Quality of Service (QoS) in LTE
Background: Why we need QoS ?
There are premium subscribers who always want to have better user experience on their 4G LTE device. These users are willing to pay more for high bandwidth and better network access on their devices. Not only the subscribers but some services itself need better priority handling in the network (e.g. VoIP call). To be able to full fill this, QOS plays the key role. QOS defines priorities for certain customers / services during the time of high congestion in the network
3GPP definition for QoS
between UE and PDN Gateway and is applied to a set of bearers. 'Bearer'
is basically a virtual concept and is a set of network configuration to
provide special treatment to set of traffic e.g. VoIP packets
are prioritized by network compared to web browser traffic.
In LTE, QoS is applied on Radio bearer, S1 bearer and S5/S8 bearer, collectively called as EPS bearer as shown in figure below.

bearer types and properties associated with each bearer
through hierarchical chart as shown below. First there are two types of
Bearer, i.e. Dedicated bearer and Default bearer. There is at-least one
default bearer established when UE is attached to LTE network while
dedicated bearer is always established when there is need to provide QoS
to specific service (like VoIP, video etc). Please go through the
article Default and Dedicated Bearer which hopefully will help to explain the concept in more detail.
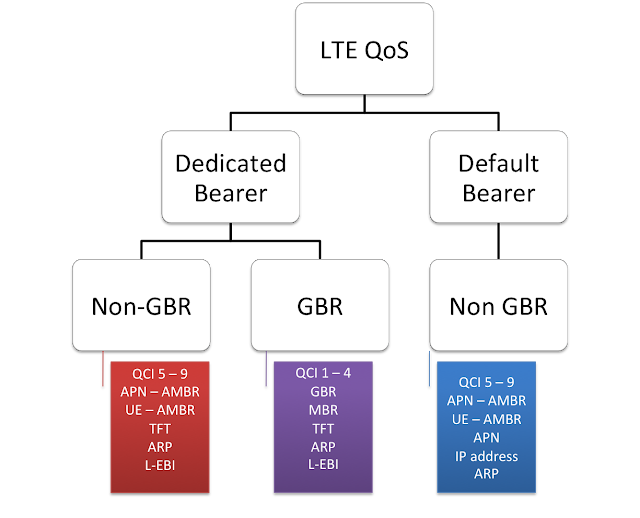
maximum bit rate is the maximum allowed total non-GBR throughput to
specific APN. It is specified interdependently for uplink an downlink
can only be non-GBR type. Some other important terms associated with
each bearer type are discussed below:
retention priority is basically used for deciding whether new bearer
modification or establishment request should be accepted considering the
current resource situation.
is always associated with dedicated bearer and while default bearer may
or may not have TFT. As mentioned earlier, dedicated bearer provides QoS
to special service or application and TFT defines rules so that UE and
Network knows which IP packet should be sent on particular dedicated
bearer. It usually has rules on the basis of IP packet
destination/source or protocol used.
EPS bearer ID. As I discussed in previous article about dedicated and
default bearer, we know that each dedicated bearer is always linked to
one of default bearers. L-EBI tells Dedicated bearer which default
bearer it is attached to.
bearer is attached to some PDN network and has its own IP address while
dedicated bearer does not need this since it is linked to default
bearer.
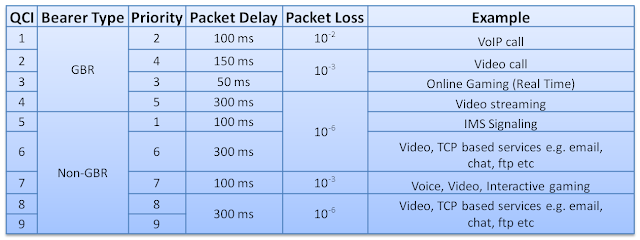
associated with all bearers i.e. QoS class of identifier (QCI).This
parameter basically defines IP level packets characteristics as shown
below
Default bearer 1: Used for signaling messages (sip signaling) related to IMS network. It uses qci 5
Dedicated bearer: Used for VoLTE VoIP traffic. It uses qci 1 and is linked to default bearer 1
Default bearer 2: Used for all other smartphone traffic (video, chat, email, browser etc), assuming qci 9 is used here
associated with IMS PDN and has specific IP address. It has throughput
limitations defined in terms of A-AMBR and UE-AMBR. Since it has qci 5
which means that its IP packets has the highest priority over other IP
packets and maximum delay as 100ms between UE and PGW with packet loss
percentage up to 10-6
internet PDN and has specific IP. It has throughput limitations defined
in terms of A-AMBR and UE-AMBR as well. Since it has qci 9 which means
that its IP packets has the lowest priority over other IP packets and
maximum delay possible as 300ms between UE and PGW with packet loss
percentage up to 10-6
Default bearer 1 with L-EBI and it also has TFT which basically defines
which IP packets should be allowed to travel on this bearer. It has
throughput limitations defined in terms of MBR and GBR. Since it is
using QCI 1, the IP packets traveling on this bearer have the second
highest priority. The maximum delay possible to IP packets on this
bearer is 100 ms and the percentage of packet loss will be under 10-2
Quality of Service (QoS) in LTE的更多相关文章
- [转] Quality Of Service In OpenStack
http://tropicaldevel.wordpress.com/2013/07/15/quality-of-service-in-openstack/ In this post I will b ...
- Quality of Service 0, 1 & 2
来自:http://www.hivemq.com/blog/mqtt-essentials-part-6-mqtt-quality-of-service-levels Quality of Servi ...
- Quality of service
w https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quality_of_service Quality of service (QoS) is the overall performan ...
- MQTT协议QoS服务质量 (Quality of Service 0, 1 & 2)概念学习
什么是 QoS ? QoS (Quality of Service) 是发送者和接收者之间,对于消息传递的可靠程度的协商. QoS 的设计是 MQTT 协议里的重点.作为专为物联网场景设计的协议,MQ ...
- neutron qos Quality of Service
Quality of Service advanced service is designed as a service plugin. The service is decoupled from t ...
- [译]Ocelot - Quality of Service
原文 可以针对每个ReRoute设置对下游服务的熔断器circuit breaker.这部分是通过Polly实现的. 将下面的配置添加到一个ReRoute下面去. "QoSOptions&q ...
- Default Bearer, Dedicated Bearer... What exactly is bearer ?
Default Bearer, Dedicated Bearer... What exactly is bearer ? While trying to get a better understa ...
- LTE QOS
http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=ziFIkdKaC7MU2RY-bTOp2bt87WFPw5_02bqmYs5W6w4ktOfPHEcWesK1U2T7YiyXjVSM ...
- Information Centric Networking Based Service Centric Networking
A method implemented by a network device residing in a service domain, wherein the network device co ...
随机推荐
- SpringMvc之参数绑定注解详解之三
2. @RequestHeader.@CookieValue @RequestHeader 注解,可以把Request请求header部分的值绑定到方法的参数上. 示例代码: 这是一个Request ...
- python 基础 字典 增删改查
content = {"name":"wd","pc":{"phone":111111,"age": ...
- Eclipse调试Java程序技巧
主要步骤.Debug As"->"Java Application".双击设置断点,F5是跳进,F6是执行下一步,F7是跳出 在看这篇文章前,我推荐你看一下Ecli ...
- Linux下统计代码行数
使用wc统计代码行数 最近写了一些代码,想统计一下代码的行数,在eclipse中好像没这功能,网上搜了一下才发现原来Linux有一个统计文件行数的命令wc.使用wc可以打印出每个文件和总文件的行数.字 ...
- 网络编程之socket编程
TCP/IP协议 网络层的“ip地址”可以唯一标识网络中的主机,而传输层的“协议+端口”可以唯一标识主机中的应用程序(进程).这样利用三元组(ip地址,协议,端口)就可以标识网络的进程了,网络中的进程 ...
- xdu2017校赛F
Problem F Dogs of Qwordance Senior Backend R&D Engineers 问题描述 那年夏天,锘爷和杰师傅漫步在知春公园的小道上.他们的妻子.孩子牵 着 ...
- [HDU1754]I Hate It线段树裸题
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1754 解题关键:刚开始死活超时,最后发现竟然是ch,和t1.t2每次循环都定义的锅,以后养成建全局变量的习惯. ...
- mongodb插入时间
插入时间: db.test.insert({time:new Date()}) 给mongodb插入日期格式的数据时发现,日期时间相差8个小时,原来存储在mongodb中的时间是标准时间UTC +0: ...
- 15、使用ggtree实现进化树的可视化和注释(转载)
本文作者:余光创,目前就读于香港大学公共卫生系,开发过多个R/Bioconductor包,包括ChIPseeker, clusterProfiler, DOSE,ggtree,GOSemSim和Rea ...
- Note: Bimodal Content Defined Chunking for Backup Streams
CDC算法给出了一个chunk的大小的最小值.最大值.平均值的界定. Method Using chunk existence information breaking-apart algorithm ...
