SoC的Testbench中的简易bus_monitor(加入print函数)
SoC的Testbench中的简易bus_monitor(加入print函数)
主要思路 向固定地址写信息
- 使用工具链将C写的print/printf函数编译成hex文件
- 在testbench中创建bus_monitor来监控总线上信息
- 当监控print对总线上的固定地址操作时将数据存储到预先定义的memory中
- 使用verilog的write处理memory中的ASCII码,打印到屏幕上
testbench下的bus_monitor
module bus_monitor();
`define DIGITAL_TOP testbench.u0_riscv_platform_demo.u0_digital_top
`define BUSMON `DIGITAL_TOP.u0_Insight_E21_ECoreIPSubsystem
`define LED_DRIVER_BASE (32'h4FF00000) //4FF0_0000
`define LED_RETURN_CHAR 16'h0a
`define LED_FINISH 16'h00
//RISCV
`define RISCV_START 16'h80 // "Test start by RISCV";
`define RISCV_FINISH 16'h81 // "Test complete by RISCV";
`define RISCV_FAIL 16'h82 // "Msg code FAIL by RISCV";
`define RISCV_PASS 16'h83 // "Msg code PASS by RISCV";
//open Memory For CPU Print Messeage storge
parameter ADDR_DEPTH =15;
parameter WORD_DEPTH = (1<<ADDR_DEPTH) ; // Memory depth in K,16bit
reg [7:0] memory [0:(WORD_DEPTH - 1)]; // Memory register array
reg [7:0] led_data;
reg led_valid;
wire cclk = `DIGITAL_TOP.cpu_clock;
wire [7:0] ext_mem_din = `BUSMON.sys_port_ahb_0_hwdata[7:0];
always @(posedge cclk) begin
led_valid <= (`BUSMON.sys_port_ahb_0_haddr == `LED_DRIVER_BASE)
&& `BUSMON.sys_port_ahb_0_hwrite
&& `BUSMON.sys_port_ahb_0_hsel;
end
// wire [7:0] ext_mem_din = `BUSMON.E31.auto_rational_xing_sourcelzy_out_a_bits1_data[31:0];
// always @(posedge cclk) begin
// led_valid <= (`BUSMON.E31.auto_rational_xing_sourcelzy_out_a_bits0_address[31:0] == `LED_DRIVER_BASE)
// && `BUSMON.E31.auto_rational_xing_sourcelzy_out_a_valid;
// end
integer i;
integer m;
initial begin
i=0;
m=0;
end
always @ (negedge cclk)
begin
if (led_valid)
begin
led_data = ext_mem_din[7:0];
if(ext_mem_din[7]== 1'b1)
print_code(ext_mem_din[7:0]);
else
case(ext_mem_din[7:0])
`LED_RETURN_CHAR: begin // Nul character check by monitor
memory[i] = ext_mem_din[7:0];
i=i+1;
for(m=0;m<i;m=m+1) begin
$write ("%c",memory[m]);
end
i=0;
end
`LED_FINISH: begin //$finish test
$display ("Terminate detect by bus_monitor - mcu terminating simulation\n");
#100 $finish;
end
default: begin
memory[i] = ext_mem_din[7:0];
i=i+1;
end
endcase
end
end
task print_code;
input [7:0] code;
reg [8*60:1] message;
begin
case (code)
// RISCV Signal
`RISCV_START : message = "Test start by RISCV";
`RISCV_FINISH : message = "Test complete by RISCV";
`RISCV_FAIL : message = "Msg code FAIL by RISCV";
`RISCV_PASS : message = "Msg code PASS by RISCV";
default : message = "Unrecognized message code";
endcase
$display ("print_code message: %0s (Msg code %h)", message, code);
end
endtask
endmodule
print/printf函数(C代码)
注意:向一个固定的总线地址写信息
sim_show.h
#define LED_REG_BASE 0x4FF00000
// Global Signal
#define RISCV_QUIT 0x00 // "NULL Char detected by led_model";
// RISCV Signal
#define RISCV_START 0x80 // "Test start by RISCV";
#define RISCV_FINISH 0x81 // "Test complete by RISCV";
#define RISCV_FAIL 0x82 // "Msg code FAIL by RISCV";
#define RISCV_PASS 0x83 // "Msg code PASS by RISCV";
void sim_start();
void sim_pass();
void sim_fail();
void sim_finish();
void print_led(char string_val []);
void printf_led(const char* fmt, ...);
sim_show.c
可移植的print底层函数
#include <stdint.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stddef.h> // headers for the print functions
#include <stdarg.h> // support variable length arguments (printf)
#include <string.h>
#include "sim_show.h"
void sim_start() {
*(volatile char *)LED_REG_BASE = RISCV_START;
}
void sim_pass() {
*(volatile char *)LED_REG_BASE = RISCV_PASS;
*(volatile char *)LED_REG_BASE = RISCV_QUIT;
}
void sim_fail() {
*(volatile char *)LED_REG_BASE = RISCV_FAIL;
*(volatile char *)LED_REG_BASE = RISCV_QUIT;
}
void sim_finish() {
*(volatile char *)LED_REG_BASE = RISCV_FINISH;
*(volatile char *)LED_REG_BASE = RISCV_QUIT;
}
// print_led - print any size constant array of characters to the LED driver
// - faster than printf_led but less robust
void print_led(char string_val []) {
int i;
for(i=0;string_val[i] != '\0';i++) {
*(volatile char *)LED_REG_BASE = string_val[i];
}
} // void print_led()
static void sprintf_putch(int ch, void** data)
{
char** pstr = (char**)data;
**pstr = ch;
(*pstr)++;
}
int putchar(int ch)
{
*(volatile char *)LED_REG_BASE = ch;
}
static unsigned long getuint(va_list *ap, int lflag)
{
if (lflag)
return va_arg(*ap, unsigned long);
else
return va_arg(*ap, unsigned int);
}
static long getint(va_list *ap, int lflag)
{
if (lflag)
return va_arg(*ap, long);
else
return va_arg(*ap, int);
}
static inline void printnum(void (*putch)(int, void**), void **putdat,
uint64_t num, unsigned base, int width, int padc)
{
unsigned digs[sizeof(num)*8];
int pos = 0;
while (1)
{
digs[pos++] = num % base;
if (num < base)
break;
num /= base;
}
while (width-- > pos)
putch(padc, putdat);
while (pos-- > 0)
putch(digs[pos] + (digs[pos] >= 10 ? 'a' - 10 : '0'), putdat);
}
static inline void print_double(void (*putch)(int, void**), void **putdat,
double num, int width, int prec)
{
union {
double d;
uint64_t u;
} u;
u.d = num;
if (u.u & (1ULL << 63)) {
putch('-', putdat);
u.u &= ~(1ULL << 63);
}
for (int i = 0; i < prec; i++)
u.d *= 10;
char buf[32], *pbuf = buf;
printnum(sprintf_putch, (void**)&pbuf, (uint64_t)u.d, 10, 0, 0);
if (prec > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < prec; i++) {
pbuf[-i] = pbuf[-i-1];
}
pbuf[-prec] = '.';
pbuf++;
}
for (char* p = buf; p < pbuf; p++)
putch(*p, putdat);
}
static void vprintfmt(void (*putch)(int, void**), void **putdat, const char *fmt, va_list ap)
{
register const char* p;
const char* last_fmt;
register int ch, err;
unsigned long num;
int base, lflag, width, precision, altflag;
char padc;
while (1) {
while ((ch = *(unsigned char *) fmt) != '%') {
if (ch == '\0')
return;
fmt++;
putch(ch, putdat);
}
fmt++;
// Process a %-escape sequence
last_fmt = fmt;
padc = ' ';
width = -1;
precision = -1;
lflag = 0;
altflag = 0;
reswitch:
switch (ch = *(unsigned char *) fmt++) {
// flag to pad on the right
case '-':
padc = '-';
goto reswitch;
// flag to pad with 0's instead of spaces
case '0':
padc = '0';
goto reswitch;
// width field
case '1':
case '2':
case '3':
case '4':
case '5':
case '6':
case '7':
case '8':
case '9':
for (precision = 0; ; ++fmt) {
precision = precision * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = *fmt;
if (ch < '0' || ch > '9')
break;
}
goto process_precision;
case '*':
precision = va_arg(ap, int);
goto process_precision;
case '.':
if (width < 0)
width = 0;
goto reswitch;
case '#':
altflag = 1;
goto reswitch;
process_precision:
if (width < 0)
width = precision, precision = -1;
goto reswitch;
// long flag
case 'l':
if (lflag)
goto bad;
goto reswitch;
// character
case 'c':
putch(va_arg(ap, int), putdat);
break;
// double
case 'f':
print_double(putch, putdat, va_arg(ap, double), width, precision);
break;
// string
case 's':
if ((p = va_arg(ap, char *)) == NULL)
p = "(null)";
if (width > 0 && padc != '-')
for (width -= strnlen(p, precision); width > 0; width--)
putch(padc, putdat);
for (; (ch = *p) != '\0' && (precision < 0 || --precision >= 0); width--) {
putch(ch, putdat);
p++;
}
for (; width > 0; width--)
putch(' ', putdat);
break;
// (signed) decimal
case 'd':
num = getint(&ap, lflag);
if ((long) num < 0) {
putch('-', putdat);
num = -(long) num;
}
base = 10;
goto signed_number;
// unsigned decimal
case 'u':
base = 10;
goto unsigned_number;
// (unsigned) octal
case 'o':
// should do something with padding so it's always 3 octits
base = 8;
goto unsigned_number;
// pointer
case 'p':
lflag = 1;
putch('0', putdat);
putch('x', putdat);
/* fall through to 'x' */
// (unsigned) hexadecimal
case 'x':
base = 16;
unsigned_number:
num = getuint(&ap, lflag);
signed_number:
printnum(putch, putdat, num, base, width, padc);
break;
// escaped '%' character
case '%':
putch(ch, putdat);
break;
// unrecognized escape sequence - just print it literally
default:
bad:
putch('%', putdat);
fmt = last_fmt;
break;
}
}
}
void printf_led(const char* fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
va_start(ap, fmt);
vprintfmt((void *)putchar, 0, fmt, ap);
va_end(ap);
}
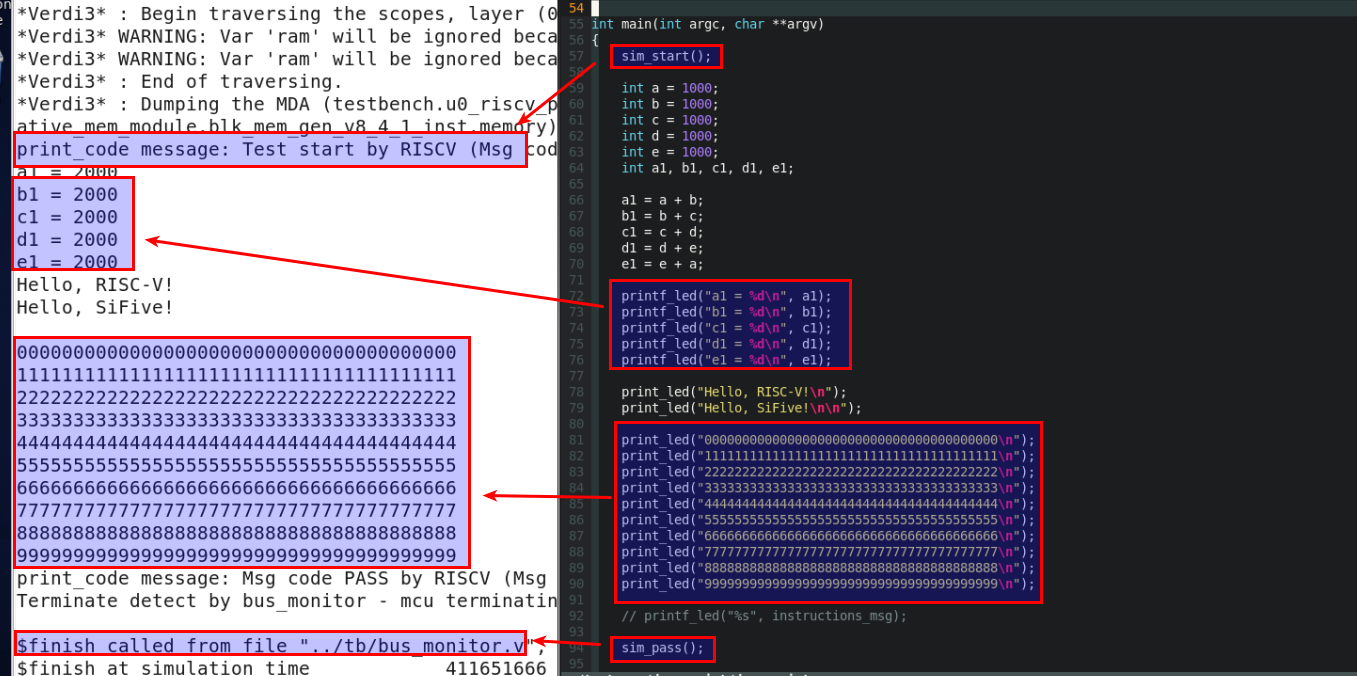
仿真结果显示
附:RISC-V 工具链
[1].Prebuilt RISC‑V GCC Toolchain
[2].elf2hex
SoC的Testbench中的简易bus_monitor(加入print函数)的更多相关文章
- python中print()函数的“,”与java中System.out.print()函数中的“+”
python中的print()函数和java中的System.out.print()函数都有着打印字符串的功能. python中: print("hello,world!") 输出 ...
- Python中print函数输出时的左右对齐问题
为了将print函数输出的内容对齐,笔者在http://www.jb51.net/article/55768.htm中找到了左右对齐的方法.整理如下: 一.数值类型(int.float) # %d. ...
- CentOS 6中MATLAB print函数“所见非所得”bug的解决方案
0 系统配置+软件版本 主机:Dell optiplex 390 MT (i5) 系统+软件:CentOS 6.5 x64, Matlab R2012, R2013 系统+软件:CentOS 6.7 ...
- MATLAB中白噪声的WGN和AWGN函数的使用
MATLAB中白噪声的WGN和AWGN函数的使用如下: MATLAB中产生高斯白噪声非常方便,可以直接应用两个函数,一个是WGN,另一个是AWGN.WGN用于产生高斯白噪声,AWGN则用于在某一 信号 ...
- FastReport调用Delphi中的人民币大写转换自定义函数
FastReport调用Delphi中的人民币大写转换自定义函数 FastReport调用Delphi中的人民币大写转换自定义函数 function TJzpzEdit1.MoneyCn(mmje ...
- Matlab中如何将(自定义)函数作为参数传递给另一个函数
假如我们编写了一个积分通用程序,想使它更具有通用性,那么可以把被积函数也作为一个参数.在c/c++中,可以使用函数指针来实现上边的功能,在matlab中如何实现呢?使用函数句柄--这时类似于函数指针的 ...
- 【SAP BusinessObjects】WEBI中的动态求和,累加函数的使用
在WEBI中,提供了这样一个函数: RunningSum([字段名]) 其作用是,将[字段名]这一列进行累加动态求和 对于需要进行计算累加值的列就不必写复杂的SQL,直接使用此函数即可解决.
- php中base64_decode与base64_encode加密解密函数
php中base64_decode与base64_encode加密解密函数,实例分析了base64加密解密函数的具体用法,具有一定的实用价值,需要的朋友可以参考下 本文实例讲述了php中base64_ ...
- Linux 多线程应用中如何编写安全的信号处理函数
http://blog.163.com/he_junwei/blog/static/1979376462014021105242552/ http://www.ibm.com/developerwor ...
随机推荐
- VS书签的应用
为某一行添加书签,方便快速定位. 添加书签, 查找上一个书签, 查找下一个书签, 清空所有书签. 有意思.
- 详解Android插件化开发-资源访问
动态加载技术(也叫插件化技术),当项目越来越庞大的时候,我们通过插件化开发不仅可以减轻应用的内存和CPU占用,还可以实现热插拔,即在不发布新版本的情况下更新某些模块. 通常我们把安卓资源文件制 ...
- geotif格式的波段描述信息探究
作者:朱金灿 来源:http://blog.csdn.net/clever101 有时打开一些geotif文件,可以看到它的波段描述,但是它究竟存储在文件的什么位置呢?今天研究了一下,大致搞清了这个问 ...
- 基于Linux平台Softimage XSI 演示
2009年底上映的<阿凡达>是电影特效的巅峰之作,就在本月初上映的变形金刚3每次观看之后看得眼花缭乱总能让我热血沸腾,要是自己能做出那样的特效该多好,Linux下研究Maya已经有一段日 ...
- 浏览器下管理Linux系统--记webmin的使用
本文介绍一款浏览器方式来管理linux的一种方式,这款软件就叫webmin,Webmin 让您能够在远程使用支持 HTTPS (SSL 上的 HTTP)协议的 Web 浏览器通过 Web 界面管理您的 ...
- Autoencoders and Sparsity(一)
An autoencoder neural network is an unsupervised learning algorithm that applies backpropagation, se ...
- Kinect 开发 —— 骨骼数据与彩色影像和深度影像的对齐
在显示彩色影像和深度影像时最好使用WriteableBitmap对象: 要想将骨骼数据影像和深度影像,或者彩色影像叠加到一起,首先要确定深度影像的分辨率和大小,为了方便,这里将深度影像数据和彩色影像数 ...
- vim--学习之emmet插件前端开发
Emmet 在vim的使用: 1.嵌套 <ctr+y>+,(ctr+y+逗号三者的组合键,ctr+y一起按在按逗号)相当于Ememet中的Tab键. 2.内容的包围: 写好内容,退出编辑模 ...
- HTML 页面内容禁止选中
写一个小笔记,怎么禁止HTML页面不被选中,复制. CSS: *{ moz-user-select: -moz-none; -moz-user-select: none; -o-user-select ...
- mycat 不得不说的缘分(转)
,尾声,左兄与任正非.leader-us与马云 新成立的公司里面,有个左兄,很传奇,大一在大学入伍,然后复员专业,来上海学IT,年纪轻轻,睡在地铁站,苦心专研数据库.系统.中间件,现在已经成为了业界大 ...