Shiro的Filter机制详解---源码分析(转)
Shiro的Filter机制详解
首先从spring-shiro.xml的filter配置说起,先回答两个问题:
1, 为什么相同url规则,后面定义的会覆盖前面定义的(执行的时候只执行最后一个)。
2, 为什么两个url规则都可以匹配同一个url,只执行第一个呢。
下面分别从这两个问题入手,最终阅读源码得到解答。
问题一解答
相同url但定义在不同的行,后面覆盖前面
如
/usr/login.do=test3
/usr/login.do=test1,test2
不会执行test3的filter
要解答第一个问题,需要知道shiro(或者说是spring)是如何扫描这些url规则并保存的。
Web.xml配置shiro以及spring-shiro.xml的核心配置
在web.xml中定义shiroFilter

<filter>
<filter-name>shiroFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
<init-param>
<!-- 该值缺省为false,表示生命周期由SpringApplicationContext管理,设置为true则表示由ServletContainer管理 -->
<param-name>targetFilterLifecycle</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>shiroFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>

在spring-shiro.xml中定义shiroFilter
(要和web.xml中的名称一样,因为spring就是依靠名称来获取这个bean的)

<bean id="shiroFilter" class="org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean">
<property name="securityManager" ref="securityManager" />
<property name="loginUrl" value="/login.jsp" />
<property name="unauthorizedUrl" value="/WEB-INF/405.html" />
<property name="filters">
<map>
<entry key="kickout" value-ref="kickoutSessionControlFilter" />
</map>
</property>
<property name="filterChainDefinitions">
<value>
/**=kickout
/usr/login.do=anon
/security/*=anon
/usr/login.do=authc
/usr/test/*=authc
</value>
</property>
</bean>

都定义好之后,分析org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy发现该filter类的任务是:将具体工作分派给org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean这个类中的静态内部类SpringShiroFilter做。
具体spring内部是怎么将工作委派的,暂时没有分析。
现在关注的是当spring把具体工作委派给ShiroFilterFactoryBean后,该类是怎么工作的。
Spring将配置注入到ShiroFilterFactoryBean
在这之前,spring通过bean注入,将ShiroFilterFactoryBean的相关成员通过set方法注入进去。
前面已经配置了filters和filterChainDefinitions,再次贴出如下所示:

<property name="filters">
<map>
<entry key="kickout" value-ref="kickoutSessionControlFilter" />
</map>
</property>
<property name="filterChainDefinitions">
<value>
/**=kickout
/usr/login.do=anon
/security/*=anon
/usr/login.do=authc
/usr/test/*=authc
</value>
</property>

看一下ShiroFilterFactoryBean是怎么接收他们的。
Filters很简单,只需要map接收就自动完成了。
public void setFilters(Map<String, Filter> filters) {
this.filters = filters;
}
但是filterChainDefinitions是String类型的,需要转换(使用了ini转换方法,内部使用LinkedHashMap保存url和filter的映射关系,保证了顺序)

public void setFilterChainDefinitions(String definitions) {
Ini ini = new Ini();
ini.load(definitions);
//did they explicitly state a 'urls' section? Not necessary, but just in case:
Ini.Section section = ini.getSection(IniFilterChainResolverFactory.URLS);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(section)) {
//no urls section. Since this _is_ a urls chain definition property, just assume the
//default section contains only the definitions:
section = ini.getSection(Ini.DEFAULT_SECTION_NAME);
}
setFilterChainDefinitionMap(section);
}

这两步完成后,filters被注入
filterChianDefinitions也被注入,但是注入方法通过shiro自定义了ini方式,
该方式通过LinkedHashMap保存url规则和对应的权限(键值对),所以当写了相同的url规则,后者会覆盖前者(------现在对HashMap的存储规则遗忘了,需要再看一下)
问题一解答完成
问题二解答:
同一个url可以匹配不同的规则,但只执行首行
/usr/* =test1,test2
/usr/login.do=test3
url = /usr/login.do请求来了,不会执行test3,因为已经匹配了/usr/* =test1,test2
要解答该问题,需要知道每个url的FilterChain是如何获取的
接上分析:
有了filter和filterChainDefinitionMap的数据后,下面的工作是构造FilterChainManager
构造FilterChainManager
为什么到这一步呢?
查看spring委托机制,最终找到ShiroFilterFactoryBean的createInstance()方法(这个方法是shiro的filter构造机制的主线),由于ShiroFilterFactoryBean 实现了FactoryBean,spring就是通过这个接口的createInstance方法获取到filter实例的,下面是该方法在ShiroFilterFactoryBean中的实现:

protected AbstractShiroFilter createInstance() throws Exception {
log.debug("Creating Shiro Filter instance.");
SecurityManager securityManager = getSecurityManager();
if (securityManager == null) {
String msg = "SecurityManager property must be set.";
throw new BeanInitializationException(msg);
}
if (!(securityManager instanceof WebSecurityManager)) {
String msg = "The security manager does not implement the WebSecurityManager interface.";
throw new BeanInitializationException(msg);
}
FilterChainManager manager = createFilterChainManager();
PathMatchingFilterChainResolver chainResolver </span>= <span style="color: #0000ff">new</span><span style="color: #000000"> PathMatchingFilterChainResolver();</br>
chainResolver.setFilterChainManager(manager);</br>
</span><span style="color: #0000ff">return</span> <span style="color: #0000ff">new</span><span style="color: #000000"> SpringShiroFilter((WebSecurityManager) securityManager, chainResolver);</br>
}</span></pre>

从这里可以知道,首先获取filterChainManager,具体方法如下

protected FilterChainManager createFilterChainManager() {
DefaultFilterChainManager manager = new DefaultFilterChainManager();
Map<String, Filter> defaultFilters = manager.getFilters();
//apply global settings if necessary:
for (Filter filter : defaultFilters.values()) {
applyGlobalPropertiesIfNecessary(filter);
}
//Apply the acquired and/or configured filters:
Map<String, Filter> filters = getFilters();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(filters)) {
for (Map.Entry<String, Filter> entry : filters.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
Filter filter = entry.getValue();
applyGlobalPropertiesIfNecessary(filter);
if (filter instanceof Nameable) {
((Nameable) filter).setName(name);
}
//'init' argument is false, since Spring-configured filters should be initialized
//in Spring (i.e. 'init-method=blah') or implement InitializingBean:
manager.addFilter(name, filter, false);
}
}
//build up the chains:
Map<String, String> chains = getFilterChainDefinitionMap();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(chains)) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : chains.entrySet()) {
String url = entry.getKey();
String chainDefinition = entry.getValue();
manager.createChain(url, chainDefinition);
}
}
return manager;
}

分析后得知,首先在createFilterChainManager()方法中,创建一个DefaultFilterChainManager对象,而这个对象的构造函数在最后会将DefaultFilter中定义的shiro默认的filter映射加入到该对象中。如下代码就是DefaultFilter的定义。
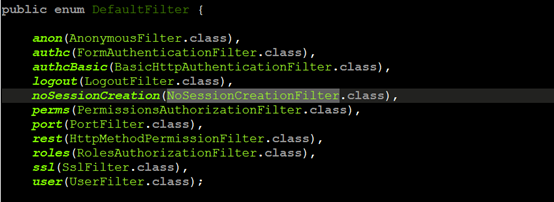
在DefaultFilterChainManager中还做了一件事就是url-filter的映射变成filterChain,这句代码就是执行这个任务(将我们在xml文件中定义的filterChainDefinitions变成filterChain)。
manager.createChain(url, chainDefinition);
作用是将权限分割:如
"authc, roles[admin,user], perms[file:edit]"
将会被分割为
{ "authc", "roles[admin,user]", "perms[file:edit]" }
具体的源代码如下:

public void createChain(String chainName, String chainDefinition) {
//。。。。。。。。
</span><span style="color: #008000">//</span><span style="color: #008000">parse the value by tokenizing it to get the resulting filter-specific config entries</br>
</span><span style="color: #008000">//</span></br>
<span style="color: #008000">//</span><span style="color: #008000">e.g. for a value of</br>
</span><span style="color: #008000">//</span></br>
<span style="color: #008000">//</span><span style="color: #008000"> "authc, roles[admin,user], perms[file:edit]"
</span><span style="color: #008000">//</span></br>
<span style="color: #008000">//</span><span style="color: #008000"> the resulting token array would equal
</span><span style="color: #008000">//</span></br>
<span style="color: #008000">//</span><span style="color: #008000"> { "authc", "roles[admin,user]", "perms[file:edit]" }
</span><span style="color: #008000">//</br>
String[] filterTokens = splitChainDefinition(chainDefinition);
for (String token : filterTokens) {
String[] nameConfigPair = toNameConfigPair(token);
addToChain(chainName, nameConfigPair[0], nameConfigPair[1]);
}
}

并且通过toNameConfigPair(token)将如:roles[admin,user]形式的变成roles,admin,user形式的分割
然后根据url规则 映射 权限和角色
可以发现,每次分割一个token,都会通过addToChain方法接受
分析public void addToChain(String chainName, String filterName, String chainSpecificFilterConfig)方法

public void addToChain(String chainName, String filterName, String chainSpecificFilterConfig) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(chainName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("chainName cannot be null or empty.");
}
Filter filter = getFilter(filterName);
if (filter == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("There is no filter with name '" + filterName +
"' to apply to chain [" + chainName + "] in the pool of available Filters. Ensure a " +
"filter with that name/path has first been registered with the addFilter method(s).");
}
applyChainConfig(chainName, filter, chainSpecificFilterConfig);
<span style="color: #ff0000">NamedFilterList chain </span></strong></span><strong><span style="color: #ff0000">=</span></strong><span style="color: #000000"><strong><span style="color: #ff0000"> ensureChain(chainName);
chain.add(filter);</span></strong></br>
}</span></pre>

分析applyChainConfig(chainName, filter, chainSpecificFilterConfig);

protected void applyChainConfig(String chainName, Filter filter, String chainSpecificFilterConfig) {
//………………………….
if (filter instanceof PathConfigProcessor) {
((PathConfigProcessor) filter).processPathConfig(chainName, chainSpecificFilterConfig);
} else {
if (StringUtils.hasText(chainSpecificFilterConfig)) {
//they specified a filter configuration, but the Filter doesn't implement PathConfigProcessor
//this is an erroneous config:
String msg = "chainSpecificFilterConfig was specified, but the underlying " +
"Filter instance is not an 'instanceof' " +
PathConfigProcessor.class.getName() + ". This is required if the filter is to accept " +
"chain-specific configuration.";
throw new ConfigurationException(msg);
}
}
}

由于我们自定义的filter都是PathMatchingFilter的子类,所以在applyChainConfig方法中完成的就是将url添加到filter的url表中。
在PathMatchingFilter中可以发现
protected Map<String, Object> appliedPaths = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
processPathConfig 方法的实现如下

public Filter processPathConfig(String path, String config) {
String[] values = null;
if (config != null) {
values = split(config);
}
this.appliedPaths.put(path, values);
return this;
}

基本上在spring-shiro.xml中定义filter的载入过程已经阅读完成,
1, 定义一个DefaultFilterChainManager对象
2, 首先加载默认的filter
3, 加载xml文件中定义的filter
4, 加载xml文件定义的url和filter映射关系
5, 将映射关系解析为以url为键,NamedFilterList为值的键值对。
6, 在解析的过程中,对每个url和对应的过滤条件,都会放到对应filter的appliedPaths中(在PathMatchingFilter中定义)。
现在FilterChainManager的对象已经创建完毕,并且每个filter也已经实例化完毕。
构造SpingShiroFilter
在创建SpringShiroFilter之前还要将刚才创建的FilterChainManager对象包装成一个PathMatchingFilterChainResolver对象(注释的意思是:不直接将FilterChainManager对象暴露给AbstractShiroFilter的实现者,在这里就是SpringShiroFilter。)
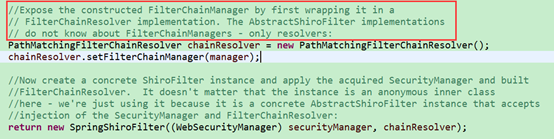
PathMatchingFilterChainResolver最重要的作用是:当请求url来的时候,他担任匹配工作(调用该类的getChain方法做匹配,暂时先不分析该方法,等知道在哪里调用该方法时候再分析。其实问题二此时已经可以解答,通过该方法就可以知道,某个url匹配到过滤链的第一个规则时就return了。)
上图最后一句话执行完成后,一个SpringShiroFilter创建完毕。
请求过滤过程分析(上)
下面分析当url请求到来的时候,shiro是如何完成过滤的。首先通过图片大致的了解一下。

现在分析AbstractShiroFilter的doFilterInternal()方法

protected void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, final FilterChain chain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
Throwable t = null;
try {
final ServletRequest request = prepareServletRequest(servletRequest, servletResponse, chain);
final ServletResponse response = prepareServletResponse(request, servletResponse, chain);
final Subject subject = createSubject(request, response);
subject.execute(new Callable() {
public Object call() throws Exception {
updateSessionLastAccessTime(request, response);
executeChain(request, response, chain);
return null;
}
});
} catch (ExecutionException ex) {
t = ex.getCause();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
t = throwable;
}
//…………
}

暂时不关心subject相关的创建等过程,只关心这行代码
executeChain(request, response, chain);
具体实现如下
protected void executeChain(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain origChain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
FilterChain chain = getExecutionChain(request, response, origChain);
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
再看getExecutionChain(request, response, origChain);具体实现如下:

protected FilterChain getExecutionChain(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain origChain) {
FilterChain chain = origChain;
FilterChainResolver resolver </span>=<span style="color: #000000"> getFilterChainResolver();</br>
</span><span style="color: #0000ff">if</span> (resolver == <span style="color: #0000ff">null</span><span style="color: #000000">) {</br>
log.debug(</span>"No FilterChainResolver configured. Returning original FilterChain."<span style="color: #000000">);</br>
</span><span style="color: #0000ff">return</span><span style="color: #000000"> origChain;</br>
}</br>
<strong><span style="color: #ff0000">FilterChain resolved </span></strong></span><strong><span style="color: #ff0000">= resolver.getChain(request, response, origChain);</br>
</span></strong><span style="color: #0000ff">if</span> (resolved != <span style="color: #0000ff">null</span><span style="color: #000000">) {</br>
log.trace(</span>"Resolved a configured FilterChain for the current request."<span style="color: #000000">);</br>
chain </span>=<span style="color: #000000"> resolved;</br>
} </span><span style="color: #0000ff">else</span><span style="color: #000000"> {</br>
log.trace(</span>"No FilterChain configured for the current request. Using the default."<span style="color: #000000">);</br>
}</br>
</span><span style="color: #0000ff">return</span><span style="color: #000000"> chain;
}</span></pre>

可以发现,这里用到了我们在创建SpringShiroFilter时传递的FilterChainResolver,至此,我们终于找到了getChain()方法在这里被调用了。其源码实现如下

public FilterChain getChain(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain originalChain) {
FilterChainManager filterChainManager = getFilterChainManager();
if (!filterChainManager.hasChains()) {
return null;
}
String requestURI </span>=<span style="color: #000000"> getPathWithinApplication(request);</br>
</span><span style="color: #008000">//</span><span style="color: #008000">the 'chain names' in this implementation are actually path patterns defined by the user. We just use them
</span><span style="color: #008000">//</span><span style="color: #008000">as the chain name for the FilterChainManager's requirements</span></br>
<span style="color: #0000ff">for</span><span style="color: #000000"> (String pathPattern : filterChainManager.getChainNames()) {</br></br>
</span><span style="color: #008000">//</span><span style="color: #008000"> If the path does match, then pass on to the subclass implementation for specific checks:</span></br>
<span style="color: #0000ff">if</span><span style="color: #000000"> (pathMatches(pathPattern, requestURI)) {</br>
</span><span style="color: #0000ff">if</span><span style="color: #000000"> (log.isTraceEnabled()) {</br>
log.trace(</span>"Matched path pattern [" + pathPattern + "] for requestURI [" + requestURI + "]. " +</br>
"Utilizing corresponding filter chain..."<span style="color: #000000">);</br>
}
</span><span style="color: #0000ff">return</span><span style="color: #000000"> filterChainManager.proxy(originalChain, pathPattern);</br>
}
}
</span><span style="color: #0000ff">return</span> <span style="color: #0000ff">null</span><span style="color: #000000">;</br>
}</span></pre>

从for循环可以看出,当匹配到第一个url规则,则return一个代表这个url规则的FilterChain给web容器执行。
问题二解答:每个url在匹配他的FilterChain时,当匹配到第一个URL规则时,就返回。
请求过滤过程分析(下)
FilterChain的实现类为org.apache.shiro.web.servlet.ProxiedFilterChain
从该类的doFilter方法可以知道,它会将Filter链的Filter的doFilter方法顺序执行一遍。下图展示了这一过程

现在只需要分析每个Filter的doFilter方法就行了。
先看一下shiro整个filter框架继承关系(图片来自第八章 拦截器机制——《跟我学Shiro》)

上面是它的继承关系:最终的doFilter方法在OncePerRequestFilter中实现,具体代码如下:

public final void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String alreadyFilteredAttributeName = getAlreadyFilteredAttributeName();
if ( request.getAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName) != null ) {
log.trace("Filter '{}' already executed. Proceeding without invoking this filter.", getName());
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
} else //noinspection deprecation
if (/* added in 1.2: */ !isEnabled(request, response) ||
/* retain backwards compatibility: */ shouldNotFilter(request) ) {
log.debug("Filter '{}' is not enabled for the current request. Proceeding without invoking this filter.",
getName());
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
// Do invoke this filter...
log.trace("Filter '{}' not yet executed. Executing now.", getName());
request.setAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName, Boolean.TRUE);
try {
doFilterInternal(request, response, filterChain);
} finally {
// Once the request has finished, we're done and we don't
// need to mark as 'already filtered' any more.
request.removeAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName);
}
}
}

可以发现该方法最终会调用doFilterInternal(request, response, filterChain);来完成具体的过滤操作,doFilterInternal方法在 SpringShiroFilter的直接父类AbstractShiroFilter的具体实现过程已经在上面分析过了:具体的就是shiro真正验证授权前的subject,session等初始化的工作,使得后面的过滤以及验证授权工作可以得到subject等然后正常工作。完成后调用其他shiro filter进行继续过滤
而除了shiroFilter之外,其余的filter都是AdviceFilter分支的子类。刚才看了AbstractShiroFilter的doFilterInternal方法,现在看一下AdviceFilter对该方法的实现:

public void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
Exception exception = null;
try {
boolean continueChain = preHandle(request, response);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Invoked preHandle method. Continuing chain?: [" + continueChain + "]");
}
if (continueChain) {
executeChain(request, response, chain);
}
postHandle(request, response);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Successfully invoked postHandle method");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
exception = e;
} finally {
cleanup(request, response, exception);
}
}

与AbstractShiroFilter的doFilterInternal方法不同的是,这里通过continueChain变量来判断到底后续的filter会不会被继续执行。而该变量的值由preHandle()函数决定。
基本上所有在系统中用到的filter都是继承PathMatchingFilter类的。看一下该类的preHandle()函数实现,可以发现,我们在xml文件中定义的url匹配,在这里面可以看到匹配原则了:

protected boolean preHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (this.appliedPaths == null || this.appliedPaths.isEmpty()) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("appliedPaths property is null or empty. This Filter will passthrough immediately.");
}
return true;
}
for (String path : this.appliedPaths.keySet()) {
// If the path does match, then pass on to the subclass implementation for specific checks
//(first match 'wins'):
if (pathsMatch(path, request)) {
log.trace("Current requestURI matches pattern '{}'. Determining filter chain execution...", path);
Object config = this.appliedPaths.get(path);
return isFilterChainContinued(request, response, path, config);
}
}
//no path matched, allow the request to go through:
return true;
}

继续调用isFilterChainContinued(request, response, path, config)--> onPreHandle(request, response, pathConfig);
分析onPreHandle(),PathMatchingFilter自己并没有实现,只是简单的返回true。所以当我们自定义filter的时候,要将具体的逻辑实现在该方法中,或者实现该类的子类AccessControlFilter(该类对onPreHandle()方法进行了更细致的划分,大部分一般会继承该类)
有兴趣的可以分析一下shiro自带的这些filter

Shiro的Filter机制详解---源码分析(转)的更多相关文章
- Shiro的Filter机制详解---源码分析
Shiro的Filter机制详解 首先从spring-shiro.xml的filter配置说起,先回答两个问题: 1, 为什么相同url规则,后面定义的会覆盖前面定义的(执行的时候只执行最后一个). ...
- ArrayList详解-源码分析
ArrayList详解-源码分析 1. 概述 在平时的开发中,用到最多的集合应该就是ArrayList了,本篇文章将结合源代码来学习ArrayList. ArrayList是基于数组实现的集合列表 支 ...
- LinkedList详解-源码分析
LinkedList详解-源码分析 LinkedList是List接口的第二个具体的实现类,第一个是ArrayList,前面一篇文章已经总结过了,下面我们来结合源码,学习LinkedList. 基于双 ...
- Java开源生鲜电商平台-盈利模式详解(源码可下载)
Java开源生鲜电商平台-盈利模式详解(源码可下载) 该平台提供一个联合买家与卖家的一个平台.(类似淘宝购物,这里指的是食材的购买.) 平台有以下的盈利模式:(类似的平台有美菜网,食材网等) 1. 订 ...
- quartz集群调度机制调研及源码分析---转载
quartz2.2.1集群调度机制调研及源码分析引言quartz集群架构调度器实例化调度过程触发器的获取触发trigger:Job执行过程:总结:附: 引言 quratz是目前最为成熟,使用最广泛的j ...
- 定时组件quartz系列<三>quartz调度机制调研及源码分析
quartz2.2.1集群调度机制调研及源码分析引言quartz集群架构调度器实例化调度过程触发器的获取触发trigger:Job执行过程:总结:附: 引言 quratz是目前最为成熟,使用最广泛的j ...
- (1)quartz集群调度机制调研及源码分析---转载
quartz2.2.1集群调度机制调研及源码分析 原文地址:http://demo.netfoucs.com/gklifg/article/details/27090179 引言quartz集群架构调 ...
- 微服务生态组件之Spring Cloud LoadBalancer详解和源码分析
Spring Cloud LoadBalancer 概述 Spring Cloud LoadBalancer目前Spring官方是放在spring-cloud-commons里,Spring Clou ...
- Go Revel - Filter(过滤器)源码分析
在 Go Revel - server.go 源码分析 http://www.cnblogs.com/hangxin1940/p/3265538.html 说到revel框架很多重要的东西都Filte ...
随机推荐
- Linux下安装zip解压功能
liunx服务器上默认没有安装zip命令,所以使用时需安装:apt-get install zip 或 yum install zip linux安装unzip命令:apt-get install ...
- 5.brackets 快捷键 有大用
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u012011360/article/details/41209223 ctrl+b 当选中一个文本时,会出现相同的文本,被高亮显示 按ctrl+b ...
- 洛谷P2251 质量检测
题目背景 无 题目描述 为了检测生产流水线上总共N件产品的质量,我们首先给每一件产品打一个分数A表示其品质,然后统计前M件产品中质量最差的产品的分值Q[m] = min{A1, A2, ... Am} ...
- Vectorized implementation
Vectorization Vectorization refers to a powerful way to speed up your algorithms. Numerical computin ...
- Gym 100952 H. Special Palindrome
http://codeforces.com/gym/100952/problem/H H. Special Palindrome time limit per test 1 second memory ...
- noi2019模拟测试赛(四十七)
noi2019模拟测试赛(四十七) T1与运算(and) 题意: 给你一个序列\(a_i\),定义\(f_i=a_1\&a_2\&\cdots\&a_i\),求这个序列的所 ...
- 【Django】序列化
Django中序列化主要应用于将数据库中检索的数据返回给客户端用户,特别是Ajax请求一般返回为Json格式. * 1.from django.core import serializers** fr ...
- 开始刷SGU
计划一天3题 请监督我 谢谢
- 安卓使用WebView下载文件,安卓实现软件升级功能
由于调用系统默认浏览器下载更新,造成用户体验非常不好,所以决定在webview中直接下载系统更新.然后直接安装. 由于要下载,所以必须用webview,联网权限这里不说了,直接写在manifafest ...
- 深度学习 Deep LearningUFLDL 最新Tutorial 学习笔记 2:Logistic Regression
1 Logistic Regression 简述 Linear Regression 研究连续量的变化情况,而Logistic Regression则研究离散量的情况.简单地说就是对于推断一个训练样本 ...
