6LoWPAN - Transmission of IPv6 Packets over IEEE 802.15.4 Networks
6LoWPAN covered topics include the following:
- Frame format for transmission of IPv6 packets
- Method of forming IPv6 link-local addresses
- Statelessly autoconfigured addresses on IEEE 802.15.4 networks
- Simple header compression scheme using shared context
- Provisions for packet delivery in IEEE 802.15.4 meshes
IEEE 802.15.4 Mode for IP
- IEEE 802.15.4 defines four types of frames: beacon frames, MAC command frames, acknowledgement frames, and data frames.
- IPv6 packets MUST be carried on data frames.
- IEEE 802.15.4 networks can either be nonbeacon-enabled or beaconenabled.
- 6LoWPAN does not require that IEEE networks run in beacon-enabled mode.
- Beacons are still useful for link-layer device discovery to aid in association and disassociation events.
- 6LoWPAN requires both source and destination addresses be included in the IEEE 802.15.4 frame header.
- The source or destination PAN ID fields may also be included.
Addressing Modes
- IEEE 802.15.4 defines several addressing modes: IEEE 64-bit extended addresses or 16-bit short addresses unique within the PAN.
- 6LoWPAN supports both 64-bit extended addresses, and 16-bit short addresses.
- 6LoWPAN assumes that a PAN maps to a specific IPv6 link.
- Multicast is not supported natively in IEEE 802.15.4.
- IPv6 level multicast packets MUST be carried as link-layer broadcast frames in IEEE 802.15.4 networks.
- Broadcast frames are only heeded by devices within the specific PAN of the link:
- A destination PAN identifier is included in the frame, and it MUST match the PAN ID of the link in question.
- A short destination address is included in the frame, and it MUST match the broadcast address (0xffff).
- Hosts learn IPv6 prefixes via router advertisements.
Maximum Transmission Unit
- IEEE 802.15.4 frame sizes:
- Maximum physical layer packet size of 127 octets (aMaxPHYPacketSize) –
- Maximum frame overhead of 25 (aMaxFrameOverhead) –
- Link-layer security overhead (21 octets in AES-CCM-128, 9 and 13 in AES-CCM-32 and AES-CCM-64)
- leaves only 81 octets for IPv6 -
- IPv6 header of 40 octets
- leaves only 41 octets for upper-layer protocols, like UDP
- UDP uses 8 octets in the header
- leaves only 33 octets for application data.
- fragmentation and reassembly layer will use even more octets.
- Fragmention and reassembly adaptation layer must be provided at the layer below IP.
LoWPAN Adaptation Layer and Frame Format
- All LoWPAN encapsulated datagrams transported over IEEE 802.15.4 are prefixed by an encapsulation header stack.
- LoWPAN header sequence is mesh (L2) addressing, hop-by-hop options (including L2 broadcast/multicast), fragmentation, and finally payload.


- When more than one LoWPAN header is used in the same packet, they MUST appear in the following order:
- Mesh Addressing Header
- Broadcast Header
- Fragmentation Header
Dispatch Type and Header

 、
、

Mesh Addressing Type and Header


Fragmentation Type and Header
- All link fragments for a datagram except the last one MUST be multiples of eight bytes in length.




Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
- All 802.15.4 devices have an IEEE EUI-64 address, but 16-bit short addresses are also possible.
- Interface Identifier is formed from the EUI-64 according to the "IPv6 over Ethernet" specification.
- When 16-bit short addressing is used, a "pseudo 48-bit address" is formed as follows:
- First, the left-most 32 bits are formed by concatenating 16 zero bits to the 16-bit PAN ID (or 16 zero bits) - 16_bit_PAN:16_zero_bits.
- Then, these 32 bits are concatenated with the 16-bit short address - 32_bits_as_specified_previously:16_bit_short_address.
- A different MAC address set manually or by software MAY be used to derive the Interface Identifier.
IPv6 Link Local Address

Unicast Address Mapping
- The Source/Target Link-layer Address option has the following forms when the link layer is IEEE 802.15.4 and the addresses are EUI-64 or 16-bit short addresses, respectively.


Multicast Address Mapping
- An IPv6 packet with a multicast destination address (DST), consisting of the sixteen octets DST[1] through DST[16], is transmitted to the following 802.15.4 16-bit multicast address:

Header Compression
Encoding of IPv6 Header Fields
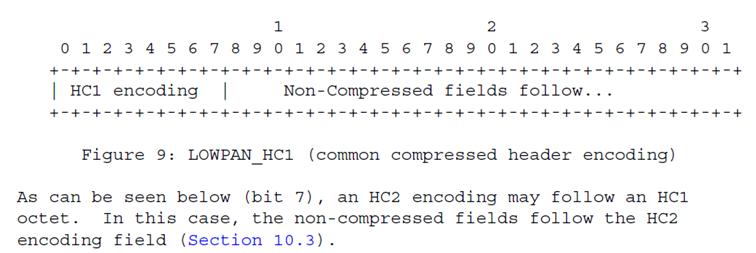
- A packet is compressible via the LOWPAN_HC1 format by using a Dispatch value of LOWPAN_HC1 followed by a LOWPAN_HC1 header "HC1 encoding" field (8 bits) to encode the different combinations as shown below.
- This header may be preceded by a fragmentation header, which may be preceded by a mesh header.\



Encoding of UDP Header Fields


6LoWPAN - Transmission of IPv6 Packets over IEEE 802.15.4 Networks的更多相关文章
- 蓝牙(Bluetooth) IEEE 802.15.1 协议学习
catalogue . 蓝牙概念 . 配对和连接 . 机密安全性 . 蓝牙协议分类 . 蓝牙协议栈 1. 蓝牙概念 蓝牙(Bluetooth)是一种无线技术标准,可实现固定设备.移动设备和楼宇个人域网 ...
- IEEE 802.15介绍
1. 无线通信 无线通信主要是利用无线电(Radio)射频(RF)技术的通信方式,无线网络是采用无线通信技术实现的网络无线网络可为两种: 近距离无线网络和远距离无线网络 近距离无线网络主要可分为如下两 ...
- IEEE 802.15.4协议学习之物理层
在详细讲述IEEE 802.15.4协议之前,谈谈自己这两个星期看协议过程中的一点心得,或者是收获吧. 看协议文档,一定要看有书签的,边看边在旁边做些备注,以便于后期整理.对于协议层次相关的,最好在纸 ...
- IEEE 802.15.4协议学习之MAC层
MAC负责建立于网络的同步,支持关联和取消关联.MAC层的安全以及控制物理信道访问机制.信道访问机制主要有以下几种: 1. 有序的物理无线信道访问机制 2. 协调器启动和维 ...
- 计算机网络六:无线局域网、IEEE 802.11、WIFI和蓝牙
无线局域网.IEEE 802.11.WIFI和蓝牙 ㈠无线局域网 1.定义 无线局域网络(Wireless Local Area Networks),简称WLAN.它是相当便利的数据传输系 ...
- XBee 802.15.4/Digimesh FAQs:如何为2.4G模块选择合适的信道
XBee 802.15.4模块和XBee Digimesh模块在硬件上完全相同,只是出厂带有不同固件,如果测试需要,这两个固件可以都可以互换烧入模块中. 如何为2.4G模块选择合适的信道 IEEE 8 ...
- IEEE 802.3 Ethernet
Introduction Ethernet 是过去30年以来最为成功的局域网(local area networking)技术. 1. First widely used LAN technology ...
- IEEE 802.11p (WAVE,Wireless Access in the Vehicular Environment)
IEEE 802.11p(又称WAVE,Wireless Access in the Vehicular Environment)是一个由IEEE 802.11标准扩充的通讯协定.这个通讯协定主要用在 ...
- IEEE 802.11 标准列表
IEEE 802.11 标准列表 IEEE 802.11,1997年,原始标准(2Mbit/s,播在2.4GHz). IEEE 802.11a,1999年,物理层补充(54Mbit/s,播在5GHz) ...
随机推荐
- 2013腾讯编程马拉松初赛第〇场(HDU 4503) 湫湫系列故事——植树节
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4503 题目: 已知湫湫的班里共有n个孩子,每个孩子有Bi个朋友(i从1到n),且朋友关系是相互的,如果a小朋友和 ...
- 【AtCoder Beginner Contest 074 D】Restoring Road Network
[链接]h在这里写链接 [题意] 给你任意两点之间的最短路. 让你求出原图. 或者输出原图不存在. 输出原图的边长总和的最小值. [题解] floyd算法. 先在原有的矩阵上. 做一遍floyd. 如 ...
- 关于 /etc/zabbix/zabbix_agentd.conf 文件 Hostname 文件的说明
前提 (1) /etc/hosts 文件如下 [root@testdb ~]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain loc ...
- [arm]虚拟机,2440开发板,主机三者互通
想实现3着互通先必须保证三者的网段是相同的: 首先查看电脑主机的IP: 然后再看看虚拟机的IP: 惊喜的发现,他们在一个网段上---那就不用改了-- 再去看看开发板上的IP: 这里注意,输入命令时,是 ...
- LA 5902 - Movie collection 树状数组(Fenwick树)
看题传送门 题目大意:XXX喜欢看电影,他有好多好多的影碟,每个影碟都有个独立的编号.开始是从下往上影碟的顺序是n~1,他每次拿出影碟的时候,你需要输出压在该影碟上的有几个.(拿出后其他影碟顺序不变) ...
- 【u252】泽泽在巴西
Time Limit: 1 second Memory Limit: 128 MB [问题描述] 泽泽帮助了英国某街道尽量减少酸雨的伤害,街道办主任非常感激他,就把他领到一扇门前,告诉他这扇门能通往好 ...
- 切换根控制器UIApplication 主屏幕UIScreen 读取文件资源NSBundle
//主屏幕设为webView CGRect frame = [UIScreen mainScreen].applicationFrame; UIWebView *webView = [[[UIWebV ...
- ZOJ 1494 Climbing Worm 数学水题
http://acm.zju.edu.cn/onlinejudge/showProblem.do?problemId=494 题目大意: 一只蜗牛要从爬上n英寸高的地方,他速度为u每分钟,他爬完u需要 ...
- 6 、字符编码笔记:ASCII,Unicode和UTF-8
1. ASCII码 我们知道,在计算机内部,所有的信息最终都表示为一个二进制的字符串.每一个二进制位(bit)有0和1两种状态,因此八个二进制位就可以组合出 256种状态,这被称为一个字节(byte) ...
- 服务器svn 小乌龟 visualsvn server manager Tortoisesvn的部署使用
这个主要说说实现hook,就是本地上传文件后,服务器svn将相应的文件也修改了,实现本地上传,可以及时在浏览器查看效果 首先安装visualsvn 可参考http://blog.csdn.net/zl ...
