BASEADDR;//Dst
DmaCmd->BD.Length = DMA_LENGTH * sizeof(int);
}
psdma_intr.c
#ifndef SRC_PSDMA_INTR_H_
#define SRC_PSDMA_INTR_H_ #define DMA_DONE_INTR_0 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_0
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_1 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_1
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_2 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_2
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_3 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_3
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_4 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_4
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_5 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_5
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_6 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_6
#define DMA_DONE_INTR_7 XPAR_XDMAPS_0_DONE_INTR_7
#define DMA_FAULT_INTR XPAR_XDMAPS_0_FAULT_INTR #define DDR_BASEADDR 0x00600000//XPAR_PS7_DDR_0_S_AXI_BASEADDR 0x00100000
#define DMA_LENGTH 1024 /* Length of the Dma Transfers */ int Src[DMA_LENGTH] __attribute__ ((aligned ()));
volatile int Checked[XDMAPS_CHANNELS_PER_DEV]; int PS_DMA_IntrInit(XDmaPs *DmaInst,u16 DeviceId);
int PS_DMA_SetupIntr(XScuGic *GicPtr,XDmaPs *DmaPtr,unsigned Channel);
void DmaDoneHandler(unsigned int Channel, XDmaPs_Cmd *DmaCmd, void *CallbackRef);
void PS_DMA_InitPara(XDmaPs_Cmd* DmaCmd); #endif /* SRC_PSDMA_INTR_H_ */
psdma_intr.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "sleep.h"
#include "xparameters.h"
#include "xil_types.h"
#include "xil_assert.h"
#include "xil_io.h"
#include "xil_exception.h"
#include "xil_cache.h"
#include "xil_printf.h"
#include "xscugic.h"
#include "xdmaps.h" #include "sys_intr.h"
#include "psdma_intr.h" #define DMA_DEVICE_ID XPAR_XDMAPS_1_DEVICE_ID
#define INTC_DEVICE_ID XPAR_SCUGIC_SINGLE_DEVICE_ID #define TEST_ROUNDS 1 /* Number of loops that the Dma transfers run.*/
#define TIMEOUT_LIMIT 0x2000 /* Loop count for timeout */ static XScuGic GicInstance;
static XDmaPs DmaInstance;
static XDmaPs_Cmd DmaCmd;
unsigned int Channel = ; /************************** Function Prototypes ******************************/ int PS_DMA_WriteTest();
int SetupInterruptSystem(XScuGic *GicPtr, XDmaPs *DmaPtr);
void DmaDoneHandler(unsigned int Channel, XDmaPs_Cmd *DmaCmd,
void *CallbackRef);
int dataCheck(u32 baseAddr,u32 len);
int systemInit(XScuGic *GicPtr,u16 DeviceId); int main(void)
{
int Status;
Status = systemInit(&GicInstance,DMA_DEVICE_ID);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("System initialization is failed\r\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
} Status = PS_DMA_WriteTest();
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("Error: XDMaPs_Example_W_Intr failed\r\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
}
xil_printf("Checking data...\n");
Status = dataCheck(DDR_BASEADDR,DMA_LENGTH);
if(Status != XST_SUCCESS)
{
xil_printf("Error:check failed\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
} xil_printf("Writing data to DDR using DMA test passed!\r\n");
return XST_SUCCESS; } int dataCheck(u32 baseAddr,u32 len)
{
u32 DDR_ReadData[];
int i;
for(i=;i<len;i++)
{
DDR_ReadData[i] = Xil_In32(baseAddr+i*);
if(DDR_ReadData[i]!=Src[i])
return XST_FAILURE;
//else //将写入DDR数据读回 并打印
// xil_printf("data at %x is %d\n",baseAddr+i*4,DDR_ReadData[i]);
}
return XST_SUCCESS;
} /*****************************************************************************/
/**
*
* Interrupt Example to test the DMA.
*
* @param DeviceId is the Device ID of the DMA controller.
*
* @return XST_SUCCESS to indicate success, otherwise XST_FAILURE.
*
* @note None.
*
****************************************************************************/
int PS_DMA_WriteTest()
{
int Index;
int Status;
int TestStatus;
int TestRound;
int TimeOutCnt; TestStatus = XST_SUCCESS; for (TestRound = ; TestRound < TEST_ROUNDS; TestRound++) {
xil_printf("Test round %d\r\n", TestRound);
for (Channel = ;Channel < ;Channel++)
{
/* Initialize source */
for (Index = ; Index < DMA_LENGTH; Index++)
Src[Index] = DMA_LENGTH - Index; Checked[Channel] = ; Status = XDmaPs_Start(&DmaInstance, Channel, &DmaCmd, );
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("Starting the DMA is failed.\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
}
xil_printf("Starting the DMA is successful.\n");
TimeOutCnt = ; while (!Checked[Channel]
&& TimeOutCnt < TIMEOUT_LIMIT) {
TimeOutCnt++;
}
/* Now the DMA is done */
xil_printf("Jump out of the interrupt\n");
if (TimeOutCnt >= TIMEOUT_LIMIT) {
xil_printf("Overtime!\n");
TestStatus = XST_FAILURE;
} if (Checked[Channel] < ) {
/* DMA controller failed */
xil_printf("Checking failure!\n");
TestStatus = XST_FAILURE;
}
}
} return TestStatus; } int systemInit(XScuGic *GicPtr,u16 DeviceId)
{
xil_printf("Start to initialize interrupt system.\n"); PS_DMA_InitPara(&DmaCmd);//主要设置DMA的源目的地址
//xil_printf("Configuring DMA parameters is successful.\n"); int Status; Status = PS_DMA_IntrInit(&DmaInstance,DeviceId);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("DMA initialization is failed.\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
}
//xil_printf("DMA initialization is successful.\n"); Status = sys_IntrInit(GicPtr);
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("Initialization of the interrupt system is failed.\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
}
//xil_printf("Initialization of the interrupt system is successful.\n"); setupIntrException(GicPtr); Status = PS_DMA_SetupIntr(GicPtr,&DmaInstance,Channel);//////////////////////////DMA中断入口///////////////////////
if (Status != XST_SUCCESS) {
xil_printf("Setting up DMA interrupt is failed.\n");
return XST_FAILURE;
}
//xil_printf("Setting up DMA interrupt is successful.\n"); xil_printf("System initialization is finished.\n");
xil_printf("------------------------------------------\n");
return XST_SUCCESS;
}
main.c
上述代码的封装方式参考了米联客教程中的思想。先说明系统中断部分:sys_IntrInit()函数中进行查找表配置和中断控制器初始化操作,setupIntrException()函数负责使能中断异常处理。再来说说PS_DMA中断部分:PS_DMA_IntrInit()函数与系统中断中sys_IntrInit()从操作到格式几乎完成相同,亦是查找表配置和DMA的初始化。PS_DMA_SetupIntr()函数完成了中断源和中断控制器的连接和设置中断处理器,以及中断使能,也就是所有PS_DMA的专用中断操作。
PS_DMA_SetupIntr()内最重要的部分是XDmaPs_SetDoneHandler(),其相当于一个调用中断函数的通用处理框架,它的第三个参数DoneHandler才是真正的中断处理函数。这里涉及到C语言的高级话题:函数通过函数指针调用另一个函数,被函数指针调用的函数就是通常讲的“回调函数”了。指针调用函数的方式兼顾了程序的通用架构和灵活性,具体参考文章:不懂C语言回调函数,那就看这篇文章吧! - 简书 https://www.jianshu.com/p/2f695d6fd64f 在该程序中,中断回调函数为DmaDoneHandler()。
PS_DMA_InitPara()是自行添加的PS_DMA参数初始化函数,内部的参数更是重中之重了,我们来查看Xilinx官方文档ug585的DMA Controller章节。

简要来说,DMA以burst形式传输数据,意思是分批次搬移。手册说明原或目的burst_size位宽不能超过64bit,这也是其挂载AXI总线的数据位宽。PS_DMA_InitPara()里的SrcBurstSize为源突发传输位宽字节数,最大为8.SrcBurstLen是手册中所说的“burst length”,即突发传输数据个数。SrcInc表示burst types为地址自增(1)还是地址固定(0)模式。目的控制字同理。剩下的三个参数最重要:SrcAddr DstAddr Length分别代表源首地址 目的首地址和一共需要搬移的数据字节数。需要注意的是,一定要满足srcburstsize*srcburstlen == dstburstsize*dstburstlen,否则发生错误。这一点也比较好理解,相当于FPGA逻辑设计中的异步FIFO两侧数据带宽要匹配。
那么要想完成OCM到DDR的数据搬移,改动下地址就可以嘛。由于读写DDR要访问绝对地址,所以要格外注意读写操作的地址不能和DDR内存储程序代码和中间数据的地址段重叠。避免程序崩溃很简单的做法就是在XPAR_PS7_DDR_0_S_AXI_BASEADDR 的基础上加一段偏移量,具体加多少的问题本人也不是很明确,希望看到的朋友能在评论中指点一二。
明确了PS_DMA的参数和使用方式,还有一点非常重要:PS_DMA的工作时钟是多少?这就需要继续看ug585了。

DMA控制器工作在CPU_2*时钟速率下,那这个CPU_2*的频率值具体是多少呢?
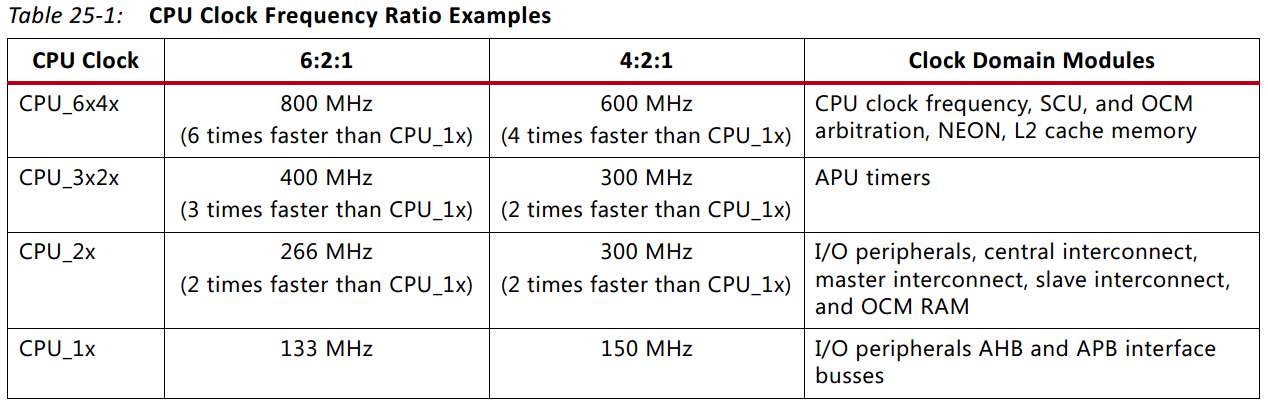
从上表可以看出,CPU的时钟系统有两种时钟比例关系,分别是:6:2:1和4:2:1。对应的时钟名称依次是:CPU_6*4* CPU_3*2* CPU_2* CPU_1*。后边的N*就是该时钟频率与CPU_1*的频率的倍数。确定CPU_6*4*的数值和当前的时钟比例关系,也就确定了其他时钟的频率。PS_CLK频率与PLL Feedback Divider Value值相乘得到ARM PLL output frequency。之后经过二分频获得CPU_6*4*。在IP Integrator中打开ZYNQ的时钟配置界面:
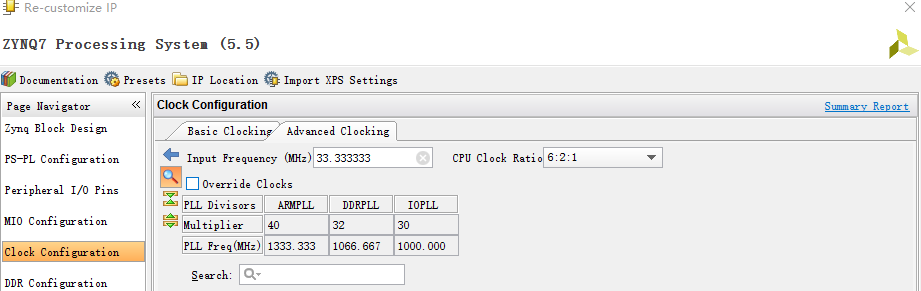
当前使用时钟比例关系是6:2:1,PLL时钟频率是1333.333MHz,也就是CPU_6*4*的频率是1333.33/2=667MHz。综上,DMA的工作时钟CPU_2*的频率值是667/3=222MHz。
对于ZYNQ这一SOC架构来说,PS端连接如以太网,USB等高带宽外设计接口更加方便,所以PS_DMA的灵活运用还好是十分必要的,更灵活高效的利用这一硬件资源还要后期继续探索。PS端和PL端高速数据交互就需要用到另一个DMA成员AXI_DMA,可以说它利用片内总线打破了CPU+FPGA架构的性能瓶颈,该部分内容将在后续说明。
利用ZYNQ SOC快速打开算法验证通路(3)——PS端DMA缓存数据到PS端DDR的更多相关文章
- 利用ZYNQ SOC快速打开算法验证通路(1)——MATLAB浮点数与定点二进制补码互转
最近本人一直在学习ZYNQ SOC的使用,目的是应对科研需要,做出通用的算法验证平台.大概思想是:ZYNQ PS端负责与MATLAB等上位机数据分析与可视化软件交互:既可传输数据,也能通过上位机配置更 ...
- 利用ZYNQ SOC快速打开算法验证通路(6)——利用AXI总线实时配置sysGen子系统
利用ZYNQ验证算法的一大优势在于,可以在上位机发送指令借助CPU的控制能力和C语言易开发特点,实时配置算法模块的工作模式.参数等对来对其算法模块性能进行全面的评估.最重要的是无需重新综合硬件模块. ...
- 利用ZYNQ SOC快速打开算法验证通路(4)——AXI DMA使用解析及环路测试
一.AXI DMA介绍 本篇博文讲述AXI DMA的一些使用总结,硬件IP子系统搭建与SDK C代码封装参考米联客ZYNQ教程.若想让ZYNQ的PS与PL两部分高速数据传输,需要利用PS的HP(高性能 ...
- 利用ZYNQ SOC快速打开算法验证通路(2)——数据传输最简方案:网络调试助手+W5500协议栈芯片
在上一篇该系列博文中讲解了MATLAB待处理数据写入.bin二进制数据文件的过程,接下来需要将数据通过以太网发送到ZYNQ验证平台.之前了解过Xilinx公司面向DSP开发的System Genera ...
- 利用ZYNQ SOC快速打开算法验证通路(6)——LWIP实现千兆TCP/IP网络传输
一.前言 之前ZYNQ与PC之间的网络连接依赖于外接硬件协议栈芯片,虽然C驱动非常简单,但网络带宽受限.现采用LWIP+PS端MAC控制器+PHY芯片的通用架构.关于LWIP库,已经有很多现成的资料和 ...
- 利用ZYNQ SOC快速打开算法验证通路(5)——system generator算法IP导入IP integrator
一.前言 利用FPGA设计算法一直以来都是热点,同样也是难点.将复杂的数学公式 模型通过硬件系统来搭建,在低延时 高并行性等优势背后极大提高了设计难度和开发周期.Xilinx公司的sysGen(sys ...
- 利用Zynq Soc创建一个嵌入式工程
英文题目:Using the Zynq SoC Processing System,参考自ADI的ug1165文档. 利用Zynq Soc创建一个嵌入式工程,该工程总体上包括五个步骤: 步骤一.新建空 ...
- 基于Python的函数回归算法验证
看机器学习看到了回归函数,看了一半看不下去了,看到能用方差进行函数回归,又手痒痒了,自己推公式写代码验证: 常见的最小二乘法是一阶函数回归回归方法就是寻找方差的最小值y = kx + bxi, yiy ...
- 利用朴素贝叶斯算法进行分类-Java代码实现
http://www.crocro.cn/post/286.html 利用朴素贝叶斯算法进行分类-Java代码实现 鳄鱼 3个月前 (12-14) 分类:机器学习 阅读(44) 评论(0) ...
随机推荐
- Xapian的内存索引
关键字:xapian.内存索引 xapian除了提供用于生产环境的磁盘索引,也提供了内存索引(InMemoryDatabase).内存索引.我们可以通过观察内存索引的设计,来了解xapian的设计思路 ...
- Centos7 防火墙 firewalld 实用操作
一.前言 Centos7以上的发行版都试自带了firewalld防火墙的,firewalld去带了iptables防火墙.其原因是iptables的防火墙策略是交由内核层面的netfilter网络过滤 ...
- ES 04 - 安装Kibana插件(6.6.0版本)
目录 1 Kibana是什么 2 安装并启动Kibana 2.1 准备安装包 2.2 修改配置文件 2.3 启动Kibana并验证 2.4 关闭Kibana服务 3 Kibana功能测试 3.1 关于 ...
- node 调试相关
#0 node 正确的书写方式 为了防止后面出现混乱的各种书写,先来了解一下如何正确书写 node 的名称. 下面使用来自@bitandbang 推文中的图片展示如何正确书写 node 名称. nod ...
- 带着新人学springboot的应用04(springboot+mybatis+redis 完)
对于缓存也说了比较多了,大家对下图这一堆配置类现在应该有些很粗略的认识了(因为我也就很粗略的认识了一下,哈哈!),咳,那么我们怎么切换这个缓存呢?(就是不用springboot提供的默认的Simple ...
- 《深入java虚拟机》读书笔记之Java内存区域
前言 该读书笔记用于记录在学习<深入理解Java虚拟机--JVM高级特性与最佳实践>一书中的一些重要知识点,对其中的部分内容进行归纳,主要是方便之后进行复习. 运行时数据区域 Java虚拟 ...
- java中用MessageFormat格式化json字符串用占位符时出现的问题can't parse argument number
在MessageFormat.format方法中组装jason数据字符串:{code:"w1",des:"w2"},起止分别有左大括号和右大括号. 直接写的点位 ...
- leetcode — remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array
import java.util.Arrays; /** * Source : https://oj.leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sort ...
- -1-5 java 多线程 概念 进程 线程区别联系 java创建线程方式 线程组 线程池概念 线程安全 同步 同步代码块 Lock锁 sleep()和wait()方法的区别 为什么wait(),notify(),notifyAll()等方法都定义在Object类中
本文关键词: java 多线程 概念 进程 线程区别联系 java创建线程方式 线程组 线程池概念 线程安全 同步 同步代码块 Lock锁 sleep()和wait()方法的区别 为什么wait( ...
- python数据包之利器scapy用法!
scapy介绍: 在python中可以通过scapy这个库轻松实现构造数据包.发送数据包.分析数据包,为网络编程之利器! scapy安装: pip install scapy ======> ...
