HDU-3839-Ancient Messages(DFS)
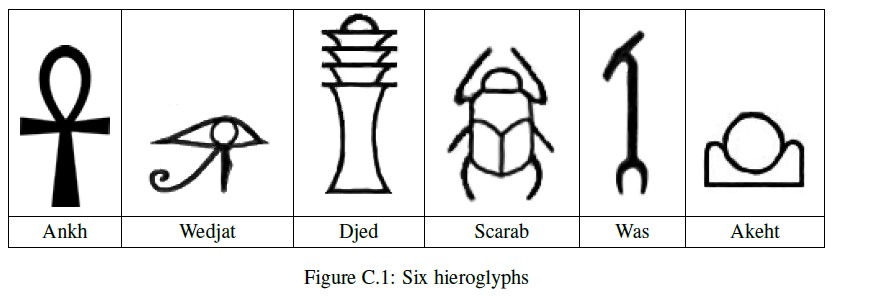
hieroglyphs and their names. In this problem, you will write a program to recognize these six characters.
of black pixels (represented by 1) and white pixels (represented by 0). In the input data, each scan line is encoded in hexadecimal notation. For example, the sequence of eight pixels 10011100 (one black pixel, followed by two white pixels, and so on) would
be represented in hexadecimal notation as 9c. Only digits and lowercase letters a through f are used in the hexadecimal encoding. The first line of each test case contains two integers, H and W: H (0 < H <= 200) is the number of scan lines in the image. W
(0 < W <= 50) is the number of hexadecimal characters in each line. The next H lines contain the hexadecimal characters of the image, working from top to bottom. Input images conform to the following rules:
- The image contains only hieroglyphs shown in Figure C.1.
- Each image contains at least one valid hieroglyph.
- Each black pixel in the image is part of a valid hieroglyph.
- Each hieroglyph consists of a connected set of black pixels and each black pixel has at least one other black pixel on its top, bottom, left, or right side.
- The hieroglyphs do not touch and no hieroglyph is inside another hieroglyph.
- Two black pixels that touch diagonally will always have a common touching black pixel.
- The hieroglyphs may be distorted but each has a shape that is topologically equivalent to one of the symbols in Figure C.11.
The last test case is followed by a line containing two zeros.
1Two figures are topologically equivalent if each can be transformed into the other by stretching without tearing.
Ankh: A
Wedjat: J
Djed: D
Scarab: S
Was: W
Akhet: K
In each output string, print the codes in alphabetic order. Follow the format of the sample output.
The sample input contains descriptions of test cases shown in Figures C.2 and C.3. Due to space constraints not all of the sample input can be shown on this page.

100 25
0000000000000000000000000
0000000000000000000000000
...(50 lines omitted)...
00001fe0000000000007c0000
00003fe0000000000007c0000
...(44 lines omitted)...
0000000000000000000000000
0000000000000000000000000
150 38
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
...(75 lines omitted)...
0000000003fffffffffffffffff00000000000
0000000003fffffffffffffffff00000000000
...(69 lines omitted)...
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
0 0
Case 1: AKW
Case 2: AAAAA
思路:依据圈的数量来识别。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; char ts[201],mes[6]={'W','A','K','J','S','D'},ans[10];
bool vis[205][205];
int n,m,mp[205][205],nxt[4][2]={{1,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1}},num; void dfs(int x,int y)
{
int i; for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
x+=nxt[i][0];
y+=nxt[i][1]; if(x>=0 && x<n && y>=0 && y<m && !vis[x][y] && !mp[x][y])
{
vis[x][y]=1;
dfs(x,y);
} x-=nxt[i][0];
y-=nxt[i][1];
}
} void dfs3(int x,int y)
{
int i; for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
x+=nxt[i][0];
y+=nxt[i][1]; if(x>=0 && x<n && y>=0 && y<m && !vis[x][y] && !mp[x][y])
{
vis[x][y]=1;
dfs3(x,y);
} x-=nxt[i][0];
y-=nxt[i][1];
}
} void dfs2(int x,int y)
{
int i; for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
x+=nxt[i][0];
y+=nxt[i][1]; if(x>=0 && x<n && y>=0 && y<m && !vis[x][y])
{
if(mp[x][y])
{
vis[x][y]=1;
dfs2(x,y);
}
else
{
vis[x][y]=1;
num++;
dfs3(x,y);
} } x-=nxt[i][0];
y-=nxt[i][1];
}
} int main()
{
int i,j,t,casenum=1,cnt; while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) && n)
{
n++;
m*=4;
m++; for(i=0;i<=n;i++) for(j=0;j<=m;j++) vis[i][j]=0; for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
gets(ts); if(!ts[0])
{
i--;
continue;
} for(j=0;ts[j];j++)
{
if(ts[j]>='a' && ts[j]<='f')
{
t=ts[j]-'a'+10; mp[i][j*4+1]=t/8;
mp[i][j*4+2]=t%8/4;
mp[i][j*4+3]=t%4/2;
mp[i][j*4+4]=t%2/1;
}
else
{
t=ts[j]-'0'; mp[i][j*4+1]=t/8;
mp[i][j*4+2]=t%8/4;
mp[i][j*4+3]=t%4/2;
mp[i][j*4+4]=t%2/1;
}
}
} for(i=0;i<=m;i++) mp[n][i]=0;
for(i=0;i<=n;i++) mp[i][m]=0; n++;
m++; vis[0][0]=1;
dfs(0,0); cnt=0; for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<m;j++)
{
if(mp[i][j] && !vis[i][j])
{
num=0; vis[i][j]=1; dfs2(i,j); ans[cnt++]=mes[num];
}
}
} sort(ans,ans+cnt); ans[cnt]=0; printf("Case %d: ",casenum++); puts(ans);
}
}
版权声明:本文博客原创文章,博客,未经同意,不得转载。
HDU-3839-Ancient Messages(DFS)的更多相关文章
- HDU 3839 Ancient Messages(DFS)
In order to understand early civilizations, archaeologists often study texts written in ancient lang ...
- hdu 3839 Ancient Messages (dfs )
题目大意:给出一幅画,找出里面的象形文字. 要你翻译这幅画,把象形文字按字典序输出. 思路:象形文字有一些特点,分别有0个圈.1个圈.2个圈...5个圈.然后dfs或者bfs,就像油井问题一样,找出在 ...
- K - Ancient Messages(dfs求联通块)
K - Ancient Messages Time Limit:3000MS Memory Limit:0KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu Subm ...
- HDOJ(HDU).2660 Accepted Necklace (DFS)
HDOJ(HDU).2660 Accepted Necklace (DFS) 点我挑战题目 题意分析 给出一些石头,这些石头都有自身的价值和重量.现在要求从这些石头中选K个石头,求出重量不超过W的这些 ...
- HDOJ(HDU).1045 Fire Net (DFS)
HDOJ(HDU).1045 Fire Net [从零开始DFS(7)] 点我挑战题目 从零开始DFS HDOJ.1342 Lotto [从零开始DFS(0)] - DFS思想与框架/双重DFS HD ...
- HDOJ(HDU).1241 Oil Deposits(DFS)
HDOJ(HDU).1241 Oil Deposits(DFS) [从零开始DFS(5)] 点我挑战题目 从零开始DFS HDOJ.1342 Lotto [从零开始DFS(0)] - DFS思想与框架 ...
- HDOJ(HDU).1035 Robot Motion (DFS)
HDOJ(HDU).1035 Robot Motion [从零开始DFS(4)] 点我挑战题目 从零开始DFS HDOJ.1342 Lotto [从零开始DFS(0)] - DFS思想与框架/双重DF ...
- HDU 1501 Zipper 【DFS+剪枝】
HDU 1501 Zipper [DFS+剪枝] Problem Description Given three strings, you are to determine whether the t ...
- HDU 1401 Solitaire 双向DFS
HDU 1401 Solitaire 双向DFS 题意 给定一个\(8*8\)的棋盘,棋盘上有4个棋子.每一步操作可以把任意一个棋子移动到它周围四个方向上的空格子上,或者可以跳过它四个方向上的棋子(就 ...
- ACM: HDU 2563 统计问题-DFS+打表
HDU 2563 统计问题 Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u HDU 2 ...
随机推荐
- 使用Apache FtpServer搭建FTP服务器 [FlashFXP]
<server xmlns="http://mina.apache.org/ftpserver/spring/v1" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w ...
- XML输出到浏览器报错
在使用Firefox浏览器测试我编写的xml文件时,遇到如下错误:我的xml源代码如下: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8&q ...
- C#+HtmlAgilityPack
C#+HtmlAgilityPack—糗事百科桌面版V2.0 最近在浏览以前自己上传的源码,发现在糗事百科桌面端源码评论区中,有人说现在程序不能用了.查看了一下源码运行情况,发现是正则表达式解析问 ...
- 解决duilib水平布局(HorizontalLayout)中控件位置计算错误的问题
水平布局中的控件无法布满整个布局,右側留有缝隙 修正后的样子 原因是布局中的代码计算Padding时候逻辑不对导致 修正后的代码到https://github.com/CodeBees/duilib- ...
- C++常用数据结构的实现
常用数据结构与算法的实现.整理与总结 我将我所有数据结构的实现放在了github中:Data-Structures-Implemented-By-Me 常用数据结构与算法的实现.整理与总结 KMP字符 ...
- Android中蓝牙的基本使用----BluetoothAdapter类简介
天气逐渐热了,自己也越来越懒了,虽然看着了很多东西,解决了很多问题,有些收获却不想写着.主要有一下两方面原因: 第一.以前写的一些关于Android知识的Blog,都是在学习过程中发现网络上没有相关知 ...
- JM-1 手机网站开发测试环境搭建
JM-1 手机网站开发测试环境搭建 一.总结 一句话总结:WEB服务器环境可实现局域网内轻松访问.360wifi可以实现局域网. 二.微网站开发环境: 1.把微网站放到本机wamp环境下,用pc浏览器 ...
- mybatis结合log4j打印SQL日志
mybatis结合log4j打印SQL日志 1.Maven引用jar包 默认的mybatis不能打印出SQL日志,不便于查看调试,须要结合log4jdbc-log4j2就能够完整的输入SQL的调试信息 ...
- combobox添加选项
如果不需要绑定字段,只需要显示列表 cmb_Type.Items.AddRange(new object[] {"姓名","年龄","性别" ...
- leetcode——Reverse Words in a String 旋转字符串中单词顺序(AC)
题目例如以下: Given an input string, reverse the string word by word. For example, Given s = "the sky ...
