C++与C的区别二
1. new,delete的局部重载:
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- int objs = ;
- class myclass
- {
- public:
- myclass()
- {
- //objs++;
- cout << "create" << endl;
- }
- ~myclass()
- {
- //objs--;
- cout << "delete" << endl;
- }
- //operator重载,针对new重新作出一种解释,只针对当前类
- static void * operator new(size_t size)
- {
- objs++;
- cout << "new-call" << endl;
- myclass *p = ::new myclass; //全局new
- return p;
- }
- static void operator delete(void *p)
- {
- objs--;
- cout << "delete-call" << endl;
- ::delete p;
- }
- };
- //功能1:无法在堆上被创建的类
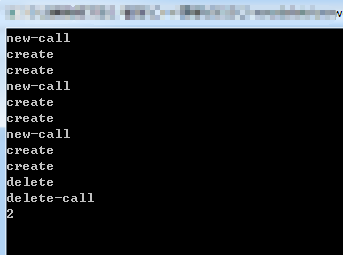
- void main()
- {
- myclass *p1 = new myclass;
- myclass *p2 = new myclass;
- myclass *p3 = new myclass;
- delete p1;
- int *p = new int(); //此时new重载对于这一句无效
- cout << objs << endl;
- cin.get();
- }
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- int objs = ;
- void *g_p = nullptr;
- class myclass
- {
- public:
- myclass()
- {
- //objs++;
- cout << "create" << endl;
- }
- ~myclass()
- {
- //objs--;
- cout << "delete" << endl;
- }
- //operator重载,针对new重新作出一种解释,只针对当前类
- static void * operator new(size_t size)
- {
- if (g_p==nullptr)
- {
- objs++;
- cout << "new-call" << endl;
- myclass *p = ::new myclass; //全局new
- g_p = p; //单例,堆上创建对象只有一个
- return p;
- }
- else
- {
- return g_p;
- }
- }
- static void operator delete(void *p)
- {
- if (g_p!=nullptr)
- {
- objs--;
- cout << "delete-call" << endl;
- ::delete p;
- g_p = nullptr;
- }
- }
- };
- //功能1:无法在堆上被创建的类
- //功能2:实现统计分配内存,释放内存的次数
- //实现单例设计模式,实现避免反复delete出错
- //new delete在内部,只针对当前类,int double 无影响
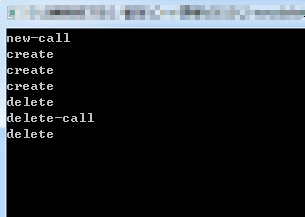
- void main()
- {
- myclass *p1 = new myclass;
- myclass *p2 = new myclass;
- delete p1;
- delete p1; //规避了两次delete的错误
- cin.get();
- }
2. 全局new,delete重载:
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- //全局内存管理,统计释放内存,分配内存
- //new new [] delete delete []
- //分配内存优先于构造
- //析构优先于释放内存
- void * operator new(size_t size)
- {
- cout << "g_new call" << endl;
- void *p = malloc(size); //全局的new,只能使用malloc
- return p;
- }
- void * operator new [](size_t size)
- {
- cout << "g_new [] call" << endl;
- cout << size << endl;
- return operator new(size); //每个元素调用一次new
- }
- void operator delete(void *p)
- {
- cout << "g_delete call" << endl;
- free(p);
- }
- void operator delete [](void *p)
- {
- cout << "g_delete [] call" << endl;
- free(p);
- }
- class myclass
- {
- public:
- myclass()
- {
- cout << "create call" << endl;
- }
- ~myclass()
- {
- cout << "delete call" << endl;
- }
- };
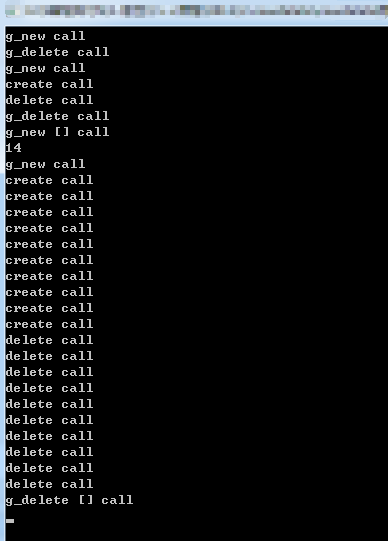
- void main()
- {
- int *p1 = new int();
- delete p1;
- myclass *p2 = new myclass;
- delete p2;
- myclass *px = new myclass[];
- delete[]px;
- cin.get();
- }
3. 绑定类成员函数:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <functional>
- using namespace std;
- using namespace std::placeholders;//站位
- struct MyStruct
- {
- void add1(int a)
- {
- cout << a << endl;
- }
- void add2(int a, int b)
- {
- cout << a << b << endl;
- }
- void add3(int a, int b, int c)
- {
- cout << a << b << c << endl;
- }
- };
- void main()
- {
- MyStruct my1;
- //my1.add(10);
- //绑定包装器,包装类成员函数,用于使用
- auto fun1 = bind(&MyStruct::add1, &my1, _1);//有1个参数 函数名、对象地址、参数
- fun1();
- auto fun2 = bind(&MyStruct::add2, &my1, _1,_2);//有2个参数
- fun2(,);
- auto fun3 = bind(&MyStruct::add3, &my1, _1,_2,_3);//有3个参数
- fun3(,,);
- cin.get();
- }
4. 绑定lambda表达式以及仿函数:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <functional>
- using namespace std;
- using namespace std::placeholders;
- int add(int a, int b,int c)
- {
- return a + b+c;
- }
- struct MyStruct
- {
- int operator()(int a,int b) //仿函数
- {
- return a + b;
- }
- };
- void main()
- {
- auto fun1 = bind(add, ,, _1);//适配器模式
- cout << fun1() << endl; //
- auto fun2 = bind([](int a, int b)->int {return a + b; }, , _1);
- cout << fun2() << endl; //
- MyStruct my1;
- cout << my1(, ) << endl; //
- auto fun3 = bind(my1, , _1); //绑定
- cout << fun3() << endl; //
- cin.get();
- }
5. 静态断言:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <cassert>
- using namespace std;
- int divv(int a, int b)
- {
- assert(b != ); //断言
- return a / b;
- }
- void main()
- {
- cout << divv(, ) << endl;
- cin.get();
- }
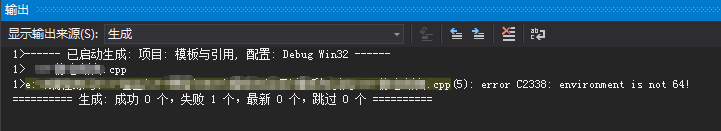
- #include <iostream>
- #include <cassert>
- using namespace std;
- static_assert(sizeof(void *) >= , "environment is not 64!");
- void main()
- {
- cin.get();
- }
6. 内联函数:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <cstdlib>
- using namespace std;
- #define f(x) x*x*x //C语言内联,C++要求类型严格匹配
- inline int get(int x) //C++的内联函数
- {
- return x*x*x;
- }
- //提高程序运行速度
- //inline 只是对于编译器的建议
- //一般情况下,我们对内联函数做如下的限制:
- //(1)不能有递归;
- //(2)不能包含静态数据;
- //(3)不能包含循环;
- //(4)不能包含switch和goto语句;
- //(5)不能包含数组。
- //若一个内联函数定义不满足以上限制,则编译系统把它当做普通函数对待
- template<class T>
- inline T go(T t)
- {
- return t*t;
- }
- void main()
- {
- get();
- go(); //优化为内联函数
- auto fun = []() {}; //lambda表达式实际上也是内联函数
- cin.get();
- }
7. CPP处理转义字符:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <cstdlib>
- using namespace std;
- void main()
- {
- //string str("\"C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Google\\Chrome\\Application\\chrome.exe\"");
- string str(R"("C:\Program Files (x86)\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe")"); // R"(......)"
- system(str.c_str());
- cin.get();
- }
C++与C的区别二的更多相关文章
- C#中抽象类和接口的区别(二)
一.抽象类: 抽象类是特殊的类,只是不能被实例化:除此以外,具有类的其他特性:重要的是抽象类可以包括抽象方法,这是普通类所不能的.抽象方法只能声明于抽象类中,且不包含任何实现,派生类必须覆盖它们.另外 ...
- Python协程与Go协程的区别二
写在前面 世界是复杂的,每一种思想都是为了解决某些现实问题而简化成的模型,想解决就得先面对,面对就需要选择角度,角度决定了模型的质量, 喜欢此UP主汤质看本质的哲学科普,其中简洁又不失细节的介绍了人类 ...
- vue1.0和vue2.0的区别(二)
这篇我们继续之前的vue1.0和vue2.0的区别(一)继续说 四.循环 学过vue的同学应该知道vue1.0是不能添加重复数据的,否则它会报错,想让它重复添加也不是不可以,不过需要定义别的东西 而v ...
- Linux内存管理--虚拟地址、逻辑地址、线性地址和物理地址的区别(二)【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/yusiguyuan/article/details/9668363 这篇文章中介绍了四个名词的概念,下面针对四个地址的转换进行分析 CPU将一个 ...
- java集合对象区别二
集合包是Java中最常用的包,它最常用的有Collection和Map两个接口的实现类,Collection用于存放多个单对象,Map用于存放Key-Value形式的键值对. Collection中常 ...
- OC与Swift的区别二(常量、变量、运算符)
4.常量与变量声明 oc的变量声明使用 类型 变量名 = 变量值的方式,其中类型为系统内置数据类型或自定义类型,变量名需由英文字母开头且不能包含特殊字符 swift变量声明使用 var 变量名 = ...
- 传统IO与NIO区别二
nio是new io的简称,从jdk1.4就被引入了.现在的jdk已经到了1.6了,可以说不是什么新东西了.但其中的一些思想值得我来研究.这两天,我研究了下其中的套接字部分,有一些心得,在此分享. ...
- Cocos2d中update与fixedUpdate的区别(二)
关于update:方法的目的 update:方法的目的在于给你一个更新你的游戏(你游戏中的所有对象,标签等待)的机会,在它们被渲染到屏幕之前. 换句话说,如果你想要一些游戏对象显示在屏幕的特定位置,你 ...
- java static成员变量方法和非static成员变量方法的区别 ( 二 )
原创文章,未经作者允许,禁止转载!!! 静态成员变量不用new对象,在类加载的过程中就已经初始化存放在数据区域,静态成员变量是类和所有对象共有的,类和对象都可以改变它的值,每一次改变值之后,静态成员变 ...
随机推荐
- netbeans下调试php程序-xdebug
环境说明: pc系统:ubuntu 16.04 php版本:5.6.23 apache:Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu) 第一步:修改xdebug.ini 打开文件/etc/php/5.6 ...
- smarty if
<{if data}> <input type="submit" value="修改" /> <{else}> <in ...
- linux 查找php.ini在那个文件夹
第一种方法:通过phpinfo查看 第二种方法: 执行 php -i | grep php.ini 结果如下:
- RocketMQ 使用及常见问题
前言 本文档是针对RocketMQ使用及常见问题的说明. 一.获取项目.安装包及文档 1. alibaba/RocketMQ https://github.com/alibaba/RocketMQ 2 ...
- HBase & thrift & C++编程
目录 目录 1 1. 前言 1 2. 启动和停止thrift2 1 2.1. 启动thrift2 1 2.2. 停止thrift2 1 2.3. 启动参数 2 3. hbase.thrift 2 3. ...
- linux每天一小步---alias命令详解
1 命令功能 alias命令用来设置指令的别名,alias命令设置的别名只限于该次登陆操作,若要每次登入即自动设好别名,可在/etc/profile或自己的~/.bashrc中设定指令的别名. ...
- Image 和byte[]之间的转换
1.Image 转 byte[] public byte[] GetByteByImage(Image image) { byte[] bt = null; try { if (!image.Equa ...
- oracle 索引的分类
1. B树索引(默认索引,保存讲过排序过的索引列和对应的rowid值) 1)说明: 1.oracle中最常用的索引:B树索引就是一颗二叉树:叶子节点(双向链表)包含索引列和指向表中每个匹配行的ROWI ...
- 動態修改 XML 欄位
/* -- for test DECLARE @content VARCHAR(50) DECLARE @folioId VARCHAR(50) DECLARE @opinionType VARCHA ...
- php萌新|学习|排坑|のmysqli_error()方法的妙用
从开始学习php当现在已经有一个月多.除了每天完成公司布置的日常汇报,也没有耐下性子写一写自己想写的东西.今天就当起个头,坚持一周有个两三片文章或者小总结,也不枉费自己的付出.(我自己都不信,你会信吗 ...
