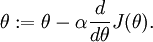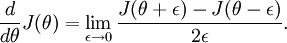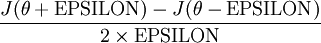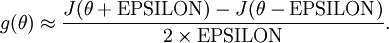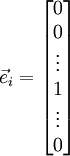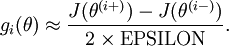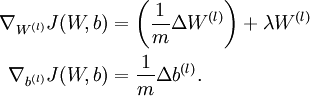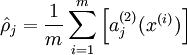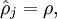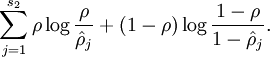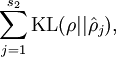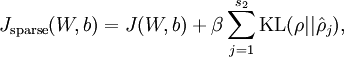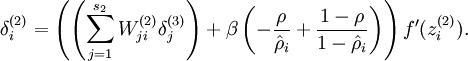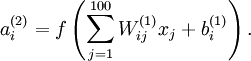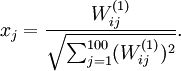Sparse Autoencoder(二)
Gradient checking and advanced optimization
In this section, we describe a method for numerically checking the derivatives computed by your code to make sure that your implementation is correct. Carrying out the derivative checking procedure described here will significantly increase your confidence in the correctness of your code.
Suppose we want to minimize
as a function of
. For this example, suppose
, so that
. In this 1-dimensional case, one iteration of gradient descent is given by
Suppose also that we have implemented some function
that purportedly computes
, so that we implement gradient descent using the update
.
Recall the mathematical definition of the derivative as
Thus, at any specific value of
, we can numerically approximate the derivative as follows:
Thus, given a function
that is supposedly computing
, we can now numerically verify its correctness by checking that
The degree to which these two values should approximate each other will depend on the details of
. But assuming
, you'll usually find that the left- and right-hand sides of the above will agree to at least 4 significant digits (and often many more).
Suppose we have a function
that purportedly computes
; we'd like to check if
is outputting correct derivative values. Let
, where
is the
-th basis vector (a vector of the same dimension as
, with a "1" in the
-th position and "0"s everywhere else). So,
is the same as
, except its
-th element has been incremented by EPSILON. Similarly, let
be the corresponding vector with the
-th element decreased by EPSILON. We can now numerically verify
's correctness by checking, for each
, that:
参数为向量,为了验证每一维的计算正确性,可以控制其他变量
When implementing backpropagation to train a neural network, in a correct implementation we will have that
This result shows that the final block of psuedo-code in Backpropagation Algorithm is indeed implementing gradient descent. To make sure your implementation of gradient descent is correct, it is usually very helpful to use the method described above to numerically compute the derivatives of
, and thereby verify that your computations of
and
are indeed giving the derivatives you want.
Autoencoders and Sparsity
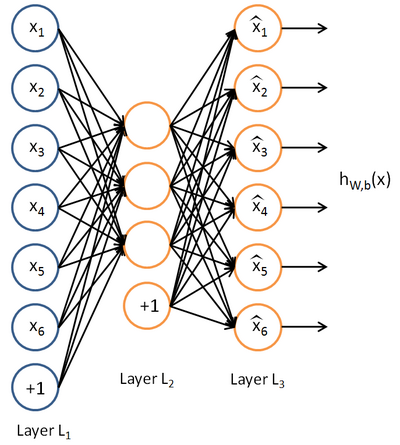
Anautoencoder neural network is an unsupervised learning algorithm that applies backpropagation, setting the target values to be equal to the inputs. I.e., it uses
.
Here is an autoencoder:
we will write
to denote the activation of this hidden unit when the network is given a specific input
. Further, let
be the average activation of hidden unit
(averaged over the training set). We would like to (approximately) enforce the constraint
where
is a sparsity parameter, typically a small value close to zero (say
). In other words, we would like the average activation of each hidden neuron
to be close to 0.05 (say). To satisfy this constraint, the hidden unit's activations must mostly be near 0.
To achieve this, we will add an extra penalty term to our optimization objective that penalizes
deviating significantly from
. Many choices of the penalty term will give reasonable results. We will choose the following:
Here,
is the number of neurons in the hidden layer, and the index
is summing over the hidden units in our network. If you are familiar with the concept of KL divergence, this penalty term is based on it, and can also be written
Our overall cost function is now
where
is as defined previously, and
controls the weight of the sparsity penalty term. The term
(implicitly) depends on
also, because it is the average activation of hidden unit
, and the activation of a hidden unit depends on the parameters
.
Visualizing a Trained Autoencoder
Consider the case of training an autoencoder on
images, so that
. Each hidden unit
computes a function of the input:
We will visualize the function computed by hidden unit
---which depends on the parameters
(ignoring the bias term for now)---using a 2D image. In particular, we think of
as some non-linear feature of the input
If we suppose that the input is norm constrained by
, then one can show (try doing this yourself) that the input which maximally activates hidden unit
is given by setting pixel
(for all 100 pixels,
) to
By displaying the image formed by these pixel intensity values, we can begin to understand what feature hidden unit
is looking for.
对一幅图像进行Autoencoder ,前面的隐藏结点一般捕获的是边缘等初级特征,越靠后隐藏结点捕获的特征语义更深。
Sparse Autoencoder(二)的更多相关文章
- DL二(稀疏自编码器 Sparse Autoencoder)
稀疏自编码器 Sparse Autoencoder 一神经网络(Neural Networks) 1.1 基本术语 神经网络(neural networks) 激活函数(activation func ...
- Deep Learning 1_深度学习UFLDL教程:Sparse Autoencoder练习(斯坦福大学深度学习教程)
1前言 本人写技术博客的目的,其实是感觉好多东西,很长一段时间不动就会忘记了,为了加深学习记忆以及方便以后可能忘记后能很快回忆起自己曾经学过的东西. 首先,在网上找了一些资料,看见介绍说UFLDL很不 ...
- (六)6.5 Neurons Networks Implements of Sparse Autoencoder
一大波matlab代码正在靠近.- -! sparse autoencoder的一个实例练习,这个例子所要实现的内容大概如下:从给定的很多张自然图片中截取出大小为8*8的小patches图片共1000 ...
- UFLDL实验报告2:Sparse Autoencoder
Sparse Autoencoder稀疏自编码器实验报告 1.Sparse Autoencoder稀疏自编码器实验描述 自编码神经网络是一种无监督学习算法,它使用了反向传播算法,并让目标值等于输入值, ...
- 七、Sparse Autoencoder介绍
目前为止,我们已经讨论了神经网络在有监督学习中的应用.在有监督学习中,训练样本是有类别标签的.现在假设我们只有一个没有带类别标签的训练样本集合 ,其中 .自编码神经网络是一种无监督学习算法,它使用 ...
- CS229 6.5 Neurons Networks Implements of Sparse Autoencoder
sparse autoencoder的一个实例练习,这个例子所要实现的内容大概如下:从给定的很多张自然图片中截取出大小为8*8的小patches图片共10000张,现在需要用sparse autoen ...
- 【DeepLearning】Exercise:Sparse Autoencoder
Exercise:Sparse Autoencoder 习题的链接:Exercise:Sparse Autoencoder 注意点: 1.训练样本像素值需要归一化. 因为输出层的激活函数是logist ...
- Sparse AutoEncoder简介
1. AutoEncoder AutoEncoder是一种特殊的三层神经网络, 其输出等于输入:\(y^{(i)}=x^{(i)}\), 如下图所示: 亦即AutoEncoder想学到的函数为\(f_ ...
- Exercise:Sparse Autoencoder
斯坦福deep learning教程中的自稀疏编码器的练习,主要是参考了 http://www.cnblogs.com/tornadomeet/archive/2013/03/20/2970724 ...
随机推荐
- UI Framework-1: Aura Focus and Activation
Focus and Activation Focus and Activation are closely related. Definitions Focused window - this i ...
- Chromium Graphics: Graphics and Skia
Graphics and Skia Chrome uses Skia for nearly all graphics operations, including text rendering. GDI ...
- bzoj 2287: 【POJ Challenge】消失之物 动态规划
Code: #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<cstring> ...
- element-ui table 行内编辑
EditRow.ts vue+element-ui+slot-scope原生实现可编辑表格 interface NoParamConstructor<T> { new(): T; } ex ...
- vue+element-ui的简洁导入导出功能
1.前段后台管理系统中数据展示一般都是用表格,表格会涉及到导入和导出;原生js导出excel2.导入是利用element-ui的Upload 上传组件; <el-upload class=&qu ...
- python虚拟环境virtualenv、virtualenv下运行IDLE、powershell 运行脚本由执行策略引起的问题
一.为什么要创建虚拟环境: 应为在开发中会有同时对一个包不同版本的需求,创建多个开发环境就能解决这个问题.或许也会有对python不同版本的需求,这就需要使用程序来管理不同的版本,virtualenv ...
- P4287 [SHOI2011]双倍回文(回文树)
题目描述 记字符串 w 的倒置为 w^R^ .例如 (abcd)^R^=dcba , (abba)^R^=abba . 对字符串x,如果 x 满足 x^R^=x ,则称之为回文:例如abba是一个回文 ...
- 华为:一张图看懂 HBase
来自为知笔记(Wiz)
- FZOJ 2176 easy problem ( 树链剖分 )
pid=2176" target="_blank">题目链接~~> 做题感悟:感觉做多了树链剖分的题目,有很多是树链剖分 + 想法.. 解题思路: 这题非常明 ...
- HDOJ 5098 Smart Software Installer 拓扑排序
拓扑排序: 两个队列,一个放不须要重新启动入度为0的,一个放须要重新启动入度为0的....从不须要重新启动的队列開始,每弹出一个数就更新下入度,遇到入读为0的就增加到对应队列里,当队列空时,记录重新启 ...