2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛 maze(bfs)
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/105/F
来源:牛客网
一个格子可能既有多个入口,又有多个出口,小明可以选择任意一个入口开启传送阵。使用传送阵是非常危险的,因为有的传送阵的出口在陷阱里,如果小明使用这样的传送阵,那他就会死亡。也有一些传送阵的入口在陷阱里,这样的传送阵是没有用的,因为小明不能活着进入。请告诉小明活着到达目的地的最短时间。
输入描述:
- 有多组数据。对于每组数据:
第一行有三个整数n,m,q(2≤ n,m≤300,0≤ q ≤ 1000)。
接下来是一个n行m列的矩阵,表示迷宫。
最后q行,每行四个整数
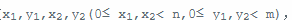
- 表示一个传送阵的入口在x
1
- 行y
1
- 列,出口在x
2
- 行y
2
- 列。
输出描述:
- 如果小明能够活着到达目的地,则输出最短时间,否则输出-1。
输入
- 5 5 1
- ..S..
- .....
- .###.
- .....
- ..T..
- 1 2 3 3
- 5 5 1
- ..S..
- .....
- .###.
- .....
- ..T..
- 3 3 1 2
- 5 5 1
- S.#..
- ..#..
- ###..
- .....
- ....T
- 0 1 0 2
- 4 4 2
- S#.T
- .#.#
- .#.#
- .#.#
- 0 0 0 3
- 2 0 2 2
输出
- 6
- 8
- -1
- 3
bfs,注意,可能通过不止一个传送阵
- #include <iostream>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <cstring>
- #include <cstdio>
- #include <vector>
- #include <queue>
- #include <stack>
- #include <cstdlib>
- #include <iomanip>
- #include <cmath>
- #include <cassert>
- #include <ctime>
- #include <map>
- #include <set>
- using namespace std;
- #pragma comment(linker, "/stck:1024000000,1024000000")
- #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
- #define max(x,y) (x>=y?x:y)
- #define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y)
- #define MAX 100000000000000000
- #define MOD 1000000007
- #define pi acos(-1.0)
- #define ei exp(1)
- #define PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832
- #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(true)
- #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
- #define mem(a) ((a,0,sizeof(a)))
- typedef long long ll;
- struct node
- {
- int x,y,step;
- node(int x=,int y=,int t=):x(x),y(y),step(step){};
- bool operator<(const node a) const
- {
- return a.step<step;
- }
- }ans,pos;
- int dir[][]={{,},{,},{,-},{-,}};
- int n,m,k,xs,ys;
- int dis[][];
- char a[][];
- int xa,xb,ya,yb;
- vector<node>vis[][];
- int bfs(int u,int v)
- {
- priority_queue<node>q;
- memset(dis,INF,sizeof(dis));
- ans.x=u;ans.y=v;
- ans.step=;
- dis[u][v]=;
- q.push(ans);
- while(!q.empty())
- {
- pos=q.top();
- q.pop();
- if(a[pos.x][pos.y]=='T') return pos.step;
- for(int i=;i<vis[pos.x][pos.y].size();i++)
- {
- ans=vis[pos.x][pos.y][i];
- if(dis[ans.x][ans.y]>pos.step+)
- {
- ans.step=pos.step+;
- dis[ans.x][ans.y]=pos.step+;
- q.push(ans);
- }
- }
- for(int i=;i<;i++)
- {
- ans.x=pos.x+dir[i][];
- ans.y=pos.y+dir[i][];
- ans.step=pos.step+;
- if(ans.x>= && ans.x<n && ans.y>= && ans.y<m && a[ans.x][ans.y]!='#' && dis[ans.x][ans.y]>ans.step)
- {
- dis[ans.x][ans.y]=pos.step+;
- q.push(ans);
- }
- }
- }
- return -;
- }
- int main()
- {
- while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k))
- {
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- {
- scanf("%s",&a[i]);
- for(int j=;j<m;j++)
- {
- vis[i][j].clear();
- if(a[i][j]=='S') xs=i,ys=j;
- }
- }
- for(int i=;i<k;i++)
- {
- scanf("%d%d%d%d",&xa,&ya,&xb,&yb);
- if(a[xa][ya]!='#' && a[xb][yb]!='#')
- vis[xa][ya].push_back(node(xb,yb));
- }
- int cnt=bfs(xs,ys);
- printf("%d\n",cnt);
- }
- return ;
- }#include <iostream>
- #include <algorithm>
- #include <cstring>
- #include <cstdio>
- #include <vector>
- #include <queue>
- #include <stack>
- #include <cstdlib>
- #include <iomanip>
- #include <cmath>
- #include <cassert>
- #include <ctime>
- #include <map>
- #include <set>
- using namespace std;
- #pragma comment(linker, "/stck:1024000000,1024000000")
- #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x))
- #define max(x,y) (x>=y?x:y)
- #define min(x,y) (x<=y?x:y)
- #define MAX 100000000000000000
- #define MOD 1000000007
- #define pi acos(-1.0)
- #define ei exp(1)
- #define PI 3.1415926535897932384626433832
- #define ios() ios::sync_with_stdio(true)
- #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
- #define mem(a) ((a,0,sizeof(a)))
- typedef long long ll;
- struct node
- {
- int x,y,step;
- node(int x=,int y=,int t=):x(x),y(y),step(step){};
- bool operator<(const node a) const
- {
- return a.step<step;
- }
- }ans,pos;
- int dir[][]={{,},{,},{,-},{-,}};
- int n,m,k,xs,ys;
- int dis[][];
- char a[][];
- int xa,xb,ya,yb;
- vector<node>vis[][];
- int bfs(int u,int v)
- {
- priority_queue<node>q;
- memset(dis,INF,sizeof(dis));
- ans.x=u;ans.y=v;
- ans.step=;
- dis[u][v]=;
- q.push(ans);
- while(!q.empty())
- {
- pos=q.top();
- q.pop();
- if(a[pos.x][pos.y]=='T') return pos.step;
- for(int i=;i<vis[pos.x][pos.y].size();i++)
- {
- ans=vis[pos.x][pos.y][i];
- if(dis[ans.x][ans.y]>pos.step+)
- {
- ans.step=pos.step+;
- dis[ans.x][ans.y]=pos.step+;
- q.push(ans);
- }
- }
- for(int i=;i<;i++)
- {
- ans.x=pos.x+dir[i][];
- ans.y=pos.y+dir[i][];
- ans.step=pos.step+;
- if(ans.x>= && ans.x<n && ans.y>= && ans.y<m && a[ans.x][ans.y]!='#' && dis[ans.x][ans.y]>ans.step)
- {
- dis[ans.x][ans.y]=pos.step+;
- q.push(ans);
- }
- }
- }
- return -;
- }
- int main()
- {
- while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k))
- {
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- {
- scanf("%s",&a[i]);
- for(int j=;j<m;j++)
- {
- vis[i][j].clear();
- if(a[i][j]=='S') xs=i,ys=j;
- }
- }
- for(int i=;i<k;i++)
- {
- scanf("%d%d%d%d",&xa,&ya,&xb,&yb);
- if(a[xa][ya]!='#' && a[xb][yb]!='#')
- vis[xa][ya].push_back(node(xb,yb));
- }
- int cnt=bfs(xs,ys);
- printf("%d\n",cnt);
- }
- return ;
- }
2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛 maze(bfs)的更多相关文章
- 2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛 F - maze
把点抽出来 跑个最短路就好啦. #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define LL long long #define pii pair<int,int> # ...
- 2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛G又见斐波那契
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/105/G来源:牛客网 时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒 空间限制:C/C++ 32768K,其他语言65536 ...
- 牛客网-2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛-F
题目链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/105/F 解题思路:这道题第一眼直接思路就是搜索,但想了半天没想到有什么好办法搜,然后就转成最短路写了, 因为多入 ...
- 2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛 H统计颜色
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/105/H来源:牛客网 时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒 空间限制:C/C++ 32768K,其他语言65536 ...
- 2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛 G- 又见斐波那契
推一推矩阵直接快速幂. #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define LL long long #define pii pair<int,int> #defi ...
- 2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛 E 吃货
题目描述 作为一个标准的吃货,mostshy又打算去联建商业街觅食了.混迹于商业街已久,mostshy已经知道了商业街的所有美食与其价格,而且他给每种美食都赋予了一个美味度,美味度越高表示他越喜爱这种 ...
- 2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛G又见斐波那契(矩阵快速幂)
题意 题目链接 Sol 直接矩阵快速幂 推出来的矩阵应该长这样 \begin{equation*}\begin{bmatrix}1&1&1&1&1&1\\1 & ...
- 2018年湘潭大学程序设计竞赛 Fibonacci进制
Fibonacci数是非常有名的一个数列,它的公式为 f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2),f(0)=1,f(1)=2. 我们可以把任意一个数x表示成若干不相同的Fibonacci数的和, 比如说1 ...
- 2018中国大学生程序设计竞赛 - 网络选拔赛 1001 - Buy and Resell 【优先队列维护最小堆+贪心】
题目传送门:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6438 Buy and Resell Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/O ...
随机推荐
- bzoj4519: [Cqoi2016]不同的最小割(分治最小割)
4519: [Cqoi2016]不同的最小割 题目:传送门 题解: 同BZOJ 2229 基本一样的题目啊,就最后用set记录一下就ok 代码: #include<cstdio> #inc ...
- java中的输入输出<1>
java中的输入输出基础(1) java中的IO支持通过java.io包下的类和接口来支持.在java.io包下主要包括输入.输出两种io流,每种输入.输出流又分为字节流和字符流. 字节流就是以字节为 ...
- 洛谷P1339 [USACO09OCT]热浪Heat Wave(最短路)
题目描述 The good folks in Texas are having a heatwave this summer. Their Texas Longhorn cows make for g ...
- PostgreSQL 数据库性能调优的注意点
PostgreSQL提供了一些性能调优的功能.主要有如下几个方面.1.使用EXPLAIN EXPLAIN命令可以查看执行计划,这个方法是我们最主要的调试工具. 2.及时更新执行计划中使用的统计信息 ...
- IE6 css fixed
.fixed-top{position:fixed;bottom:auto;top:0px;} .fixed-bottom{position:fixed;bottom:0px;top:auto;} . ...
- hdu 6082 - 完全背包,打表。
2017-08-06 15:02:50 Accepted 1003 187 MS 2168 K G++ redips 对背包有了进一步的认识 ----------------------------- ...
- Matlab 从入门到精通 Chapter11 文件读取I/O
11.1 工作空间数据读取 将工作空间的变量保存为文件,可以使用save命令. save('filename') 将文件保存在当前目录下,文件名为filename.mat save('filenam ...
- LightOJ-1074 Extended Traffic 最短路问题 注意连通性
题目链接:https://cn.vjudge.net/problem/LightOJ-1074 题意 给一图 求最短路 若最短路<3或没有最短路,则输出'?' 思路 首先注意到可能存在负环,所以 ...
- [UVa10188]Automated Judge Script
题目大意:叫你写一个判断答案的系统. 解题思路:模拟即可.AC条件为,答案条数相等,所有字符相等.PE条件为,答案条数可能不等,所有数字字符相等.其他为WA. UVa现在的C++已经不支持gets了, ...
- 使用systemctl自定义系统服务
1.创建系统服务文件,格式如下: [Unit] Description=httpd After=network.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/usr ...
